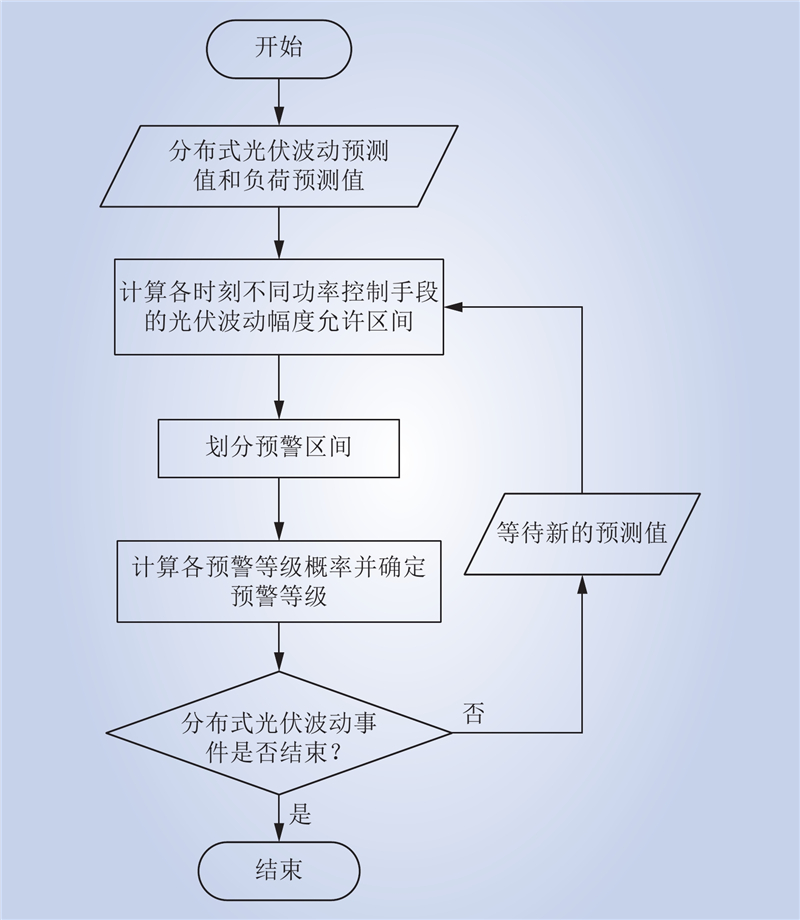
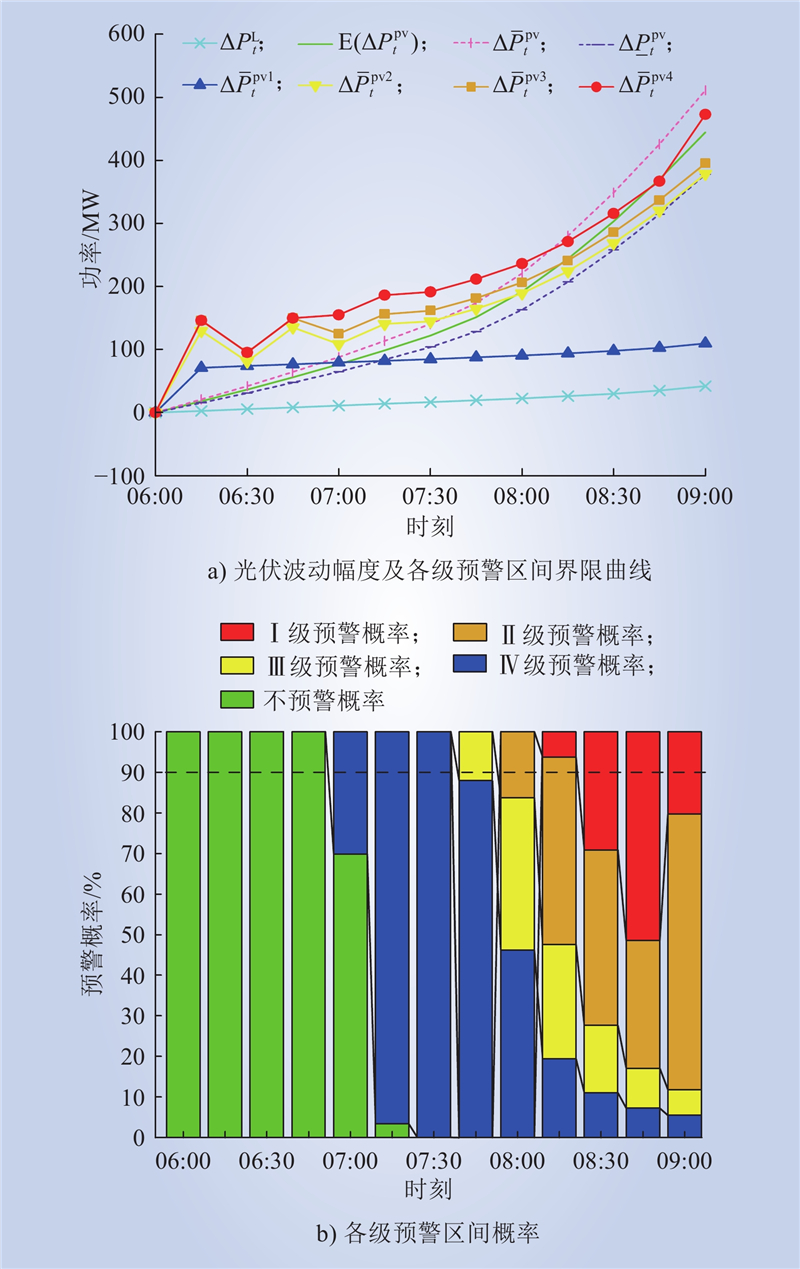
