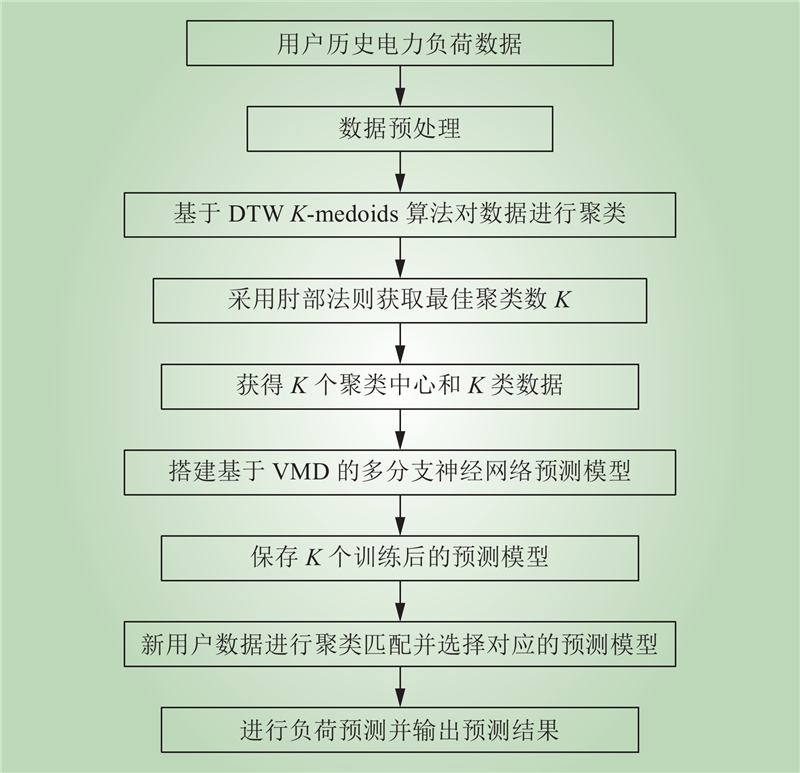
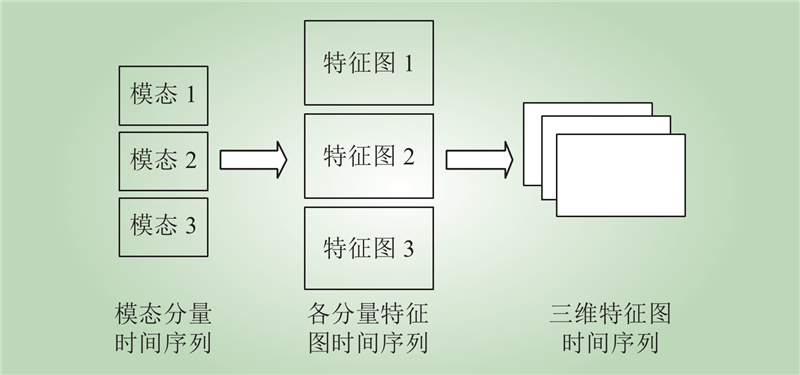
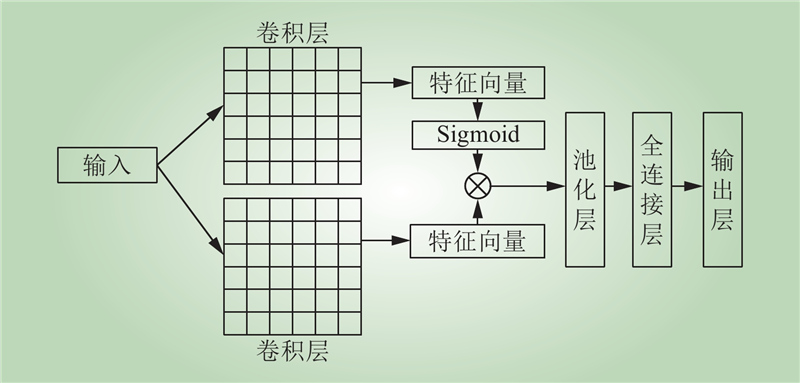
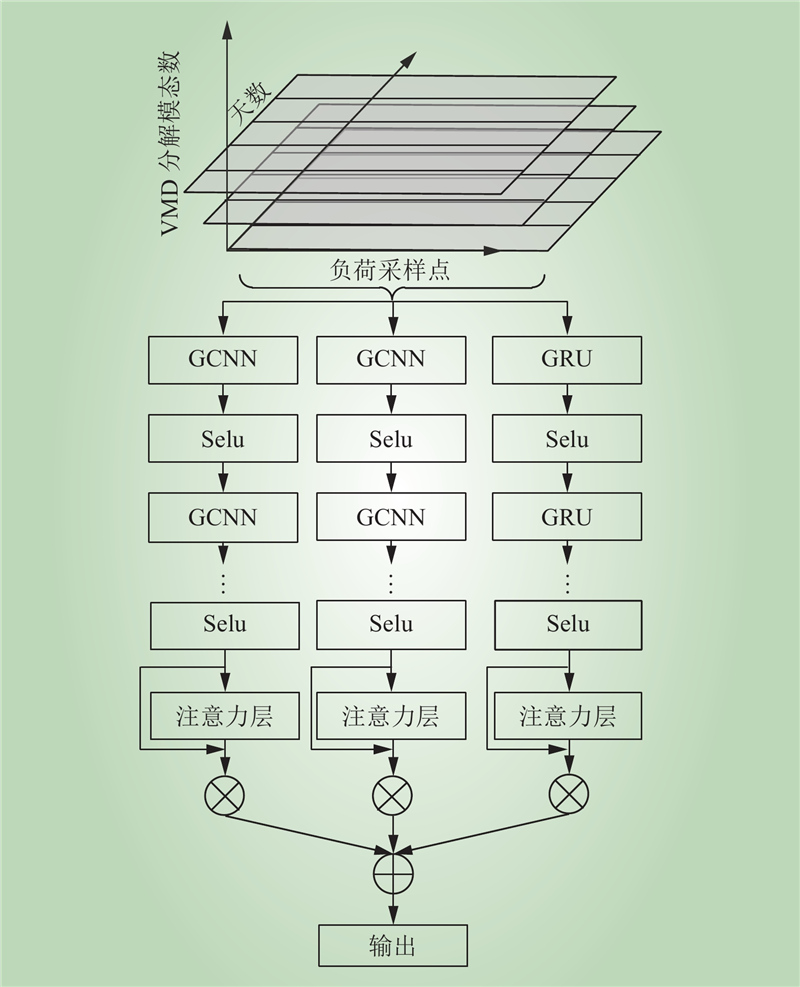
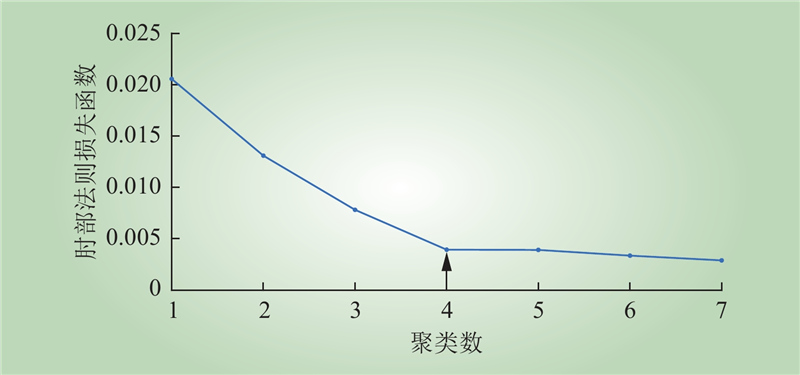
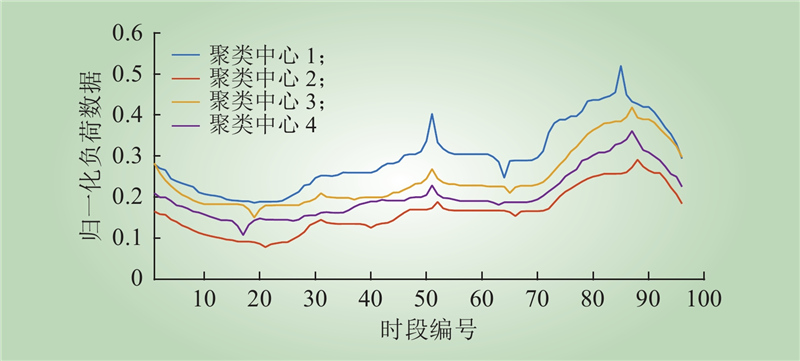
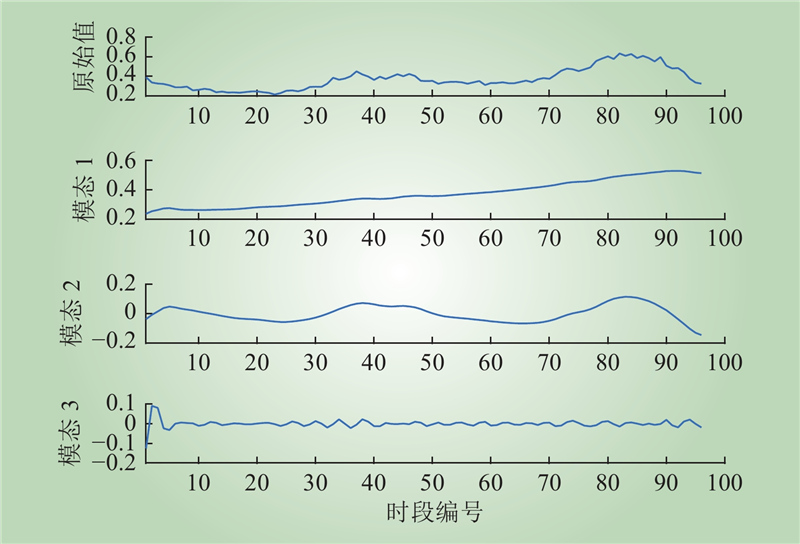
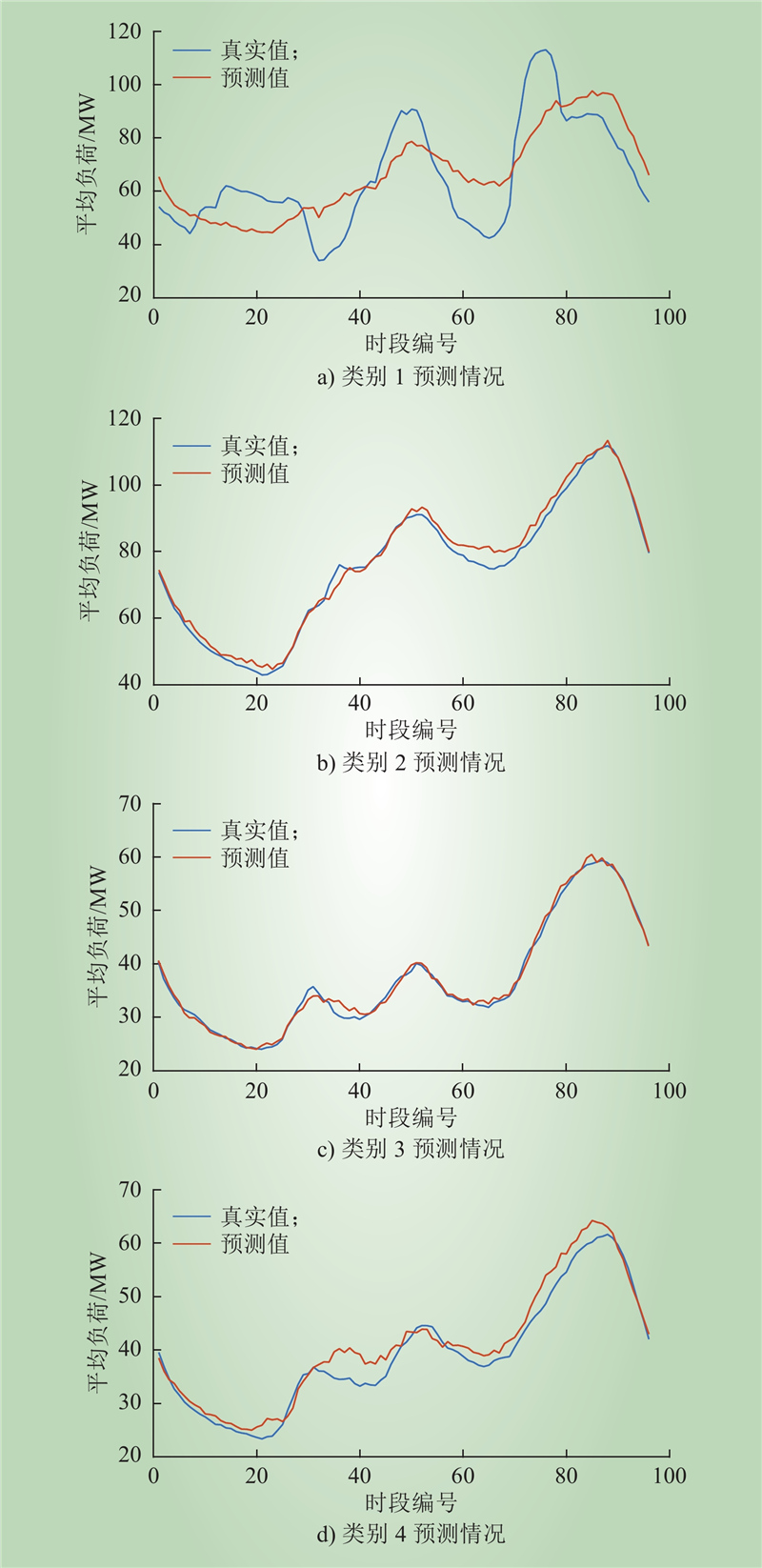
| 1 |
孔祥玉, 马玉莹, 艾芊, 等. 新型电力系统多元用户的用电特征建模与用电负荷预测综述[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2023, 47 (13): 2- 17.
