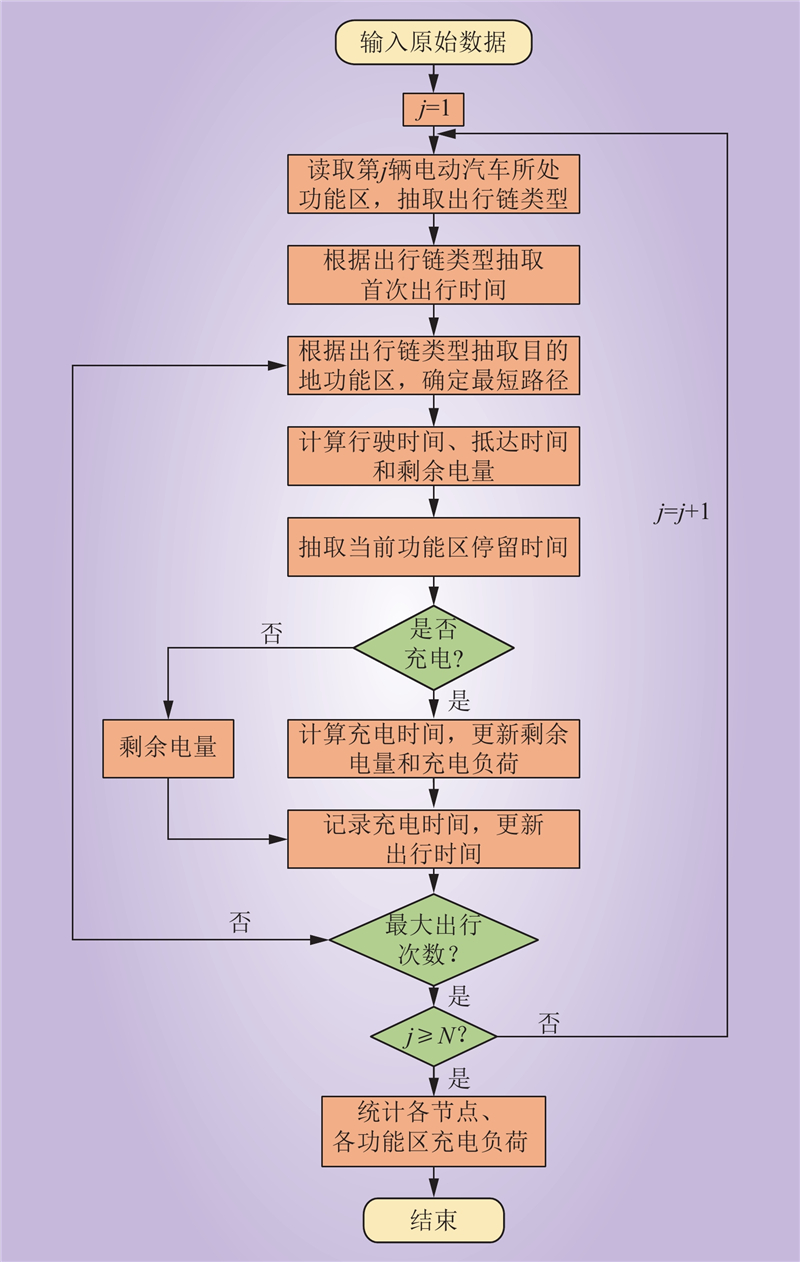
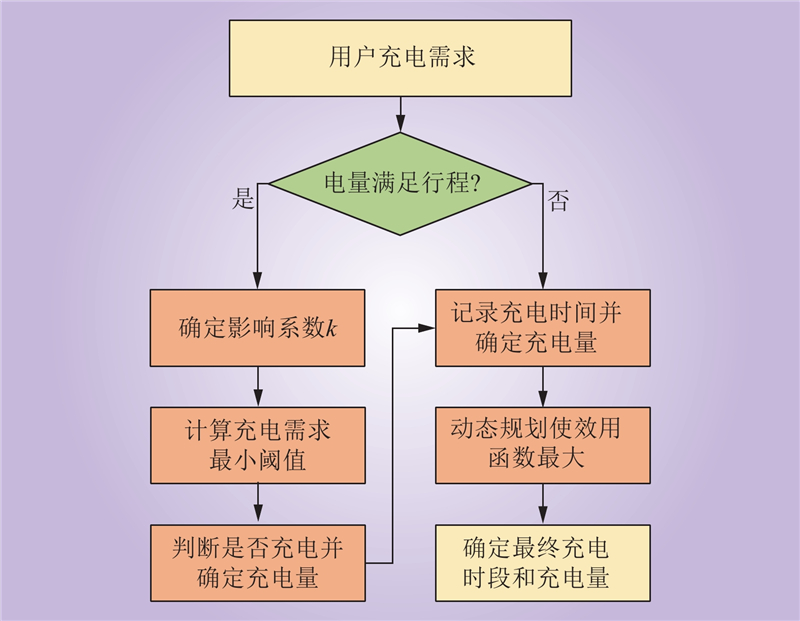
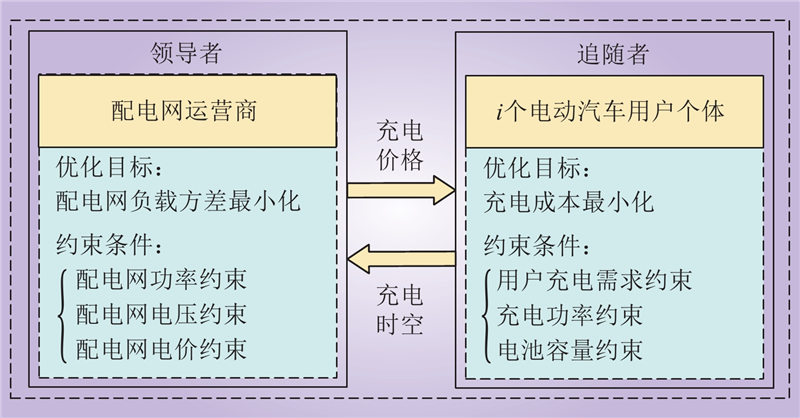
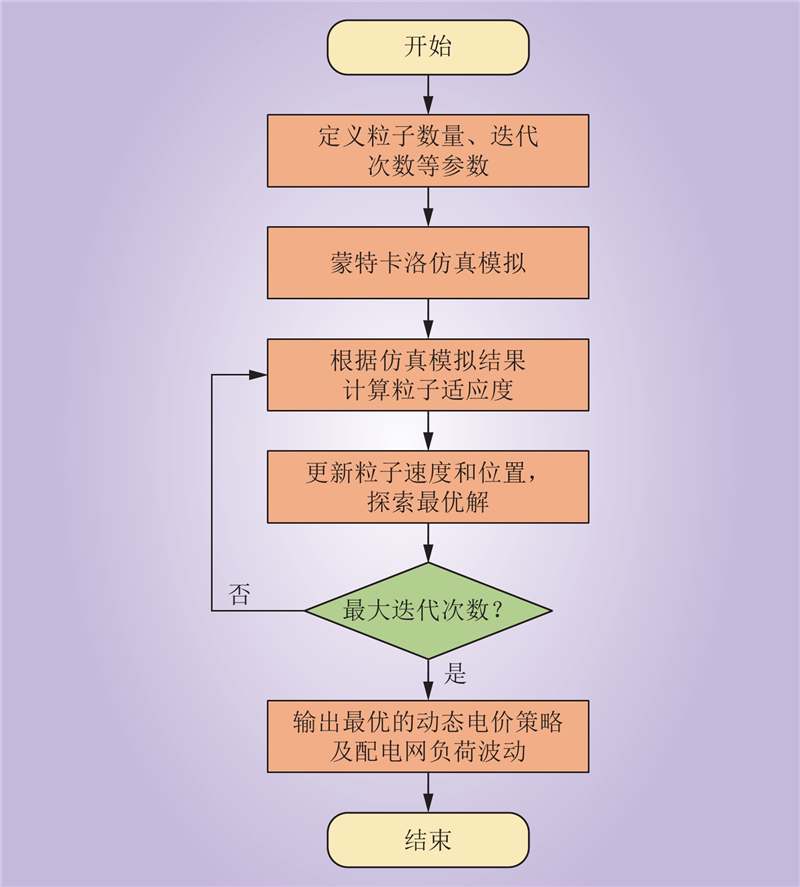
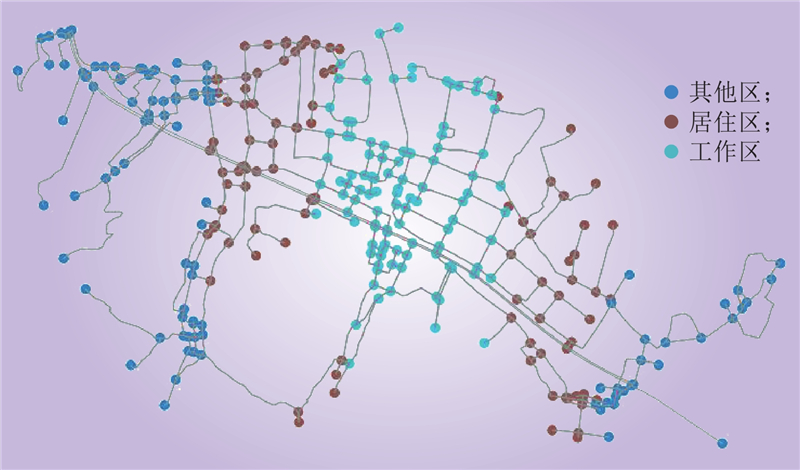
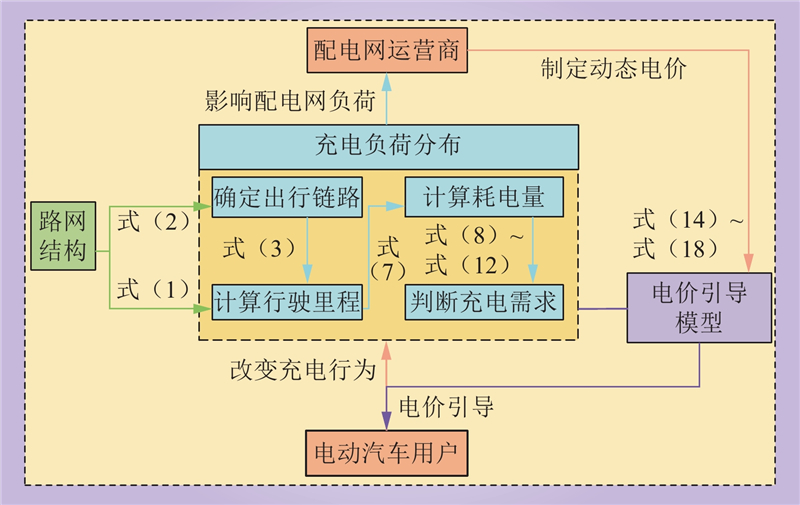
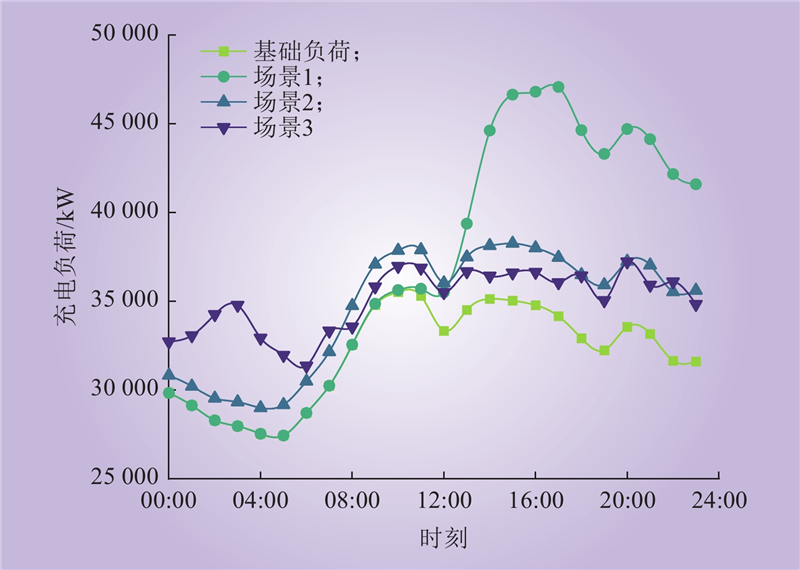
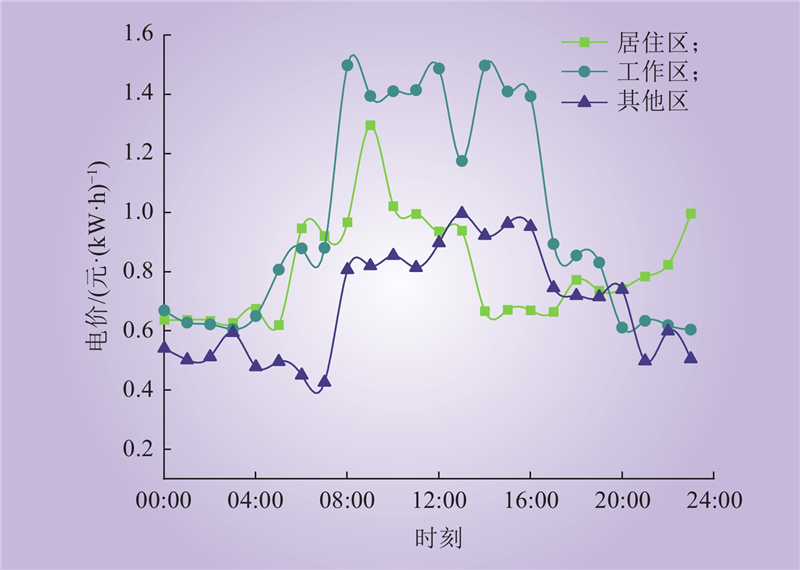
| 1 |
