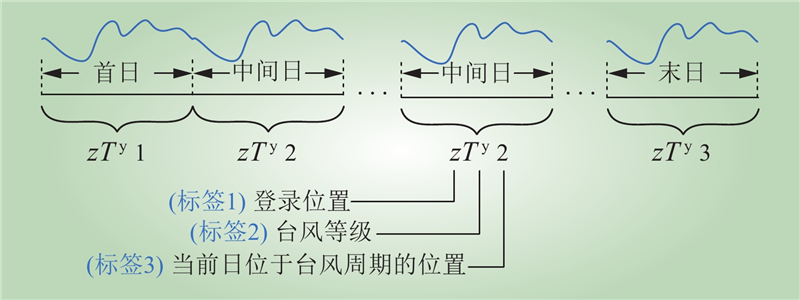
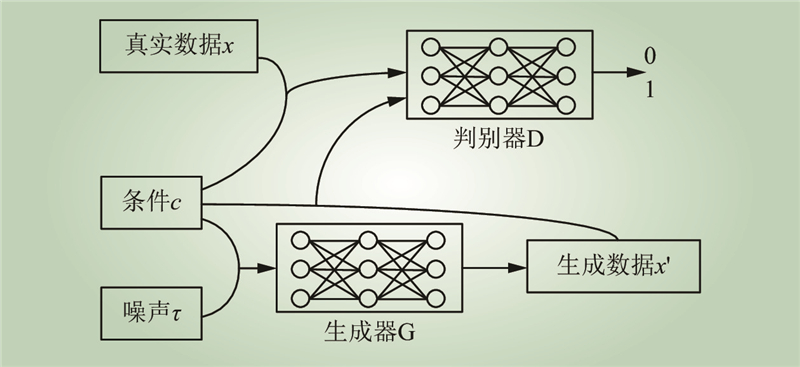
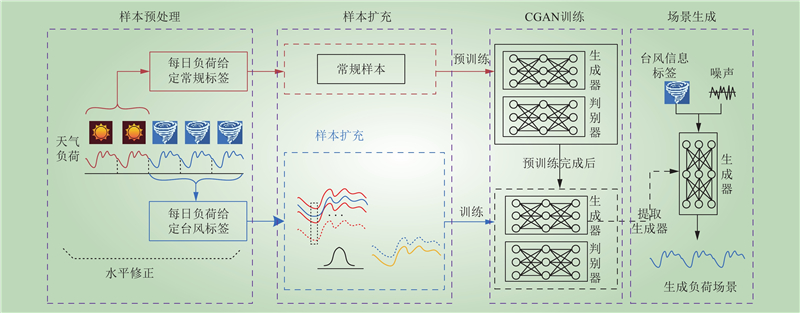
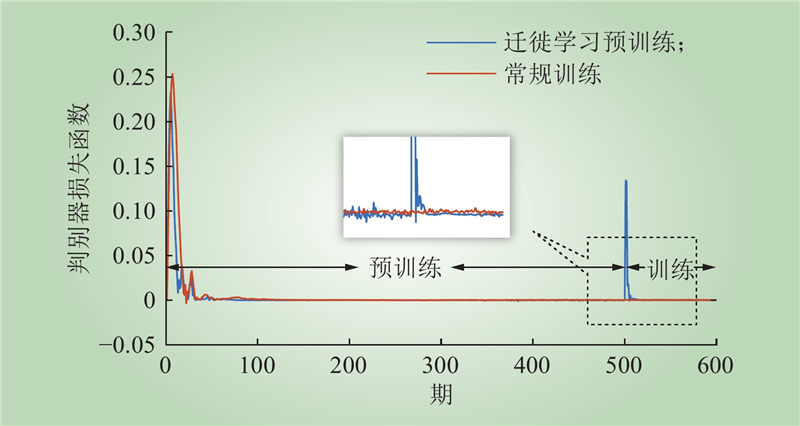
| 1 |
李明节, 梁志峰, 许涛, 等. 基于敏感气温空间分布的度夏度冬日最大负荷预测与应用研究[J]. 电网技术, 2023, 47 (3): 1088- 1097.
|
|
LI Mingjie, LIANG Zhifeng, XU Tao, et al. Prediction and application of maximum daily load in summer and winter based on spatial distribution of sensitive temperatures[J]. Power System Technology, 2023, 47 (3): 1088- 1097.
