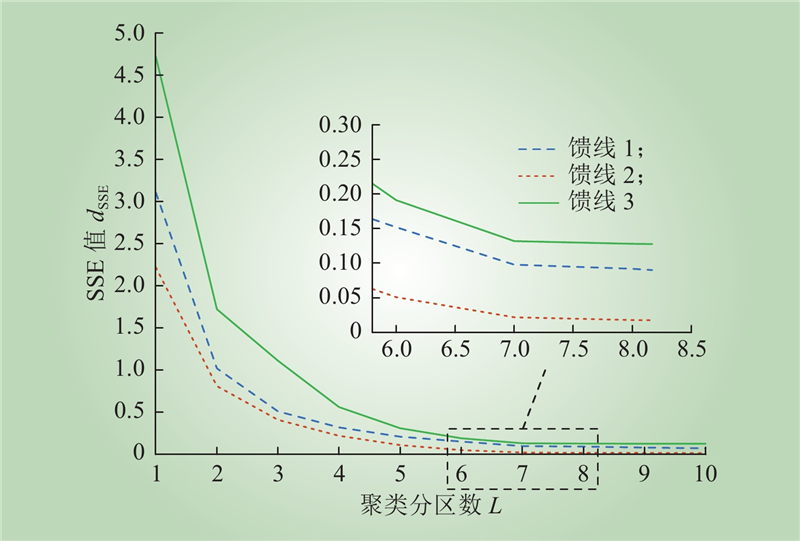
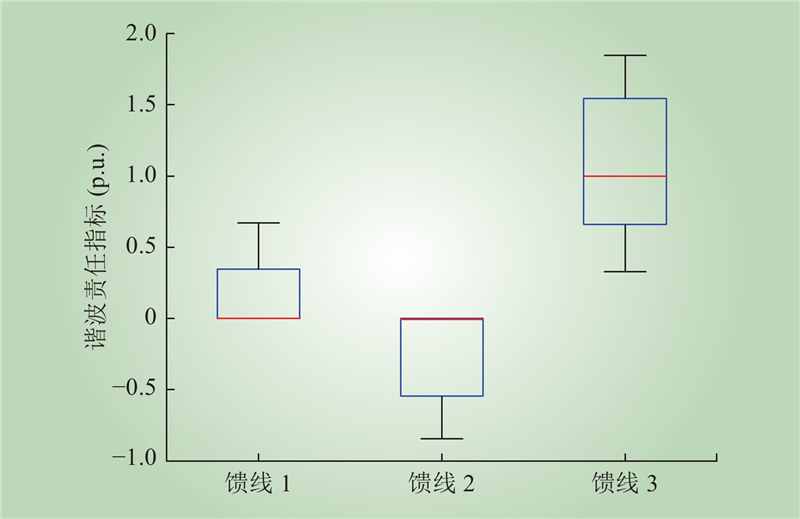
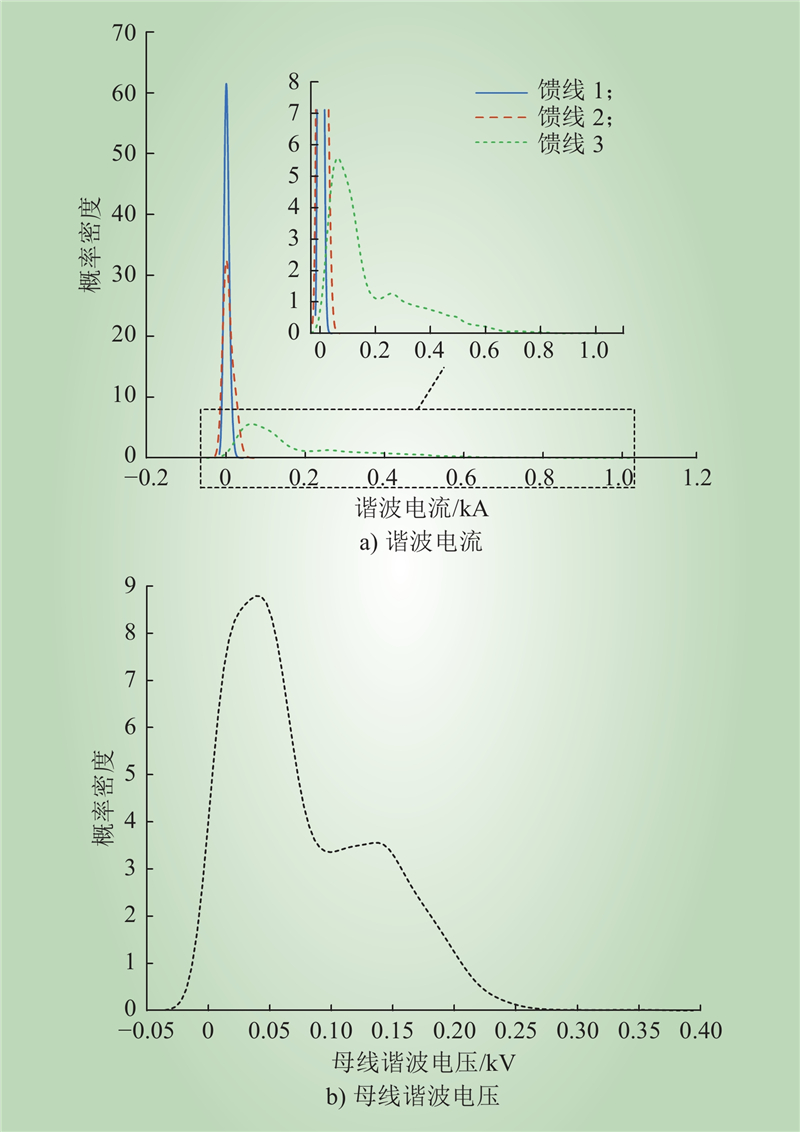
| 1 |
刘可, 王轩, 王杨, 等. 静止无功发生器谐波模型及其对谐振影响分析[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 51 (9): 174- 182.