中国人民共和国公安部. 2024年上半年全国机动车达4.4亿辆 驾驶人达5.32亿人 新能源汽车保有量达2472万辆[EB/OL]. (2024-07-09) [2025-07-17]. https://www.mps.gov.cn/n2254314/n6409334/n9194010/c9648257/content.html.
|
| 2 |
张晓虎, 张熊, 张克良, 等. 储能技术在轨道交通再生制动能量回收的应用[J]. 电气工程学报, 2023, 18 (2): 210- 220.
|
|
ZHANG Xiaohu, ZHANG Xiong, ZHANG Keliang, et al. Application of energy storage technology in regenerative braking energy recovery of rail transit[J]. Journal of Electrical Engineering, 2023, 18 (2): 210- 220.
|
| 3 |
宁达文. 混合动力汽车再生制动控制策略仿真研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2021.
|
|
NING Dawen. Research on regenerative braking control strategy simulation of hybrid electric vehicle[D]. Beijing: Beijing Jiaotong University, 2021.
|
| 4 |
朱法华, 徐静馨. 双碳背景下中国与主要发达国家电力低碳转型比较[J]. 电力科技与环保, 2024, 40 (6): 561- 571.
|
|
ZHU Fahua, XU Jingxin. Comparison of low-carbon transformation in electricity between China and major developed countries under the background of carbon peaking and carbon neutrality[J]. Electric Power Technology and Environmental Protection, 2024, 40 (6): 561- 571.
|
| 5 |
许翔泰, 张仰飞, 陈光宇, 等. 计及光伏发电的电动汽车充电优化调度研究[J]. 智慧电力, 2019, 47 (10): 44- 50.
