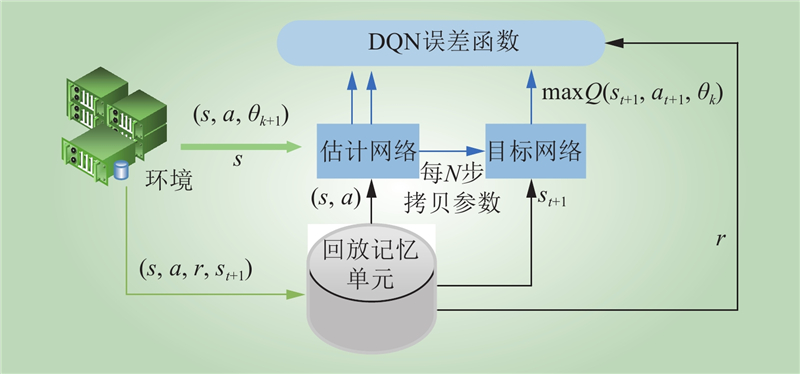
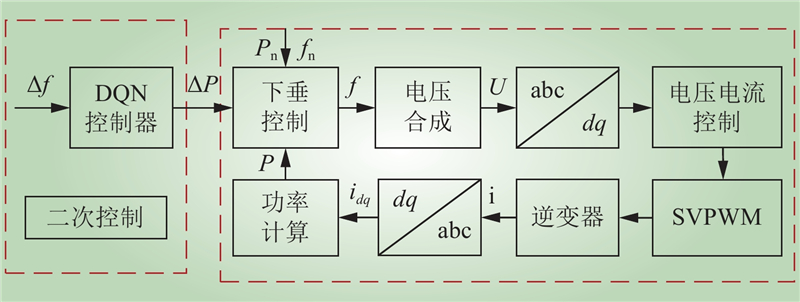
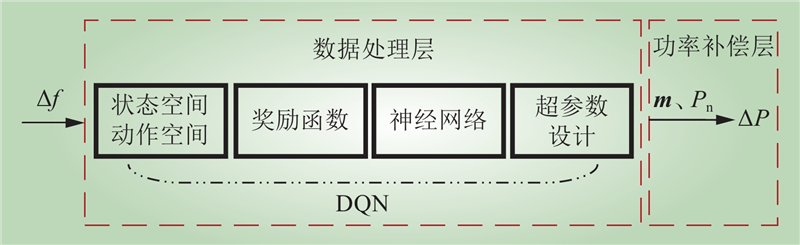
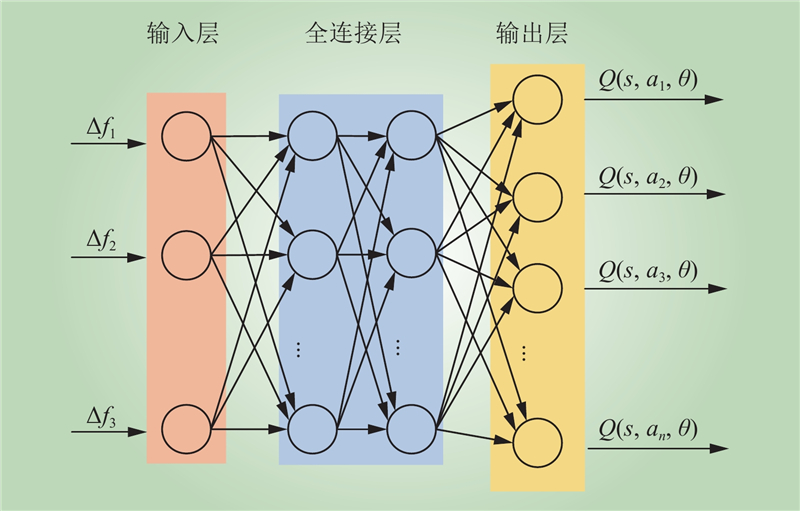
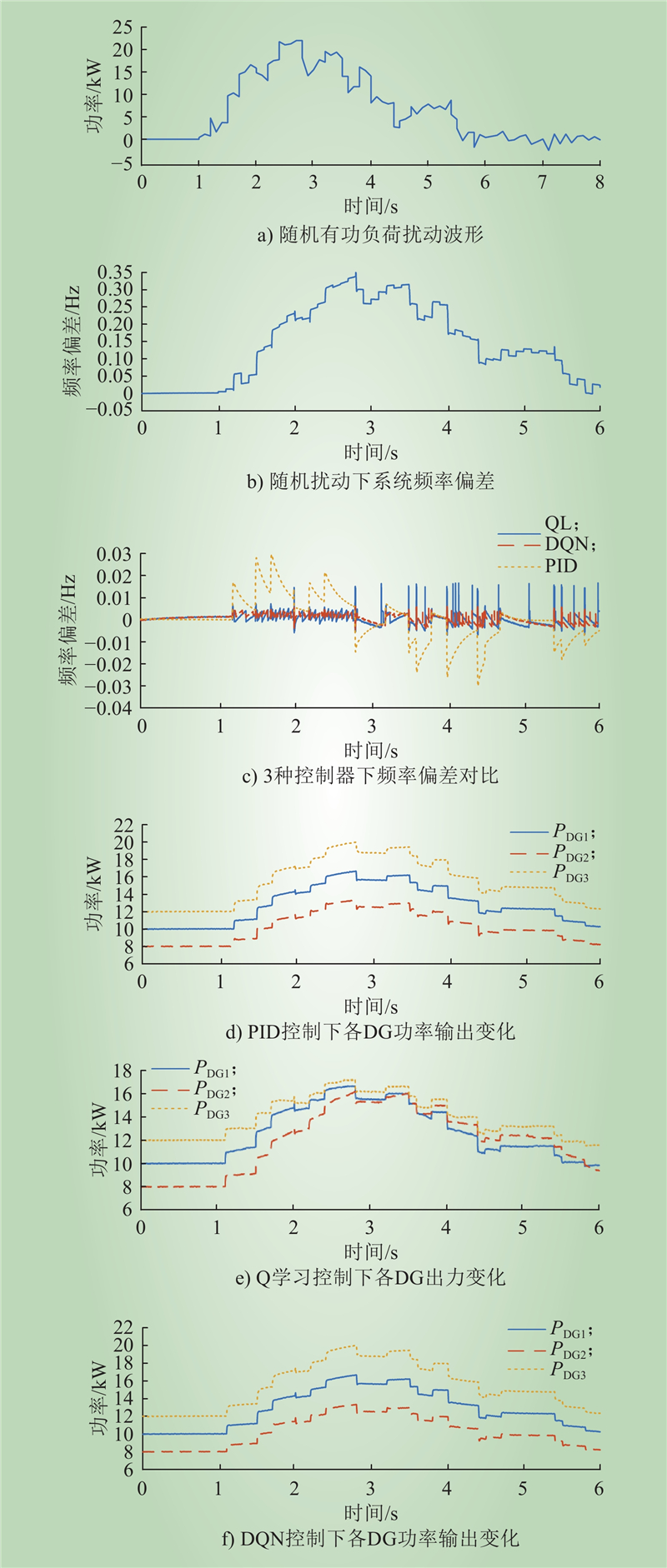
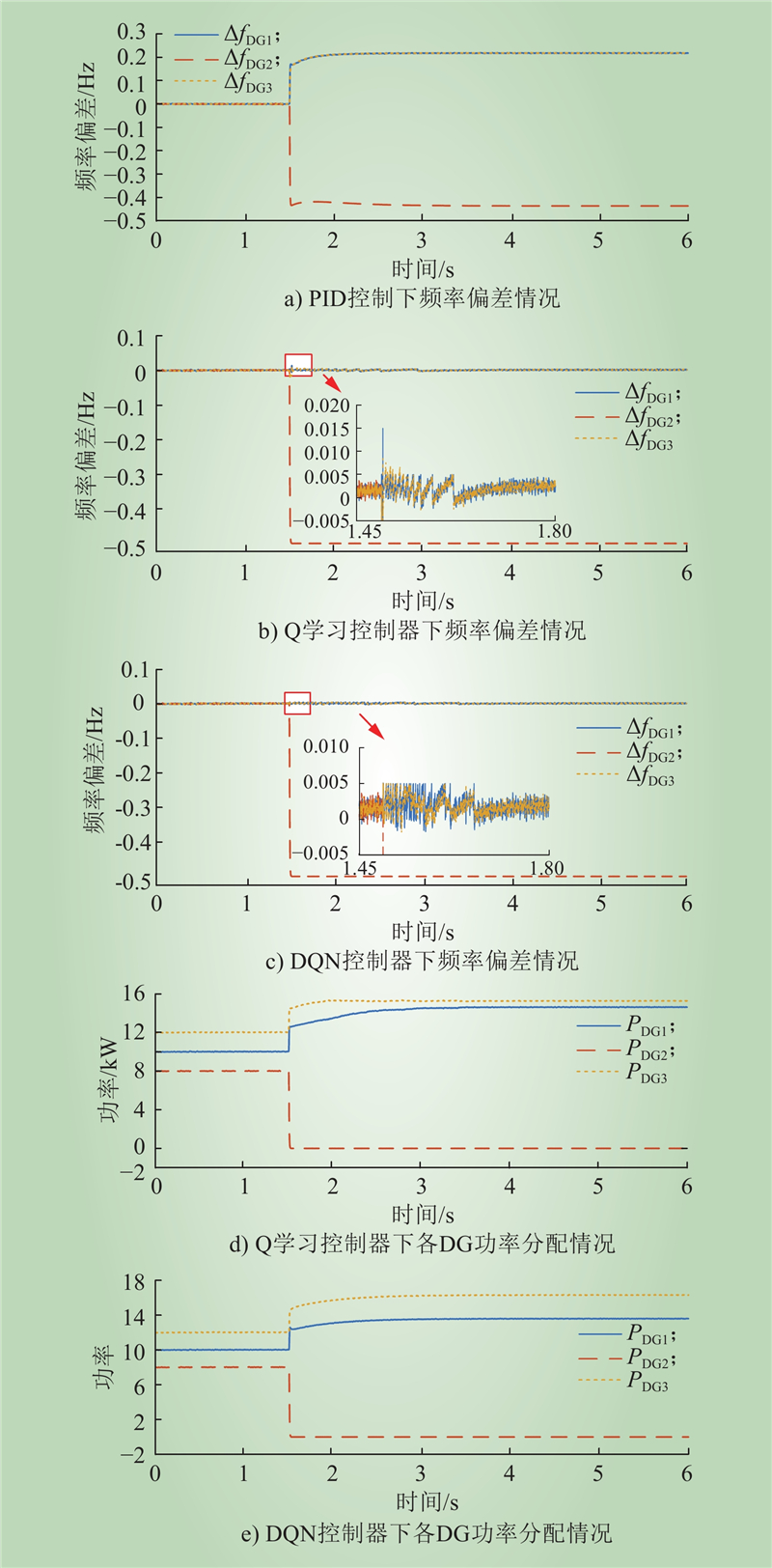
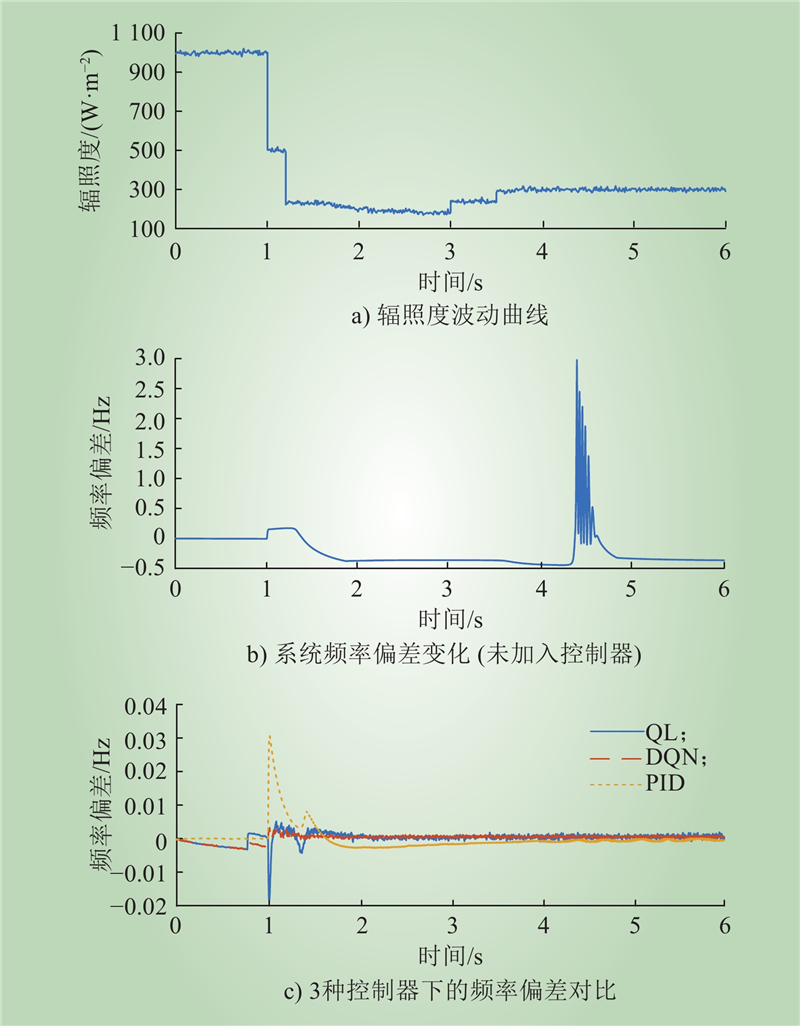
| 1 |
王新宝, 葛景, 韩连山, 等. 构网型储能支撑新型电力系统建设的思考与实践[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2023, 51 (5): 172- 179.
|
|
WANG Xinbao, GE Jing, HAN Lianshan, et al. Theory and practice of grid-forming BESS supporting the construction of a new type of power system[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2023, 51 (5): 172- 179.
|
| 2 |
王大兴, 宁妍, 汪敬培, 等. 构建新型电力系统背景下的微电网鲁棒简化建模[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (1): 148- 157.
|
|