|
|
KONG Xiangyu, MA Yuying, AI Qian, et al. Review on electricity consumption characteristic modeling and load forecasting for diverse users in new power system[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2023, 47 (13): 2- 17.
|
| 2 |
白星振, 赵康, 葛磊蛟, 等. 基于EWT-GRU-RR的配电网短期电力负荷预测模型[J]. 山东科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 42 (5): 77- 87.
|
|
BAI Xingzhen, ZHAO Kang, GE Leijiao, et al. Short-term power load forecasting model based on EWT-GRU-RR[J]. Journal of Shandong University of Science and Technology (Natural Science), 2023, 42 (5): 77- 87.
|
| 3 |
董雷, 陈振平, 韩富佳, 等. 基于图卷积神经网络与K-means聚类的居民用户集群短期负荷预测[J]. 电网技术, 2023, 47 (10): 4291- 4301.
|
|
DONG Lei, CHEN Zhenping, HAN Fujia, et al. Short-term load forecasting of residential user groups based on graph convolutional neural network and K-means clustering[J]. Power System Technology, 2023, 47 (10): 4291- 4301.
|
| 4 |
朱子意, 孙晓燕, 柳先彪, 等. 基于相似用电单元及图卷积神经网络的电力负荷预测[J]. 电力科学与工程, 2023, 39 (7): 9- 23.
|
|
ZHU Ziyi, SUN Xiaoyan, LIU Xianbiao, et al. Power load forecasting based on similar power units and graph convolution neural network[J]. Electric Power Science and Engineering, 2023, 39 (7): 9- 23.
|
| 5 |
梁京章, 黄星舒, 吴丽娟, 等. 基于KPCA和改进K-means的电力负荷曲线聚类方法[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 48 (6): 143- 150.