|
|
XU Xiangtai, ZHANG Yangfei, CHEN Guangyu, et al. Optimal scheduling of charging for electric vehicle considering photovoltaic power generation[J]. Smart Power, 2019, 47 (10): 44- 50.
|
| 6 |
喻恒凝, 黄力, 张思东, 等. 分布式光伏和电动汽车接入对配电网网损和电压偏移影响的分析研究[J]. 智慧电力, 2020, 48 (1): 28- 34.
|
|
YU Hengning, HUANG Li, ZHANG Sidong, et al. Effects of distributed photovoltaic generation and electric vehicle integrating into distribution network on line loss and voltage drift[J]. Smart Power, 2020, 48 (1): 28- 34.
|
| 7 |
胡继匀, 杨镜非, 傅长熠. 基于两阶段优化模型的电动汽车充电站放电策略[J]. 智慧电力, 2021, 49 (1): 83- 89.
|
|
HU Jiyun, YANG Jingfei, FU Changyi. Two-stage optimization strategy for electric vehicle charging station based on Nash negotiation method and reinforcement learning algorithm[J]. Smart Power, 2021, 49 (1): 83- 89.
|
| 8 |
姚明, 毛文杰, 曹淑超, 等. 基于多源数据的电动汽车充电设施布局优化方法研究[J]. 智慧电力, 2023, 51 (9): 31- 37.
|
|
YAO Ming, MAO Wenjie, CAO Shuchao, et al. Optimization method of electric vehicle charging facility layout based on multi-source data[J]. Smart Power, 2023, 51 (9): 31- 37.
|
| 9 |
HAN S, HAN S, SEZAKI K. Development of an optimal vehicle-to-grid aggregator for frequency regulation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2010, 1 (1): 65- 72.
|
| 10 |
WANG M S, MU Y F, SHI Q X, et al. Electric vehicle aggregator modeling and control for frequency regulation considering progressive state recovery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2020, 11 (5): 4176- 4189.
|
| 11 |
周原冰, 龚乃玮, 王皓界, 等. 中国电动汽车发展及车网互动对新型储能配置的影响[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (10): 1- 11.
|
|
ZHOU Yuanbing, GONG Naiwei, WANG Haojie, et al. Study on the influence of electric vehicle development and the vehicle-grid interaction on new energy storage configuration in China[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (10): 1- 11.
|
| 12 |
赵梓潼, 顾兵. 需求响应下基于电动汽车负荷聚合商的充放电电价与时段研究[J]. 东北电力大学学报, 2023, 43 (6): 79- 86.
|
|
ZHAO Zitong, GU Bing. Research on charging and discharging price and time period basedon electric vehicle load aggregator under demand response[J]. Journal of Northeast Electric Power University, 2023, 43 (6): 79- 86.
|
| 13 |
于雷, 饶磊, 向官腾, 等. 小容量光伏发电系统接入配电网的电压特性分析[J]. 内蒙古电力技术, 2024, 42 (6): 26- 30.
|
|
YU Lei, RAO Lei, XIANG Guanteng, et al. Analysis of voltage characteristics of small capacity photovoltaic power generation system connected to distribution network[J]. Inner Mongolia Electric Power, 2024, 42 (6): 26- 30.
|
| 14 |
沈筱琦, 方鑫, 谭林林, 等. 基于居民出行模拟的电动汽车负荷时空分布预测[J]. 电力工程技术, 2024, 43 (3): 130- 139.
|
|
SHEN Xiaoqi, FANG Xin, TAN Linlin, et al. Prediction of spatio-temporal distribution of electric vehicle load based on residential travel simulation[J]. Electric Power Engineering Technology, 2024, 43 (3): 130- 139.
|
| 15 |
屈克庆, 赵登辉, 毛玲, 等. 考虑城市空间结构和用户有限理性的电动汽车快充负荷预测[J]. 南方电网技术, 2024, 18 (10): 151- 160.
