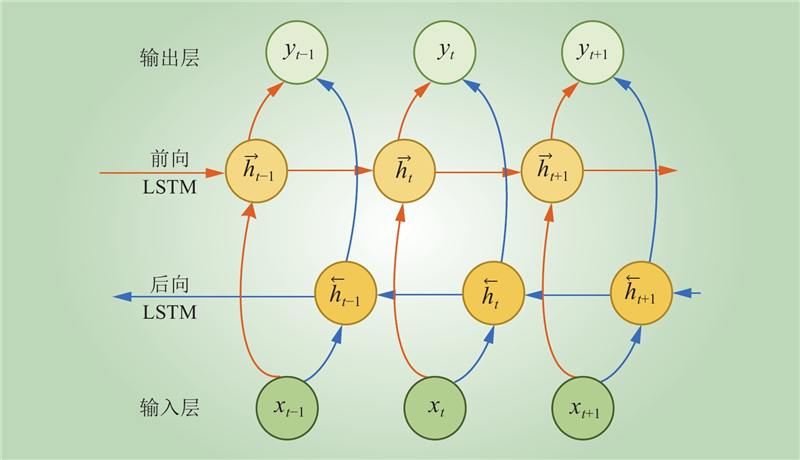
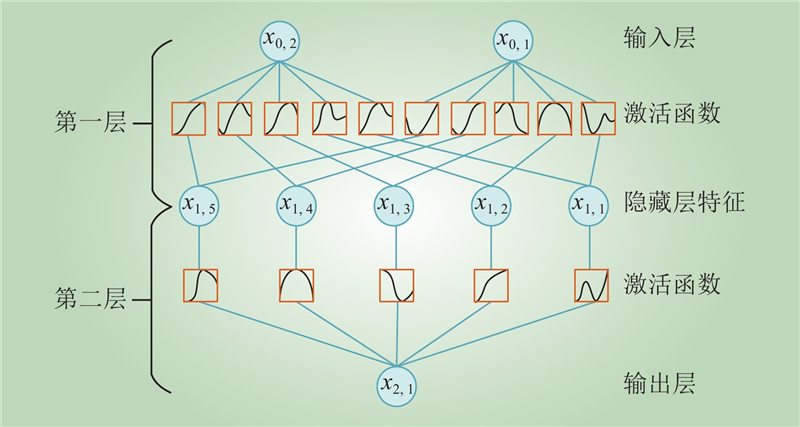
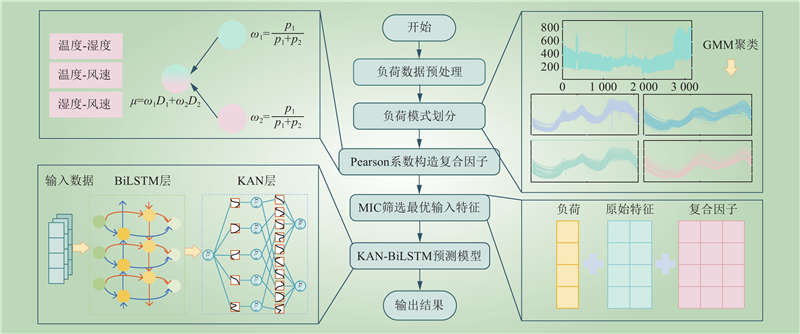
