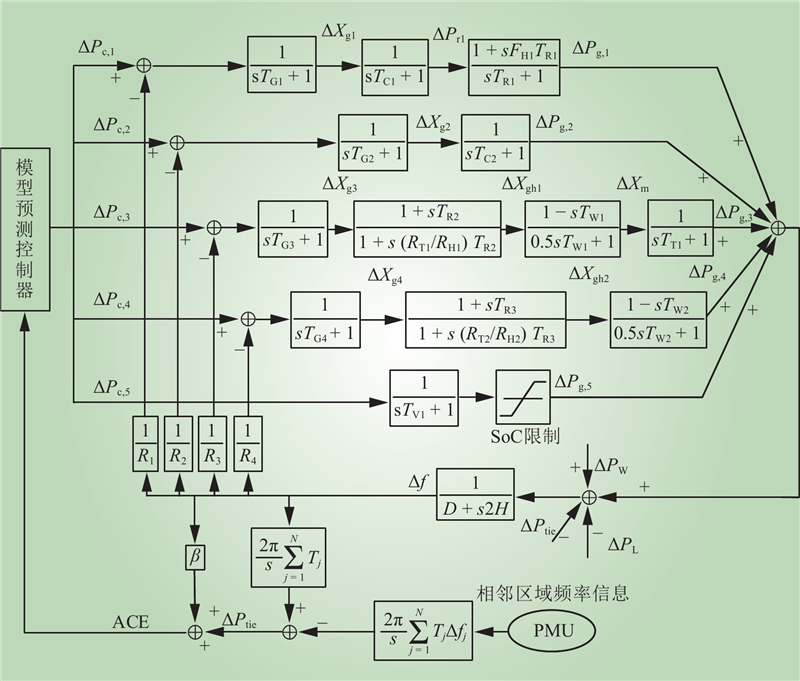
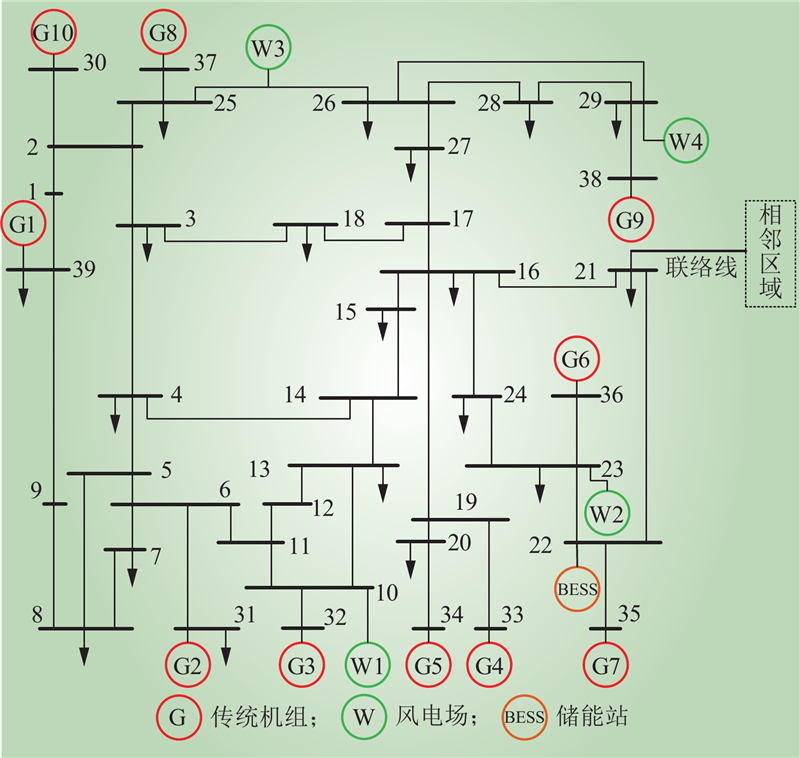
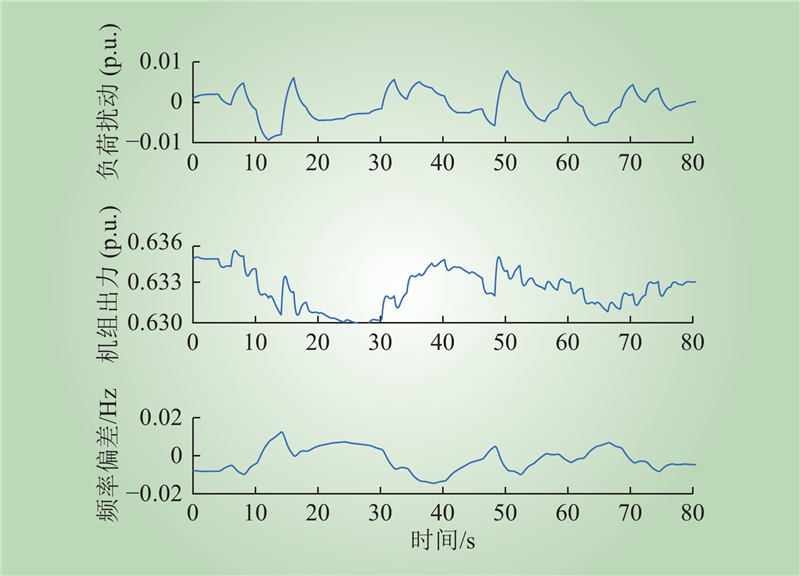
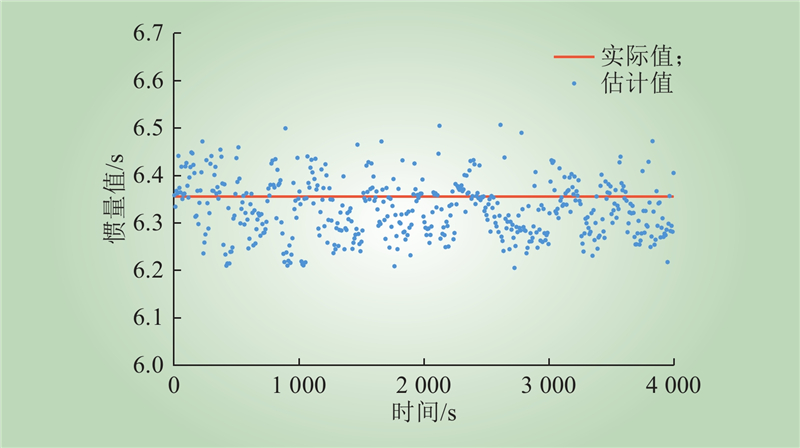
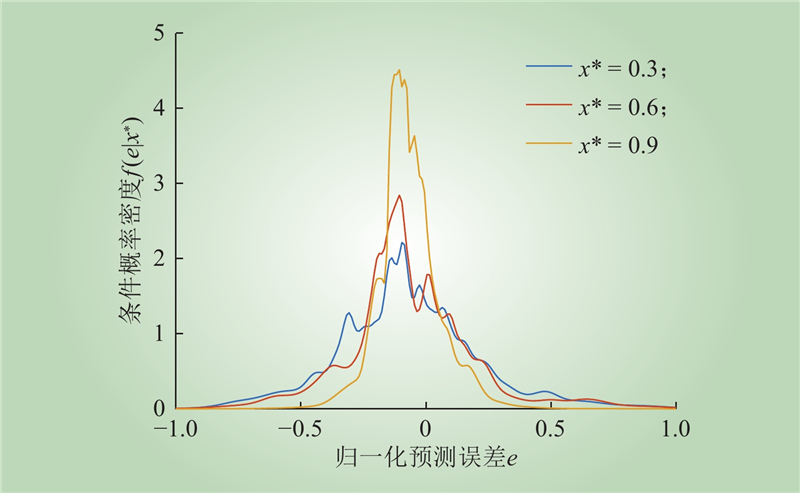
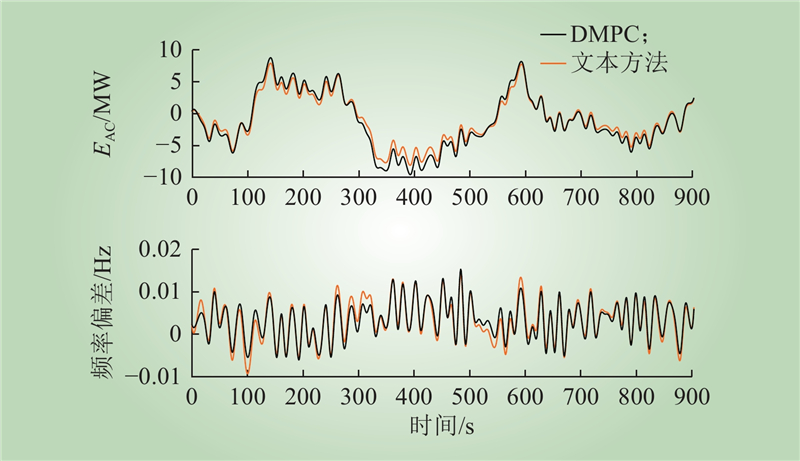
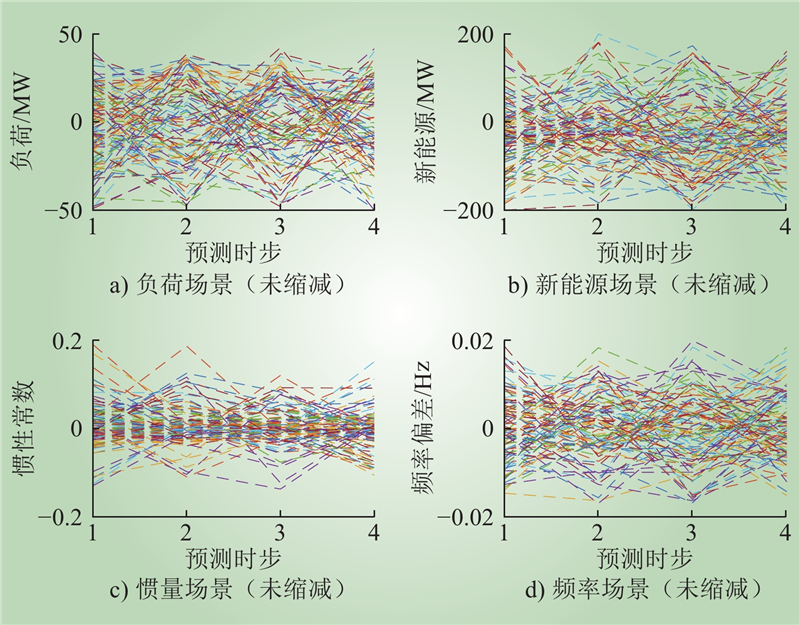
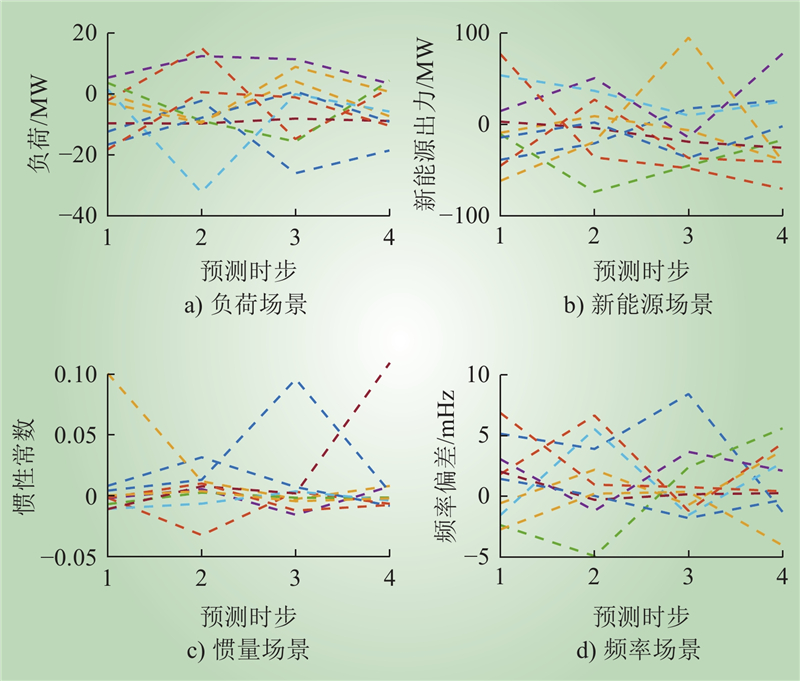
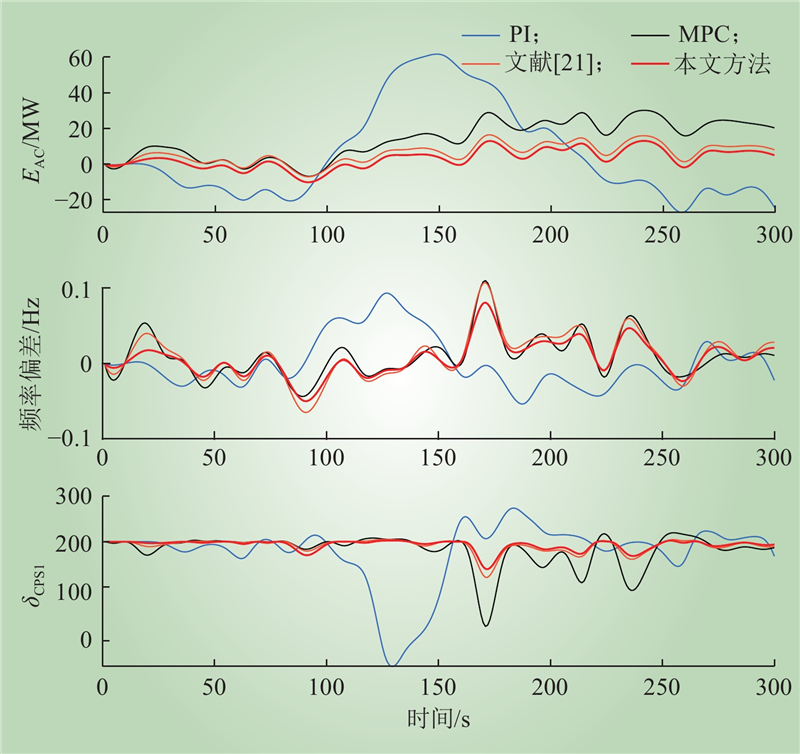