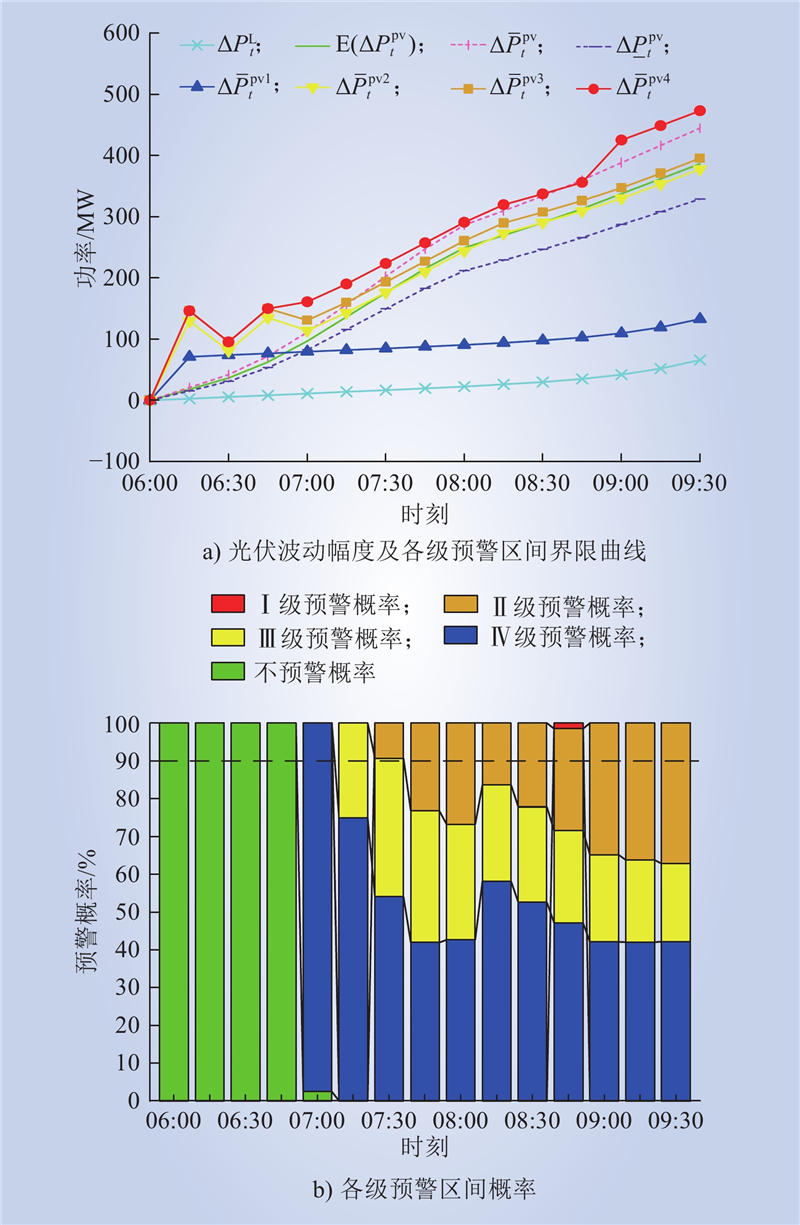
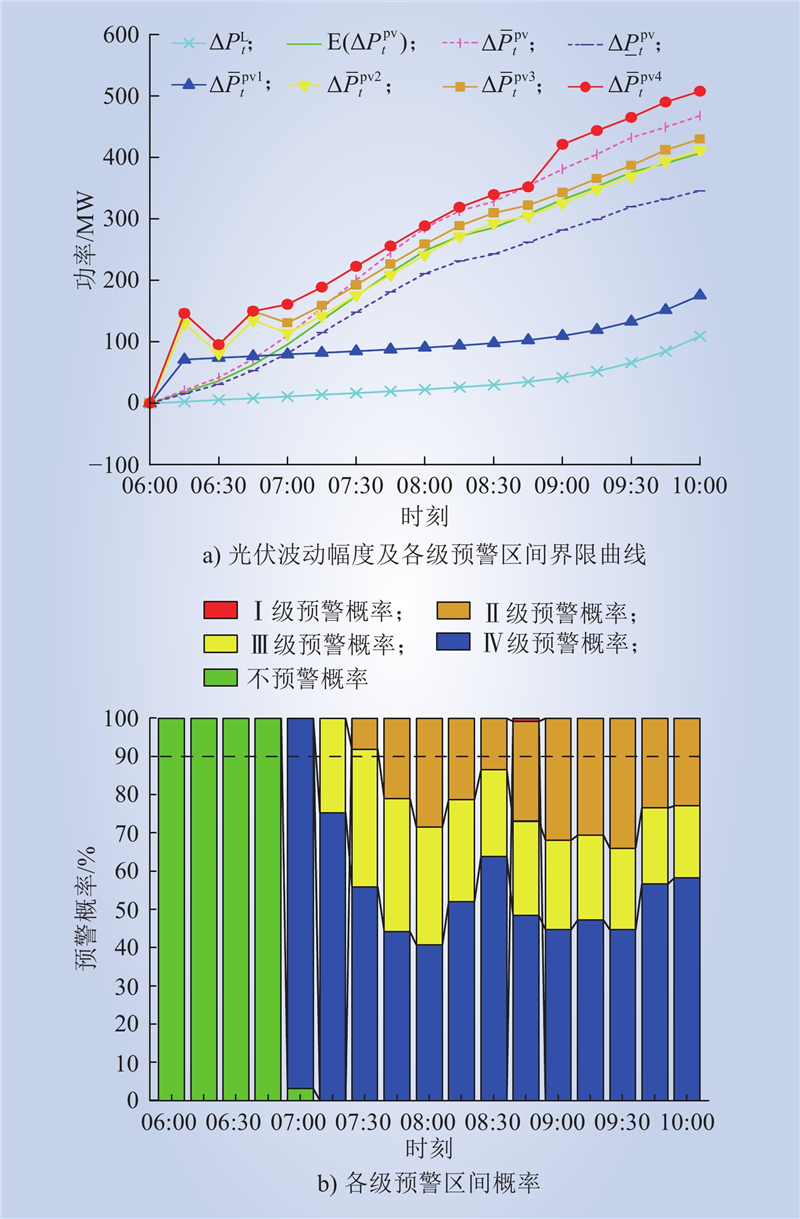
