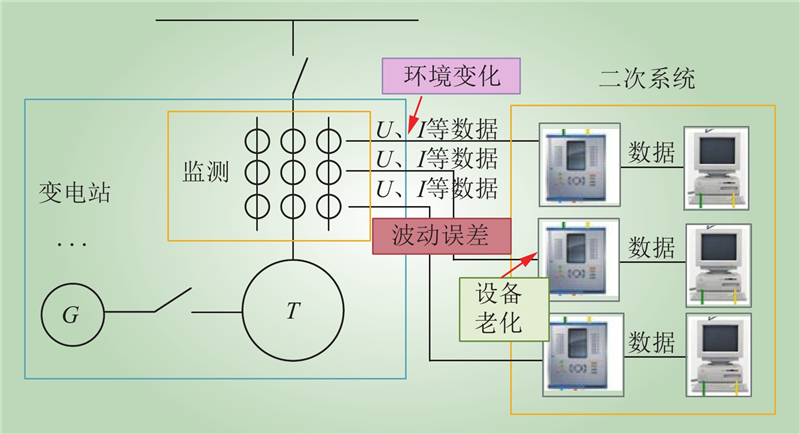
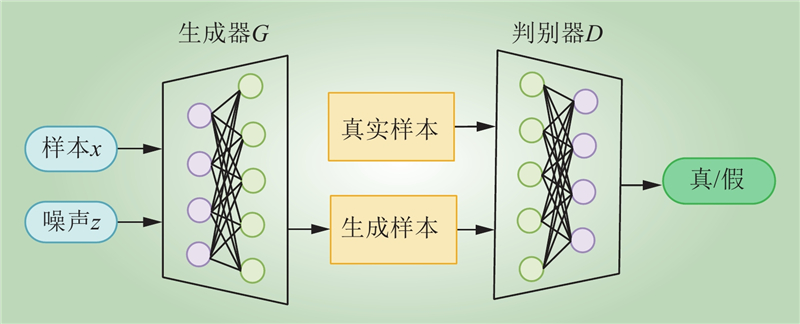
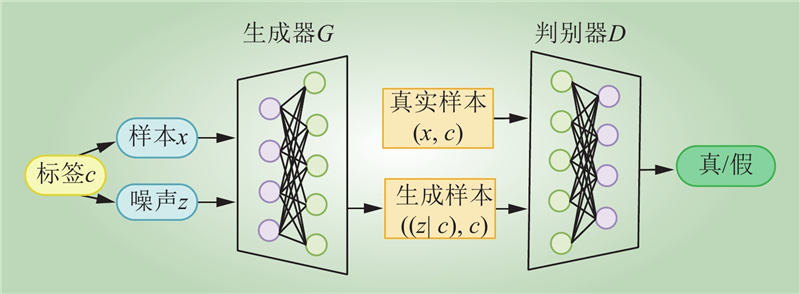
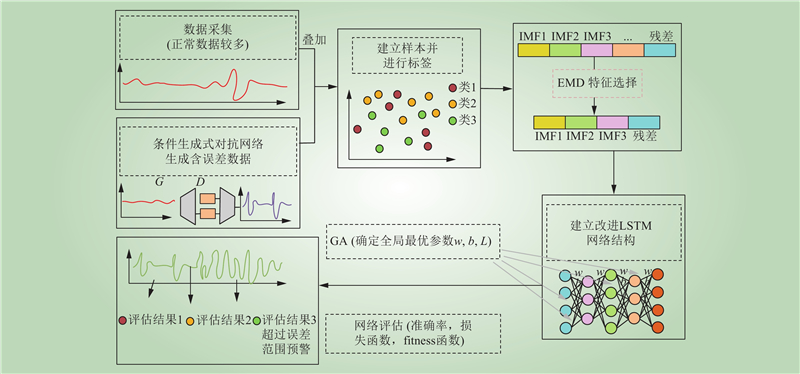
| 1 |
计荣荣, 王梦芝, 周国伟, 等. 基于云端优化的智能变电站二次系统快速测试建模与系统设计[J]. 中国电力, 2025, 58 (5): 152- 157.
|
|
JI Rongrong, WANG Mengzhi, ZHOU Guowei, et al. Cloud-based optimized intelligent substation secondary system rapid test model and system design[J]. Electric Power, 2025, 58 (5): 152- 157.