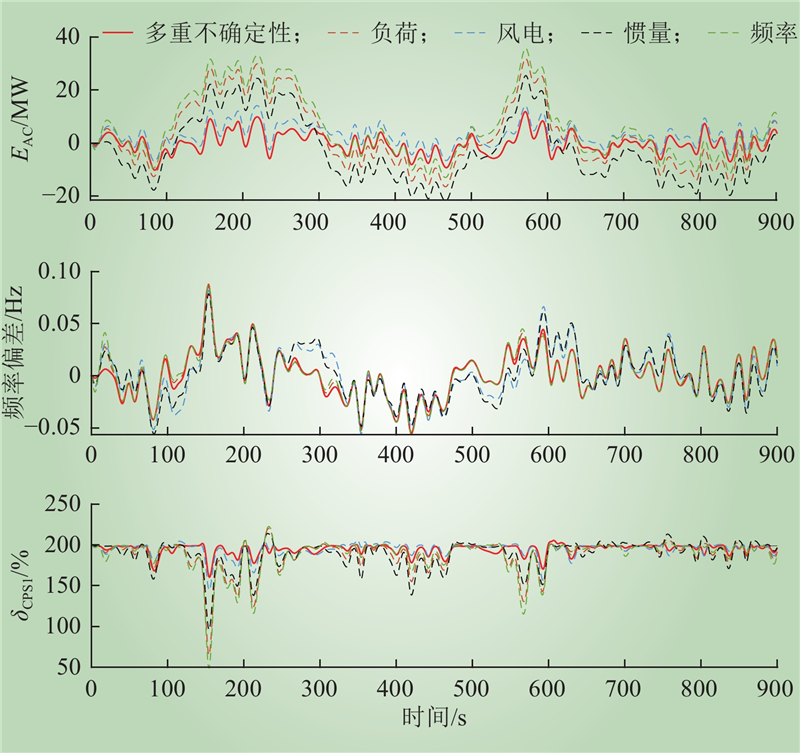
| 1 |
张磊, 马晓伟, 王满亮, 等. 互联新能源电力系统区内AGC机组分布式协同控制策略[J]. 中国电力, 2025, 58 (3): 8- 19.
DOI
|
|
ZHANG Lei, MA Xiaowei, WANG Manliang, et al. Distributed collaborative control strategy for intra-regional AGC units in interconnected power system with renewable energy[J]. Electric Power, 2025, 58 (3): 8- 19.
DOI
|
| 2 |
ABAZARI A, MONSEF H, WU B. Load frequency control by de-loaded wind farm using the optimal fuzzy-based PID droop controller[J]. IET Renewable Power Generation, 2019, 13 (1): 180- 190.
|
| 3 |
ZHANG CK, JIANG L, WU Q H, et al. Delay-dependent robust load frequency control for time delay power systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2013, 28 (3): 2192- 2201.
DOI
|
| 4 |
薛飞, 李宏强, 田蓓, 等. 储能辅助的孤岛微网自适应事件触发二次调频策略[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (9): 196- 205.
DOI
|
|
XUE Fei, LI Hongqiang, TIAN Bei, et al. Adaptive event-triggered secondary frequency control in islanded microgrids with auxiliary energy storage systems[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (9): 196- 205.
