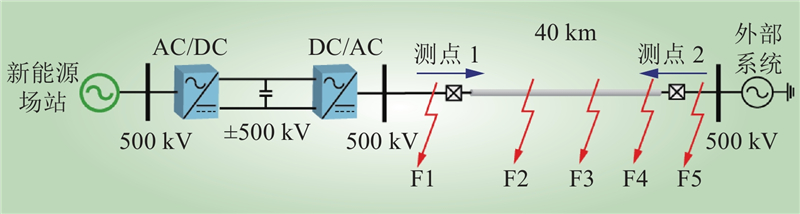
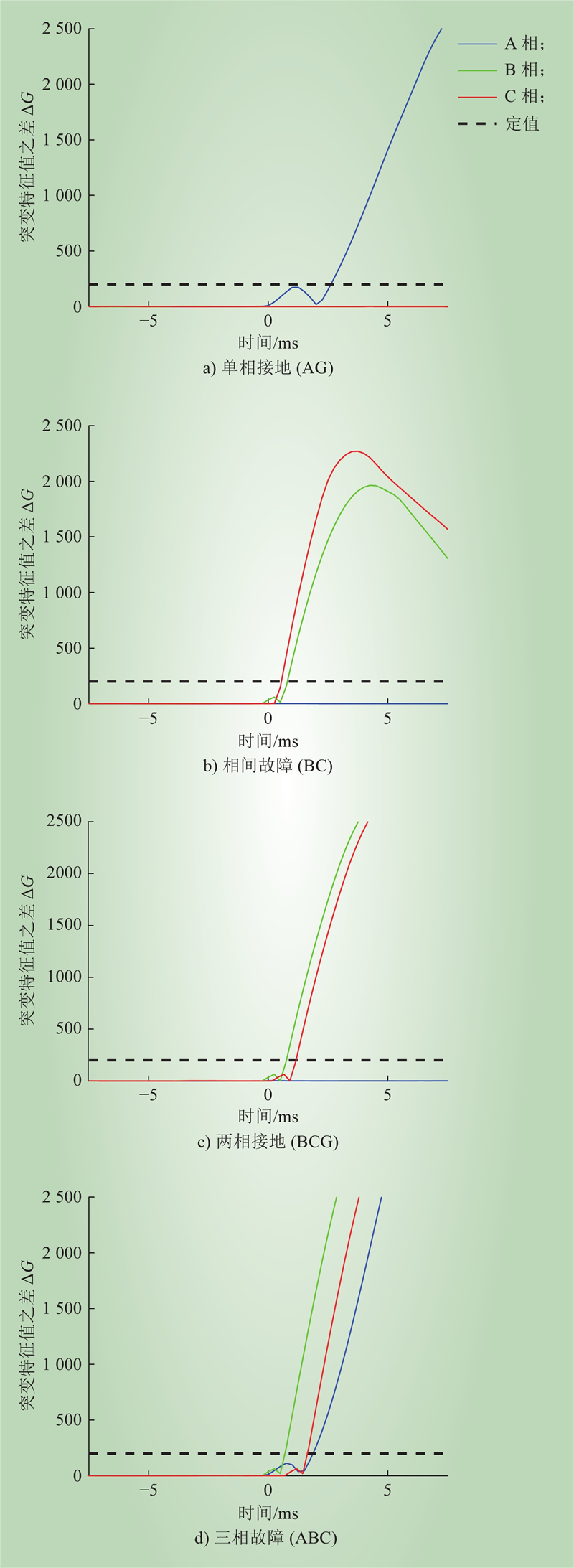
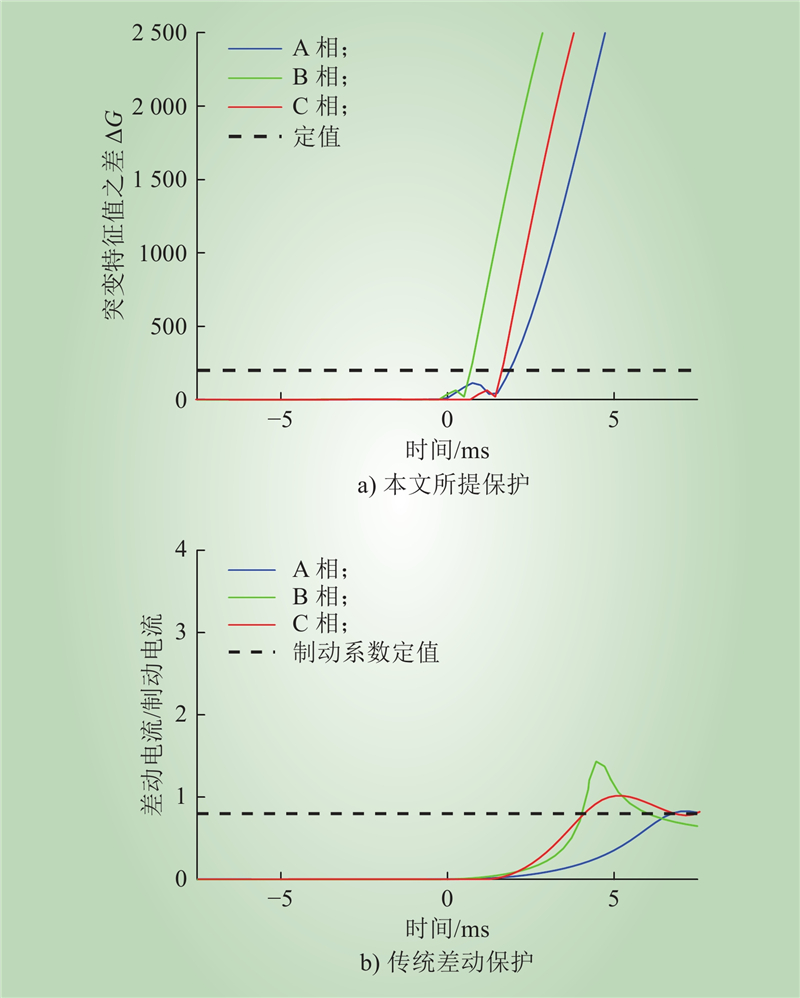