WANG Daxing, NING Yan, WANG Jingpei, et al. Robust simplified modeling of microgrid in the context of constructing new power systems[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (1): 148- 157.
|
| 3 |
王德志, 张孝顺, 刘前进, 等. 基于集成学习的孤岛微电网源—荷协同频率控制[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2018, 42 (10): 46- 52.
|
|
WANG Dezhi, ZHANG Xiaoshun, LIU Qianjin, et al. Ensemble learning for generation-consumption coordinated frequency control in an islanded microgrid[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2018, 42 (10): 46- 52.
|
| 4 |
张宇, 王洪希, 王璞. 交直流混合微电网互联变流器微分平坦控制[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (7): 102- 109, 120.
|
|
ZHANG Yu, WANG Hongxi, WANG Pu. Flatness-based control of AC/DC hybrid microgrid interconnected converter[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (7): 102- 109, 120.
|
| 5 |
吴忠强, 程洪强. 考虑状态受限和一致性的微电网二次控制[J]. 控制理论与应用, 2024, 41 (1): 183- 188.
|
|
WU Zhongqiang, CHENG Hongqiang. Secondary control for microgrid considering state constraint and consensus[J]. Control Theory & Applications, 2024, 41 (1): 183- 188.
|
| 6 |
董家伟, 王志新, 朱国忠, 等. 孤岛运行下垂逆变器二次调频方法[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2022, 42 (5): 40- 46.
|
|
DONG Jiawei, WANG Zhixin, ZHU Guozhong, et al. Secondary frequency regulation method for droop inverters in island operation[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2022, 42 (5): 40- 46.
|
| 7 |
李忠文, 程志平, 张书源, 等. 考虑经济调度及电压恢复的直流微电网分布式二次控制[J]. 电工技术学报, 2021, 36 (21): 4482- 4492.
|
|
LI Zhongwen, CHENG Zhiping, ZHANG Shuyuan, et al. Distributed secondary control for economic dispatch and voltage restoration of DC microgrid[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2021, 36 (21): 4482- 4492.
|
| 8 |
VAISHNAV V, SHARMA D, JAIN A. Quadratic-droop-based distributed secondary control of microgrid with detail-balanced communication topology[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2023, 17 (3): 3401- 3412.
|
| 9 |
曹晓, 李泽, 崔国增. 孤岛微电网固定时间分布式鲁棒二次控制[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2024, 52 (12): 143- 153.
|
|
CAO Xiao, LI Ze, CUI Guozeng. Distributed robust fixed-time secondary control of islanded microgrids[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2024, 52 (12): 143- 153.