|
| 2 |
金国锋, 杨世峰, 刘玲玲, 等. 基于二维混沌映射正余弦算法的智能变电站虚回路自动连接技术[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (8): 152- 158.
|
|
JIN Guofeng, YANG Shifeng, LIU Lingling, et al. Automatic connection of virtual circuits in smart substations based on chaotic two-dimensional mapping sine and cosine algorithm[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (8): 152- 158.
|
| 3 |
曹一家, 赵一睿, 李勇, 等. 考虑针对变电站网络攻击风险的脆弱元件筛选方法[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2023, 47 (8): 25- 33.
|
|
CAO Yijia, ZHAO Yirui, LI Yong, et al. Vulnerable component screening method considering cyber-attack risk in substation[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2023, 47 (8): 25- 33.
|
| 4 |
严亚兵, 褚旭, 肖豪龙, 等. 基于改进支持向量机的数字化变电站安全措施生成技术[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (10): 194- 201.
|
|
YAN Yabing, CHU Xu, XIAO Haolong, et al. Automatic generation technology of safety measures for digital substation based on improved support vector machine[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (10): 194- 201.
|
| 5 |
刘健, 朱青松, 王毅钊, 等. 基于变电站稳态监测信息的小电阻接地系统单相接地检测性能提升方法[J]. 浙江电力, 2023, 42 (4): 1- 8.
|
|
LIU Jian, ZHU Qingsong, WANG Yizhao, et al. Improvement of single-phase grounding fault detection for small resistance grounding systems based on steady-state monitoring information in the substation[J]. Zhejiang Electric Power, 2023, 42 (4): 1- 8.
|
| 6 |
朱智, 张永宏, 吕帅, 等. 基于数据通信建模技术的移动式智能变电站安措防误预警系统研究与应用[J]. 内蒙古电力技术, 2023, 41 (4): 54- 59.
|
|
ZHU Zhi, ZHANG Yonghong, LYU Shuai, et al. Research and application on security precaution misoperation early warning system of mobile intelligent substation based on data communication modeling technology[J]. Inner Mongolia Electric Power, 2023, 41 (4): 54- 59.
|
| 7 |
李振华, 郑严钢, 李振兴, 等. 基于传递熵和小波神经网络的电子式电压互感器误差预测[J]. 电测与仪表, 2021, 58 (3): 146- 152.
|
|
LI Zhenhua, ZHENG Yangang, LI Zhenxing, et al. Error prediction of electronic voltage transformer based on transfer entropy and wavelet neural network[J]. Electrical Measurement & Instrumentation, 2021, 58 (3): 146- 152.
|
| 8 |
赵鹏, 马克琪, 李红斌, 等. 计及一次电压波动的电压互感器误差状态在线评估方法[J]. 高电压技术, 2022, 48 (3): 1042- 1051.
|
|
ZHAO Peng, MA Keqi, LI Hongbin, et al. On-line error evaluation method of instrument voltage transformers considering primary voltage fluctuations[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2022, 48 (3): 1042- 1051.
|
| 9 |
高书垚, 安泰, 宋剑. 基于熵权-正态云模型的智能电能表状态评估研究[J]. 电测与仪表, 2022, 59 (1): 190- 194.
|
|
GAO Shuyao, AN Tai, SONG Jian. Status evaluation of smart meter based on entropy weight-normal cloud model[J]. Electrical Measurement & Instrumentation, 2022, 59 (1): 190- 194.
|
| 10 |
南东亮, 王维庆, 张陵, 等. 基于关联规则挖掘与组合赋权-云模型的电网二次设备运行状态风险评估[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2021, 49 (10): 67- 76.
|
|
NAN Dongliang, WANG Weiqing, ZHANG Ling, et al. Risk assessment of the operation state of power grid secondary equipment based on association rule mining and combination weighting-cloud model[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2021, 49 (10): 67- 76.
|
| 11 |
顾佳浩, 淡淑恒. 考虑HI理论和在线监测误差的配电网可靠性评估[J]. 电力系统及其自动化学报, 2021, 33 (4): 127- 134.