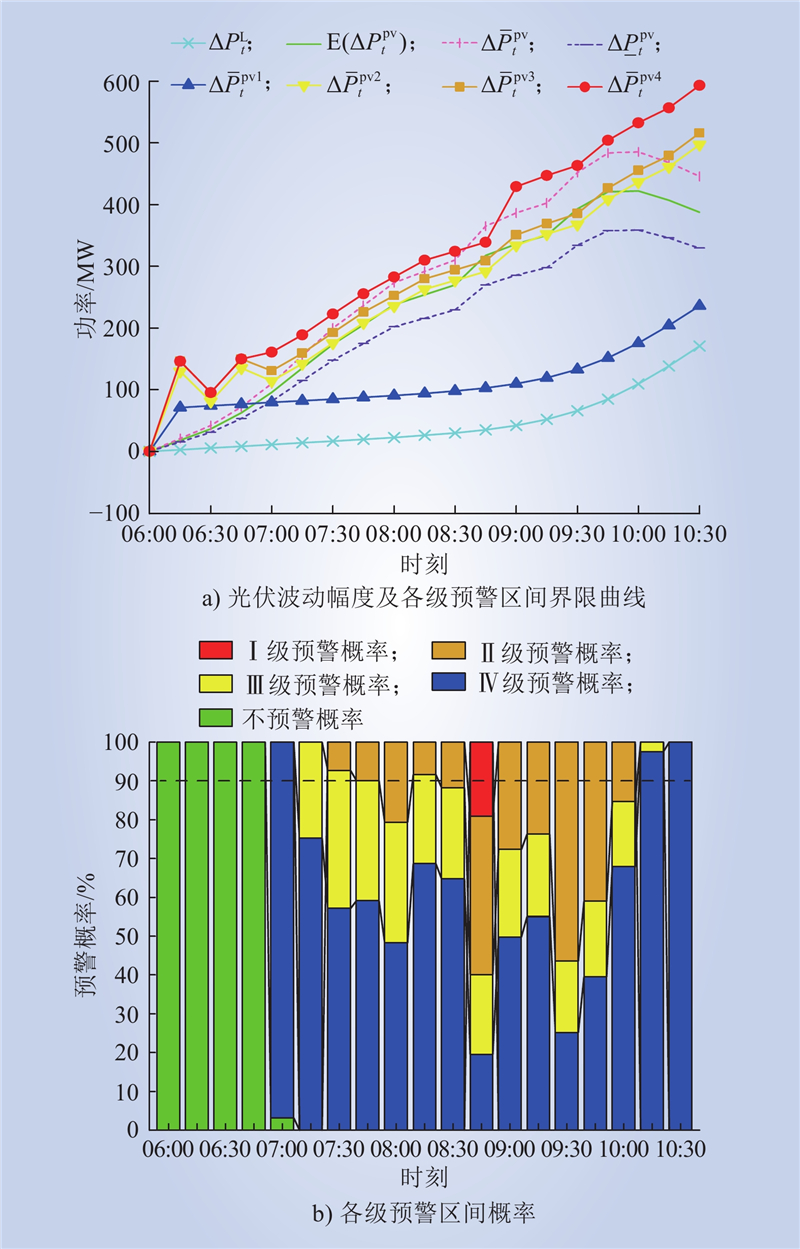
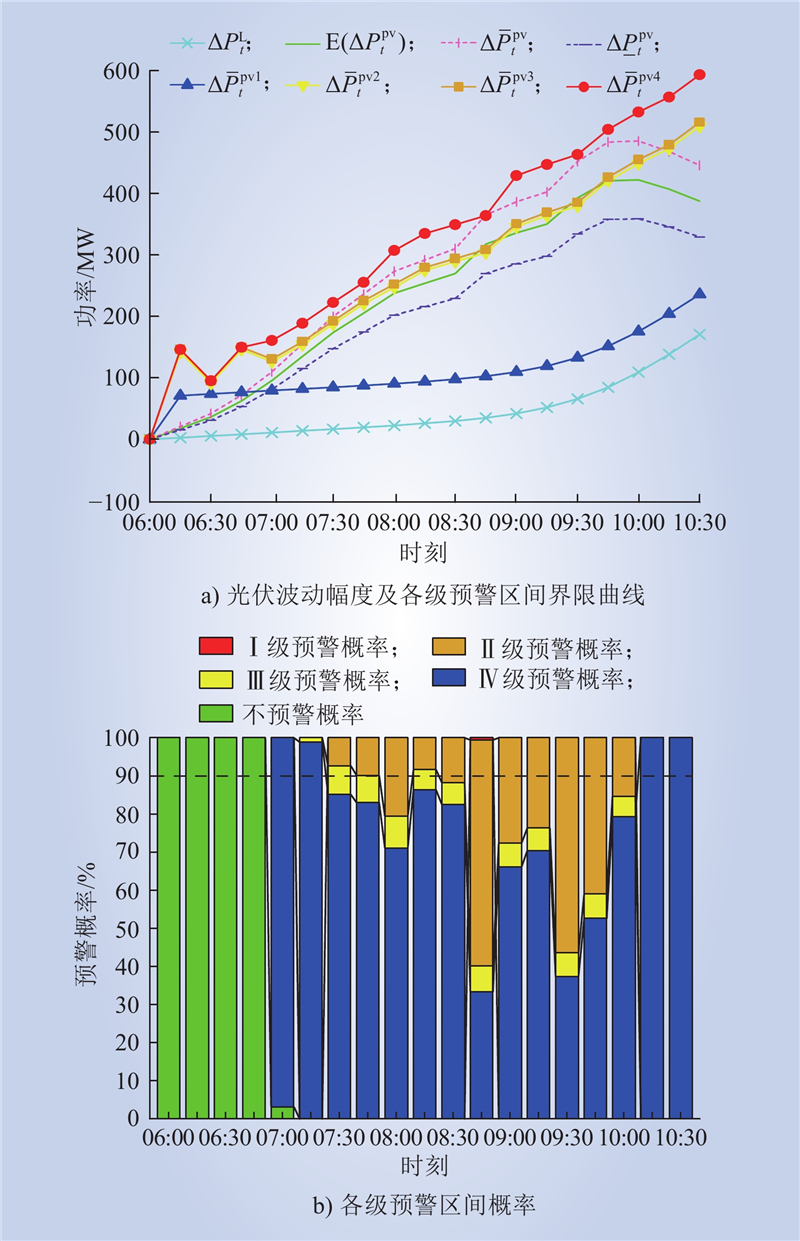
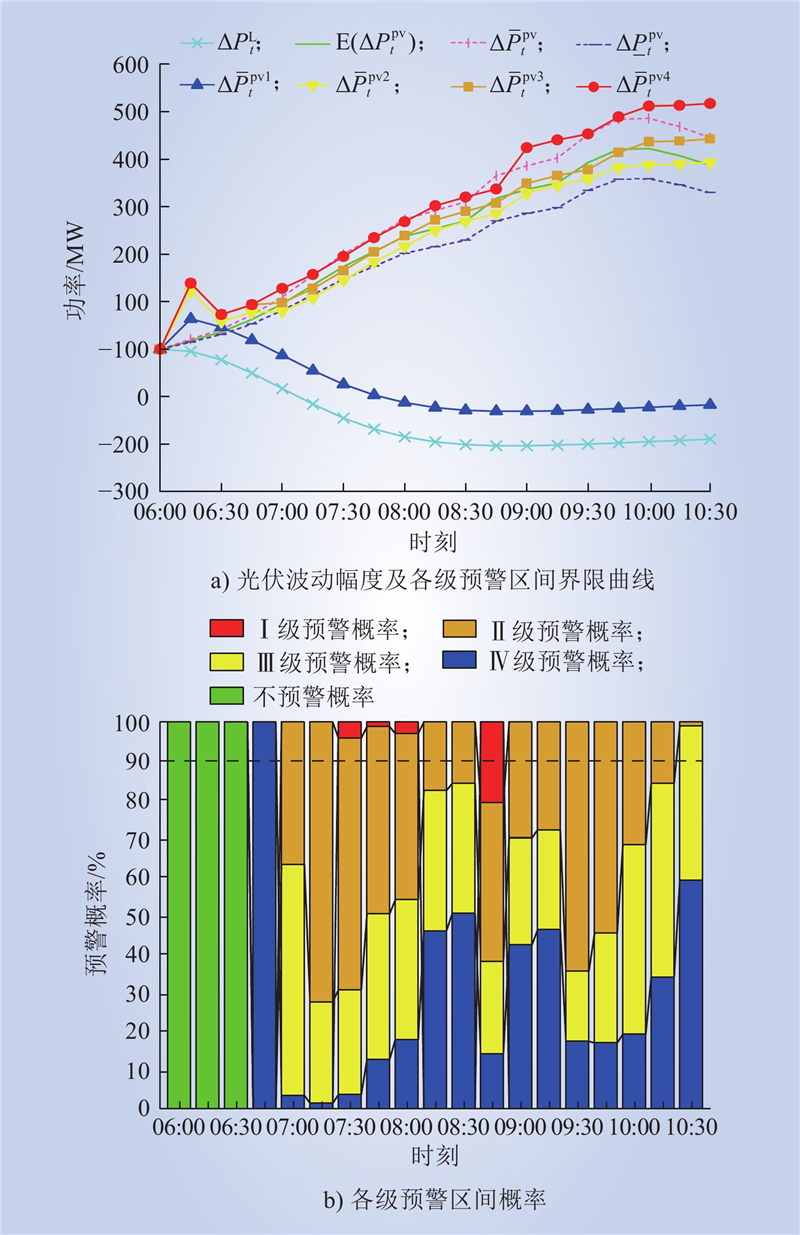