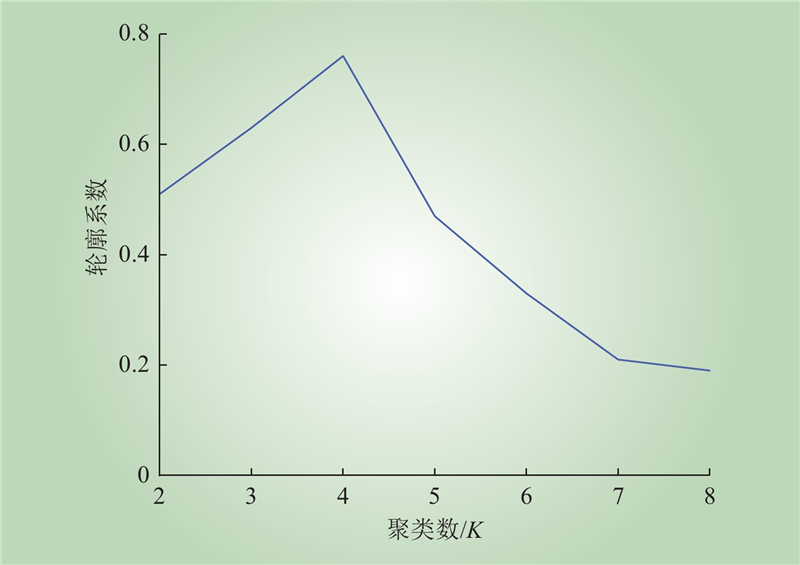
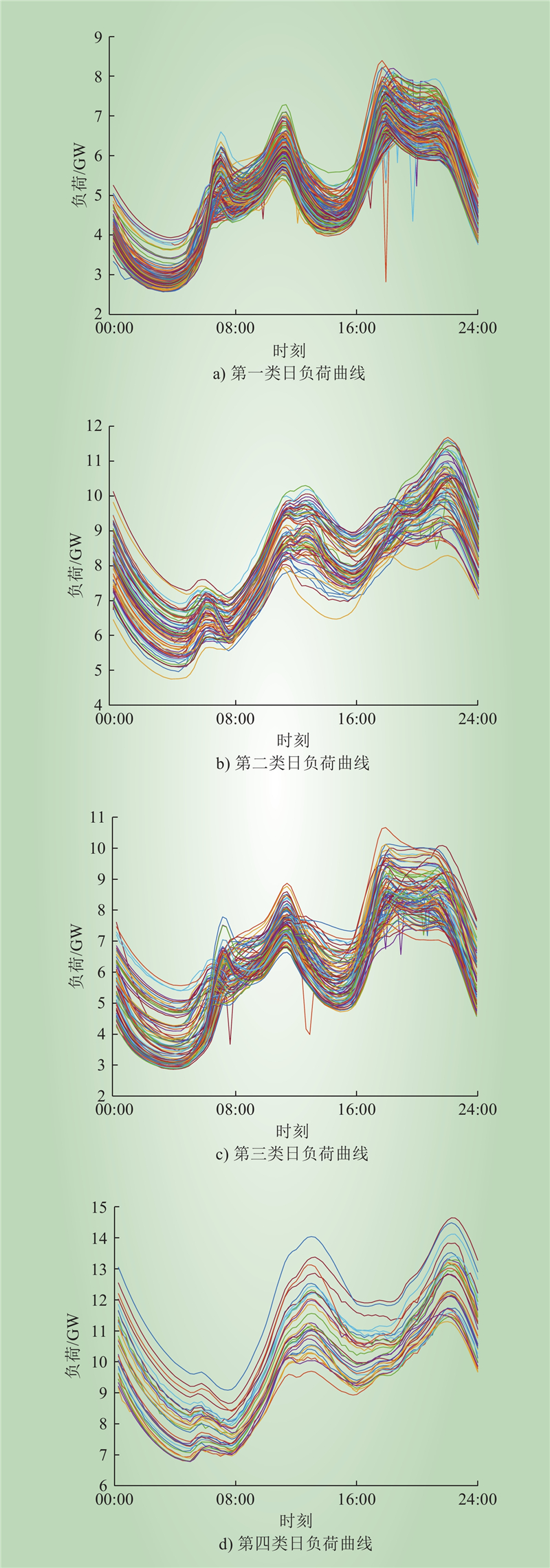
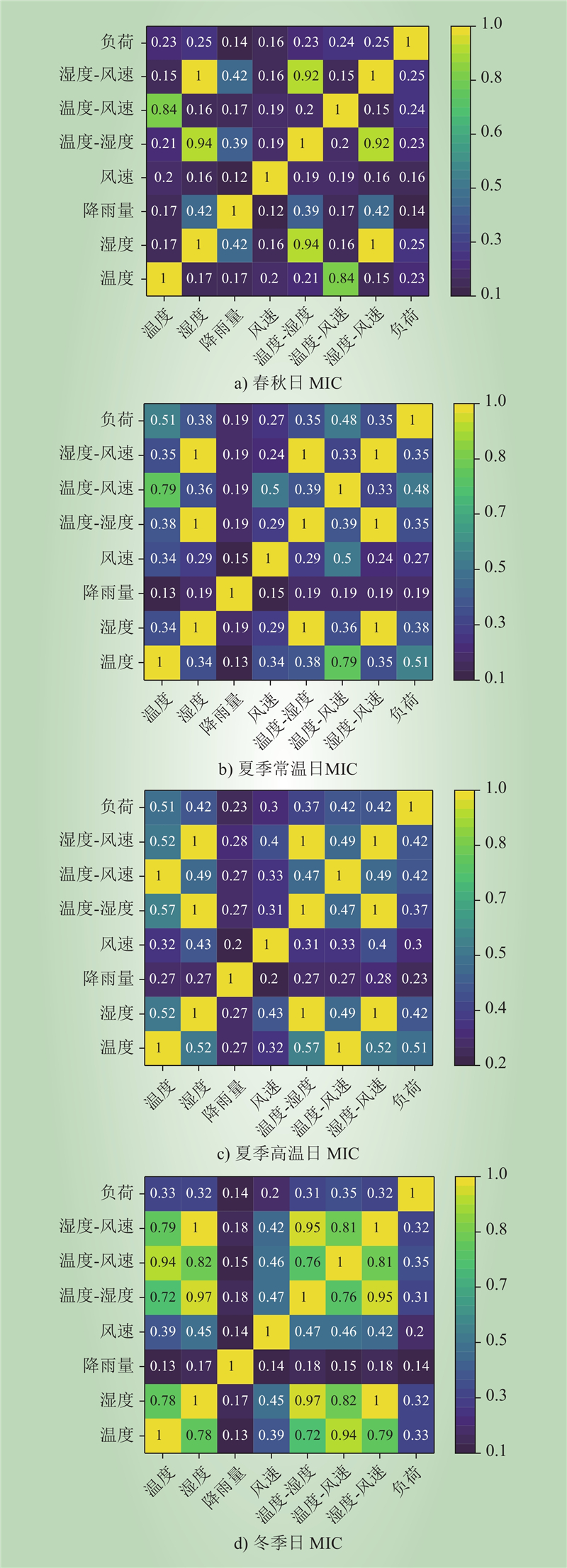
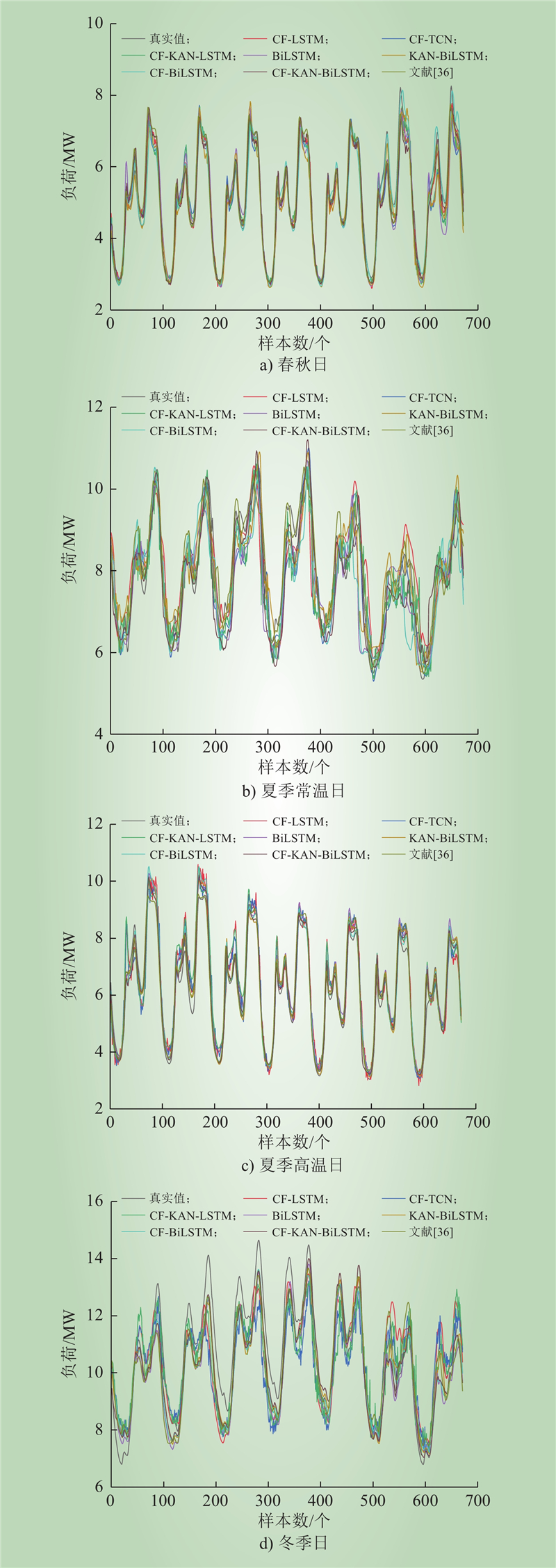
| 1 |
舒印彪, 张正陵, 汤涌, 等. 新型电力系统构建的若干基本问题[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2024, 44 (21): 8327- 8341.