|
| 10 |
李志军, 苗庆玉, 张家安. 基于虚拟领导节点改进的孤岛微电网完全分布式二次调频策略[J]. 太阳能学报, 2024, 45 (5): 333- 342.
|
|
LI Zhijun, MIAO Qingyu, ZHANG Jia’an. Fully distributed secondary frequency control strategy for island microgrids based on improved virtual leader node[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2024, 45 (5): 333- 342.
|
| 11 |
孙伟, 方昭, 杨建平, 等. 考虑随机时变延时的孤岛微电网分布式二次控制[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2022, 42 (3): 864- 875.
|
|
SUN Wei, FANG Zhao, YANG Jianping, et al. Distributed secondary control of islanded microgrid with stochastic time-varying delay[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2022, 42 (3): 864- 875.
|
| 12 |
孙永辉, 孟雲帆, 葛磊蛟, 等. 人工智能赋能微电网运行优化的应用及展望[J]. 高电压技术, 2023, 49 (6): 2239- 2252.
|
|
SUN Yonghui, MENG Yunfan, GE Leijiao, et al. Application and prospect of microgrid operation optimization enabled by artificial intelligence[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2023, 49 (6): 2239- 2252.
|
| 13 |
熊珞琳, 毛帅, 唐漾, 等. 基于强化学习的综合能源系统管理综述[J]. 自动化学报, 2021, 47 (10): 2321- 2340.
|
|
XIONG Luolin, MAO Shuai, TANG Yang, et al. Reinforcement learning based integrated energy system management: a survey[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47 (10): 2321- 2340.
|
| 14 |
汪超, 赵婵娟, 程志友, 等. 基于协同强化学习的微电网分布式两级电压优化控制[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2022, 50 (21): 22- 32.
|
|
WANG Chao, ZHAO Chanjuan, CHENG Zhiyou, et al. Distributed secondary voltage optimization control for a microgrid based on cooperative reinforcement learning[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2022, 50 (21): 22- 32.
|
| 15 |
LI J, CAI C, SU Q Y. Secondary restoration of islanded alternating current microgrids under a neural inverse optimal control[J]. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2024, 133, 108538.
|
| 16 |
ADIBI M, VAN DER WOUDE J. Secondary frequency control of microgrids: an online reinforcement learning approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2022, 67 (9): 4824- 4831.
|
| 17 |
沈珺, 柳伟, 李虎成, 等. 基于强化学习的多微电网分布式二次优化控制[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2020, 44 (5): 198- 206.
|
|
SHEN Jun, LIU Wei, LI Hucheng, et al. Reinforcement learning based distributed secondary optimal control for multiple microgrids[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2020, 44 (5): 198- 206.
|
| 18 |
符杨, 郭笑岩, 米阳, 等. 基于强化学习的直流微电网分布式经济下垂控制[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2021, 41 (11): 1- 7.
|
|
FU Yang, GUO Xiaoyan, MI Yang, et al. Distributed economic droop control for DC microgrid based on reinforcement learning[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2021, 41 (11): 1- 7.
|
| 19 |
江昌旭, 刘晨曦, 林铮, 等. 基于深度强化学习的电力系统暂态稳定控制策略研究综述[J]. 高电压技术, 2023, 49 (12): 5171- 5186.
|
|
JIANG Changxu, LIU Chenxi, LIN Zheng, et al. Review of power system transient stability control strategies based on deep reinforcement learning[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2023, 49 (12): 5171- 5186.
|
| 20 |
LI J W, CHENG Y Y. Deep meta-reinforcement learning-based data-driven active fault tolerance load frequency control for islanded microgrids considering Internet of Things[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2024, 11 (6): 10295- 10303.
|
| 21 |
谢黎龙, 李勇汇, 范培潇, 等. 基于深度强化学习的孤立多微电网系统频率和电压综合控制[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2024, 44 (6): 118- 126.
|
|
XIE Lilong, LI Yonghui, FAN Peixiao, et al. Deep reinforcement learning-based integrated frequency and voltage control for isolated multi-microgrid system[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2024, 44 (6): 118- 126.
|
| 22 |
LI J W, ZHOU T. Prior knowledge incorporated large-scale multiagent deep reinforcement learning for load frequency control of isolated microgrid considering multi-structure coordination[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2024, 20 (3): 3923- 3934.