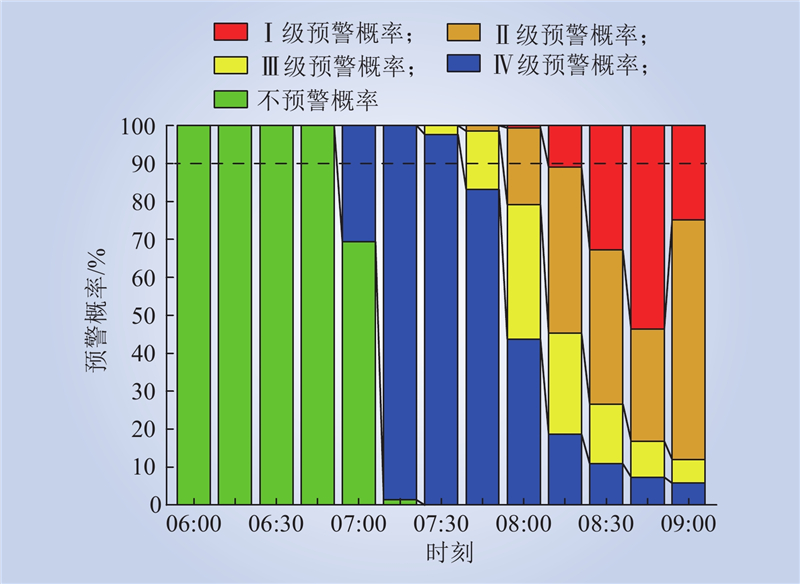
| 1 |
吉兴全, 刘健, 叶平峰, 等. 计及灵活性与可靠性的综合能源系统优化调度[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2023, 47 (8): 132- 144.
