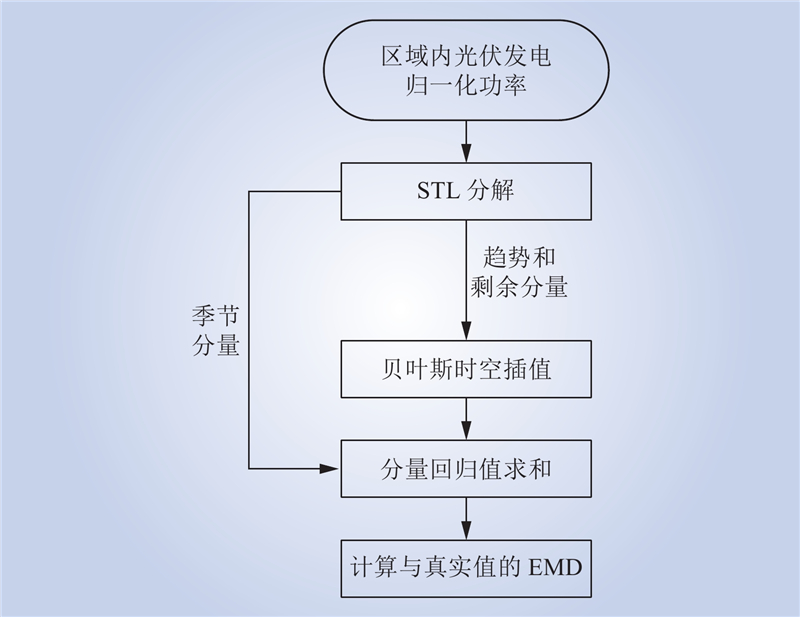
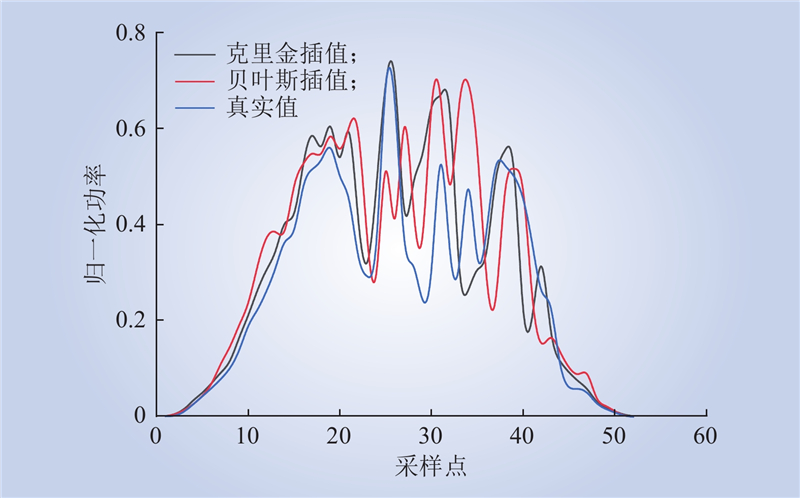
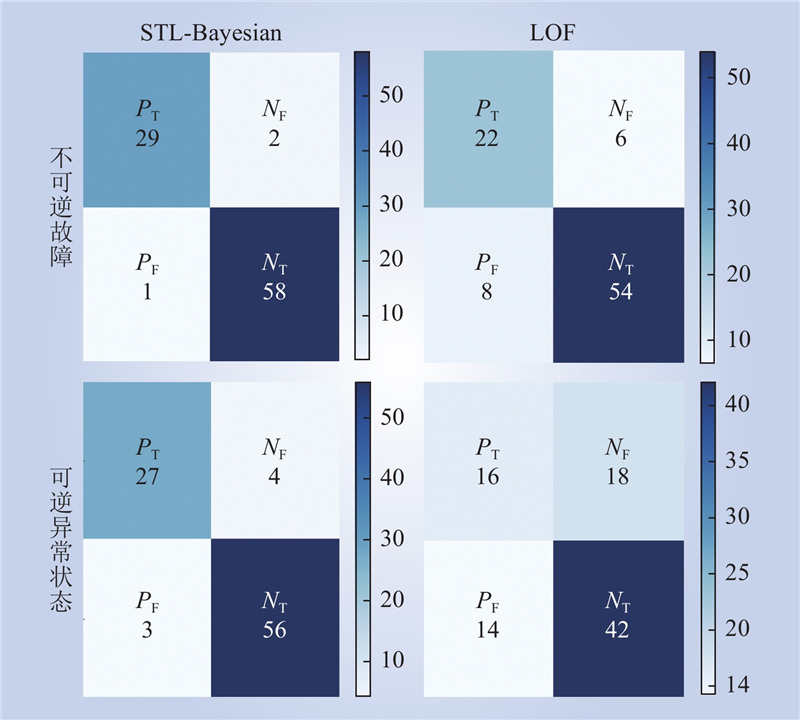
| 1 |
曹仟妮, 贾孟硕, 沈沉. 针对复杂安装条件的光伏电站光伏板异常状态检测技术[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2022, 42 (5): 1917- 1925.