|
|
SHU Yinbiao, ZHANG Zhengling, TANG Yong, et al. Fundamental issues of new-type power system construction[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2024, 44 (21): 8327- 8341.
|
| 2 |
李科, 潘庭龙, 许德智. 基于MSCNN-BiGRU-Attention的短期电力负荷预测[J]. 中国电力, 2025, 58 (6): 10- 18.
|
|
LI Ke, PAN Tinglong, XU Dezhi. Short-term power load forecasting based on MSCNN-BiGRU-attention[J]. Electric Power, 2025, 58 (6): 10- 18.
|
| 3 |
罗凯鸿, 徐茹枝, 夏迪娅, 等. 基于匿名性差分隐私联邦学习的负荷预测模型训练方法[J]. 电力信息与通信技术, 2024, 22 (11): 25- 33.
|
|
LUO Kaihong, XU Ruzhi, XIA Diya, et al. A training method for load forecasting models based on anonymity differential privacy federated learning[J]. Electric Power Information and Communication Technology, 2024, 22 (11): 25- 33.
|
| 4 |
李磊, 林珊, 贾颉辉. 基于TCN-Attention神经网络的短期负荷预测[J]. 电力信息与通信技术, 2023, 21 (3): 10- 16.
|
|
LI Lei, LIN Shan, JIA Jiehui. Short-term load forecasting based on TCN-attention neural network[J]. Electric Power Information and Communication Technology, 2023, 21 (3): 10- 16.
|
| 5 |
徐玉婷, 田世明, 陈宋宋, 等. 基于LSTM的居民负荷预测及其可调节潜力分析[J]. 电力信息与通信技术, 2023, 21 (5): 1- 8.
|
|
XU Yuting, TIAN Shiming, CHEN Songsong, et al. Resident load forecasting based on LSTM and its adjustable potential analysis[J]. Electric Power Information and Communication Technology, 2023, 21 (5): 1- 8.
|
| 6 |
YAZICI I, BEYCA O F, DELEN D. Deep-learning-based short-term electricity load forecasting: a real case application[J]. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2022, 109, 104645.
|
| 7 |
张淑清, 李君, 姜安琦, 等. 基于FPA-VMD和BiLSTM神经网络的新型两阶段短期电力负荷预测[J]. 电网技术, 2022, 46 (8): 3269- 3279.
|
|
ZHANG Shuqing, LI Jun, JIANG Anqi, et al. A novel two-stage model based on FPA-VMD and BiLSTM neural network for short-term power load forecasting[J]. Power System Technology, 2022, 46 (8): 3269- 3279.
|
| 8 |
胡威, 张新燕, 李振恩, 等. 基于优化的VMD-mRMR-LSTM模型的短期负荷预测[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2022, 50 (1): 88- 97.
|
|
HU Wei, ZHANG Xinyan, LI Zhenen, et al. Short-term load forecasting based on an optimized VMD-m RMR-LSTM model[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2022, 50 (1): 88- 97.
|
| 9 |
JAHANGIR H, TAYARANI H, GOUGHERI S S, et al. Deep learning-based forecasting approach in smart grids with microclustering and bidirectional LSTM network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2021, 68 (9): 8298- 8309.
|
| 10 |
陈锦鹏, 胡志坚, 陈纬楠, 等. 二次模态分解组合DBiLSTM-MLR的综合能源系统负荷预测[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2021, 45 (13): 85- 94.
|
|
CHEN Jinpeng, HU Zhijian, CHEN Weinan, et al. Load prediction of integrated energy system based on combination of quadratic modal decomposition and deep bidirectional long short-term memory and multiple linear regression[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2021, 45 (13): 85- 94.
|
| 11 |
杨龙, 吴红斌, 丁明, 等. 新能源电网中考虑特征选择的Bi-LSTM网络短期负荷预测[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2021, 45 (3): 166- 173.
|
|
YANG Long, WU Hongbin, DING Ming, et al. Short-term load forecasting in renewable energy grid based on bi-directional long short-term memory network considering feature selection[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2021, 45 (3): 166- 173.
