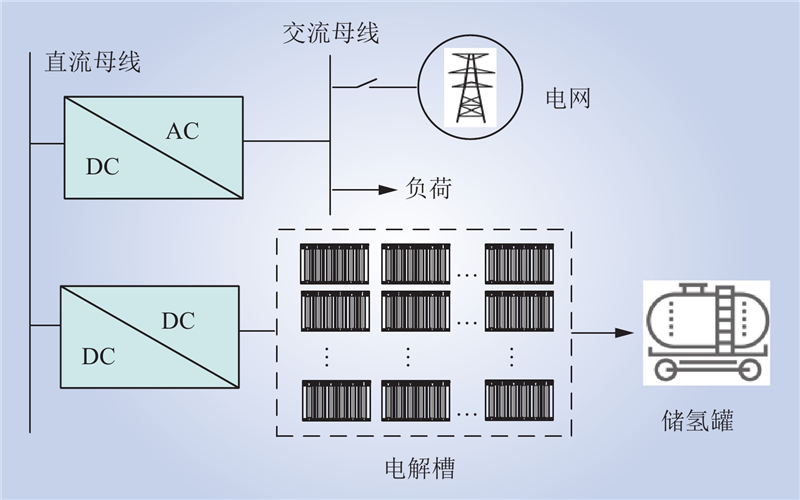
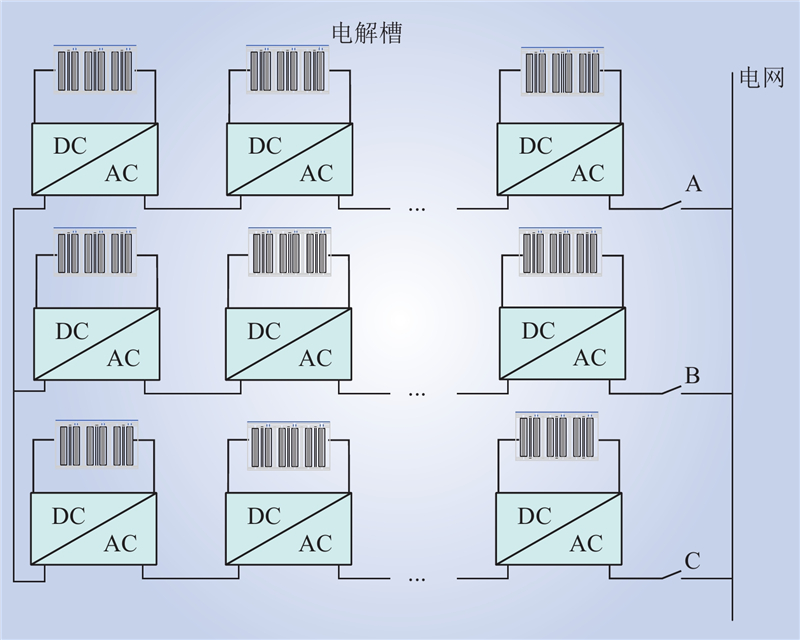
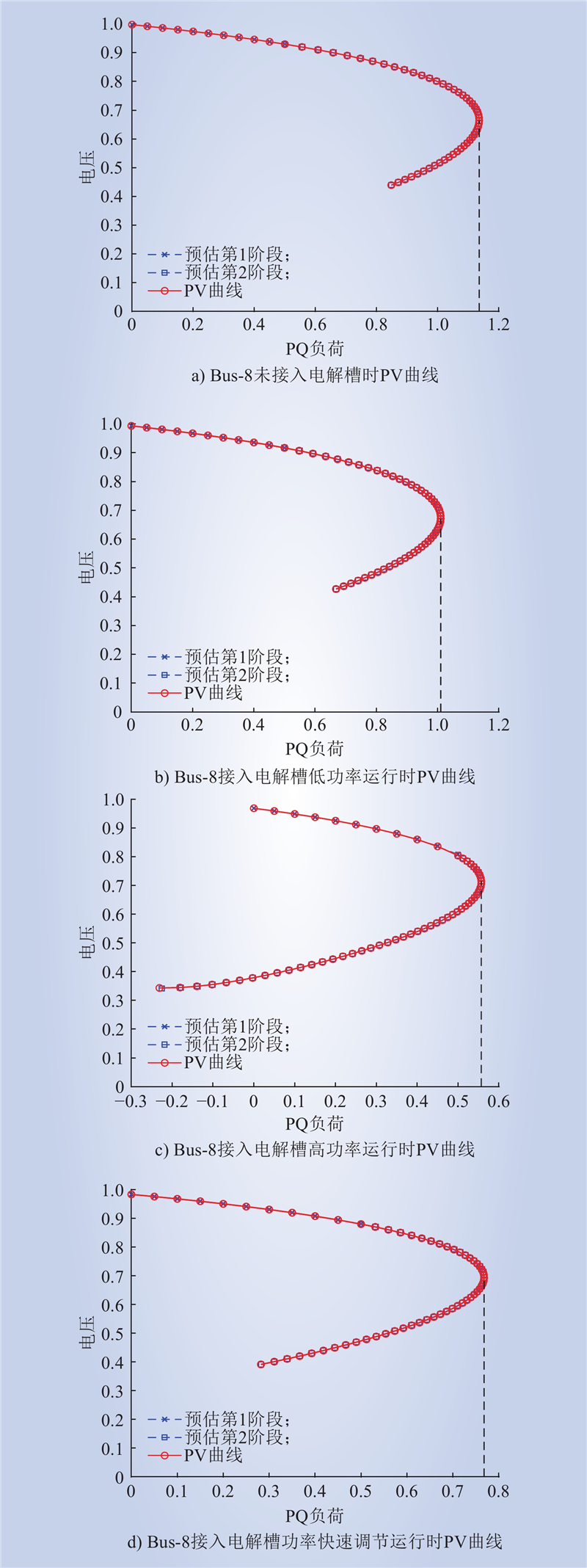
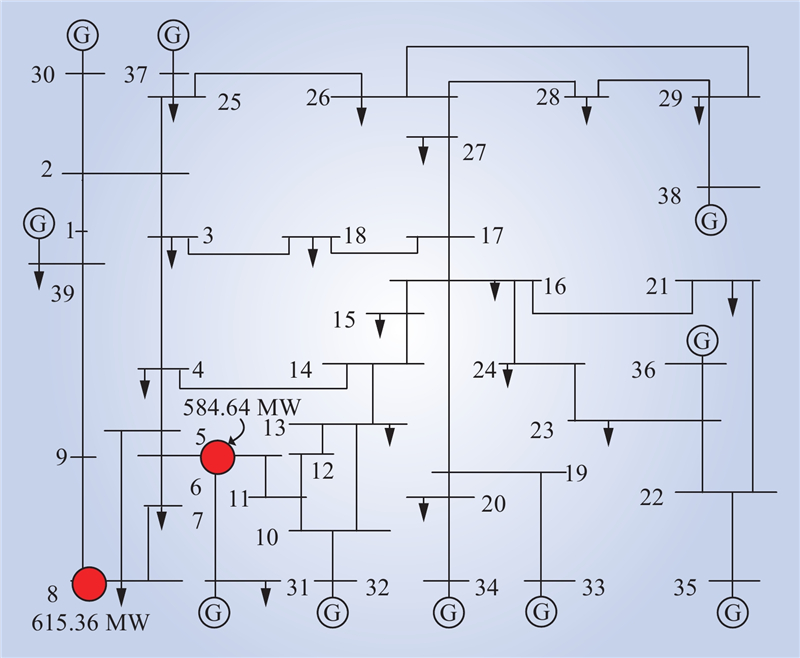
| 1 |
袁铁江, 蒋平, 孙谊媊, 等. 风储一体化电站容量双层优化规划研究[J]. 高电压技术, 2015, 41 (10): 3204- 3212.
|
|
YUAN Tiejiang, JIANG Ping, SUN Yiqian, et al. Research on bi-level capacity programming optimization for the integration of wind farm energy storage power station[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2015, 41 (10): 3204- 3212.