|
|
LIANG Jingzhang, HUANG Xingshu, WU Lijuan, et al. Clustering method of power load profiles based on KPCA and improved K-means[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 48 (6): 143- 150.
|
| 6 |
李康宇, 吴青娥, 刘磊, 等. 聚类算法在用户电力负荷分类中的应用[J]. 智能电网, 2018, 8 (2): 189- 203.
|
|
LI Kangyu, WU Qing’e, LIU Lei, et al. Application of clustering algorithm in user power load classification[J]. Smart Grid, 2018, 8 (2): 189- 203.
|
| 7 |
荀超, 陈伯建, 吴翔宇, 等. 基于改进K-means算法的电力短期负荷预测方法研究[J]. 电力科学与技术学报, 2022, 37 (1): 90- 95.
|
|
XUN Chao, CHEN Bojian, WU Xiangyu, et al. Research on short-term power load forecasting method based on improved K-means algorithm[J]. Journal of Electric Power Science and Technology, 2022, 37 (1): 90- 95.
|
| 8 |
KOIVISTO M, HEINE P, MELLIN I, et al. Clustering of connection points and load modeling in distribution systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2013, 28 (2): 1255- 1265.
|
| 9 |
SYED D, ABU-RUB H, GHRAYEB A, et al. Deep learning-based short-term load forecasting approach in smart grid with clustering and consumption pattern recognition[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9, 54992- 55008.
|
| 10 |
宗文泽, 吴永明, 徐计, 等. 基于DTW-kmedoids算法的时间序列数据异常检测[J]. 组合机床与自动化加工技术, 2022, (5): 120- 124, 128.
|
|
ZONG Wenze, WU Yongming, XU Ji, et al. Anomaly detection of time series data based on DTW-kmedois clustering algorithm[J]. Modular Machine Tool & Automatic Manufacturing Technique, 2022, (5): 120- 124, 128.
|
| 11 |
丛玮, 谢道仪, 严仪炅. 基于DTW的K-Medoids扇区交通特征聚类研究[J]. 交通技术, 2021, 10 (1): 59- 69.
|
|
CONG Wei, XIE Daoyi, YAN Yijiong. Clustering of sector traffic characteristics based on DTW K-Medoids[J]. Open Journal of Transportation Technologies, 2021, 10 (1): 59- 69.
|
| 12 |
SEMERO Y K, ZHANG J H, ZHENG D H. EMD–PSO–ANFIS-based hybrid approach for short-term load forecasting in microgrids[J]. IET Generation, Transmission & Distribution, 2020, 14 (3): 470- 475.
|
| 13 |
雷炳银, 王子驰, 苏雨晴, 等. 基于EEMD-CS-LSSVM的短期负荷预测方法研究[J]. 电力系统及其自动化学报, 2021, 33 (9): 117- 122.
|
|
LEI Bingyin, WANG Zichi, SU Yuqing, et al. Research on short-term load forecasting method based on EEMD-CS-LSSVM[J]. Proceedings of the CSU-EPSA, 2021, 33 (9): 117- 122.
|
| 14 |
盛四清, 金航, 刘长荣. 基于VMD-WSGRU的风电场发电功率中短期及短期预测[J]. 电网技术, 2022, 46 (3): 897- 904.
|
|
SHENG Siqing, JIN Hang, LIU Changrong. Short-term and mid-short-term wind power forecasting based on VMD-WSGRU[J]. Power System Technology, 2022, 46 (3): 897- 904.
|
| 15 |
李文武, 石强, 李丹, 等. 基于VMD和PSO-SVR的短期电力负荷多阶段优化预测[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (8): 171- 177.
|
|
LI Wenwu, SHI Qiang, LI Dan, et al. Multi-stage optimization forecast of short-term power load based on VMD and PSO-SVR[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (8): 171- 177.
|
| 16 |
叶剑华, 曹旌, 杨理, 等. 基于变分模态分解和多模型融合的用户级综合能源系统超短期负荷预测[J]. 电网技术, 2022, 46 (7): 2610- 2622.
