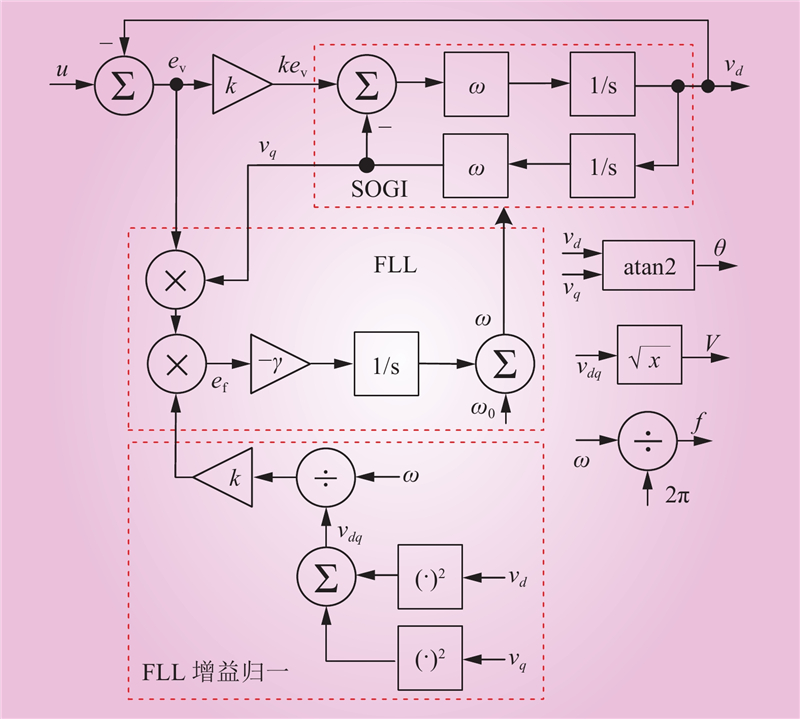
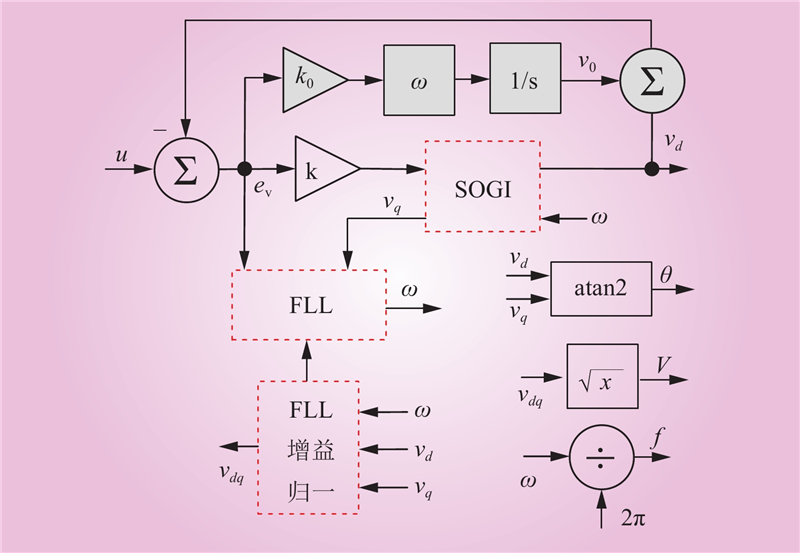
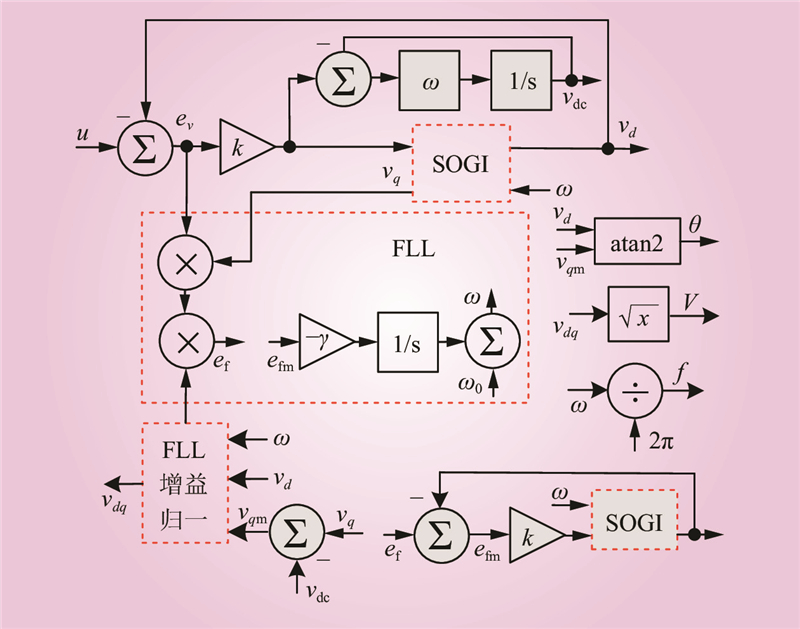
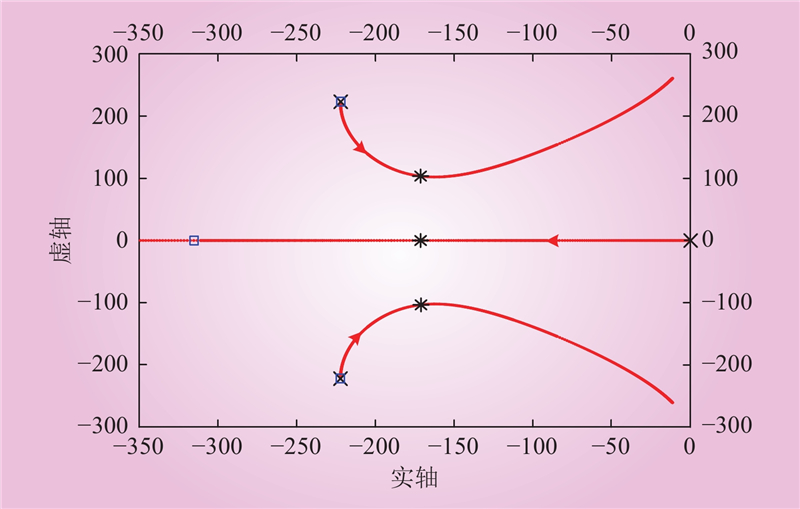
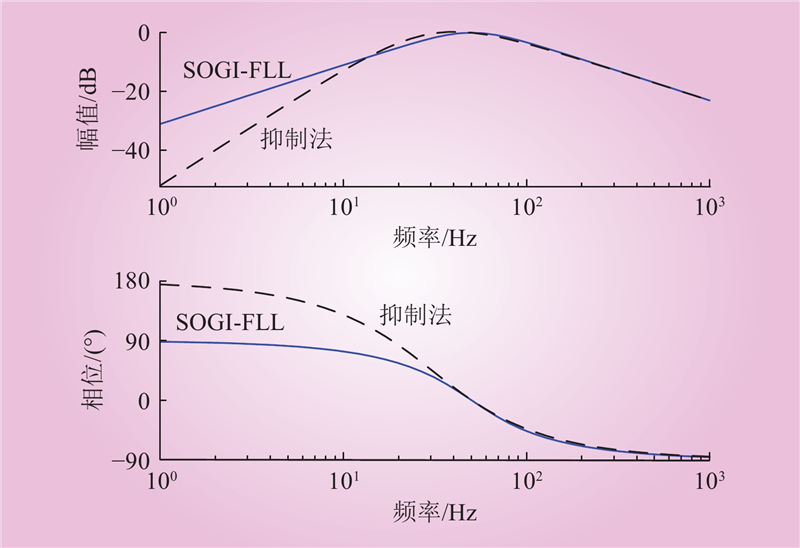
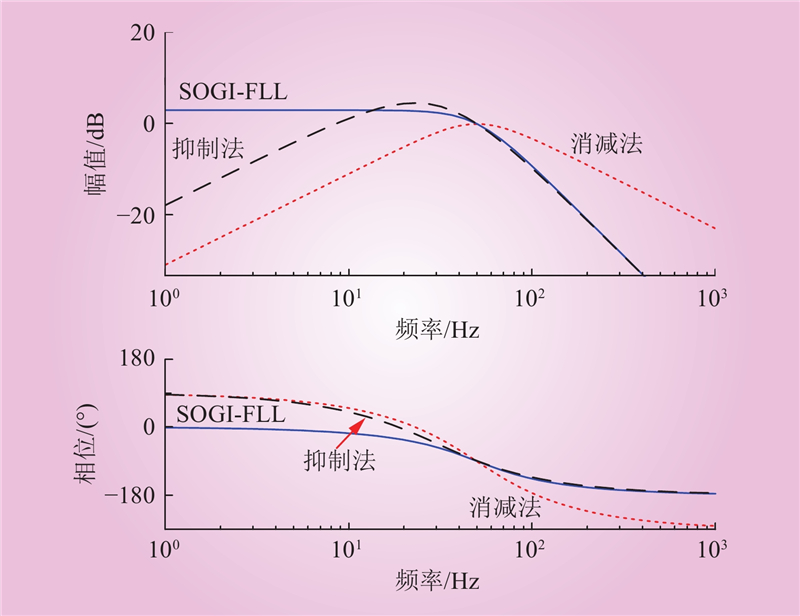
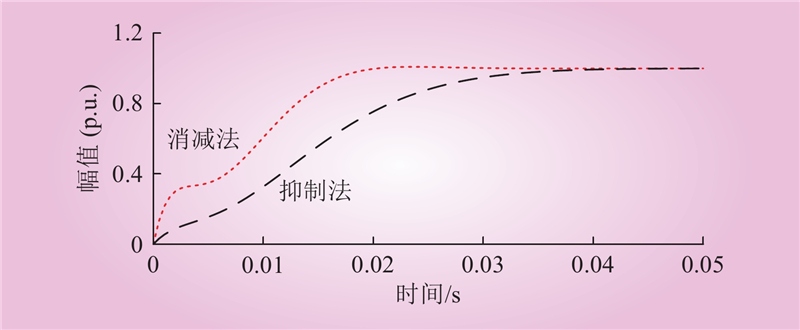