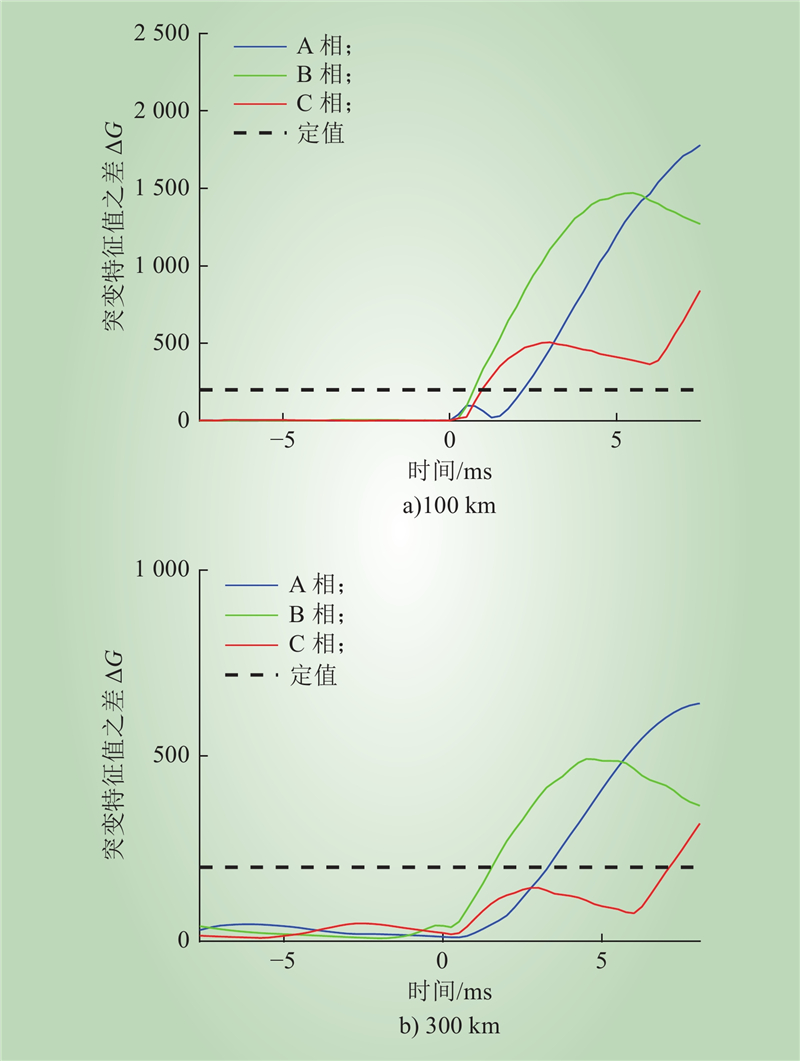
| 1 |
丁怡婷. “十四五”现代能源体系这样建[N]. 人民日报, 2022-03-24(2).