|
|
QU Keqing, ZHAO Denghui, MAO Ling, et al. Fast charging load forecasting of electric vehicles considering urban spatial structure and user's bounded rationality[J]. Southern Power System Technology, 2024, 18 (10): 151- 160.
|
| 16 |
丁乐言, 柯松, 张帆, 等. 考虑出行需求和引导策略的电动汽车充电负荷预测[J]. 电力建设, 2024, 45 (6): 10- 26.
|
|
DING Leyan, KE Song, ZHANG Fan, et al. Forecasting of electric-vehicle charging load considering travel demand and guidance strategy[J]. Electric Power Construction, 2024, 45 (6): 10- 26.
|
| 17 |
韩林阳, 叶承晋, 朱超, 等. 高温天气下计及用户意愿的城市充电负荷空间引导策略[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2024, 48 (10): 139- 150.
|
|
HAN Linyang, YE Chengjin, ZHU Chao, et al. Spatial guidance strategy for urban charging loads in high-temperature weather considering user willingness[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2024, 48 (10): 139- 150.
|
| 18 |
程杉, 钟仕凌, 尚冬冬, 等. 考虑电动汽车时空负荷分布特性的主动配电网动态重构[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2022, 50 (17): 1- 13.
|
|
CHENG Shan, ZHONG Shiling, SHANG Dongdong, et al. Dynamic reconfiguration of an active distribution network considering temporal and spatial load distribution characteristics of electric vehicles[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2022, 50 (17): 1- 13.
|
| 19 |
MA S C, YI B W, FAN Y. Research on the valley-filling pricing for EV charging considering renewable power generation[J]. Energy Economics, 2022, 106, 105781.
|
| 20 |
邓衍辉, 李剑, 卢国强, 等. 考虑分区域动态电价机制引导的电动汽车充电优化策略[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2024, 52 (7): 33- 44.
|
|
DENG Yanhui, LI Jian, LU Guoqiang, et al. Charging optimization strategy of electric vehicles guided by the dynamic tariff mechanism of a subregion[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2024, 52 (7): 33- 44.
|
| 21 |
肖白, 吕会森, 杨士伟, 等. 考虑电动汽车用户有限理性的定制化电价套餐设计[J]. 电气应用, 2024, 43 (2): 91- 100.
|
|
XIAO Bai, LV Huisen, YANG Shiwei, et al. The design of customized electricity price package considering the limited rationality of electric vehicle users[J]. Electrotechnical Application, 2024, 43 (2): 91- 100.
|
| 22 |
杨帅, 戴朝华, 郭爱, 等. 考虑负荷空间均衡和充电站合作博弈的快速充电定价机制[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2024, 48 (7): 190- 200.
|
|
YANG Shuai, DAI Chaohua, GUO Ai, et al. Fast charging pricing mechanism considering load space balance and cooperative game of charging stations[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2024, 48 (7): 190- 200.
|
| 23 |
姜晓锋, 魏巍, 王永灿, 等. “车—路—网”协同优化下的电动汽车有序充电引导策略[J]. 电力科学与技术学报, 2023, 38 (5): 44- 56.
|
|
JIANG Xiaofeng, WEI Wei, WANG Yongcan, et al. Orderly charging guidance strategies for electric vehicles under EVs-Traffic-Distribution collaborative optimization[J]. Journal of Electric Power Science and Technology, 2023, 38 (5): 44- 56.
|
| 24 |
叶文浩, 陈耀红, 颜勤, 等. 基于动态分时电价引导的电动汽车需求侧响应[J]. 电力科学与技术学报, 2024, 39 (4): 138- 145.
|
|
YE Wenhao, CHEN Yaohong, YAN Qin, et al. Demand response of electric vehicle based on dynamic time-to-use electricity price[J]. Journal of Electric Power Science and Technology, 2024, 39 (4): 138- 145.
|
| 25 |
潘廷哲, 靳丰源, 陆泳昊, 等. 智能小区电动汽车充电动态电价策略设计[J/OL]. 中国电力, 2025: 1–11. (2025-07-17). https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=ZGDL20250716002&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ.