|
| 2 |
樊晓伟, 王瑞妙, 杨海峰, 等. 计及源荷不确定的综合能源微电网集群优化运行[J]. 电力建设, 2024, 45 (8): 128- 139.
|
|
FAN Xiaowei, WANG Ruimiao, YANG Haifeng, et al. Optimization operation of integrated energy microgrid cluster considering source-load uncertainty[J]. Electric Power Construction, 2024, 45 (8): 128- 139.
|
| 3 |
朱海军, 鞠立伟, 杨慧, 等. 计及不确定性的新型灵活性资源两阶段鲁棒配置优化模型[J]. 电力建设, 2024, 45 (7): 1- 11.
|
|
ZHU Haijun, JU Liwei, YANG Hui, et al. Optimal two-stage robust configuration model and algorithm of new flexibility resources considering uncertainty[J]. Electric Power Construction, 2024, 45 (7): 1- 11.
|
| 4 |
李滨, 陆明珍. 考虑实时气象耦合作用的地区电网短期负荷预测建模[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2020, 44 (17): 60- 68.
|
|
LI Bin, LU Mingzhen. Short-term load forecasting modeling of regional power grid considering real-time meteorological coupling effect[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2020, 44 (17): 60- 68.
|
| 5 |
申洪涛, 李飞, 史轮, 等. 基于气象数据降维与混合深度学习的短期电力负荷预测[J]. 电力建设, 2024, 45 (1): 13- 21.
|
|
SHEN Hongtao, LI Fei, SHI Lun, et al. Short-term power load forecasting based on reduction of meteorological data dimensionality and hybrid deep learning[J]. Electric Power Construction, 2024, 45 (1): 13- 21.
|
| 6 |
李雪玲, 刘洋, 李振伟, 等. 基于气象分型改进构造不确定集的多微网低碳鲁棒经济调度[J]. 电力建设, 2023, 44 (8): 142- 156.
|
|
LI Xueling, LIU Yang, LI Zhenwei, et al. Robust low-carbon economic dispatch of multiple microgrids based on improved uncertainty set of meteorological classification[J]. Electric Power Construction, 2023, 44 (8): 142- 156.
|
| 7 |
李宝聚, 齐宏伟, 傅吉悦, 等. 极端气象天气对新能源运行影响分析[J]. 吉林电力, 2022, 50 (1): 10- 13.
|
|
LI Baoju, QI Hongwei, FU Jiyue, et al. Analysis on the impact of extreme weather on new energy operation[J]. Jilin Electric Power, 2022, 50 (1): 10- 13.
|
| 8 |
李帅, 李哲, 梁允, 等. 气象因素对电力行业的影响研究[J]. 东北电力技术, 2019, 40 (8): 7- 10.
|
|
LI Shuai, LI Zhe, LIANG Yun, et al. Research on influence of meteorology on electric power industry[J]. Northeast Electric Power Technology, 2019, 40 (8): 7- 10.
|
| 9 |
方华亮, 李大虎, 彭辉, 等. 基于“互联网+” 的分散式太阳能规划方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2017, 37 (5): 1316- 1323.
|
|
FANG Hualiang, LI Dahu, PENG Hui, et al. Distributed solar energy planning method based on Internet plus[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2017, 37 (5): 1316- 1323.
|
| 10 |
MOTLAGH O, BERRY A, O’NEIL L. Clustering of residential electricity customers using load time series[J]. Applied Energy, 2019, 237, 11- 24.
|
| 11 |
李博, 孙建军, 余攀, 等. 基于负荷聚类与网络等效的配电网多维典型场景生成方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2021, 41 (8): 2661- 2670.
|
|
LI Bo, SUN Jianjun, YU Pan, et al. A multi-dimensional typical scenarios generation algorithm for distribution network based on load clustering and network structure equivalence[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2021, 41 (8): 2661- 2670.
|
| 12 |
曲凯, 李湃, 黄越辉, 等. 面向新能源消纳能力评估的年负荷序列建模及场景生成方法[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2021, 45 (1): 123- 131.
|
|
QU Kai, LI Pai, HUANG Yuehui, et al. Modeling and scenario generation method of annual load series for evaluation of renewable energy accommodation capacity[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2021, 45 (1): 123- 131.
|
| 13 |
李辉, 任洲洋, 胡博, 等. 基于时序生成对抗网络的月度风光发电功率场景分析方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2022, 42 (2): 537- 547.