|
| 12 |
邓皓云, 陈卓. 基于EEMD-IWOA-TCN的电网短期负荷预测[J]. 电力信息与通信技术, 2024, 22 (1): 70- 76.
|
|
DENG Haoyun, CHEN Zhuo. Short-term load forecasting of power gird based on EEMD-IWOA-TCN[J]. Electric Power Information and Communication Technology, 2024, 22 (1): 70- 76.
|
| 13 |
王继东, 于俊源, 孔祥玉. 基于双重分解和双向长短时记忆网络的中长期负荷预测模型[J]. 电网技术, 2024, 48 (8): 3418- 3426.
|
|
WANG Jidong, YU Junyuan, KONG Xiangyu. Medium-and long-term load forecasting model based on double decomposition and BiLSTM[J]. Power System Technology, 2024, 48 (8): 3418- 3426.
|
| 14 |
SHARMA A, JAIN S K. A novel two-stage framework for mid-term electric load forecasting[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2024, 20 (1): 247- 255.
|
| 15 |
WAN A P, CHANG Q, AL-BUKHAITI K, et al. Short-term power load forecasting for combined heat and power using CNN-LSTM enhanced by attention mechanism[J]. Energy, 2023, 282, 128274.
|
| 16 |
钟燕, 王军, 宋戈, 等. 基于二次重构分解去噪及双向长短时记忆网络的极端天气下超短期电力负荷预测[J]. 电网技术, 2025, 49 (11): 4791- 4800.
|
|
ZHONG Yan, WANG Jun, SONG Ge, et al. Ultra-short-term power load prediction under extreme weather based on secondary reconstruction denoising and BiLSTM[J]. Power System Technology, 2025, 49 (11): 4791- 4800.
|
| 17 |
盛雷, 李丽娟, 付西红, 等. 基于KAN-Transformer的离轴三反装调仿真技术[J]. 光学学报, 2025, 45 (5): 0522002.
|
|
SHENG Lei, LI Lijuan, FU Xihong, et al. Simulation technology for assembly of off-axis three-mirror optical systems based on KAN-transformer[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2025, 45 (5): 0522002.
|
| 18 |
LIU Z M, WANG Y X, VAIDYA S, et al. KAN: Kolmogorov-Arnold networks [EB/OL]. (2525-02-09) [2025-08-22]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2404.19756.
|
| 19 |
朱凌建, 荀子涵, 王裕鑫, 等. 基于CNN-Bi LSTM的短期电力负荷预测[J]. 电网技术, 2021, 45 (11): 4532- 4539.
|
|
ZHU Lingjian, XUN Zihan, WANG Yuxin, et al. Short-term power load forecasting based on CNN-BiLSTM[J]. Power System Technology, 2021, 45 (11): 4532- 4539.
|
| 20 |
姚芳, 汤俊豪, 陈盛华, 等. 基于ISSA-CNN-GRU模型的电动汽车充电负荷预测方法[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2023, 51 (16): 158- 167.
|
|
YAO Fang, TANG Junhao, CHEN Shenghua, et al. Charging load prediction method for electric vehicles based on an ISSA-CNN-GRU model[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2023, 51 (16): 158- 167.
|
| 21 |
郑豪丰, 杨国华, 康文军, 等. 基于多负荷特征和TCN-GRU神经网络的负荷预测[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (11): 142- 148.
|
|
ZHENG Haofeng, YANG Guohua, KANG Wenjun, et al. Load forecasting based on multiple load features and TCN-GRU neural network[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (11): 142- 148.
|
| 22 |
韩富佳, 王晓辉, 乔骥, 等. 基于人工智能技术的新型电力系统负荷预测研究综述[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2023, 43 (22): 8569- 8592.
|
|
HAN Fujia, WANG Xiaohui, QIAO Ji, et al. Review on artificial intelligence based load forecasting research for the new-type power system[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2023, 43 (22): 8569- 8592.
|
| 23 |
邓明亮, 张钊, 周红艳, 等. 基于PCA-PSO_KFCM聚类和BiLSTM-Attention的短期电力负荷预测[J]. 计算机工程与科学, 2025, 47 (11): 2067- 2081.
|
|
DENG Mingliang, ZHANG Zhao, ZHOU Hongyan, et al. Short-term power load forecasting based on PCA-PSO_KFCM clustering and BiLSTM-Attention[J]. Computer Engineering & Science, 2025, 47 (11): 2067- 2081.
