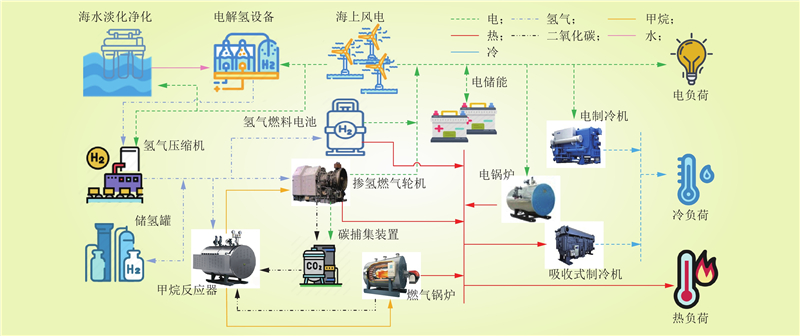
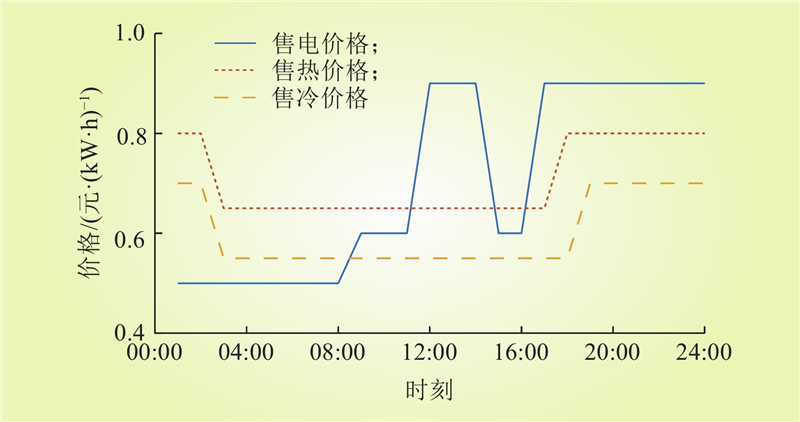
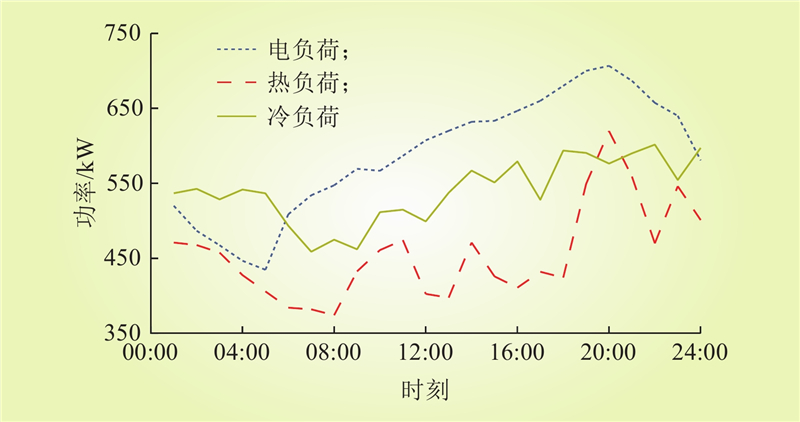
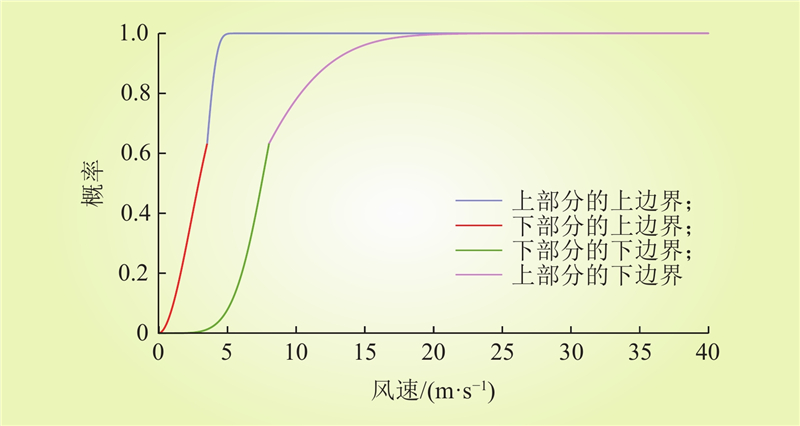
| 1 |
丰力, 张莲梅, 韦家佳, 等. 基于全生命周期经济评估的海上风电发展与思考[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (9): 80- 93.
|
|
FENG Li, ZHANG Lianmei, WEI Jiajia , et al. Development & thinking of offshore wind power based on life cycle economic evaluation[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (9): 80- 93.
|
| 2 |
刘钟淇, 刘耀, 侯金鸣. 以深远海风电为核心的能源岛能源外送经济性分析[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (9): 94- 102.
|
|
LIU Zhongqi, LIU Yao, HOU Jinming. Economic analysis of energy transmission for energy island based on deep-sea offshore wind farms[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (9): 94- 102.