|
| 23 |
毕聪博, 唐聿劼, 罗永红, 等. 电力系统优化控制中强化学习方法应用及挑战[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2024, 44 (1): 1- 22.
|
|
BI Congbo, TANG Yujie, LUO Yonghong, et al. Review on critical problems in reinforcement learning methods applied in power system optimization and control scenarios[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2024, 44 (1): 1- 22.
|
| 24 |
LIN S W, CHU C C, TUNG C F. Data-driven distributed Q-learning droop control for frequency synchronization and voltage restoration in isolated AC micro-grids[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 2023, 59 (6): 7306- 7317.
|
| 25 |
ALABDULLAH M H, ABIDO M A. Microgrid energy management using deep Q-network reinforcement learning[J]. Alexandria Engineering Journal, 2022, 61 (11): 9069- 9078.
|
| 26 |
刘俊峰, 陈剑龙, 王晓生, 等. 基于深度强化学习的微能源网能量管理与优化策略研究[J]. 电网技术, 2020, 44 (10): 3794- 3803.
|
|
LIU Junfeng, CHEN Jianlong, WANG Xiaosheng, et al. Energy management and optimization of multi-energy grid based on deep reinforcement learning[J]. Power System Technology, 2020, 44 (10): 3794- 3803.
|
| 27 |
胡正伟, 夏思懿, 王文彬, 等. 基于深度强化学习的Π型阻抗匹配网络多参数最优求解方法[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2024, 52 (6): 152- 163.
|
|
HU Zhengwei, XIA Siyi, WANG Wenbin, et al. Multi-parameter optimal solution method for Π-type impedance matching networks based on deep reinforcement learning[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2024, 52 (6): 152- 163.
|
| 28 |
董光德, 李道明, 陈咏涛, 等. 基于粒子群优化与卷积神经网络的电能质量扰动分类方法[J]. 发电技术, 2023, 44 (1): 136- 142.
|
|
DONG Guangde, LI Daoming, CHEN Yongtao, et al. Power quality disturbance classification method based on particle swarm optimization and convolutional neural network[J]. Power Generation Technology, 2023, 44 (1): 136- 142.
|
| 29 |
武同心, 纪鑫, 杨成月, 等. 基于双层注意力机制的电力文本分类模型[J/OL]. 中国电力, 1–8 [2025-05-09]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.3265.TM.20250425.1604.002.html.
|
|
WU Tongxin, JI Xin, YANG Chengyue, et al. A power text classification model based on deep learning[J/OL]. Electric power, 1–8[2025-05-09]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.3265.TM.20250425.1604.002.html.
|
| 30 |
付红军, 朱劭璇, 王步华, 等. 基于长短期记忆神经网络的检修态电网低频振荡风险预测方法[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45 (2): 353- 362.
|
|
FU Hongjun, ZHU Shaoxuan, WANG Buhua, et al. Risk prediction method of low frequency oscillation in maintenance power network based on long short term memory neural network[J]. Power Generation Technology, 2024, 45 (2): 353- 362.
|
| 31 |
李卓, 王胤喆, 叶林, 等. 从感知-预测-优化综述图神经网络在电力系统中的应用[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (12): 2- 16.
|
|
LI Zhuo, WANG Yinzhe, YE Lin, et al. The application of graph neural networks in power systems from perspective of perception-prediction-optimization[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (12): 2- 16.
|
| 32 |
邵宜祥, 刘剑, 胡丽萍, 等. 一种改进组合神经网络的超短期风速预测方法研究[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45 (2): 323- 330.
|
|
SHAO Yixiang, LIU Jian, HU Liping, et al. Research on an ultra-short-term wind speed prediction method based on improved combined neural networks[J]. Power Generation Technology, 2024, 45 (2): 323- 330.
|
| 33 |
闫志彬, 李立, 阳鹏, 等. 考虑构网型储能支撑能力的微电网优化调度策略[J]. 中国电力, 2025, 58 (2): 103- 110.
|
|
YAN Zhibin, LI Li, YANG Peng, et al. Optimal scheduling strategy for microgrid considering the support capabilities of grid Forming energy storage[J]. Electric Power, 2025, 58 (2): 103- 110.
|