|
| 24 |
TAN M, LIAO C C, CHEN J, et al. A multi-task learning method for multi-energy load forecasting based on synthesis correlation analysis and load participation factor[J]. Applied Energy, 2023, 343, 121177.
|
| 25 |
黄南天, 孙赫宏, 王圣元, 等. 计及多公共充电站差异化耦合关联的电动汽车充电负荷时-空短期预测[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2025, 45 (4): 1424- 1436.
|
|
HUANG Nantian, SUN Hehong, WANG Shengyuan, et al. Short-term spatial-temporal forecasting of electric vehicle charging load with differentiated spatial-temporal coupling correlation of multiple public charging stations[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2025, 45 (4): 1424- 1436.
|
| 26 |
谭海旺, 杨启亮, 邢建春, 等. 基于XGBoost-LSTM组合模型的光伏发电功率预测[J]. 太阳能学报, 2022, 43 (8): 75- 81.
|
|
TAN Haiwang, YANG Qiliang, XING Jianchun, et al. Photovoltaic power prediction based on combined XGBOOST-LSTM model[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2022, 43 (8): 75- 81.
|
| 27 |
陈仕启, 吴燕, 杨德昌, 等. 基于负荷二次分解与特征处理的电力系统短期负荷预测[J]. 高电压技术, 2025, 51 (5): 2571- 2581.
|
|
CHEN Shiqi, WU Yan, YANG Dechang, et al. Short-term load forecasting of power system based on secondary load decomposition and feature processing[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2025, 51 (5): 2571- 2581.
|
| 28 |
NOWAKOWSKA E, KORONACKI J, LIPOVETSKY S. Clusterability assessment for Gaussian mixture models[J]. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2015, 256, 591- 601.
|
| 29 |
YANG M S, LAI C Y, LIN C Y. A robust EM clustering algorithm for Gaussian mixture models[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2012, 45 (11): 3950- 3961.
|
| 30 |
RESHEF D N, RESHEF Y A, FINUCANE H K, et al. Detecting novel associations in large data sets[J]. Science, 2011, 334 (6062): 1518- 1524.
|
| 31 |
MASSAOUDI M, CHIHI I, SIDHOM L, et al. An effective hybrid NARX-LSTM model for point and interval PV power forecasting[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9, 36571- 36588.
|
| 32 |
刘灿锋, 孙浩, 东辉. 结合Transformer与Kolmogorov Arnold网络的分子扩增时序预测研究[J]. 图学学报, 2024, 45 (6): 1256- 1265.
|
|
LIU Canfeng, SUN Hao, DONG Hui. Molecular amplification time series prediction research combining Transformer with Kolmogorov-Arnold network[J]. Journal of Graphics, 2024, 45 (6): 1256- 1265.
|
| 33 |
郭朝泽. 基于组合模型的短期电力负荷预测研究[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古工业大学, 2022.
|
|
GUO ZhaoZe. Research on short-term power load forecasting based on combined model[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia University of Tehchnology, 2022.
|
| 34 |
王凌云, 周翔, 田恬, 等. 基于多维气象信息时空融合和MPA-VMD的短期电力负荷组合预测模型[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2024, 44 (2): 190- 197.
|
|
WANG Lingyun, ZHOU Xiang, TIAN Tian, et al. Combination forecasting model of short-term power load based on multi-dimensional meteorological information spatio-temporal fusion and MPA-VMD[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2024, 44 (2): 190- 197.
|
| 35 |
刘蓉晖, 石炬烽, 孙改平, 等. 基于MV-WC和门控循环单元的短期净负荷概率预测[J]. 南方电网技术, 2025, 19 (6): 152- 161.
|
|
LIU Ronghui, SHI Jufeng, SUN Gaiping, et al. Short-term net load probability forecasting based on MV-WC and gated recurrent unit[J]. Southern Power System Technology, 2025, 19 (6): 152- 161.
|
| 36 |
周泽楷, 侯宏娟, 孙莉, 等. 基于CNN和BiLSTM神经网络模型的太阳能供暖负荷预测研究[J]. 太阳能学报, 2024, 45 (10): 415- 422.
|
|
ZHOU Zekai, HOU Hongjuan, SUN Li, et al. Research on solar heating load forecasting based on cnn and bilstm neural network model[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2024, 45 (10): 415- 422.
|