|
|
CAO Qianni, JIA Mengshuo, SHEN Chen. A fault detection scheme for PV modules in large scale PV stations with complex installation conditions[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2022, 42 (5): 1917- 1925.
|
| 2 |
李光辉, 段晨东, 武珊. 基于半监督机器学习法的光伏阵列故障诊断[J]. 电网技术, 2020, 44 (5): 1908- 1913.
|
|
LI Guanghui, DUAN Chendong, WU Shan. Fault diagnosis of PV array based on semi-supervised machine learning[J]. Power System Technology, 2020, 44 (5): 1908- 1913.
|
| 3 |
焦田利, 章坚民, 李熊, 等. 基于空间相关性的大规模分布式用户光伏空间分群方法[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2019, 43 (21): 97- 102, 162.
|
|
JIAO Tianli, ZHANG Jianmin, LI Xiong, et al. Spatial clustering method for large-scale distributed user photovoltaics based on spatial correlation[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2019, 43 (21): 97- 102, 162.
|
| 4 |
张青山, 王丽婕, 郝颖, 等. 基于卫星云图和晴空模型的分布式光伏电站太阳辐照度超短期预测[J]. 高电压技术, 2022, 48 (8): 3271- 3281.
|
|
ZHANG Qingshan, WANG Lijie, HAO Ying, et al. Ultra-short-term solar irradiance prediction of distributed photovoltaic power stations based on satellite cloud images and clear sky model[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2022, 48 (8): 3271- 3281.
|
| 5 |
SHI Y C, HE W G, ZHAO J, et al. Expected output calculation based on inverse distance weighting and its application in anomaly detection of distributed photovoltaic power stations[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 253, 119965.
|
| 6 |
张童彦, 廖清芬, 唐飞, 等. 基于气象资源插值与迁移学习的广域分布式光伏功率预测方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2023, 43 (20): 7929- 7940.
|
|
ZHANG Tongyan, LIAO Qingfen, TANG Fei, et al. Wide-area distributed photovoltaic power forecast method based on meteorological resource interpolation and transfer learning[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2023, 43 (20): 7929- 7940.
|
| 7 |
王本涛, 白杨, 邢红涛, 等. 基于STL与MMoE多任务学习的区域多光伏电站超短期功率联合预测方法[J]. 电力系统及其自动化学报, 2022, 34 (9): 17- 23, 31.
|
|
WANG Bentao, BAI Yang, XING Hongtao, et al. Combined ultra-short-term power prediction method for regional multi-photovoltaic power stations based on STL and MMoE multi-task learning[J]. Proceedings of the CSU-EPSA, 2022, 34 (9): 17- 23, 31.
|
| 8 |
孙一浩, 肖先勇, 张文海, 等. 基于伪异常点辨识的关口电能表计量数据异常研究[J]. 电网技术, 2021, 45 (11): 4568- 4576.
|
|
SUN Yihao, XIAO Xianyong, ZHANG Wenhai, et al. Abnormal measurement data of gateway energy meter based on pseudo outlier identification[J]. Power System Technology, 2021, 45 (11): 4568- 4576.
|
| 9 |
熊寿遥, 邓仁毅, 黄创霞, 等. 气象因素对分布式光伏功率的影响分析[J]. 系统科学与数学, 2022, 42 (8): 2092- 2106.
|
|
XIONG Shouyao, DENG Renyi, HUANG Chuangxia, et al. Analysis on the impact of meteorological factors on distributed photovoltaic power[J]. Journal of Systems Science and Mathematical Sciences, 2022, 42 (8): 2092- 2106.
|
| 10 |
杨文海, 程华新, 高亚静, 等. 计及雾霾影响的短期光伏出力预测和负荷预测[J]. 中国电力, 2016, 49 (S): 148- 153.
|
|
YANG Wenhai, CHENG Xinhua, GAO Yajing, et al. Short-term photovoltaic output forecast considering the influence of fog and haze weather[J]. Electric Power, 2016, 49 (S): 148- 153.
|
| 11 |
陆双, 彭曙蓉, 杨云皓, 等. 基于平均影响值-启发式前向搜索的异常光伏用户识别方法[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2022, 42 (2): 106- 111.
|
|
LU Shuang, PENG Shurong, YANG Yunhao, et al. Identification method of abnormal photovoltaic users based on mean impact value and heuristic forward searching[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2022, 42 (2): 106- 111.
|
| 12 |
徐一伦, 张彬桥, 黄婧, 等. 考虑天气类型和相似日的IWPA-LSSVM光伏发电功率预测[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (2): 143- 149.
|
|
XU Yilun, ZHANG Binqiao, HUANG Jing, et al. Forecast of photovoltaic power based on IWPA-LSSVM considering weather types and similar days[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (2): 143- 149.
|
| 13 |
邵尹池, 袁绍军, 孙荣富, 等. 基于空间相关性的分布式光伏实用化功率预测及误差分析[J]. 中国电力, 2021, 54 (7): 185- 191, 207.