|
| 2 |
任大伟, 肖晋宇, 侯金鸣, 等. 计及多种灵活性约束和基于时序模拟的广域电力系统源-网-储协同规划方法[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (1): 55- 63.
|
|
REN Dawei, XIAO Jinyu, HOU Jinming, et al. Wide-area power system generation-transmission-storage coordinated planning method based on multiple flexibility constraints and time-series simulation[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (1): 55- 63.
|
| 3 |
顾慧杰, 彭超逸, 孙书豪, 等. 风电-光伏-电制氢-抽蓄零碳电力系统短期生产模拟模型[J]. 上海交通大学学报, 2023, 57 (5): 505- 512.
|
|
GU Huijie, PENG Chaoyi, SUN Shuhao, et al. A short-term production simulation model of wind-PV-hydrogen-pumped storage zero carbon power system[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2023, 57 (5): 505- 512.
|
| 4 |
潘光胜, 顾钟凡, 罗恩博, 等. 新型电力系统背景下的电制氢技术分析与展望[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2023, 47 (10): 1- 13.
|
|
PAN Guangsheng, GU Zhongfan, LUO Enbo, et al. Analysis and prospect of electrolytic hydrogen technology under background of new power systems[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2023, 47 (10): 1- 13.
|
| 5 |
OLABI A G, BAHRI A S, ABDELGHAFAR A A, et al. Large-vscale hydrogen production and storage technologies: current status and future directions[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2021, 46 (45): 23498- 23528.
|
| 6 |
宫娅宁, 苏舒, 林湘宁, 等. 独立光伏发电储能系统能量管理与经济调度研究[J]. 电力科学与技术学报, 2017, 32 (2): 3- 9, 30.
|
|
GONG Yaning, SU Shu, LIN Xiangning, et al. Study on energy management and economic dispatch of stand-alone photovoltaic generation system with hybrid energy storage[J]. Journal of Electric Power Science and Technology, 2017, 32 (2): 3- 9, 30.
|
| 7 |
崔丽瑶, 刘怀东, 刘豪, 等. 基于氢能经济的电网大规模风电消纳模式[J]. 电力系统及其自动化学报, 2022, 34 (2): 108- 115.
|
|
CUI Liyao, LIU Huaidong, LIU Hao, et al. Large-scale wind power accommodation mode of power grid based on hydrogen energy economy[J]. Proceedings of the CSU-EPSA, 2022, 34 (2): 108- 115.
|
| 8 |
李广, 樊艳芳. 基于自适应功率阈值的电网辅助光伏制氢控制策略及容量优化配置[J]. 可再生能源, 2022, 40 (9): 1215- 1222.
|
|
LI Guang, FAN Yanfang. Grid-assisted photovoltaic hydrogen production control strategy and capacity optimization configuration based on adaptive power threshold[J]. Renewable Energy Resources, 2022, 40 (9): 1215- 1222.
|
| 9 |
陈维荣, 傅王璇, 韩莹, 等. 计及需求侧的风-光-氢多能互补微电网优化配置[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2021, 56 (3): 640- 649.
|
|
CHEN Weirong, FU Wangxuan, HAN Ying, et al. Optimal configuration of wind-solar-hydrogen multi-energy complementary microgrid with demand side[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2021, 56 (3): 640- 649.
|
| 10 |
HADIDIAN MOGHADDAM M J, KALAM A, NOWDEH S A, et al. Optimal sizing and energy management of stand-alone hybrid photovoltaic/wind system based on hydrogen storage considering LOEE and LOLE reliability indices using flower pollination algorithm[J]. Renewable Energy, 2019, 135, 1412- 1434.
|
| 11 |
JAHANNOOSH M, NOWDEH S A, NADERIPOUR A, et al. New hybrid meta-heuristic algorithm for reliable and cost-effective designing of photovoltaic/wind/fuel cell energy system considering load interruption probability[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021, 278, 123406.