|
|
PAN Tingzhe, JIN Fengyuan, LU Yonghao, et al. Design of dynamic prices strategy for electric vehicles charging in smart communities[J/OL]. Electric Power, 2025: 1–11. (2025-07-17). https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=ZGDL20250716002&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ.
|
| 26 |
张美霞, 吴子敬, 杨秀. 基于动态能耗模型与用户心理的电动汽车充电负荷预测[J]. 现代电力, 2022, 39 (6): 710- 719.
|
| 27 |
侯慧, 王逸凡, 吴细秀, 等. 长时间尺度下计及里程焦虑心理效应的电动汽车充放电调度策略[J]. 高电压技术, 2023, 49 (1): 85- 93.
|
|
HOU Hui, WANG Yifan, WU Xixiu, et al. Electric vehicle charging and discharging scheduling strategy considering psychological effect of mileage anxiety on a long-time scale[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2023, 49 (1): 85- 93.
|
| 28 |
孙磊, 冯智伟, 韩美灵, 等. 面向成本优化的电动汽车弹性充电策略[J]. 小型微型计算机系统, 2024, 45 (1): 132- 138.
|
|
SUN Lei, FENG Zhiwei, HAN Meiling, et al. Cost-optimized elastic charging strategy for electric vehicles[J]. Journal of Chinese Computer Systems, 2024, 45 (1): 132- 138.
|
| 29 |
李宏伟, 宋玉峰, 李帅兵, 等. 基于ArcGIS路网结构与交通拥挤度分析的电动汽车充电负荷预测方法[J]. 电网技术, 2025, 49 (5): 1920- 1930.
|
|
LI Hongwei, SONG Yufeng, LI Shuaibing, et al. Electric vehicle charging load prediction based on ArcGIS road network structure and traffic congestion analysis[J]. Power System Technology, 2025, 49 (5): 1920- 1930.
|
| 30 |
李晓涵, 曹伟. 弹性充电需求下电动汽车调频激励机制及控制策略[J]. 中国电力, 2025, 58 (4): 148- 158.
|
|
LI Xiaohan, CAO Wei. Frequency regulation incentive mechanism and control strategy for electric vehicles under elastic charging demand[J]. Electric Power, 2025, 58 (4): 148- 158.
|
| 31 |
贾世成, 廖凯, 杨健维, 等. 考虑交通负荷时空需求及区域划分的配电网分布式经济调度策略[J]. 电力系统及其自动化学报, 2024, 36 (11): 30- 42.
|
|
JIA Shicheng, LIAO Kai, YANG Jianwei, et al. Distributed economic dispatching strategy for distribution network considering temporal and spatial demand of traffic load and area division[J]. Proceedings of the CSU-EPSA, 2024, 36 (11): 30- 42.
|
| 32 |
陈丽丹, 张尧, Antonio Figueiredo. 融合多源信息的电动汽车充电负荷预测及其对配电网的影响[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2018, 38 (12): 1- 10.
|
|
CHEN Lidan, ZHANG Yao, FIGUEIREDO A. Charging load forecasting of electric vehicles based on multi-source information fusion and its influence on distribution network[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2018, 38 (12): 1- 10.
|
| 33 |
Federal Highway Administration. 2017 National Household Travel Survey, U. S. Department of Transportation, Washington, DC[EB/OL]. (2021-02-21) [2024-10-30]. https://nhts.ornl.gov.
|
| 34 |
ZHANG W, DOU Y F. Coping with spatial mismatch: subsidy design for electric vehicle and charging markets[J]. Manufacturing & Service Operations Management, 2021, 24 (3): 1595- 1610.
|
| 35 |
GUILLET M, SCHIFFER M. Coordinated charging station search in stochastic environments: a multiagent approach[J]. Production and Operations Management, 2023, 32 (8): 2596- 2618.