|
|
LIU Ke, WANG Xuan, WANG Yang, et al. Harmonic model of static var generator and analysis of its resonance influence[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 51 (9): 174- 182.
|
| 2 |
DING T, CHEN H K, WU B, et al. Harmonic characteristics analysis of PWM-based electric vehicle chargers considering control strategy[C]//2018 18th International Conference on Harmonics and Quality of Power (ICHQP). Ljubljana, Slovenia. IEEE, 2018: 1–5.
|
| 3 |
丁同, 陈红坤, 吴斌, 等. 多谐波源定位及谐波责任量化区分方法综述[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2020, 40 (1): 19- 30.
|
|
DING Tong, CHEN Hongkun, WU Bin, et al. Overview on location and harmonic responsibility quantitative determination methods of multiple harmonic sources[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2020, 40 (1): 19- 30.
|
| 4 |
XU W, LIU Y L. A method for determining customer and utility harmonic contributions at the point of common coupling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery, 2000, 15 (2): 804- 811.
|
| 5 |
商立群, 许海洋, 臧鹏, 等. 基于DFT和群组谐波能量回收理论的谐波与间谐波检测算法[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2022, 0 (15): 91- 98.
|
|
YONG Jing, CHEN Liang, CHEN Shuangyan. A harmonic and interharmonic detection algorithm based on DFT and group harmonic energy recovery theory[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2022, 0 (15): 91- 98.
|
| 6 |
李清, 张东辉, 陈名, 等. 多直流馈入输电系统中高压柔性直流高频风险评估计算方法[J]. 南方电网技术, 2023, (4): 1- 9.
|
|
LI Qing, ZHANG Donghui, CHEN Ming, et al. Calculation method for high frequency risk assessment of VSC-HVDC in multi-infeed DC transmission system[J]. Southern Power System Technology, 2023, (4): 1- 9.
|
| 7 |
陈思源, 景巍巍, 史明明, 等. 新能源接入背景下的谐波源建模方法综述[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2022, 50 (7): 162- 175.
|
|
CHEN Siyuan, JING Weiwei, SHI Mingming, et al. Review of harmonic source modeling methods with the background of renewable energy access[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2022, 50 (7): 162- 175.
|
| 8 |
马思棋, 王忠. 基于贝叶斯优化弹性网络回归的谐波状态估计方法[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (8): 104- 112.
|
|
MA Siqi, WANG Zhong. Harmonic state estimation method based on Bayesian optimized elastic network regression[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (8): 104- 112.
|
| 9 |
XU W, BAHRY R, MAZIN H E, et al. A method to determine the harmonic contributions of multiple loads[C]//2009 IEEE Power & Energy Society General Meeting. Calgary, AB, Canada. IEEE, 2009: 1–6.
|
| 10 |
孙媛媛, 李佳奇, 尹志明. 基于实测数据的集中式多谐波源责任评估[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2014, 34 (13): 2164- 2171.
|
|
SUN Yuanyuan, LI Jiaqi, YIN Zhiming. Quantifying harmonic impacts for concentrated multiple harmonic sources using actual data[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2014, 34 (13): 2164- 2171.
|
| 11 |
赵冬梅, 谢家康, 王闯, 等. 基于Bagging集成学习的电力系统暂态稳定在线评估[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2022, 50 (8): 1- 10.
|
|
ZHAO Dongmei, XIE Jiakang, WANG Chuang, et al. On-line transient stability assessment of a power system based on Bagging ensemble learning[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2022, 50 (8): 1- 10.
|
| 12 |
王行亚, 肖先勇, 吴俊, 等. 基于线性度校验的二元线性回归系统谐波阻抗估计方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2020, 40 (9): 2826- 2835.
|
|
WANG Hangya, XIAO Xianyong, WU Jun, et al. Utility harmonic impedance estimation based on binary linear regression with linearity calibration[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2020, 40 (9): 2826- 2835.
|
| 13 |
惠锦, 杨洪耕, 叶茂清. 多谐波源条件下的谐波污染责任划分研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2011, 31 (13): 48- 54.