|
|
LI Hui, REN Zhouyang, HU Bo, et al. A sequential generative adversarial network based monthly scenario analysis method for wind and photovoltaic power[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2022, 42 (2): 537- 547.
|
| 14 |
董骁翀, 孙英云, 蒲天骄. 基于条件生成对抗网络的可再生能源日前场景生成方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2020, 40 (17): 5527- 5535.
|
|
DONG Xiaochong, SUN Yingyun, PU Tianjiao. Day-ahead scenario generation of renewable energy based on conditional GAN[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2020, 40 (17): 5527- 5535.
|
| 15 |
SARMAS E, SPILIOTIS E, STAMATOPOULOS E, et al. Short-term photovoltaic power forecasting using meta-learning and numerical weather prediction independent long short-term memory models[J]. Renewable Energy, 2023, 216, 118997.
|
| 16 |
肖白, 黄钰茹, 姜卓, 等. 数据匮乏场景下采用生成对抗网络的空间负荷预测方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2020, 40 (24): 7990- 8001.
|
|
XIAO Bai, HUANG Yuru, JIANG Zhuo, et al. The method of spatial load forecasting based on the generative adversarial network for data scarcity scenarios[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2020, 40 (24): 7990- 8001.
|
| 17 |
JING H, ZHAO C H. A data expansion based piecewise regression strategy for incrementally monitoring the wind turbine with power curve[J]. Journal of Central South University, 2023, 30 (5): 1601- 1617.
|
| 18 |
PENG X S, YANG Z M, LI Y H, et al. Short-term wind power prediction based on stacked denoised auto-encoder deep learning and multi-level transfer learning[J]. Wind Energy, 2023, 26 (10): 1066- 1081.
|
| 19 |
朱涛, 陈翔, 高强, 等. 基于Logsitic回归模型和自适应密度聚类算法的分行业负荷增长规律[J]. 电网与清洁能源, 2019, 35 (5): 20- 28.
|
|
ZHU Tao, CHEN Xiang, GAO Qiang, et al. Law of load growth in different industries based on logsitic regression model and adaptive density clustering algorithm[J]. Power System and Clean Energy, 2019, 35 (5): 20- 28.
|
| 20 |
郑凌蔚, 刘士荣, 周文君, 等. 并网型可再生能源发电系统容量配置与优化[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2014, 42 (17): 31- 37.
|
|
ZHENG Lingwei, LIU Shirong, ZHOU Wenjun, et al. Capacity configuration and optimization of grid-connected renewable energy power generation system[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2014, 42 (17): 31- 37.
|
| 21 |
陈国民, 杨梦琪, 张喜平, 等. 2020年西北太平洋和南海台风预报精度评定[J]. 气象, 2022, 48 (4): 516- 525.
|
|
CHEN Guomin, YANG Mengqi, ZHANG Xiping, et al. Verification on forecasts of typhoons over western North Pacific and South China Sea in 2020[J]. Meteorological Monthly, 2022, 48 (4): 516- 525.
|
| 22 |
欧阳誉波. 基于混合藤Copula模型的多风电场出力相关性建模及其在无功优化中的应用[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2016.
|
|
OUYANG Yubo. Modeling of multi-dimensional wind farms output correlation based on mixture vine Copula structures and its application in reactive power optimization[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2016.
|
| 23 |
MIRZA M, OSINDERO S. Conditional generative adversarial nets[EB/OL].(2014-11-06) [2024-05-16]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1411.1784.
|
| 24 |
ARJOVSKY M, BOTTOU L. Towards principled methods for training generative adversarial networks[EB/OL]. (2017-01-17) [2024-05-16].http://arxiv.org/abs/1701.04862v1.
|
| 25 |
HOCHREITER R, PFLUG G C. Financial scenario generation for stochastic multi-stage decision processes as facility location problems[J]. Annals of Operations Research, 2007, 152 (1): 257- 272.
|
| 26 |
ZHUANG F Z, QI Z Y, DUAN K Y, et al. A comprehensive survey on transfer learning[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2021, 109 (1): 43- 76.
|
| 27 |
李湃, 刘纯, 黄越辉, 等. 基于隐马尔科夫模型的多风电场相关性出力时间序列建模方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2019, 39 (19): 5683- 5691.
|
|
LI Pai, LIU Chun, HUANG Yuehui, et al. Modeling correlated power time series of multiple wind farms based on hidden Markov model[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2019, 39 (19): 5683- 5691.
|