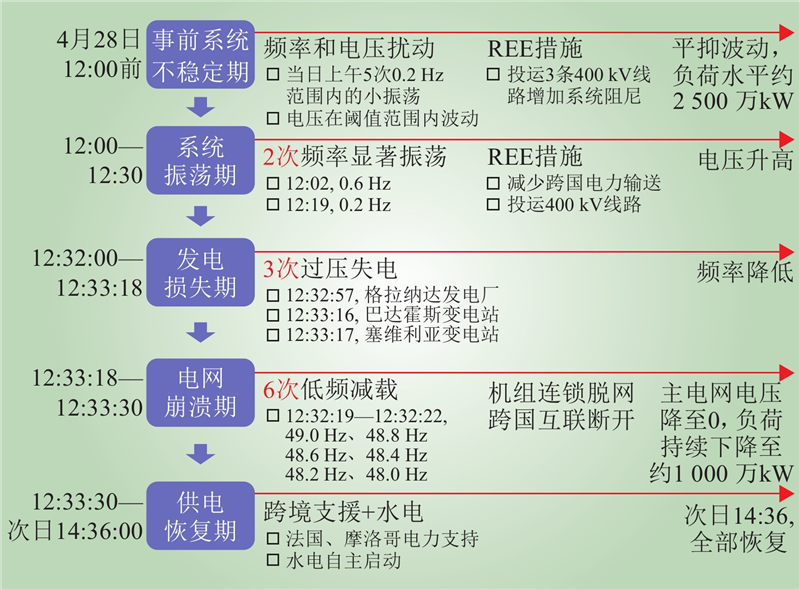
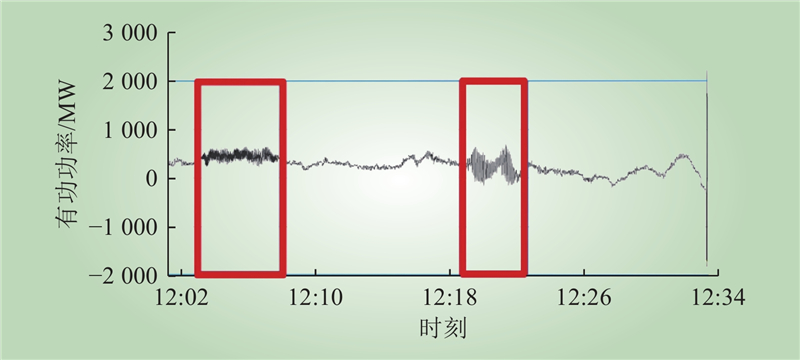
| 1 |
舒印彪, 汤涌, 张正陵, 等. 欧洲伊比利亚半岛电网“4·28”大停电事故分析及启示[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2025, 45 (17): 6603- 6612.
|
|
SHU Yinbiao, TANG Yong, ZHANG Zhengling, et al. Analysis and lessons of the April 28, 2025 blackout in the Iberian Peninsula power system[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2025, 45 (17): 6603- 6612.
|
| 2 |
郭琦, 王庆红, 谭伟涛, 等. “4·28”西班牙、葡萄牙大停电事故分析及对我国电网的启示[J]. 南方电网技术, 2025, 19 (08): 1- 10.
|
|
GUO Qi, WANG Qinghong, TAN Weitao, et al. Analysis on blackout in Spanish and Portuguese power systems on April 28th, 2025 and its enlightenment to power system in China[J]. Southern Power System Technology, 2025, 19 (08): 1- 10.
|
| 3 |
孙华东. 国外大停电事故分析[M]. 北京: 中国电力出版社, 2022: 166–173.
|
| 4 |
杨涛, 周洪, 魏凤, 等. 新型电力系统下的电网安全挑战与对策研究[J]. 电力信息与通信技术, 2024, 22 (8): 18- 26.
|
|
YANG Tao, ZHOU Hong, WEI Feng, et al. Challenges and countermeasures of grid security towards a new type of power system[J]. Electric Power Information and Communication Technology, 2024, 22 (8): 18- 26.
