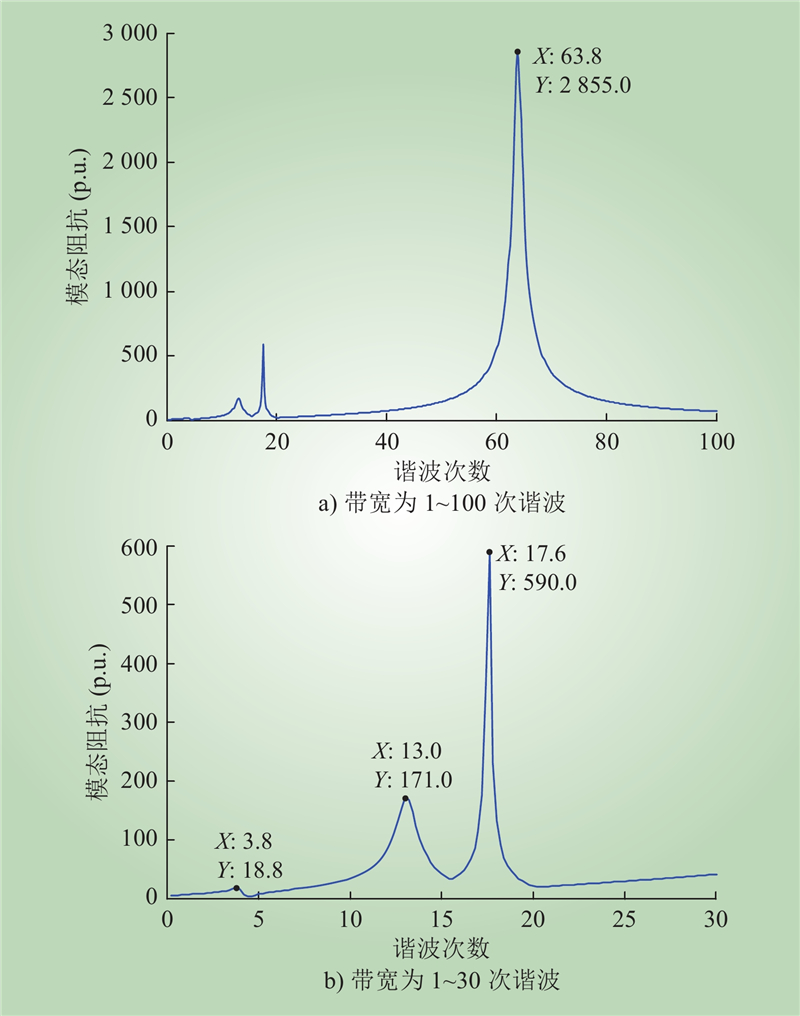
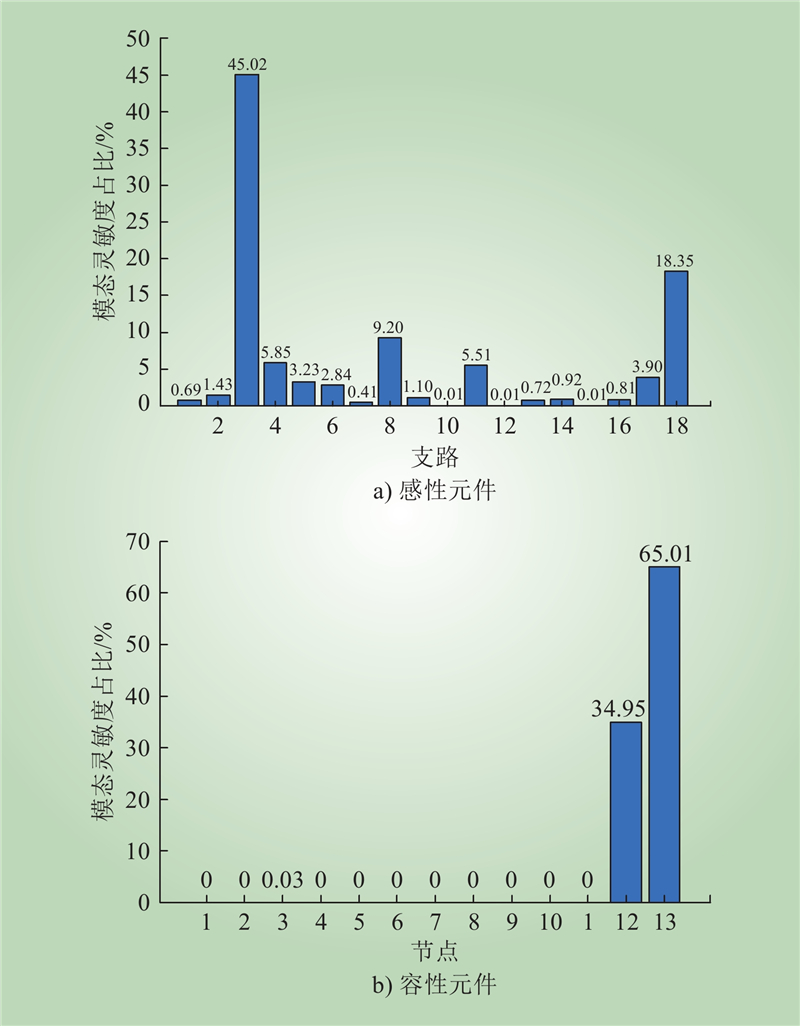
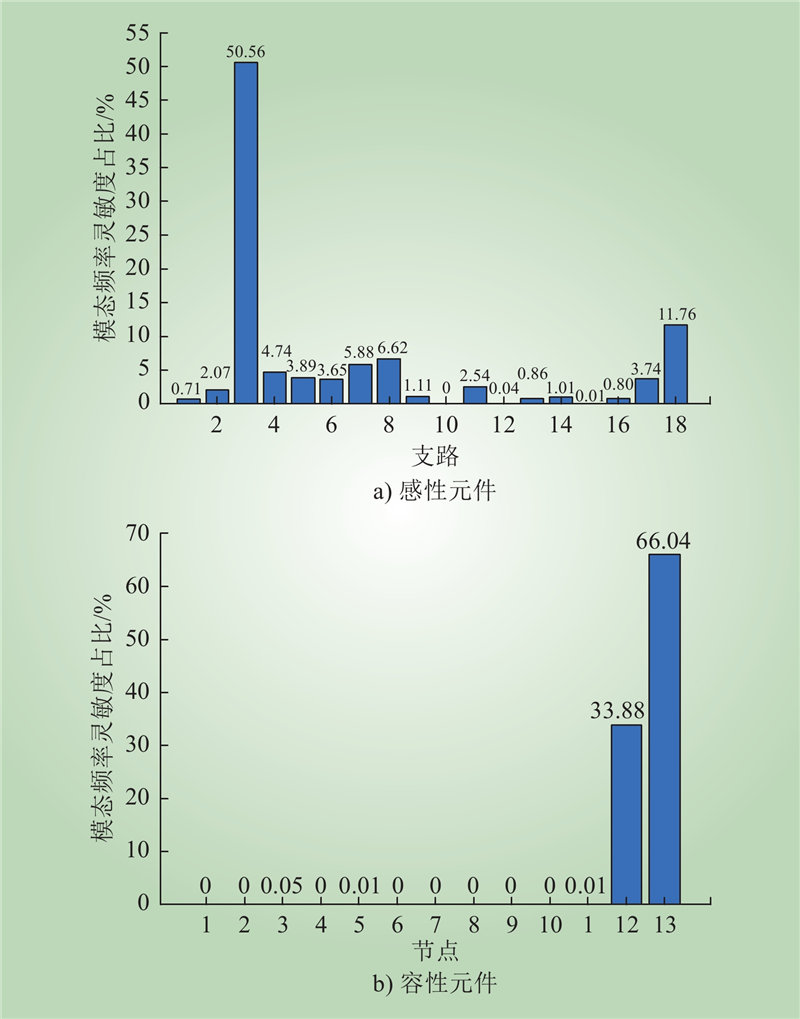
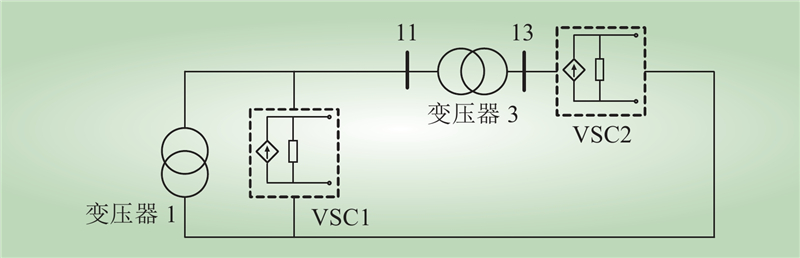
| 1 |
李朝阳. 电力系统谐波谐振概率评估方法研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2020.