|
| 36 |
HE C, OZTURK O C, GU C, et al. Consumer tax credits for EVs: some quasi-experimental evidence on consumer demand, product substitution, and carbon emissions[J]. Management Science, 2023, 69 (12): 7759- 7783.
|
| 37 |
YANG C, SUN T L, WANG W D, et al. Regenerative braking system development and perspectives for electric vehicles: an overview[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2024, 198, 114389.
|
| 38 |
《中国公路学报》编辑部. 中国汽车工程学术研究综述·2023[J]. 中国公路学报, 2023, 36 (11): 1- 192.
|
| 39 |
黄伟, 张桂连, 周登辉, 等. 基于能量流分析的纯电动汽车电耗优化研究[J]. 汽车工程, 2021, 43 (2): 171- 180.
|
|
HUANG Wei, ZHANG Guilian, ZHOU Denghui, et al. Research on optimization of power consumption of pure electric vehicle based on energy flow analysis[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2021, 43 (2): 171- 180.
|
| 40 |
赵敬玉, 徐铖, 李晓宇. 基于实际行驶数据的电动汽车能耗分析与预测[J]. 机械工程学报, 2023, 59 (10): 263- 274.
|
|
ZHAO Jingyu, XU Cheng, LI Xiaoyu. Electric vehicle energy consumption analysis and prediction based on real-world driving data[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2023, 59 (10): 263- 274.
|
| 41 |
张树培, 黄璇, 张玮. 电动汽车道路行驶制动能量回收特性研究[J]. 汽车技术, 2014 (12): 49- 53.
|
|
ZHANG Shupei, HUANG Xuan, ZHANG Wei. Research on braking energy recovery characteristics of electric vehicle in road driving[J]. Automobile Technology, 2014 (12): 49- 53.
|
| 42 |
齐彩娟, 陈宝生, 韦冬妮, 等. 考虑主从博弈定价模式的共享储能分布鲁棒优化配置方法研究[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (7): 40- 53.
|
|
QI Caijuan, CHEN Baosheng, WEI Dongni, et al. Distributionally robust optimal configuration for shared energy storage based on Stackelberg game pricing model[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (7): 40- 53.
|
| 43 |
王一飞, 王秀丽, 黄晶, 等. 动态电价机制下电动汽车竞争性充电的阻塞管理模型[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2023, 47 (12): 103- 110.
|
|
WANG Yifei, WANG Xiuli, HUANG Jing, et al. Congestion management model for competitive charging of electric vehicles under dynamic electricity price mechanism[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2023, 47 (12): 103- 110.
|
| 44 |
夏鑫, 钟浩, 张磊, 等. 计及动态电价的电动汽车参与微电网调度双层优化策略[J]. 电力工程技术, 2024, 43 (3): 140- 150.
|
|
XIA Xin, ZHONG Hao, ZHANG Lei, et al. A two-layer optimization strategy for electric vehicles participating in microgrid scheduling considering dynamic electricity prices[J]. Electric Power Engineering Technology, 2024, 43 (3): 140- 150.
|
| 45 |
段梅梅, 程含渺, 方凯杰, 等. 基于分时电碳耦合定价的虚拟电厂主从博弈策略[J]. 电测与仪表, 2024, 61 (11): 1- 11.
|
|
DUAN Meimei, CHENG Hanmiao, FANG Kaijie, et al. Research on Stackelberg game strategy for virtual power plant considering time-of-use electricity and carbon coupled price[J]. Electrical Measurement & Instrumentation, 2024, 61 (11): 1- 11.
|
| 46 |
余梦龙, 张进朝, 文豪, 等. 改进PSO-BPNN供水泵站变频恒压PID控制[J]. 电子测量技术, 2023, 46 (17): 64- 70.
|
|
YU Menglong, ZHANG Jinchao, WEN Hao, et al. Variable frequency and constant pressure PID control of water supply pump station based on improved PSO-BPNN algorithm[J]. Electronic Measurement Technology, 2023, 46 (17): 64- 70.
|