DOI
|
| 5 |
MI Y, FU Y, WANG CS, et al. Decentralized sliding mode load frequency control for multi-area power systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2013, 28 (4): 4301- 4309.
DOI
|
| 6 |
PEDDAKAPU K, MOHAMED MR, SRINIVASARAO P, et al. A state-of-the-art review on modern and future developments of AGC/LFC of conventional and renewable energy-based power systems[J]. Renewable Energy Focus, 2022, 43, 146- 171.
DOI
|
| 7 |
席磊, 杜雄, 李彦营, 等. 基于具有强化学习思想的集成学习自动发电控制算法[J]. 南方电网技术, 2023, 17 (7): 74- 82.
|
|
XI Lei, DU Xiong, LI Yanying, et al. Automatic generation control algorithm based on ensemble learning with the idea of reinforcement learning[J]. Southern Power System Technology, 2023, 17 (7): 74- 82.
|
| 8 |
陈宋宋, 张路涛, 周颖, 等. 面向新能源并网的分布式AGC协同算法[J]. 南方电网技术, 2023, 17 (4): 58- 68.
|
|
CHEN Songsong, ZHANG Lutao, ZHOU Yin, et al. Distributed AGC cooperative algorithm for new energy grid connection[J]. Southern Power System Technology, 2023, 17 (4): 58- 68.
|
| 9 |
YU T, ZHOU B, CHAN K W, et al. Stochastic optimal relaxed automatic generation control in non-Markov environment based on multi-step Q(λ) learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2011, 26 (3): 1272- 1282.
|
| 10 |
张孝顺, 余涛, 唐捷. 基于分层相关均衡强化学习的CPS指令优化分配算法[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2015, 39 (8): 80- 86.
DOI
|
|
ZHANG Xiaoshun, YU Tao, TANG Jie. Optimal CPS command dispatch based on hierarchically correlated equilibrium reinforcement learning[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2015, 39 (8): 80- 86.
DOI
|
| 11 |
李彦营, 席磊, 郭宜果, 等. 基于权重双Q-时延更新学习算法的自动发电控制[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2022, 42 (15): 5459- 5470.
|
|
LI Yanying, XI Lei, GUO Yiguo, et al. Automatic generation control based on the weighted double Q-delayed update learning algorithm[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2022, 42 (15): 5459- 5470.
|
| 12 |
柳丹, 任建宇, 席磊, 等. 基于高维协同软演员-评论家的多智能体自动发电控制[J]. 南方电网技术, 2025, 19 (4): 93- 106.
|
|
LIU Dan, REN Jianyu , XI Lei, et al. Multi-agent automatic power generation control based on high dimensional collaborative soft actor-critic[J]. Southern Power System Technology, 2025, 19 (4): 93- 106.
|
| 13 |
YANG F, HUANG D, LI D, et al. Data-driven load frequency control based on multi-agent reinforcement learning with attention mechanism[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2023, 38 (6): 5560- 5569.
DOI
|
| 14 |
刘向杰, 孔小兵. 电力工业复杂系统模型预测控制: 现状与发展[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2013, 33 (5): 79- 85, 14.
|
|
LIU Xiangjie, KONG Xiaobing. Present situation and prospect of model predictive control application in complex power industrial process[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2013, 33 (5): 79- 85, 14.
|
| 15 |
周念成, 付鹏武, 王强钢, 等. 基于模型预测控制的两区域互联电网AGC系统研究[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2012, 40 (22): 46- 51.
DOI
|
|
ZHOU Niancheng, FU Pengwu, WANG Qianggang, et al. Research on AGC of two area interconnected power system based on MPC[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2012, 40 (22): 46- 51.
DOI
|
| 16 |
LIU XJ, ZHANG Y, LEE KY, et al. Coordinated distributed MPC for load frequency control of power system with wind farms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2017, 64 (6): 5140- 5150.
DOI
|
| 17 |
虞临波, 寇鹏, 冯玉涛, 等. 风储联合发电系统参与频率响应的模型预测控制策略[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2019, 43 (12): 36- 43.
DOI
|
|
YU Linbo, KOU Peng, FENG Yutao, et al. Model predictive control strategy for combined wind-storage system to participate in frequency response[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2019, 43 (12): 36- 43.