|
| 5 |
王国春, 董昱, 许涛, 等. 巴西“8.15”大停电事故分析及启示[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2023, 43 (24): 9461- 9470.
|
|
WANG Guochun, DONG Yu, XU Tao, et al. Analysis and lessons of Brazil blackout event on August 15, 2023[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2023, 43 (24): 9461- 9470.
|
| 6 |
侯验秋, 丁一, 包铭磊, 等. 电–气耦合视角下德州大停电事故分析及对我国新型电力系统发展启示[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2022, 42 (21): 7764- 7775.
|
|
HOU Yanqiu, DING Yi, BAO Minglei, et al. Analysis of Texas blackout from the perspective of electricity-gas coupling and its enlightenment to the development of China's new power system[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2022, 42 (21): 7764- 7775.
|
| 7 |
张玥, 谢光龙, 张全, 等. 美国得州2·15大停电事故分析及对中国电力发展的启示[J]. 中国电力, 2021, 54 (4): 192- 198, 206.
|
|
ZHANG Yue, XIE Guanglong, ZHANG Quan, et al. Analysis of 2·15 power outage in Texas and its implications for the power sector of China[J]. Electric Power, 2021, 54 (4): 192- 198, 206.
|
| 8 |
安学民, 孙华东, 张晓涵, 等. 美国得州“2.15”停电事件分析及启示[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2021, 41 (10): 3407- 3415, 3666.
|
|
AN Xuemin, SUN Huadong, ZHANG Xiaohan, et al. Analysis and lessons of Texas power outage event on February 15, 2021[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2021, 41 (10): 3407- 3415, 3666.
|
| 9 |
曾辉, 孙峰, 李铁, 等. 澳大利亚“9·28”大停电事故分析及对中国启示[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2017, 41 (13): 1- 6.
|
|
ZENG Hui, SUN Feng, LI Tie, et al. Analysis of "9·28" blackout in south Australia and its enlightenment to China[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2017, 41 (13): 1- 6.
|
| 10 |
樊陈, 姚建国, 张琦兵, 等. 英国“8·9”大停电事故振荡事件分析及思考[J]. 电力工程技术, 2020, 39 (4): 34- 41.
|
|
FAN Chen, YAO Jianguo, ZHANG Qibing, et al. Reflection and analysis for oscillation of the blackout event of 9 August 2019 in UK[J]. Electric Power Engineering Technology, 2020, 39 (4): 34- 41.
|
| 11 |
孙华东, 许涛, 郭强, 等. 英国“8·9”大停电事故分析及对中国电网的启示[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2019, 39 (21): 6183- 6192.
|
|
SUN Huadong, XU Tao, GUO Qiang, et al. Analysis on blackout in Great Britain power grid on August 9th, 2019 and its enlightenment to power grid in China[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2019, 39 (21): 6183- 6192.
|
| 12 |
Spanish National Security Council. Analysis report on the electricity crisis on April 28, 2025: unclassified version[R]. Madrid: Spanish Government, 2025.
|
| 13 |
Red Eléctrica de España. Analysis report on the accident of the Spanish peninsula power system on April 28, 2025[R]. Madrid: Red Eléctrica de España, 2025.
|
| 14 |
Asociación de Empresas de Energía Eléctrica. Statements regarding the diagnosis presented by Red Eléctrica de España[EB/OL]. (2025-06-19) [2025-08-14]. https://aelec.es/declaraciones-de-aelec-en-relacion-con-el-diagnostico-presentado-por-red-electrica-de-espana.
|
| 15 |
European Network of Transmission System Operators for Electricity. Iberian power outage on April 28, 2025[EB/OL]. (2025-07-16)[2025-08-11]. https://www.entsoe.eu/publications/blackout/28-april-2025-iberian-blackout/#Publications_&_Documents.
|
| 16 |
TORTA J M, MARSAL S, LEDO J, et al. New detailed modeling of GICs in the Spanish power transmission grid[J]. Space Weather, 2021, 19 (9): e2021SW002805.
|
| 17 |
European Committee for Electrical Standardization. Requirements for parallel access of power generation equipment to the distribution grid Part 1: Low voltage distribution grid access above 16A: EN 50549-1: 2019[S]. Brussels: European Committee for Standardization, 2019.