|
|
HUI Jin, YANG Honggeng, YE Maoqing. Research on the responsibility partition of harmonic pollution of multiple harmonic sources[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2011, 31 (13): 48- 54.
|
| 14 |
刘子腾, 徐永海, 陶顺. 基于SHIBSS方法和数据优选的系统侧谐波阻抗估算方法[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2021, 41 (2): 193- 199.
|
|
LIU Ziteng, XU Yonghai, TAO Shun. Estimation method of harmonic impedance on system side based on SHIBSS method and data optimization[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2021, 41 (2): 193- 199.
|
| 15 |
CUI Y, XU W. Assessment of potential harmonic problems for systems with distributed or random harmonic sources[C]//2007 IEEE Power Engineering Society General Meeting. Tampa, FL, USA. IEEE, 2007: 1–6.
|
| 16 |
吕洋. 电网谐波阻抗测量[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2010.
|
|
LV Yang. Measurement of power system harmonic impedance[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2010.
|
| 17 |
王辉, 刘炜, 李群湛, 等. 基于复数域偏最小二乘法与等值法的多谐波源责任划分[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2017, 41 (4): 78- 85, 119.
|
|
WANG Hui, LIU Wei, LI Qunzhan, et al. Responsibility distinction for multiple harmonic sources based on partial least square in complex field and equivalent method[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2017, 41 (4): 78- 85, 119.
|
| 18 |
MAZIN H E, XU W, HUANG B. Determining the harmonic impacts of multiple harmonic-producing loads[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery, 2011, 26 (2): 1187- 1195.
|
| 19 |
孟思雨, 肖先勇, 张逸, 等. 基于有效数据段选取的多谐波源责任划分方法[J]. 电网技术, 2017, 41 (6): 2006- 2011.
|
|
MENG Siyu, XIAO Xianyong, ZHANG Yi, et al. A valid data selection method in estimating harmonic impact of individual loads[J]. Power System Technology, 2017, 41 (6): 2006- 2011.
|
| 20 |
王瑜, 臧天磊, 符玲, 等. 考虑背景谐波电压变化的多谐波源谐波责任划分[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2015, 39 (18): 55- 61.
|
|
WANG Yu, ZANG Tianlei, FU Ling, et al. Harmonic contribution partition of multiple harmonic sources considering background harmonic voltage fluctuation[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2015, 39 (18): 55- 61.
|
| 21 |
刘苏婕, 肖先勇, 刘亚梅, 等. 基于IGG权重函数复数域多元线性回归算法的谐波责任分摊方法[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2017, 37 (3): 160- 166.
|
|
LIU Sujie, XIAO Xianyong, LIU Yamei, et al. Harmonic responsibility allocation method based on complex field multiple linear regression algorithm with IGG weight function[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2017, 37 (3): 160- 166.
|
| 22 |
马智远, 许中, 黄裕春, 等. 背景谐波阻抗变化情况下的谐波责任划分[J]. 电测与仪表, 2016, 53 (23): 78- 83, 89.
|
|
MA Zhiyuan, XU Zhong, HUANG Yuchun, et al. Harmonic contributions determination on condition of changing background harmonic impedance[J]. Electrical Measurement & Instrumentation, 2016, 53 (23): 78- 83, 89.
|
| 23 |
国家电网公司. 电能质量评估技术导则: Q/GDW 651—2011[S]. 2008.
|
|
State Grid Corporation of China. Technical guide for power quality assessment: Q/GDW 651—2011[S]. 2008.
|
| 24 |
韩兴磊. 住宅非侵入式负荷监测算法研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2018.
|
|
HAN Xinglei. Research on non-intrusive load monitoring algorithms in residential building[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2018.
|
| 25 |
张斌, 庄池杰, 胡军, 等. 结合降维技术的电力负荷曲线集成聚类算法[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2015, 35 (15): 3741- 3749.
|
|
ZHANG Bin, ZHUANG Chijie, HU Jun, et al. Ensemble clustering algorithm combined with dimension reduction techniques for power load profiles[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2015, 35 (15): 3741- 3749.
|
| 26 |
张逸, 王攸然, 刘航, 等. 基于监测数据相关性分析的用户谐波责任划分方法[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2020, 44 (2): 189- 197.
|
|
ZHANG Yi, WANG Youran, LIU Hang, et al. Determination method of user harmonic responsibility based on correlation analysis of monitoring data[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2020, 44 (2): 189- 197.
|
| 27 |
刘子腾. 考虑背景谐波电压波动的配电网谐波责任评估[D]. 北京: 华北电力大学, 2021.
|
|
LIU Ziteng. Harmonic contribution determination of distribution network considering background harmonic voltage fluctuation[D]. Beijing: North China Electric Power University, 2021.
|
| 28 |
SOUZA L C, SOUZA R M C R, AMARAL G J A, et al. A parametrized approach for linear regression of interval data[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2017, 131, 149- 159.
|