|
|
SHAO Yinchi, YUAN Shaojun, SUN Rongfu, et al. Practical method and error analysis for distributed photovoltaic power prediction based on spatial correlation[J]. Electric Power, 2021, 54 (7): 185- 191, 207.
|
| 14 |
裴哲义, 梁志峰, 陆为华, 等. 广域分布式光伏发电监测与出力估计研究[J]. 中国电力, 2020, 53 (6): 87- 96.
|
|
PEI Zheyi, LIANG Zhifeng, LU Weihua, et al. Wide-area distributed photovoltaic power generation monitoring and output estimation[J]. Electric Power, 2020, 53 (6): 87- 96.
|
| 15 |
GE L J, LIU H X, YAN J, et al. A virtual data collection model of distributed PVs considering spatio-temporal coupling and affine optimization reference[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2023, 38 (4): 3939- 3951.
|
| 16 |
赵振兵, 强一凡, 李信, 等. 基于改进循环神经网络的配电网超短期功率预测方法[J]. 电力科学与技术学报, 2022, 37 (5): 144- 154.
|
|
ZHAO Zhenbing, QIANG Yifan, LI Xin, et al. Ultra-short-term power prediction method of distribution network based on improved recurrent neural network[J]. Journal of Electric Power Science and Technology, 2022, 37 (5): 144- 154.
|
| 17 |
刘明群, 何鑫, 覃日升, 等. 基于改进K-means聚类k值选择算法的配网电压数据异常检测[J]. 电力科学与技术学报, 2022, 37 (6): 91- 99.
|
|
LIU Mingqun, HE Xin, QIN Risheng, et al. Anomaly detection of distribution network voltage data based on improved K-means clustering k-value selection algorithm[J]. Journal of Electric Power Science and Technology, 2022, 37 (6): 91- 99.
|
| 18 |
刘昳娟, 陈云龙, 刘继彦, 等. 基于集成学习的分布式光伏发电功率日前预测[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (9): 38- 45.
|
|
LIU (Die| Yi)(Juan), CHEN Yunlong, LIU Jiyan, et al. Ensemble learning-based day-ahead power forecasting of distributed photovoltaic generation[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (9): 38- 45.
|
| 19 |
OVASKA S J, VANLANDINGHAM H F, KAMIYA A. Fusion of soft computing and hard computing in industrial applications: an overview[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part C (Applications and Reviews), 2002, 32 (2): 72- 79.
|
| 20 |
AGOUA X G, GIRARD R, KARINIOTAKIS G. Short-term spatio-temporal forecasting of photovoltaic power production[J]. IEEE Transactions on Sustainable Energy, 2018, 9 (2): 538- 546.
|
| 21 |
杨龙飞, 高山, 蔡新雷, 等. 基于拉丁超立方采样的小范围分布式光伏出力时空概率分布生成方法[J]. 南方电网技术, 2023, 17 (9): 38- 48.
|
|
YANG Longfei, GAO Shan, CAI Xinlei, et al. Generating method for spatiotemporal probability distribution of distributed PV output in small range based on Latin hypercube sampling[J]. Southern Power System Technology, 2023, 17 (9): 38- 48.
|
| 22 |
高博, 茆超, 张冲标, 等. 基于时空图网络的分布式光伏发电出力预测[J]. 电力系统及其自动化学报, 2023, 35 (3): 125- 133.
|
|
GAO Bo, MAO Chao, ZHANG Chongbiao, et al. Output prediction of distributed photovoltaic power generation based on spatial-temporal graph neural network[J]. Proceedings of the CSU-EPSA, 2023, 35 (3): 125- 133.
|
| 23 |
邓序之, 刘淇, 叶傲霜, 等. 基于气象耦合特征分析及改进XGBoost算法的用户分布式光伏短期出力预测模型[J]. 南方电网技术, 2023, 17 (12): 80- 89.
|
|
DENG Xuzhi, LIU Qi, YE Aoshuang, et al. Short-term output forecasting model of user side distributed photovoltaic based on meteorological coupling characteristics analysis and improved XGBoost algorithm[J]. Southern Power System Technology, 2023, 17 (12): 80- 89.
|
| 24 |
王守相, 郭陆阳, 赵倩宇, 等. 基于参考序列与全卷积网络的风速数据缺失与异常修复方法[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2023, 47 (9): 129- 136.
|
|
WANG Shouxiang, GUO Luyang, ZHAO Qianyu, et al. Repair method for missed and abnormal wind speed data based on reference sequence and full convolution network[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2023, 47 (9): 129- 136.
|
| 25 |
赵一鉴, 林利, 王茜蒨, 等. 基于大地距离计算相似度的海上目标轨迹预测[J]. 计算机应用, 2023, 43 (11): 3594- 3598.
|
|
ZHAO Yijian, LIN Li, WANG Qianqian, et al. Trajectory prediction of sea targets based on geodetic distance similarity calculation[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2023, 43 (11): 3594- 3598.
|