|
| 2 |
杜晓磊, 郭庆雷, 吴延坤, 等. 张北柔性直流电网示范工程控制系统架构及协调控制策略研究[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2020, 48 (9): 164- 173.
|
|
DU Xiaolei, GUO Qinglei, WU Yankun, et al. Research on control system structure and coordination control strategy for Zhangbei Demonstration Project of MMC-HVDC Grid[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2020, 48 (9): 164- 173.
|
| 3 |
李惠玲. 新型电力系统背景下西部送端直流电网及系统运行特性[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (8): 166- 174.
|
|
LI Huiling. Sending-terminal DC power grid in western China and its operation characteristics in the context of new power system[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (8): 166- 174.
|
| 4 |
郑黎明, 贾科, 毕天姝, 等. 海上风电接入柔直系统交流侧故障特征及对保护的影响分析[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2021, 49 (20): 20- 32.
|
|
ZHENG Liming, JIA Ke, BI Tianshu, et al. AC-side fault analysis of a VSC-HVDC transmission system connected to offshore wind farms and the impact on protection[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2021, 49 (20): 20- 32.
|
| 5 |
郑涛, 吕文轩. 基于时序配合的柔直配电网后备保护与控制协同方案[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2022, 46 (2): 137- 145.
|
|
ZHENG Tao, LYU Wenxuan. Time-sequential coordination based collaborative backup protection and control scheme for flexible DC distribution network[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2022, 46 (2): 137- 145.
|
| 6 |
田培涛, 陈勇, 吴庆范, 等. 基于柔直电网的暂态量保护方案及配合策略研究[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2019, 47 (14): 71- 78.
|
|
TIAN Peitao, CHEN Yong, WU Qingfan, et al. Study on transient-based protection scheme and cooperation strategy based on flexible DC grid[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2019, 47 (14): 71- 78.
|
| 7 |
苏见燊, 郭敬东, 金涛. 柔性直流电网中直流故障特性分析及线路故障重启策略[J]. 电工技术学报, 2019, 34 (S1): 352- 359.
|
|
SU Jianshen, GUO Jingdong, JIN Tao. DC fault characteristics and line fault recovery strategy in flexible DC power network[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2019, 34 (S1): 352- 359.
|
| 8 |
肖超, 韩伟, 李琼林, 等. 柔性直流输电系统交流侧线路继电保护适应性研究[J]. 智慧电力, 2020, 48 (4): 1- 8.
|
|
XIAO Chao, HAN Wei, LI Qionglin, et al. Adaptability of MMC-HVDC system on relay protection of AC transmission lines[J]. Smart Power, 2020, 48 (4): 1- 8.
|
| 9 |
李彦宾, 贾科, 毕天姝, 等. 电流差动保护在逆变型新能源场站送出线路中的适应性分析[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2017, 41 (12): 100- 105.
|
|
LI Yanbin, JIA Ke, BI Tianshu, et al. Adaptability analysis of current differential protection of outgoing transmission line emanating from inverter-interfaced renewable energy power plants[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2017, 41 (12): 100- 105.
|
| 10 |
何维轩, 樊征臻, 霍姚彤, 等. 基于交叉熵的海上风电经柔性低频送出系统海缆纵联保护[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (11): 38- 48.
|
|
HE Weixuan, FAN Zhengzhen, HUO Yaogang, et al. Pilot protection scheme of submarine cable in flexible low-frequency transmission system based on cross entropy algorithm[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (11): 38- 48.
|
| 11 |
李泽文, 贺子凝, 郭田田, 等. 基于时频矩阵相似度的输电线路暂态保护方法[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2019, 43 (5): 121- 128.
|
|
LI Zewen, HE Zining, GUO Tiantian, et al. Transient protection method for transmission lines based on similarity of time-frequency matrix[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2019, 43 (5): 121- 128.
|
| 12 |
张杰, 李超, 李更达, 等. 基于小波分析的特高压直流输电线路单端电压暂态保护[J]. 电气应用, 2019, 38 (7): 12- 19.
|
|
ZHANG Jie, LI Chao, LI Gengda, et al. A single-ended transient voltage protection approach of UHVDC transmission line based on wavelet analysis[J]. Electrotechnical Application, 2019, 38 (7): 12- 19.
|
| 13 |
MIRZAHOSSEINI R, IRAVANI R, ZHANG Y. An FPGA-based digital real-time simulator for hardware-in-the-loop testing of traveling-wave relays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery, 2020, 35 (6): 2621- 2629.