|
|
GU Jiahao, DAN Shuheng. Reliability evaluation on distribution network considering HI theory and online monitoring error[J]. Proceedings of the CSU-EPSA, 2021, 33 (4): 127- 134.
|
| 12 |
陈海涛, 杨军, 施迎春, 等. 基于云模型与马尔科夫链的继电保护装置寿命预测方法[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2019, 47 (16): 94- 100.
|
|
CHEN Haitao, YANG Jun, SHI Yingchun, et al. Life prediction method of relay protection device based on could model and Markov Chain[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2019, 47 (16): 94- 100.
|
| 13 |
李俊卿, 李斯璇, 陈雅婷, 等. 一种基于CGAN-CNN的同步电机转子绕组匝间短路故障诊断方法[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2021, 41 (8): 169- 174.
|
|
LI Junqing, LI Sixuan, CHEN Yating, et al. Fault diagnosis method of inter-turn short circuit of rotor winding of synchronous motor based on CGAN-CNN[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2021, 41 (8): 169- 174.
|
| 14 |
孙宁, 陈争, 侯小强, 等. 基于MGP-GAN的27.5 kV电缆故障诊断方法[J]. 电气自动化, 2023, 45 (4): 88- 90.
|
|
SUN Ning, CHEN Zheng, HOU Xiaoqiang, et al. Fault diagnosis method of 27.5 kV cable based on MGP-GAN[J]. Electrical Automation, 2023, 45 (4): 88- 90.
|
| 15 |
邵振国, 张承圣, 陈飞雄, 等. 生成对抗网络及其在电力系统中的应用综述[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2023, 43 (3): 987- 1004.
|
|
SHAO Zhenguo, ZHANG Chengsheng, CHEN Feixiong, et al. A review on generative adversarial networks for power system applications[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2023, 43 (3): 987- 1004.
|
| 16 |
江善和, 李伟, 徐小艳, 等. 基于变分模态分解改进生成对抗网络的短期风电功率预测[J]. 综合智慧能源, 2024, 46 (2): 28- 35.
|
|
JIANG Shanhe, LI Wei, XU Xiaoyan, et al. Short-term wind power forecasting based on variational mode decomposition and generative adversarial networks[J]. Integrated Intelligent Energy, 2024, 46 (2): 28- 35.
|
| 17 |
黄海荣, 吴君, 郁丹, 等. 基于经验模态条件生成对抗网络的短期负荷预测[J]. 自动化仪表, 2022, 43 (12): 25- 29, 37.
|
|
HUANG Hairong, WU Jun, YU Dan, et al. Short-term load forecasting based on empirical modal conditional generative adversarial network[J]. Process Automation Instrumentation, 2022, 43 (12): 25- 29, 37.
|
| 18 |
邵晨颖, 刘友波, 邵安海, 等. 基于生成对抗网络与局部电流相量的配电网拓扑鲁棒辨识[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2023, 47 (1): 55- 62.
|
|
SHAO Chenying, LIU Youbo, SHAO Anhai, et al. Robust identification for distribution network topology based on generative adversarial network and partial current phasor[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2023, 47 (1): 55- 62.
|
| 19 |
罗萍萍, 盛奥, 林济铿, 等. 基于CGAN台风气象下负荷场景生成[J]. 中国电力, 2025, 58 (2): 176- 185.
|
|
LUO Pingping, SHENG Ao, LIN Jikeng, et al. CGAN-based load scenario generation under typhoon weather[J]. Electric Power, 2025, 58 (2): 176- 185.
|
| 20 |
孙浩, 万灿, 曹照静, 等. 基于条件生成对抗网络曲线生成的短期负荷概率预测[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2023, 47 (23): 189- 199.
|
|
SUN Hao, WAN Can, CAO Zhaojing, et al. Short-term load probabilistic forecasting based on conditional generative adversarial network curve generation[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2023, 47 (23): 189- 199.
|
| 21 |
杨再丞, 孙勇. 基于空间简化和CNN-LSTM的区域风电功率日前网格预测方法[J]. 东北电力大学学报, 2024, 44 (2): 35- 41.
|
|
YANG Zaicheng, SUN Yong. Foreahead grid prediction of regional wind power basedon spatial reduction and CNN-LSTM[J]. Journal of Northeast Electric Power University, 2024, 44 (2): 35- 41.