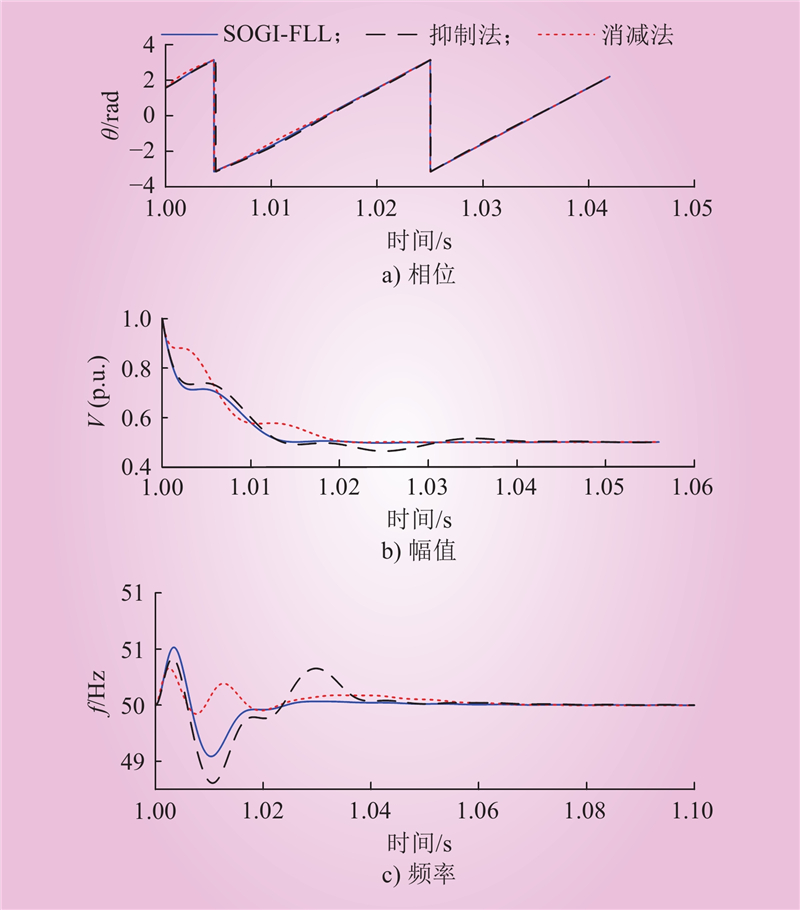
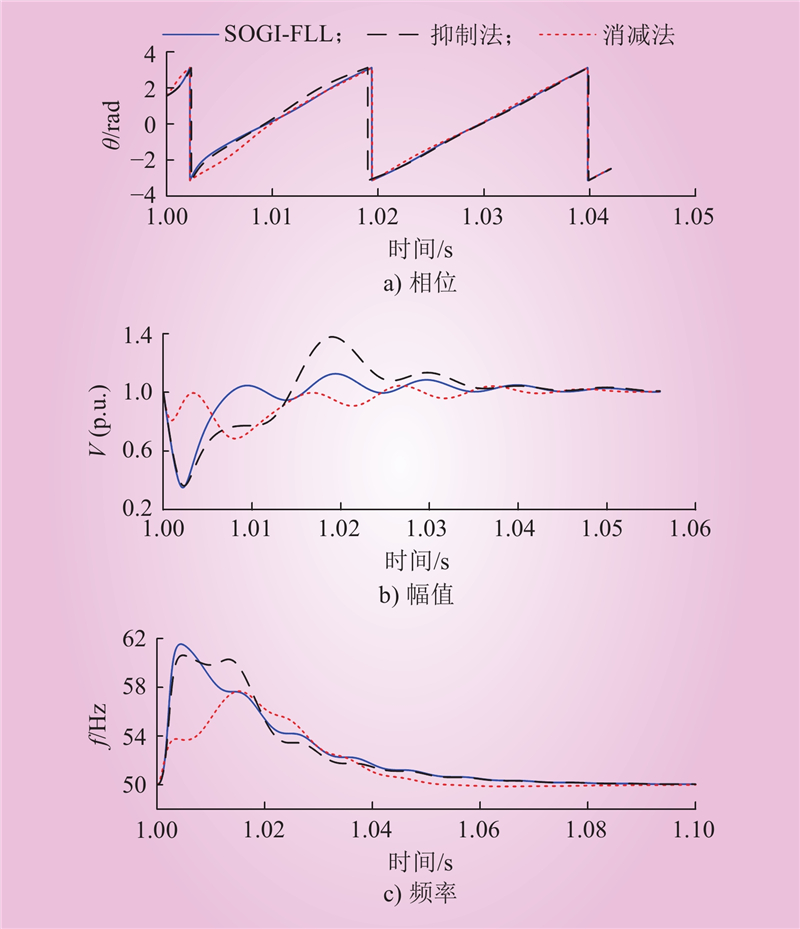
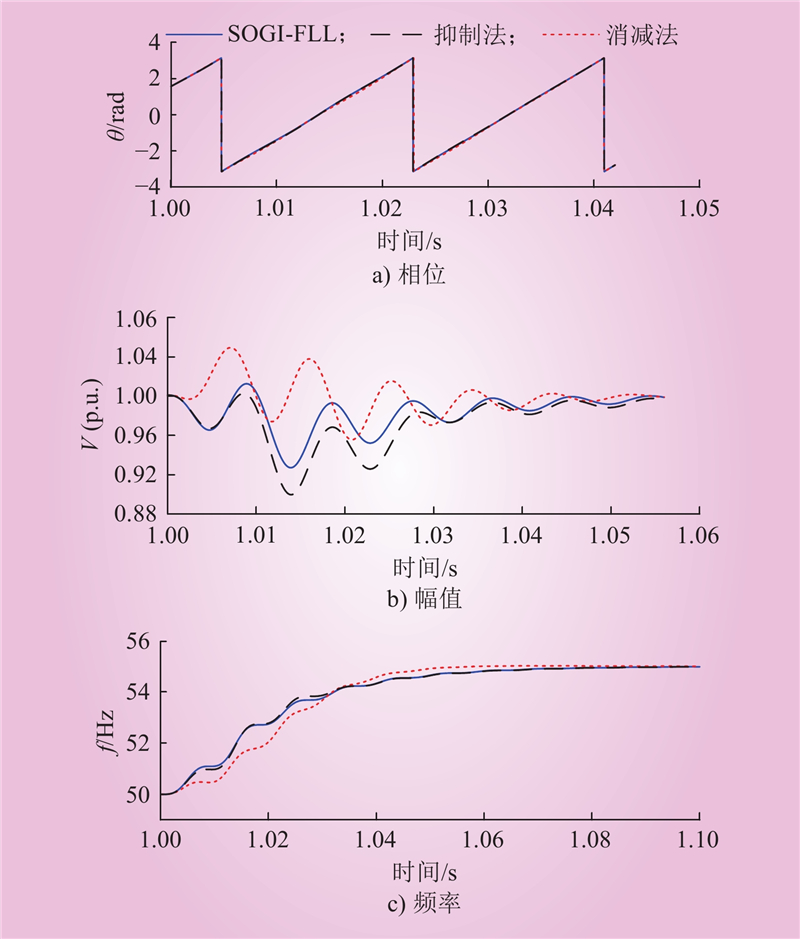
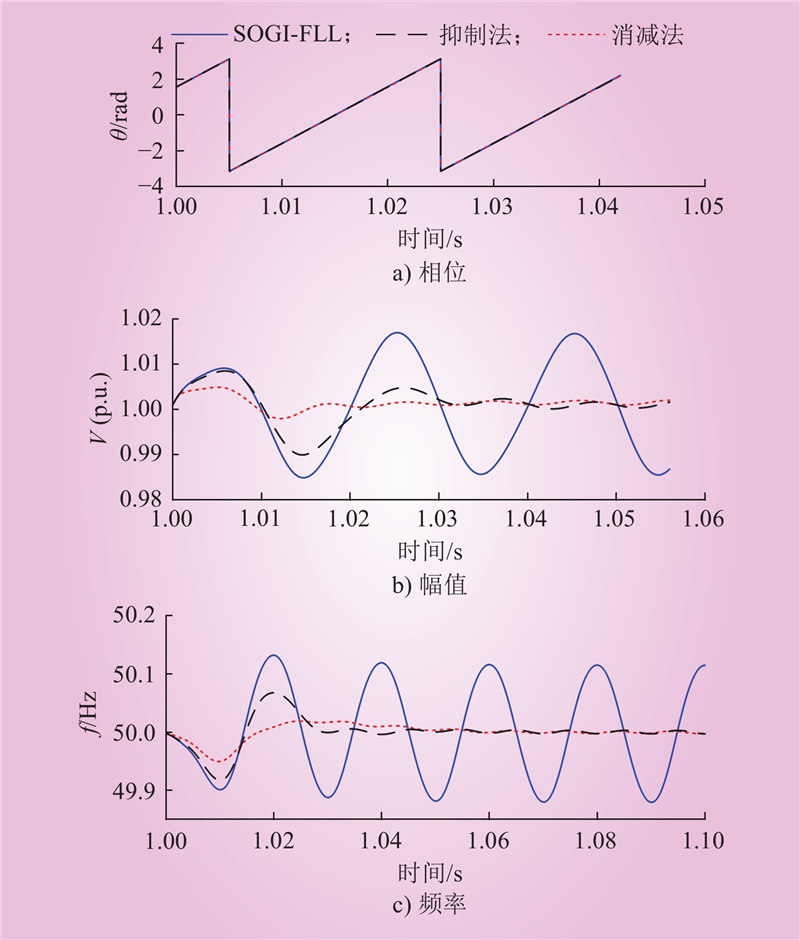
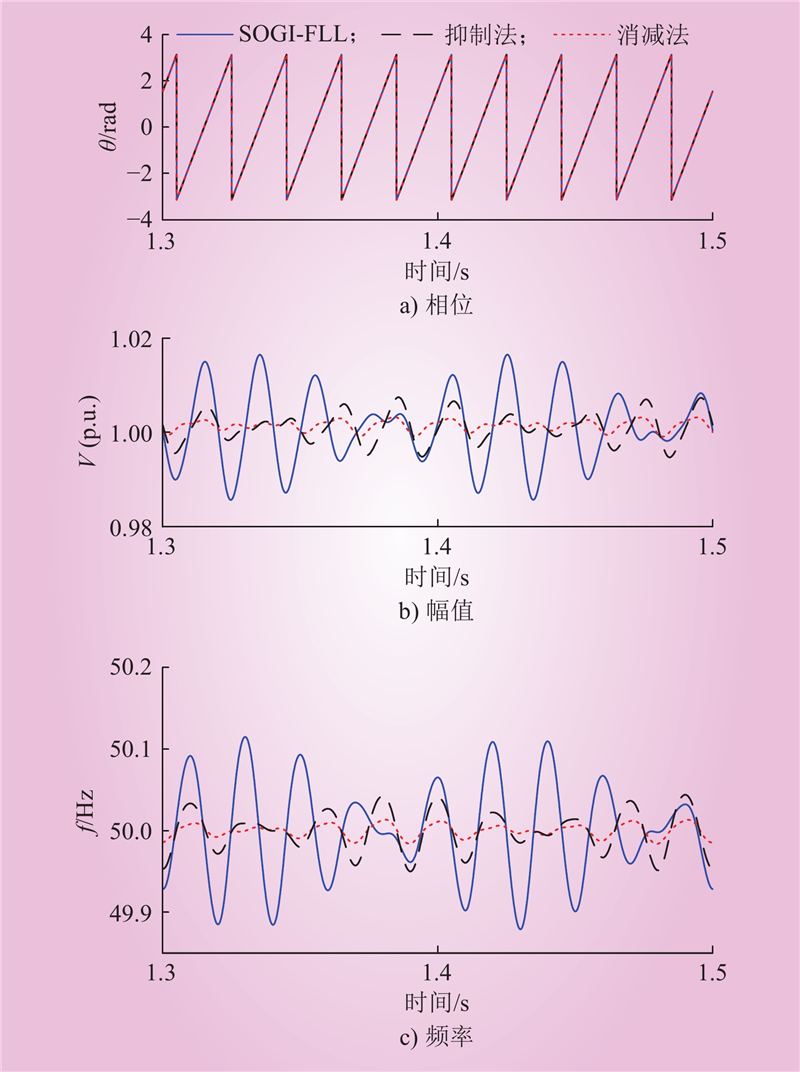
| 1 |
凌扬坚, 付熙坤, 黄萌, 等. 基于自适应锁相环的并网变流器暂态稳定提升策略研究[J]. 东北电力大学学报, 2022, 42 (5): 25- 32, 2.
|
|