|
|
JI Xingquan, LIU Jian, YE Pingfeng, et al. Optimal scheduling of integrated energy system considering flexibility and reliability[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2023, 47 (8): 132- 144.
|
| 2 |
周勤勇, 李根兆, 秦晓辉, 等. 能源革命下的电力系统范式转换分析[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (3): 1- 11.
|
|
ZHOU Qinyong, LI Genzhao, QIN Xiaohui, et al. Analysis of power system paradigm shift under energy revolution[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (3): 1- 11.
|
| 3 |
张玉敏, 孙鹏凯, 孟祥剑, 等. 基于碳势-能源价格双响应的综合能源系统低碳经济调度[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2024, 48 (9): 21- 33.
|
|
ZHANG Yumin, SUN Pengkai, MENG Xiangjian, et al. Low-carbon economic dispatching of integrated energy system based on dual response of carbon intensity and energy price[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2024, 48 (9): 21- 33.
|
| 4 |
孙启星, 张超, 李成仁, 等. “碳达峰、碳中和” 目标下的电力系统成本及价格水平预测[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (1): 9- 16.
|
|
SUN Qixing, ZHANG Chao, LI Chengren, et al. Prediction of power system cost and price level under the goal of "carbon peak and carbon neutralization"[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (1): 9- 16.
|
| 5 |
张玉敏, 孙鹏凯, 吉兴全, 等. 考虑扩展碳排放流的综合能源系统低碳经济调度[J]. 电网技术, 2023, 47 (8): 3174- 3191.
|
|
ZHANG Yumin, SUN Pengkai, JI Xingquan, et al. Low-carbon economic dispatch of integrated energy system with augmented carbon emission flow[J]. Power System Technology, 2023, 47 (8): 3174- 3191.
|
| 6 |
栗峰, 丁杰, 周才期, 等. 新型电力系统下分布式光伏规模化并网运行关键技术探讨[J]. 电网技术, 2024, 48 (1): 184- 199.
|
|
LI Feng, DING Jie, ZHOU Caiqi, et al. Key technologies of large-scale grid-connected operation of distributed photovoltaic under new-type power system[J]. Power System Technology, 2024, 48 (1): 184- 199.
|
| 7 |
王翔宇, 陈武晖, 郭小龙, 等. 发电系统数字化研究综述[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45 (1): 120- 141.
|
|
WANG Xiangyu, CHEN Wuhui, GUO Xiaolong, et al. Review of research on the digitalization of power generation system[J]. Power Generation Technology, 2024, 45 (1): 120- 141.
|
| 8 |
邓序之, 刘淇, 叶傲霜, 等. 基于气象耦合特征分析及改进XGBoost算法的用户分布式光伏短期出力预测模型[J]. 南方电网技术, 2023, 17 (12): 80- 89.
|
|
DENG Xuzhi, LIU Qi, YE Aoshuang, et al. Short-term output forecasting model of user side distributed photovoltaic based on meteorological coupling characteristics analysis and improved XGBoost algorithm[J]. Southern Power System Technology, 2023, 17 (12): 80- 89.
|
| 9 |
张玉敏, 孙鹏凯, 吉兴全, 等. 基于并行多维近似动态规划的综合能源系统动态经济调度[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2023, 47 (4): 60- 68.
|
|
ZHANG Yumin, SUN Pengkai, JI Xingquan, et al. Dynamic economic dispatch for integrated energy system based on parallel multi-dimensional approximate dynamic programming[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2023, 47 (4): 60- 68.
|
| 10 |
ZHANG Y, SUN P, JI X, et al. Low-carbon economic dispatch of integrated energy systems considering extended carbon emission flow[J/OL]. Journal of Modern Power Systems and Clean Energy: 1-12 (2024-05-31) [2024-06-21]. https://doi.org/10.35833/MPCE.2023.000743.
|
| 11 |
IMPRAM S, VARBAK NESE S, ORAL B. Challenges of renewable energy penetration on power system flexibility: a survey[J]. Energy Strategy Reviews, 2020, 31, 100539.
|
| 12 |
赵波, 肖传亮, 徐琛, 等. 基于渗透率的区域配电网分布式光伏并网消纳能力分析[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2017, 41 (21): 105- 111.
|
|
ZHAO Bo, XIAO Chuanliang, XU Chen, et al. Penetration based accommodation capacity analysis on distributed photovoltaic connection in regional distribution network[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2017, 41 (21): 105- 111.
|
| 13 |
黎静华, 谢育天, 曾鸿宇, 等. 不确定优化调度研究综述及其在新型电力系统中的应用探讨[J]. 高电压技术, 2022, 48 (9): 3447- 3464.