|
| 18 |
Red Eléctrica de España. Operating procedures for voltage control and reactive power support of grid-connected generator sets: P. O. 7.4[S]. Madrid: Red Eléctrica de España, 2020.
|
| 19 |
Gobierno de España. Royal Decree 413/2014: Legal framework for electricity production facilities[EB/OL]. (2014-06-10) [2025-01-11]. https://www.boe.es/eli/es/rd/2014/06/06/413.
|
| 20 |
Ministry of Ecological Transition and Demographic Challenges of Spain. Order on technical conditions for grid connection of new energy power generation facilities: TED/749/2020[Z]. Madrid: Official Gazette of Spain, 2020.
|
| 21 |
Red Eléctrica de España. Energy delivery conditions at the border points of the network managed by the system operator: P. O. 1.4[S]. Madrid: Red Eléctrica de España, 2020.
|
| 22 |
国网能源研究院有限公司. 中国新能源发电分析报告2025[R]. 北京: 中国电力出版社, 2025.
|
| 23 |
蒲天骄, 韩笑. 新型电力系统中人工智能应用的关键技术[J]. 电力信息与通信技术, 2024, 22 (1): 1- 13.
|
|
PU Tianjiao, HAN Xiao. Research on key technologies in the application of artificial intelligence in new type power systems[J]. Electric Power Information and Communication Technology, 2024, 22 (1): 1- 13.
|
| 24 |
周勤勇, 郝绍煦, 董武, 等. “十五五”电网规划安全稳定分析关键问题[J]. 中国电力, 2025, 58 (9): 138- 147.
|
|
ZHOU Qinyong, HAO Shaoxu, DONG Wu, et al. Key issues in security and stability analysis for the "15th five-year" power grid planning[J]. Electric Power, 2025, 58 (9): 138- 147.
|
| 25 |
董武, 张健, 周勤勇, 等. 中国电力系统安全稳定性演化综述[J]. 中国电力, 2025, 58 (1): 115- 127.
|
|
DONG Wu, ZHANG Jian, ZHOU Qinyong, et al. An overview of the evolution of security and stability of China's power system[J]. Electric Power, 2025, 58 (1): 115- 127.
|
| 26 |
蓝元良, 刘伟麟, 兰天, 等. 特高压直流输电换流阀设备数字化思考与实践[J]. 电力信息与通信技术, 2024, 22 (8): 1- 9.
|
|
LAN Yuanliang, LIU Weilin, LAN Tian, et al. Considerations and practices of UHVDC converter's digitalization[J]. Electric Power Information and Communication Technology, 2024, 22 (8): 1- 9.
|
| 27 |
步雨洛, 吴俊勇, 史法顺, 等. 考虑新能源的暂态功角与电压稳定一体化评估[J]. 中国电力, 2025, 58 (6): 122- 136.
|
|
BU Yuluo, WU Junyong, SHI Fashun, et al. Integrated assessment of transient angle stability and voltage stability considering renewable energy sources[J]. Electric Power, 2025, 58 (6): 122- 136.
|
| 28 |
张智刚, 康重庆. 碳中和目标下构建新型电力系统的挑战与展望[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2022, 42 (8): 2806- 2819.
|
|
ZHANG Zhigang, KANG Chongqing. Challenges and prospects for constructing the new-type power system towards a carbon neutrality future[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2022, 42 (8): 2806- 2819.
|
| 29 |
国家能源局. 关于汲取新疆电网“8·3”功率振荡事件教训 加强地方电网涉网安全管理工作的通知[EB/OL]. (2024-12-02)[2025-08-11]. https://zfxxgk.nea.gov.cn/2024-12/02/c_1212408383.htm.
|
| 30 |
国家能源局. 关于提升新能源和新型并网主体涉网安全能力 服务新型电力系统高质量发展的通知[EB/OL]. (2024-9-30)[2025-08-11]. https://zfxxgk.nea.gov.cn/2024-09/30/c_1310787050.htm.
|