|
| 14 |
邓丰, 李欣然, 曾祥君, 等. 基于波形唯一和时-频特征匹配的单端行波保护和故障定位方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2018, 38 (5): 1475- 1487.
|
|
DENG Feng, LI Xinran, ZENG Xiangjun, et al. Research on single-end traveling wave based protection and fault location method based on waveform uniqueness and feature matching in the time and frequency domain[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2018, 38 (5): 1475- 1487.
|
| 15 |
王晨清, 宋国兵, 徐海洋, 等. 适用于风电接入系统的相电压暂态量时域选相新原理[J]. 电网技术, 2015, 39 (8): 2320- 2326.
|
|
WANG Chenqing, SONG Guobing, XU Haiyang, et al. Novel principle of phase selection for wind power integration based on fault transient voltage in time-domain[J]. Power System Technology, 2015, 39 (8): 2320- 2326.
|
| 16 |
侯俊杰, 樊艳芳, 晁勤, 等. 基于时域全量故障模型相关性判别的集群风电送出线纵联保护[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2018, 38 (7): 89- 96.
|
|
HOU Junjie, FAN Yanfang, CHAO Qin, et al. Cluster wind power outgoing line pilot protection scheme based on time-domain full-frequency fault model correlation identification[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2018, 38 (7): 89- 96.
|
| 17 |
DANTAS D T, PELLINI E L, MANASSERO G. Time-domain differential protection method applied to transmission lines[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery, 2018, 33 (6): 2634- 2642.
|
| 18 |
郑黎明, 贾科, 侯来运, 等. 基于奇异值分解的海上风电接入柔直系统的交流线路保护[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2020, 40 (S1): 75- 83.
|
|
ZHENG Liming, JIA Ke, HOU Laiyun, et al. Singular value decomposition based protection for AC transmission lines of VSC-HVDC system with offshore wind farms[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2020, 40 (S1): 75- 83.
|
| 19 |
陈蕊. 新能源柔直送出系统故障特征及保护配置方案研究[D]. 北京: 华北电力大学, 2019.
|
|
CHEN Rui. Study on fault characteristics and protection configuration scheme of MMC-HVDC connected renewable power system[D]. Beijing: North China Electric Power University, 2019.
|
| 20 |
方万良, 李建华, 王建学. 电力系统暂态分析[M]. 4版. 北京: 中国电力出版社, 2017.
|
| 21 |
吴沛锋, 张国云, 孔令号. 基于全波电流关联性的线路差动保护算法[J]. 电网技术, 2019, 43 (7): 2584- 2591.
|
|
WU Peifeng, ZHANG Guoyun, KONG Linghao. A new line differential protection principle based on correlation of full wave current data[J]. Power System Technology, 2019, 43 (7): 2584- 2591.
|
| 22 |
徐永干, 姜杰, 唐昆明, 等. 基于Hankel矩阵和奇异值分解的局部放电窄带干扰抑制方法[J]. 电网技术, 2020, 44 (7): 2762- 2769.
|
|
XU Yonggan, JIANG Jie, TANG Kunming, et al. A method of suppressing narrow-band interference in partial discharge based on Hankel matrix and singular value decomposition[J]. Power System Technology, 2020, 44 (7): 2762- 2769.
|
| 23 |
宾子君, 袁宇波, 许瑨, 等. 基于故障录波的海上风电经柔直并网系统阻抗分析方法[J]. 电网技术, 2022, 46 (8): 2920- 2928.
|
|
BIN Zijun, YUAN Yubo, XU Jin, et al. Impedance analysis of offshore wind farms with VSC-HVDC systems based on fault record data[J]. Power System Technology, 2022, 46 (8): 2920- 2928.
|
| 24 |
叶昊亮. 海上风电场经交流海缆并网的电磁暂态建模与无功优化研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2022.
|
|
YE Haoliang. Electromagnetic transient model and reactive power optimization of grid-connected offshore wind farms via AC submarine cables[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2022.
|
| 25 |
张帆, 尹聪琦, 袁豪, 等. 风电-柔直系统次同步振荡的耦合阻抗模型分析[J]. 南方电网技术, 2022, 16 (3): 24- 31.
|
|
ZHANG Fan, YIN Congqi, YUAN Hao, et al. Impedance coupling model based sub-synchronous oscillation analysis of wind farms connected to VSC-HVDC transmission system[J]. Southern Power System Technology, 2022, 16 (3): 24- 31.
|