|
|
YE Jianhua, CAO Jing, YANG Li, et al. Ultra short-term load forecasting of user level integrated energy system based on variational mode decomposition and multi-model fusion[J]. Power System Technology, 2022, 46 (7): 2610- 2622.
|
| 17 |
GENG G C, HE Y, ZHANG J, et al. Short-term power load forecasting based on PSO-optimized VMD-TCN-attention mechanism[J]. Energies, 2023, 16 (12): 4616.
|
| 18 |
杨胡萍, 余阳, 汪超, 等. 基于VMD-CNN-BIGRU的电力系统短期负荷预测[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (10): 71- 76.
|
|
YANG Huping, YU Yang, WANG Chao, et al. Short-term load forecasting of power system based on VMD-CNN-BIGRU[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (10): 71- 76.
|
| 19 |
吕志星, 张虓, 王沈征, 等. 基于K-Means和CNN的用户短期电力负荷预测[J]. 计算机系统应用, 2020, 29 (3): 161- 166.
|
|
LYU Zhixing, ZHANG Xiao, WANG Shenzheng, et al. Hybrid method for short-term load forecasting based on K-means and convolutional neural network[J]. Computer Systems & Applications, 2020, 29 (3): 161- 166.
|
| 20 |
季玉琦, 严亚帮, 和萍, 等. 基于K-Medoids聚类与栅格法提取负荷曲线特征的CNN-LSTM短期负荷预测[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2023, 51 (18): 81- 93.
|
|
JI Yuqi, YAN Yabang, HE Ping, et al. CNN-LSTM short-term load forecasting based on the K-Medoids clustering and grid method to extract load curve features[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2023, 51 (18): 81- 93.
|
| 21 |
姚程文, 杨苹, 刘泽健. 基于CNN-GRU混合神经网络的负荷预测方法[J]. 电网技术, 2020, 44 (9): 3416- 3424.
|
|
YAO Chengwen, YANG Ping, LIU Zejian. Load forecasting method based on CNN-GRU hybrid neural network[J]. Power System Technology, 2020, 44 (9): 3416- 3424.
|
| 22 |
姚芳, 汤俊豪, 陈盛华, 等. 基于ISSA-CNN-GRU模型的电动汽车充电负荷预测方法[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2023, 51 (16): 158- 167.
|
|
YAO Fang, TANG Junhao, CHEN Shenghua, et al. Charging load prediction method for electric vehicles based on an ISSA-CNN-GRU model[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2023, 51 (16): 158- 167.
|
| 23 |
李坤奇, 孟润泉, 李凤莲. 融合聚类-卷积-门循环的居民用电短期负荷预测方法[J]. 太原理工大学学报, 2023, 54 (1): 203- 210.
|
|
LI Kunqi, MENG Runquan, LI Fenglian. Short-term load forecasting method based on BIRCH-CNN-GRU model[J]. Journal of Taiyuan University of Technology, 2023, 54 (1): 203- 210.
|
| 24 |
YANAGIMTO H, HASHIMOTO K, OKADA M. Attention visualization of gated convolutional neural networks with self attention in sentiment analysis[C]//2018 International Conference on Machine Learning and Data Engineering (iCMLDE). Sydney, NSW, Australia. IEEE, 2018: 77–82.
|
| 25 |
HEINRICH K, ZSCHECH P, JANIESCH C, et al. Process data properties matter: introducing gated convolutional neural networks (GCNN) and key-value-predict attention networks (KVP) for next event prediction with deep learning[J]. Decision Support Systems, 2021, 143, 113494.
|
| 26 |
樊江川, 于昊正, 刘慧婷, 等. 基于多分支门控残差卷积神经网络的短期电力负荷预测[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (11): 155- 162, 174.
|
|
FAN Jiangchuan, YU Haozheng, LIU Huiting, et al. Short-term load forecasting based on multi-branch residual gated convolution neural network[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (11): 155- 162, 174.
|