|
| 3 |
马向辉, 张梓铭, 吴冇, 等. 2 GW海上风电对称单极与对称双极柔直送出方案技术经济性对比[J]. 南方电网技术, 2024, 18 (2): 30- 38.
|
|
MA Xianghui , ZHANG Ziming, WU Mao, et al. Technical and economical comparisons of 2 GW offshore wind power transmission schemes by symmetrical monopole and symmetrical bipolar VSC-HVDC[J]. Southern Power System Technology, 2024, 18 (2): 30- 38.
|
| 4 |
MAHMOOD H, BLAABJERG F. Autonomous power management of distributed energy storage systems in islanded microgrids[J]. IEEE Transactions on Sustainable Energy, 2022, 13 (3): 1507- 1522.
|
| 5 |
ZHANG X Y, CHEN B, WANG F, et al. Multi-microgrids system reliability assessment considering difference characteristics and inter-connection ability among microgrids[J]. Journal of Electrical Engineering & Technology, 2019, 14 (5): 1957- 1962.
|
| 6 |
陈鸿琳, 刘新苗, 余浩, 等. 基于近似动态规划的海上风电制氢微网实时能量管理策略[J]. 电力建设, 2022, 43 (12): 94- 102.
|
|
CHEN Honglin, LIU Xinmiao, YU Hao, et al. Real-time energy management strategy based on approximate dynamic programming for offshore wind power-to-hydrogen microgrid[J]. Electric Power Construction, 2022, 43 (12): 94- 102.
|
| 7 |
李梓丘, 乔颖, 鲁宗相. 海上风电-氢能系统运行模式分析及配置优化[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2022, 46 (8): 104- 112.
|
|
LI Ziqiu, QIAO Ying, LU Zongxiang. Operation mode analysis and configuration optimization of offshore wind-hydrogen system[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2022, 46 (8): 104- 112.
|
| 8 |
黄冬梅, 陈柯翔, 孙锦中, 等. 含电解制氢装置及光热电站的海岛微网优化调度[J]. 电力系统及其自动化学报, 2022, 34 (11): 24- 31.
|
|
HUANG Dongmei, CHEN Kexiang, SUN Jinzhong, et al. Dispatch optimization of island microgrid with electrolytic hydrogen unit and CSP station[J]. Proceedings of the CSU-EPSA, 2022, 34 (11): 24- 31.
|
| 9 |
黄冬梅, 吕嘉欣, 时帅, 等. 计及需求响应的海岛微电网群优化运行研究[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2024, 52 (9): 88- 98.
|
|
HUANG Dongmei, LÜ Jiaxin, SHI Shuai, et al. Optimal operation of island microgrid clusters considering demand response[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2024, 52 (9): 88- 98.
|
| 10 |
张智泉, 陈晓杰, 符杨, 等. 含海上风电制氢的综合能源系统分布鲁棒低碳优化运行[J]. 电网技术, 2025, 49 (1): 41- 51.
|
|
ZHANG Zhiquan, CHEN Xiaojie, FU Yang, et al. Distributionally robust low-carbon optimal operation for integrated energy system including hydrogen production from offshore wind power[J]. Power System Technology, 2025, 49 (1): 41- 51.
|
| 11 |
张帅龙, 郑可迪, 刘学, 等. 基于藤Copula理论的海上风电建模及电力市场运行分析[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2024, 48 (11): 134- 142.
|
|
ZHANG Shuailong, ZHENG Kedi, LIU Xue, et al. Modeling of offshore wind power based on vine copula theory and electricity market operation analysis[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2024, 48 (11): 134- 142.
|
| 12 |
陆秋瑜, 杨银国, 陈俊生, 等. 考虑风电不确定性的海上风电场混合储能容量优化[J]. 南方电网技术, 2025, 19 (2): 115- 123, 134.
|
|
LU Qiuyu, YANG Yinguo, CHEN Junsheng, et al. Hybrid energy storage capacity optimization of offshore wind farms considering wind power uncertainty[J]. Southern Power System Technology, 2025, 19 (2): 115- 123, 134.
|
| 13 |
LI Z L, LI P, XIA J. Dispatching strategy for the multi-energy microgrid with source and load uncertainties[C]//2022 IEEE Symposium Series on Computational Intelligence (SSCI). Singapore, Singapore. IEEE, 2022: 1113–1118.
|
| 14 |
彭春华, 熊志盛, 张艺, 等. 基于多场景置信间隙决策的风光储联合鲁棒规划[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2022, 46 (16): 178- 187.
|
|
PENG Chunhua, XIONG Zhisheng, ZHANG Yi, et al. Joint robust planning of wind-photovoltaic-energy storage system based on multi-scenario confidence gap decision[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2022, 46 (16): 178- 187.
|
| 15 |
陈芷欣, 丁家满. 基于概率盒理论的源荷不确定性最优潮流[J]. 电子测量技术, 2021, 44 (7): 61- 68.