|
|
LI Zhaoyang. Study on probabiistic assessment methods of harmonic resonance in power systems[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2020.
|
| 2 |
何正友. 分布式新能源接入电网的谐波热点问题探讨[J]. 南方电网技术, 2016, 10 (3): 47- 52.
|
|
HE Zhengyou. Discussion on harmonic hot issues of distributed new energy connected to power grid[J]. Southern Power System Technology, 2016, 10 (3): 47- 52.
|
| 3 |
刘洪, 李其哲, 徐晶, 等. 网孔型中压配电网组网形态、核心特征与研究展望[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2023, 47 (16): 181- 191.
|
|
LIU Hong, LI Qizhe, XU Jing, et al. Networking morphology, key feature and research prospect of mesh-type medium-voltage distribution network[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2023, 47 (16): 181- 191.
|
| 4 |
窦真兰, 张春雁, 赵慧荣, 等. 含氢能汽车负荷的住宅光-氢耦合能源系统容量优化配置[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (7): 54- 65.
|
|
DOU Zhenlan, ZHANG Chunyan, ZHAO Huirong, et al. Optimal capacity configuration of residential solar-hydrogen coupling energy system with hydrogen vehicle load[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (7): 54- 65.
|
| 5 |
韩华春, 李强, 袁晓冬. 考虑柔性氢需求的区域综合能源系统优化调度方法[J]. 电力科学与技术学报, 2022, 37 (3): 12- 18.
|
|
HAN Huachun, LI Qiang, YUAN Xiaodong. Optimal dispatch of regional integrated energy systems considering flexible hydrogen demand[J]. Journal of Electric Power Science and Technology, 2022, 37 (3): 12- 18.
|
| 6 |
王鹏飞, 李世民, 张磊, 等. 基于合作博弈的风-光-综合能源系统多主体协同运行策略[J]. 智慧电力, 2023, 51 (9): 52- 59.
|
|
WANG Pengfei, LI Shimin, ZHANG Lei, et al. Multi-agent cooperative operation strategy of wind-photovoltaic-integrated energy system based on cooperative game[J]. Smart Power, 2023, 51 (9): 52- 59.
|
| 7 |
毕锐, 王孝淦, 袁华凯, 等. 考虑供需双侧响应和碳交易的氢能综合能源系统鲁棒调度[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2023, 51 (12): 122- 132.
|
|
BI Rui, WANG Xiaogan, YUAN Huakai, et al. Robust dispatch of a hydrogen integrated energy system considering double side response and carbon trading mechanism[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2023, 51 (12): 122- 132.
|
| 8 |
蔡含虎, 向月, 杨昕然. 计及需求响应的综合能源系统容量经济配置及效益分析[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2019, 39 (8): 186- 194.
|
|
CAI Hanhu, XIANG Yue, YANG Xinran. Economic capacity allocation and benefit analysis of integrated energy system considering demand response[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2019, 39 (8): 186- 194.
|
| 9 |
郑伟民, 王蕾, 孙可, 等. 考虑多能流广义储能作用的配电网协调规划[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2021, 41 (7): 22- 30.
|
|
ZHENG Weimin, WANG Lei, SUN Ke, et al. Coordinated planning of distribution network considering function of multi-energy flow generalized energy storage[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2021, 41 (7): 22- 30.
|
| 10 |
朱明星, 孔彬彬, 张华赢. 电缆化配电系统高频谐振频移方法[J]. 中国电力, 2021, 54 (8): 19- 26.
|
|
ZHU Mingxing, KONG Binbin, ZHANG Huaying. High frequency resonance frequency shift method for cable distribution system[J]. Electric Power, 2021, 54 (8): 19- 26.