LING Yangjian, FU Xikun, HUANG Meng, et al. Analysis and improvement of transient stability of phase-locked loop converter based on energy function[J]. Journal of Northeast Electric Power University, 2022, 42 (5): 25- 32, 2.
|
| 2 |
黄海宏, 刘远朋, 王海欣. 一种适用于复杂电网下的高精度锁相环[J]. 电机与控制学报, 2024, 28 (3): 43- 55.
|
|
HUANG Haihong, LIU Yuanpeng, WANG Haixin. High-precision phase-locked loop suitable for complex power grids[J]. Electric Machines and Control, 2024, 28 (3): 43- 55.
|
| 3 |
AHMED H. Low-order measurement offset rejection methods in single-phase SOGI-PLL[J]. IEEE Sensors Letters, 2023, 8 (1): 7000604.
|
| 4 |
张培玲, 赵可可. 基于单频通信的低压电力线通信系统设计与实现[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (3): 118- 127, 136.
|
|
ZHANG Peiling, ZHAO Keke. Design and implementation of low voltage power communication system based on single frequency communication[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (3): 118- 127, 136.
|
| 5 |
刘林, 王大龙, 綦晓, 等. 基于双锁相环的海上风场综合惯量调频策略研究[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45 (2): 282- 290.
|
|
LIU Lin, WANG Dalong, QI Xiao, et al. Study on double phase-locked loop on the synthetic inertia control of offshore wind farm frequency regulation[J]. Power Generation Technology, 2024, 45 (2): 282- 290.