|
|
CHEN Zhixin, DING Jiaman. Optimal power flow with source and demand side uncertainty based on probability box theory[J]. Electronic Measurement Technology, 2021, 44 (7): 61- 68.
|
| 16 |
ZHANG X H, GE S Y, LIU H, et al. Distributionally robust optimization for peer-to-peer energy trading considering data-driven ambiguity sets[J]. Applied Energy, 2023, 331, 120436.
|
| 17 |
易锦桂, 朱自伟, 谢青. 基于改进场景聚类算法的海上风电储能优化配置研究[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (12): 2- 10.
|
|
YI Jingui, ZHU Ziwei, XIE Qing. Research on optimal configuration of offshore wind power energy storage based on improved scene clustering algorithm[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (12): 2- 10.
|
| 18 |
闵现娟. 需求响应与碳交易的电氢耦合利用IES经济调度[D]. 北京: 北方工业大学, 2024.
|
|
MIN Xianjuan. Low carbon optimized economic dispatch of hydrogen multi-stage utilization integrated energy system under demand response[D]. Beijing: North China University of Technology, 2024.
|
| 19 |
GAO J W, GAO F J, MA Z Y, et al. Multi-objective optimization of smart community integrated energy considering the utility of decision makers based on the Lévy flight improved chicken swarm algorithm[J]. Sustainable Cities and Society, 2021, 72, 103075.
|
| 20 |
杨海柱, 白亚楠, 张鹏, 等. 考虑富氧燃烧碳捕集技术和源荷双侧响应的综合能源系统优化调度[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (8): 227- 240.
|
|
YANG Haizhu, BAI Yanan, ZHANG Peng, et al. Integrated energy system optimal dispatch considering oxy-fuel combustion carbon capture technology and source-load bilateral response[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (8): 227- 240.
|
| 21 |
DING J M, CHEN Z X, DU Y. Probability box theory-based uncertain power flow calculation for power system with wind power[J]. International Journal of Emerging Electric Power Systems, 2022, 22, 243- 253.
|
| 22 |
王娟娟, 王涛, 刘子菡, 等. 考虑风电和负荷不确定性的输电网多目标柔性规划[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (1): 168- 177.
|
|
WANG Juanjuan, WANG Tao, LIU Zihan, et al. Multi-objective flexible planning of transmission network considering wind power and load uncertainties[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (1): 168- 177.
|
| 23 |
高芳杰. 多源不确定因素下住宅区多能微网优化调度模型研究[D]. 北京: 华北电力大学, 2023.
|
|
GAO Fangjie. Research on optimal scheduling model of residential area multi-energy microgrid under multi-source uncertainties[D]. Beijing: North China Electric Power University, 2023.
|
| 24 |
LIU B D. Uncertainty theory[M]. 2nd ed. Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 2007.
|
| 25 |
MIRJALILI S, MIRJALILI S M, LEWIS A. Grey wolf optimizer[J]. Advances in Engineering Software, 2014, 69, 46- 61.
|
| 26 |
甘如美江, 傅杰, 汪正, 等. 改进灰狼算法与机器学习混合模型的时间序列预测[J/OL]. 重庆工商大学学报(自然科学版), 1–13. (2024-06-29). http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=YZZK20240628001&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ.
|
|
GAN Ru-mei-jiang, FU Jie, WANG Zheng, et al. Time series prediction of improved grey wolf algorithm and machine learning hybrid model[J/OL]. Journal of Chongqing Technology and Business University (Natural Science Edition), 1–13. (2024-06-29). http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx? filename=YZZK20240628001&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ.
|
| 27 |
GAO F J, GAO J W, HUANG N B, et al. Multi-objective robust optimization strategy for community virtual cloud power plant considering different demand responses based on correlative confidence gap decision theory[J]. Sustainable Cities and Society, 2023, 97, 104738.
|
| 28 |
崔杨, 曾鹏, 惠鑫欣, 等. 考虑碳捕集电厂综合灵活运行方式的低碳经济调度[J]. 电网技术, 2021, 45 (5): 1877- 1886.
|
|
CUI Yang, ZENG Peng, HUI Xinxin, et al. Low-carbon economic dispatch considering the integrated flexible operation mode of carbon capture power plant[J]. Power System Technology, 2021, 45 (5): 1877- 1886.
|
| 29 |
郭梦婕, 严正, 周云, 等. 含风电制氢装置的综合能源系统优化运行[J]. 中国电力, 2020, 53 (1): 115- 123, 161.
|
|
GUO Mengjie, YAN Zheng, ZHOU Yun, et al. Optimized operation design of integrated energy system with wind power hydrogen production[J]. Electric Power, 2020, 53 (1): 115- 123, 161.
|
| 30 |
徐小圣, 徐昌睿, 李梦诗, 等. 考虑风电消纳的电热联合系统优化调度模型[J]. 南方电网技术, 2024, 18 (11): 106- 118.
|
|
XU Xiaosheng, XU Changrui, LI Mengshi, et al. Optimization dispatching model of the combined heat and power system considering wind power integration[J]. Southern Power System Technology, 2024, 18 (11): 106- 118.
|