|
| 11 |
周辉, 吴耀武, 娄素华, 等. 基于模态分析和虚拟支路法的串联谐波谐振分析[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2007, 27 (28): 84- 89.
|
|
ZHOU Hui, WU Yaowu, LOU Suhua, et al. Series resonance analysis based on modal analysis and dummy branch method[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2007, 27 (28): 84- 89.
|
| 12 |
BOTTURA F B, OLESKOVICZ M, LE T D, et al. Optimal positioning of power quality meters for monitoring potential conditions of harmonic resonances in a MV distribution system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery, 2019, 34 (5): 1885- 1897.
|
| 13 |
徐文远, 张大海. 基于模态分析的谐波谐振评估方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2005, 25 (22): 89- 93.
|
|
XU Wenyuan, ZHANG Dahai. A modal analysis method for harmonic resonance assessment[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2005, 25 (22): 89- 93.
|
| 14 |
AGRAWAL B L, FARMER R G. Use of frequency scanning techniques for subsynchronous resonance analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Apparatus and Systems, 1979, PAS-98 (2): 341- 349.
|
| 15 |
HAMMAD A, KAMWA I, VIAROUGE P, et al. Modeling and simulation of the propagation of harmonics in electric power networks. I. concepts, models, and simulation techniques. discussion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery, 1996, 11 (1): 452- 465.
|
| 16 |
XU W, HUANG Z Y, CUI Y, et al. Harmonic resonance mode analysis[C]//IEEE Power Engineering Society General Meeting. San Francisco, CA, USA. IEEE, 2005: 2236(3): 16.
|
| 17 |
舒万韬, 洪芦诚, 刘宁波, 等. 多逆变器并网谐振特性分析[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2018, 38 (17): 5009- 5019, 5298.
|
|
SHU Wantao, HONG Lucheng, LIU Ningbo, et al. An analysis on resonance characteristics of multi-inverters grid-connected system[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2018, 38 (17): 5009- 5019, 5298.
|
| 18 |
HUANG Z Y, CUI Y, XU W. Application of modal sensitivity for power system harmonic resonance analysis[C]//2007 IEEE Power Engineering Society General Meeting. Tampa, FL, USA. IEEE, 2007: 1.
|
| 19 |
YANG C X, LIU K P, ZHENG X, et al. Modal sensitivity analysis for parallel harmonic resonance in power system[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2013, 732/733, 1432- 1437.
|
| 20 |
仰彩霞, 刘开培, 李建奇, 等. 谐波谐振模态灵敏度分析[J]. 电工技术学报, 2011, 26 (S1): 207- 212.
|
|
YANG Caixia, LIU Kaipei, LI Jianqi, et al. Modal sensitivity analysis for harmonic resonance[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2011, 26 (S1): 207- 212.
|
| 21 |
HU H T, HE Z Y, ZHANG Y F, et al. Modal frequency sensitivity analysis and application using complex nodal matrix[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery, 2014, 29 (2): 969- 971.
|
| 22 |
陶顺, 闫亚楠, 刘云博. 基于导纳模型的并网直驱风电场高频谐振分析[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2022, 42 (21): 7832- 7843.
|
|
TAO Shun, YAN Yanan, LIU Yunbo. High frequency resonance analysis of power system with a D-PMSG-based wind farm based on admittance model[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2022, 42 (21): 7832- 7843.
|
| 23 |
胡伟, 孙建军, 马谦, 等. 多逆变器并网系统谐振特性分析[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2014, 34 (7): 93- 98.
|
|
HU Wei, SUN Jianjun, MA Qian, et al. Resonant characteristics of multi-inverter grid-connection system[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2014, 34 (7): 93- 98.
|
| 24 |
王磊, 张凌博. 多逆变器并网等值建模及谐振抑制优化[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2021, 49 (6): 19- 29.
|
|
WANG Lei, ZHANG Lingbo. Equivalent modeling of multi-inverters connected to the grid and optimization of resonance suppression[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2021, 49 (6): 19- 29.
|
| 25 |
孙白艳. 计及谐波影响的配电网电容器优化配置研究[D]. 绵阳: 西南科技大学, 2015.
|
|
SUN Baiyan. Account harmonic effects distribution network capacitor optimization research[D]. Mianyang: Southwest University of Science and Technology, 2015.
|