|
| 6 |
PRAKASH S, SINGH J K, BEHERA R K, et al. A type-3 modified SOGI-PLL with grid disturbance rejection capability for single-phase grid-tied converters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 2021, 57 (4): 4242- 4252.
|
| 7 |
CIOBOTARU M, TEODORESCU R, AGELIDIS V G. Offset rejection for PLL based synchronization in grid-connected converters[C]//2008 Twenty-Third Annual IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition. Austin, TX, USA. IEEE, 2008: 1611–1617.
|
| 8 |
陈征, 胡鹏飞, 戴立宇, 等. 基于锁相环的并网VSC暂态失稳机理与控制方法[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (10): 77- 86.
|
|
CHEN Zheng, HU Pengfei, DAI Liyu, et al. Transient instability mechanism and control method of PLL-based grid-connected VSC[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (10): 77- 86.
|
| 9 |
汪冬辉, 方芳, 吕文韬, 等. 锁相环的动态性能及对线路保护的影响分析[J]. 中国电力, 2020, 53 (3): 110- 118.
|
|
WANG Donghui, FANG Fang, LV Wentao, et al. Analysis of dynamic performance of phase lock loop and its effect on line relay[J]. Electric Power, 2020, 53 (3): 110- 118.
|
| 10 |
李培法, 唐欣, 王文, 等. 锁相环对柔性直流输电系统换流站输入导纳的影响分析[J]. 电力科学与技术学报, 2020, 35 (4): 20- 26.
|
|
LI Peifa, TANG Xin, WANG Wen, et al. Analysis of the effect of phase-locked loop on input admittance of converter station in flexible DC transmission system[J]. Journal of Electric Power Science and Technology, 2020, 35 (4): 20- 26.
|
| 11 |
郭磊磊, 叶青洋, 金楠, 等. 一种基于双定频SOGI与交叉补偿的三相锁相环设计方法[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2024, 52 (12): 133- 142.
|
|
GUO Leilei, YE Qingyang, JIN Nan, et al. A three-phase phase-locked loop design method based on improved frequency-fixed DSOGI and cross-compensation[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2024, 52 (12): 133- 142.
|
| 12 |
马天诚, 黄云辉, 王栋, 等. 弱电网不对称故障下基于正负序解耦的锁相环设计与研究[J]. 智慧电力, 2022, 50 (1): 108- 114.
|
|
MA Tiancheng, HUANG Yunhui, WANG Dong, et al. Design and research of PLL based on positive and negative sequence decoupling under asymmetric faults in weak power grid[J]. Smart Power, 2022, 50 (1): 108- 114.
|
| 13 |
CIOBOTARU M, TEODORESCU R, BLAABJERG F. A new single-phase PLL structure based on second order generalized integrator[C]//2006 37th IEEE Power Electronics Specialists Conference. Jeju, Korea (South). IEEE, 2006: 1–6.
|
| 14 |
李锐, 李鹏, 张琦, 等. 基于SOGI的光伏并网逆变器锁相环的优化研究[J]. 电气应用, 2023, 42 (12): 77- 82.
|
|
LI Rui, LI Peng, ZHANG Qi, et al. Research on optimization of phase locked loop for PV grid-connected inverters based on SOGI[J]. Electrotechnical Application, 2023, 42 (12): 77- 82.
|
| 15 |
李圣清, 曹鹏, 李欣, 等. 电网电压不平衡下改进光储VSG控制策略[J]. 广东电力, 2024, 37 (8): 63- 69.
|
|
LI Shengqing, CAO Peng, LI Xin, et al. Improved VSG control strategy for photovoltaic-storage systems under grid voltage imbalance[J]. Guangdong Electric Power, 2024, 37 (8): 63- 69.
|
| 16 |
NGO T, MIN K, VU T. Comparative study of fault detection methods based on time domain RMS calculation[C]//2019 IEEE Power & Energy Society General Meeting (PESGM). Atlanta, GA, USA. IEEE, 2019: 1–5.
|
| 17 |
罗韡, 王琛琛. 可抑制直流偏移的软启动式单相锁频环[J]. 太阳能学报, 2024, 45 (1): 552- 562.