|
|
LI Jinghua, XIE Yutian, ZENG Hongyu, et al. Research review of uncertain optimal scheduling and its application in new-type power systems[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2022, 48 (9): 3447- 3464.
|
| 14 |
LI J C, LI J Y. Electric power supply and demand early warning based on PCA and SVM method[C]//2011 2nd International Conference on Intelligent Control and Information Processing. Harbin, China. IEEE, 2011: 1119–1123.
|
| 15 |
魏新迟, 董佳, 时珊珊, 等. 基于云模型和随机森林的韧性城市电网风险预警模型[J]. 电力建设, 2024, 45 (5): 19- 28.
|
|
WEI Xinchi, DONG Jia, SHI Shanshan, et al. Enhanced risk warning model for resilient urban power grid using cloud model and random forest[J]. Electric Power Construction, 2024, 45 (5): 19- 28.
|
| 16 |
张钢, 宗启航, 柯贤波, 等. 基于临界惯量和预想故障的含风电电力系统暂态功角稳定在线预警[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2023, 51 (16): 72- 83.
|
|
ZHANG Gang, ZONG Qihang, KE Xianbo, et al. Online warning of transient power angle stability of power systems with wind power based on critical inertia and anticipated faults[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2023, 51 (16): 72- 83.
|
| 17 |
卢明, 郭志明, 孟高军, 等. 输电线路气象风险精细化建模及气象灾害的在线预警防御策略[J]. 电力科学与技术学报, 2024, 39 (1): 208- 217.
|
|
LU Ming, GUO Zhiming, MENG Gaojun, et al. Refined meteorological risk modeling of transmission lines and online warning and defense strategies of meteorological disasters[J]. Journal of Electric Power Science and Technology, 2024, 39 (1): 208- 217.
|
| 18 |
SI Z Y, YANG M, YU Y X, et al. Photovoltaic power forecast based on satellite images considering effects of solar position[J]. Applied Energy, 2021, 302, 117514.
|
| 19 |
鲁宗相, 李海波, 乔颖. 高比例可再生能源并网的电力系统灵活性评价与平衡机理[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2017, 37 (1): 9- 20.
|
|
LU Zongxiang, LI Haibo, QIAO Ying. Flexibility evaluation and supply/demand balance principle of power system with high-penetration renewable electricity[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2017, 37 (1): 9- 20.
|
| 20 |
RYO E. A study of system frequency control of island power network using disturbance observer with adaptive behavior controller[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on Electrical Engineering, 2009.
|
| 21 |
汪海瑛, 白晓民. 并网光伏的短期运行备用评估[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2013, 37 (5): 55- 60.
|
|
WANG Haiying, BAI Xiaomin. Short-term operating reserve assessment for grid-connected photovoltaic system[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2013, 37 (5): 55- 60.
|
| 22 |
赵晋泉, 孙中昊, 杨余华, 等. 分布式光伏参与调频辅助服务交易机制研究[J]. 全球能源互联网, 2020, 3 (5): 477- 486.
|
|
ZHAO Jinquan, SUN Zhonghao, YANG Yuhua, et al. Study on frequency regulation ancillary service trading mechanisms for distributed photovoltaic generation[J]. Journal of Global Energy Interconnection, 2020, 3 (5): 477- 486.
|
| 23 |
陈灵, 黄兴华, 张功林, 等. 考虑削峰填谷的分布式电源集群协同控制方法[J]. 智慧电力, 2023, 51 (4): 8- 15.
|
|
CHEN Ling, HUANG Xinghua, ZHANG Gonglin, et al. Distributed generations clusters collaborative control method considering peak load shifting[J]. Smart Power, 2023, 51 (4): 8- 15.
|
| 24 |
SHI J, CHEN Y B, CHENG X G, et al. Four-stage space-time hybrid model for distributed photovoltaic power forecasting[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 2023, 59 (1): 1129- 1138.
|
| 25 |
吉兴全, 赵国航, 叶平峰, 等. 基于QMD- HBiGRU的短期光伏功率预测方法[J/OL]. 高电压技术: 1–18 (2023-08-04)[2024-05-21]. https://doi.org/10.13336/j.1003-6520.hve.20230333.
|
|
JI Xingquan, ZHAO Guohang, YE Pingfeng, et al. Short-term PV forecasting method based on QMD-HBiGRU model[J/OL]. High Voltage Engineering: 1–18 (2023-08-04) [2024-05-21]. https://doi.org/10.13336/j.1003-6520.hve.20230333.
|
| 26 |
LI Z M, XU Y, WANG P, et al. Coordinated preparation and recovery of a post-disaster multi-energy distribution system considering thermal inertia and diverse uncertainties[J]. Applied Energy, 2023, 336, 120736.