|
| 22 |
张哲, 王勃. 基于CBAM-LSTM的风电集群功率短期预测方法[J]. 东北电力大学学报, 2024, 44 (1): 1- 8.
|
|
ZHANG Zhe, WANG Bo. Short-term power prediction method of wind power cluster based on CBAM-LSTM[J]. Journal of Northeast Electric Power University, 2024, 44 (1): 1- 8.
|
| 23 |
袁俊球, 王迪, 谢小锋, 等. 基于广义天气分类的ICEEMDAN-LSTM网络光伏发电功率短期预测[J]. 综合智慧能源, 2024, 46 (9): 53- 60.
|
|
YUAN Junqiu, WANG Di, XIE Xiaofeng, et al. Study of short-term PV power prediction based on ICEEMDAN-LSTM networks under generalized weather classifications[J]. Integrated Intelligent Energy, 2024, 46 (9): 53- 60.
|
| 24 |
薛飞, 李宏强, 李旭涛, 等. 基于LSTM神经网络的双馈风机控制参数辨识方法[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (6): 31- 39.
|
|
XUE Fei, LI Hongqiang, LI Xutao, et al. Identification method for control parameters of doubly-fed induction generator based on LSTM neural network[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (6): 31- 39.
|
| 25 |
张宏杰, 陈贵凤, 闫宏伟, 等. 基于SMOTE与Bayes优化的LSTM网络变压器故障诊断[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (10): 164- 170.
|
|
ZHANG Hongjie, CHEN Guifeng, YAN Hongwei, et al. Fault diagnosis of LSTM network tansformer based on SMOTE and Bayes optimization[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (10): 164- 170.
|
| 26 |
杨协伟, 方文田, 蔡伟杰. 一种提升金属氧化物避雷器阻性电流计算精度的方法[J]. 浙江电力, 2023, 42 (8): 92- 99.
|
|
YANG Xiewei, FANG Wentian, CAI Weijie. A method of improving calculation accuracy of resistive current for metal oxide arrester[J]. Zhejiang Electric Power, 2023, 42 (8): 92- 99.
|
| 27 |
金恩淑, 陈和平, 夏国武. 基于开关函数的晶闸管整流器差动保护新方法[J]. 东北电力大学学报, 2023, 43 (2): 31- 38.
|
|
JIN Enshu, CHEN Heping, XIA Guowu. A new differential protection method of thyristor converter in rectifier station based on wwitching function[J]. Journal of Northeast Electric Power University, 2023, 43 (2): 31- 38.
|
| 28 |
姚创, 魏菊芳, 于顺智, 等. 基于流敏电阻的电磁式电压互感器高压侧消谐技术研究[J]. 广东电力, 2023, 36 (12): 97- 105.
|
|
YAO Chuang, WEI Jufang, YU Shunzhi, et al. Research on harmonic elimination technology at high voltage terminal of inductive voltage transformer based on current dependent resistor[J]. Guangdong Electric Power, 2023, 36 (12): 97- 105.
|
| 29 |
马文成. 电压互感器高压熔断器熔管更换辅助工具研制[J]. 内蒙古电力技术, 2023, 41 (2): 59- 63.
|
|
MA Wencheng. Development of auxiliary tool for fuse tube replacement of high voltage fuse of voltage transformer[J]. Inner Mongolia Electric Power, 2023, 41 (2): 59- 63.
|
| 30 |
谷相宏, 郭子晗, 张程, 等. 正弦波调制全光纤电流互感器光回路故障预警方法[J]. 广东电力, 2023, 36 (7): 50- 59.
|
|
GU Xianghong, GUO Zihan, ZHANG Cheng, et al. Fault early warning method for FOCT optical circuit of sine wave modulation[J]. Guangdong Electric Power, 2023, 36 (7): 50- 59.
|
| 31 |
乔胜亚, 周鸿铃, 李光茂, 等. 基于介损和电容量的电流互感器运行分布规律及现场应用研究[J]. 广东电力, 2023, 36 (3): 84- 91.
|
|
QIAO Shengya, ZHOU Hongling, LI Guangmao, et al. Research on operation distribution law and field application of current transformer based on dielectric loss and capacitance[J]. Guangdong Electric Power, 2023, 36 (3): 84- 91.
|