|
|
WANG Chenchen. Soft-start single-phase frequency-locked loop with DC component rejection capability[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2024, 45 (1): 552- 562.
|
| 18 |
AHMED H. Single-phase SOGI-PLLs for fast and accurate frequency ramp tracking[J]. IEEE Sensors Letters, 2023, 7 (11): 6008404.
|
| 19 |
严庆增, 赵仁德, 何金奎, 等. 基于SOGI-FLL的可变功率因数低压单相交流电子负载研究[J]. 实验技术与管理, 2023, 40 (6): 49- 53.
|
|
YAN Qingzeng, ZHAO Rende, HE Jinkui, et al. Research on low-voltage single-phase AC electronic loads with variable power factors based on SOGI-FLL[J]. Experimental Technology and Management, 2023, 40 (6): 49- 53.
|
| 20 |
张鑫, 林凡, 沈鑫杰. 基于改进SOGI-FLL的旋转弹舵机滞后测试方法[J]. 兵工学报, 2023, 44 (2): 428- 436.
|
|
ZHANG Xin, LIN Fan, SHEN Xinjie. A lag angle test method for actuators of spinning missiles based on improved SOGI-FLL[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2023, 44 (2): 428- 436.
|
| 21 |
ARDALAN P, RASEKH N, KHANEGHAH M Z, et al. A modified SOGI-FLL algorithm with DC-offset rejection improvement for single-phase inverter applications[J]. International Journal of Dynamics and Control, 2022, 10 (6): 2020- 2033.
|
| 22 |
黄太昱, 韩伟, 马伟东, 等. 基于双输入式改进型二阶广义积分器的频率检测优化方法研究[J]. 湖南电力, 2023, 43 (3): 16- 20.
|
|
HUANG Taiyu, HAN Wei, MA Weidong, et al. Research on frequency detection optimization method based on double input improved second order generalized integrator[J]. Hunan Electric Power, 2023, 43 (3): 16- 20.
|
| 23 |
杜维柱, 罗亚洲, 李蕴红, 等. 风电汇集系统无功盈余导致暂态过电压问题的研究综述[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2022, 42 (9): 3224- 3239.
|
|
DU Weizhu, LUO Yazhou, LI Yunhong, et al. Reviews of transient overvoltage problem cause by extra reactive power in large scale wind power systems[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2022, 42 (9): 3224- 3239.
|
| 24 |
戴朝波, 于弘洋, 赵国亮, 等. STATCOM和同步调相机响应时间的仿真分析和比较[J]. 南方电网技术, 2023, 17 (10): 85- 93.
|
|
DAI Chaobo, YU Hongyang, ZHAO Guoliang, et al. Simulation analysis and comparison of response times of STATCOM and synchronous condensers[J]. Southern Power System Technology, 2023, 17 (10): 85- 93.
|
| 25 |
ZHANG C J, ZHAO X J, WANG X H, et al. A grid synchronization PLL method based on mixed second- and third-order generalized integrator for DC offset elimination and frequency adaptability[J]. IEEE Journal of Emerging and Selected Topics in Power Electronics, 2018, 6 (3): 1517- 1526.
|
| 26 |
TEODORESCU R, LISERRE M, RODRÍGUEZ P. Grid Converters for Photovoltaic and Wind Power Systems[M]. Chichester: Wiley, 2010.
|
| 27 |
KARIMI-GHARTEMANI M, ALI KHAJEHODDIN S, JAIN P K, et al. Addressing DC component in PLL and Notch filter algorithms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2011, 27 (1): 78- 86.
|
| 28 |
戴朝波, 赵国亮, 于弘洋, 等. STATCOM响应速度对电网电压的影响和对策[J/OL]. 电源学报. (2024-04-26) [2024-10-18]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/12.1420.TM.20240426.1146.055.html.
|
|
DAI Chaobo, ZHAO Guoliang, YU Hongyang, et al. Impact and countermeasure of STATCOM response speed on grid voltage[J/OL]. Journal of power Supply. (2024-04-26) [2024-10-18]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/12.1420.TM.20240426.1146.055.html.
|