|
| 27 |
丁琦欣, 覃洪培, 万灿, 等. 基于机会约束规划的配电网分布式光伏承载能力评估[J]. 东北电力大学学报, 2022, 42 (6): 28- 38.
|
|
DING Qixin, QIN Hongpei, WAN Can, et al. Chance-constrained optimization-based distributed photovoltaic hosting capacity assessment of distribution networks[J]. Journal of Northeast Electric Power University, 2022, 42 (6): 28- 38.
|
| 28 |
AHMED R, SREERAM V, MISHRA Y, et al. A review and evaluation of the state-of-the-art in PV solar power forecasting: techniques and optimization[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2020, 124, 109792.
|
| 29 |
徐非非, 冯华, 覃洪培, 等. 计及不确定性的配电网分布式光伏承载能力区间分析方法[J]. 浙江电力, 2023, 42 (11): 86- 95.
|
|
XU Feifei, FENG Hua, QIN Hongpei, et al. An analysis method of DPV hosting capacity interval in distribution networks under uncertainties[J]. Zhejiang Electric Power, 2023, 42 (11): 86- 95.
|
| 30 |
江叶峰, 周海强, 罗建裕, 等. 计及源荷区间不确定性的电力系统日前优化调度[J]. 电力工程技术, 2022, 41 (4): 58- 66.
|
|
JIANG Yefeng, ZHOU Haiqiang, LUO Jianyu, et al. Day-ahead optimal dispatch of power system considering source and load interval uncertainties[J]. Electric Power Engineering Technology, 2022, 41 (4): 58- 66.
|
| 31 |
MOON J, PARK J, HWANG E, et al. Forecasting power consumption for higher educational institutions based on machine learning[J]. The Journal of Supercomputing, 2018, 74 (8): 3778- 3800.
|
| 32 |
JIA Y H, KWONG S, WU W H, et al. Sparse Bayesian learning-based kernel Poisson regression[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2019, 49 (1): 56- 68.
|
| 33 |
林少伯, 韩民晓, 赵国鹏, 等. 基于随机预测误差的分布式光伏配网储能系统容量配置方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2013, 33 (4): 25- 33, 5.
|
|
LIN Shaobo, HAN Minxiao, ZHAO Guopeng, et al. Capacity allocation of energy storage in distributed photovoltaic power system based on stochastic prediction error[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2013, 33 (4): 25- 33, 5.
|
| 34 |
LORENZ E, HURKA J, HEINEMANN D, et al. Irradiance forecasting for the power prediction of grid-connected photovoltaic systems[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2009, 2 (1): 2- 10.
|
| 35 |
丁明, 楚明娟, 潘浩, 等. 交直流混合微电网运行优化建模与不确定性分析[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2017, 41 (5): 1- 7, 45.
|
|
DING Ming, CHU Mingjuan, PAN Hao, et al. Operation optimization modeling and uncertainty analysis for hybrid AC/DC microgrids[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2017, 41 (5): 1- 7, 45.
|
| 36 |
KAZARLIS S A, BAKIRTZIS A G, PETRIDIS V. A genetic algorithm solution to the unit commitment problem[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 1996, 11 (1): 83- 92.
|
| 37 |
KUMAR N, PANIGRAHI B K, SINGH B. A solution to the ramp rate and prohibited operating zone constrained unit commitment by GHS-JGT evolutionary algorithm[J]. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 2016, 81, 193- 203.
|
| 38 |
杨甲甲, 刘国龙, 赵俊华, 等. 采用长短期记忆深度学习模型的工业负荷短期预测方法[J]. 电力建设, 2018, 39 (10): 20- 27.
|
|
YANG Jiajia, LIU Guolong, ZHAO Junhua, et al. A long short term memory based deep learning method for industrial load forecasting[J]. Electric Power Construction, 2018, 39 (10): 20- 27.
|
| 39 |
金娜, 刘文颖, 曹银利, 等. 大容量机组一次调频参数对电网频率特性的影响[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2012, 40 (1): 91- 95, 100.
|
|
JIN Na, LIU Wenying, CAO Yinli, et al. Influence on the grid frequency characteristic by the parameters of primary frequency modulation of large capacity generator units[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2012, 40 (1): 91- 95, 100.
|
| 40 |
王琦, 郭钰锋, 万杰, 等. 适用于高风电渗透率电力系统的火电机组一次调频策略[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2018, 38 (4): 974- 984, 1274.
|
|
WANG Qi, GUO Yufeng, WAN Jie, et al. Primary frequency regulation strategy of thermal units for a power system with high penetration wind power[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2018, 38 (4): 974- 984, 1274.
|
| 41 |
何仰赞, 温增银 编. 电力系统分析-下[M]. 4版. 武汉: 华中科技大学出版社, 2016.
|