DOI
|
| 18 |
孙舶皓, 汤涌, 叶林, 等. 基于随机分层分布式模型预测控制的风电集群频率控制规划方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2019, 39 (20): 5903- 5914.
|
|
SUN Bohao, TANG Yong, YE Lin, et al. A programming method for wind power cluster frequency control based on S-H-DMPC[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2019, 39 (20): 5903- 5914.
|
| 19 |
YANG DY, WANG B, CAI GW, et al. Inertia-adaptive model predictive control-based load frequency control for interconnected power systems with wind power[J]. IET Generation, Transmission and Distribution, 2020, 14 (22): 5029- 5036.
DOI
|
| 20 |
LIU LK, HU ZC, MUJEEB A. Automatic generation control considering uncertainties of the key parameters in the frequency response model.[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2022, 37 (6): 4605- 4617.
DOI
|
| 21 |
SHEN Y K, WU W C, SUN S M. Stochastic model predictive control based fast-slow coordination automatic generation control[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2023, 39 (3): 1- 13.
|
| 22 |
张怡, 刘向杰. 互联电力系统鲁棒分布式模型预测负荷频率控制[J]. 控制理论与应用, 2016, 33 (5): 621- 630.
|
|
ZHANG Y, LIU X J. Robust distributed model predictive control for load frequency control of uncertain power systems[J]. Control Theory & Applications, 2016, 33 (5): 621- 630.
|
| 23 |
杨冬锋, 朱军豪, 姜超, 等. 基于分布式模型预测的高比例风电系统多源协同负荷频率控制策略[J]. 电网技术, 2024, 48 (7): 2804- 2814.
|
|
YANG D F, ZHU J H, JIANG C, et al. High proportion wind power system multi-source collaborate load frequency control strategy based on distributed model prediction[J]. Power System Technology, 2024, 48 (7): 2804- 2814.
|
| 24 |
刘家豪, 王程, 毕天姝. 面向新能源电力系统频率时空动态的节点等效惯量指标及其应用[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2023, 43 (20): 7773- 7789.
|
|
LIU Jiahao, WANG Cheng, BI Tianshu. Node equivalent inertia index for temporal-spatial frequency dynamics of renewable energy power system and its applications[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2023, 43 (20): 7773- 7789.
|
| 25 |
夏飞, 袁博, 彭道刚, 等. 基于信息量准则的锂离子电池变阶RC等效电路模型建模及优化方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2018, 38 (21): 6441- 6451, 6506.
|
|
XIA Fei, YUAN Bo, PENG Daogang, et al. Modeling and optimization of variable-order RC equivalent circuit model for lithium ion batteries based on information criterion[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2018, 38 (21): 6441- 6451, 6506.
|
| 26 |
ZHANG JB, XU HC. Online Identification of Power System Equivalent Inertia Constant[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2017, 64 (10): 8098- 8107.
DOI
|
| 27 |
邓齐林, 邱天宇, 申富饶, 等. 一种自适应在线核密度估计方法[J]. 软件学报, 2020, 31 (4): 1173- 1188.
|
|
DENG Qilin, QIU Tianyu, SHEN Furao, et al. Adaptive online kernel density estimation method[J]. Journal of Software, 2020, 31 (4): 1173- 1188.
|
| 28 |
FLAM J T. The linear model under Gaussian mixture inputs: selected problems in communications[D]. Trondheim: Norwegian University of Science and Technology, 2013.
|
| 29 |
严儒井. 多重不确定性下区域综合能源系统的供需协调规划研究[D]. 北京: 华北电力大学(北京), 2022: 31–33.
|
|
YAN Rujing. Research on supply and demand coordination planning of regional integrated energy system under multiple uncertainties[D]. Beijing: North China Electric Power University, 2022: 31–33.
|
| 30 |
黄越辉, 曲凯, 李驰, 等. 基于K-means MCMC算法的中长期风电时间序列建模方法研究[J]. 电网技术, 2019, 43 (7): 2469- 2476.
|
|
HUANG Yuehui, QU Kai, LI Chi, et al. Research on modeling method of medium- and long-term wind power time series based on K-means MCMC algorithm[J]. Power System Technology, 2019, 43 (7): 2469- 2476.
|
| 31 |
李世春, 宋秋爽, 薛臻瑶, 等. 含风电虚拟惯性响应的新能源电力系统惯量估计[J]. 电力工程技术, 2023, 42 (2): 84- 93.
DOI
|
|
LI Shichun, SONG Qiushuang, XUE Zhenyao, et al. Inertia estimation of new energy power system with virtual inertia response of wind power[J]. Electric Power Engineering Technology, 2023, 42 (2): 84- 93.
DOI
|