|
| 12 |
YATES J, DAIYAN R, PATTERSON R, et al. Techno-economic analysis of hydrogen electrolysis from off-grid stand-alone photovoltaics incorporating uncertainty analysis[J]. Cell Reports Physical Science, 2020, 1 (10): 100209.
|
| 13 |
MOKHTARA C, NEGROU B, SETTOU N, et al. Design optimization of grid-connected PV-hydrogen for energy prosumers considering sector-coupling paradigm: case study of a university building in Algeria[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2021, 46 (75): 37564- 37582.
|
| 14 |
ZHANG Y S, HUA Q S, SUN L, et al. Life cycle optimization of renewable energy systems configuration with hybrid battery/hydrogen storage: a comparative study[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2020, 30, 101470.
|
| 15 |
邓智宏, 江岳文. 考虑制氢效率特性的风氢系统容量优化[J]. 可再生能源, 2020, 38 (2): 259- 266.
|
|
DENG Zhihong, JIANG Yuewen. Optimal sizing of a wind-hydrogen system under consideration of the efficiency characteristics of electrolysers[J]. Renewable Energy Resources, 2020, 38 (2): 259- 266.
|
| 16 |
贾雨龙, 米增强, 刘力卿, 等. 分布式储能系统接入配电网的容量配置和有序布点综合优化方法[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2019, 39 (4): 1- 7, 16.
|
|
JIA Yulong, MI Zengqiang, LIU Liqing, et al. Comprehensive optimization method of capacity configuration and ordered installation for distributed energy storage system accessing distribution network[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2019, 39 (4): 1- 7, 16.
|
| 17 |
URSUA A, GANDIA L M, SANCHIS P. Hydrogen production from water electrolysis: current status and future trends[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2012, 100 (2): 410- 426.
|
| 18 |
SÁNCHEZ M, AMORES E, RODRÍGUEZ L, et al. Semi-empirical model and experimental validation for the performance evaluation of a 15 kW alkaline water electrolyzer[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2018, 43 (45): 20332- 20345.
|
| 19 |
URSÚA A, BARRIOS E L, PASCUAL J, et al. Integration of commercial alkaline water electrolysers with renewable energies: limitations and improvements[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2016, 41 (30): 12852- 12861.
|
| 20 |
ZHANG C, WANG J Y, REN Z B, et al. Wind-powered 250 kW electrolyzer for dynamic hydrogen production: a pilot study[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2021, 46 (70): 34550- 34564.
|
| 21 |
牛萌, 肖宇, 刘锋, 等. 可再生能源接入对氢储能系统的影响及控制策略[J]. 电力建设, 2018, 39 (4): 28- 34.
|
|
NIU Meng, XIAO Yu, LIU Feng, et al. Influences of renewable energy on hydrogen storage system and its control strategy[J]. Electric Power Construction, 2018, 39 (4): 28- 34.
|
| 22 |
PROOST J. State-of-the art CAPEX data for water electrolysers, and their impact on renewable hydrogen price settings[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2019, 44 (9): 4406- 4413.
|
| 23 |
ZHANG H, YUAN T J. Optimization and economic evaluation of a PEM electrolysis system considering its degradation in variable-power operations[J]. Applied Energy, 2022, 324, 119760.
|
| 24 |
LEE B, HEO J, CHOI N H, et al. Economic evaluation with uncertainty analysis using a Monte-Carlo simulation method for hydrogen production from high pressure PEM water electrolysis in Korea[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2017, 42 (39): 24612- 24619.
|
| 25 |
李娟, 陈继军, 司双. 连续潮流与免疫遗传算法结合的静态电压稳定裕度计算[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2010, 38 (18): 24- 27, 32.
|
|
LI Juan, CHEN Jijun, SI Shuang. Calculation of static voltage stability margin based on continuation power flow and immune genetic algorithm[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2010, 38 (18): 24- 27, 32.
|
| 26 |
李滨, 谢旭槟, 梁振成, 等. “双高”电力系统集中式储能选址定容规划策略[J]. 电力系统及其自动化学报, 2024, 36 (9): 31- 43.
|
|
LI Bin, XIE Xubin, LIANG Zhencheng et al. Centralized energy storage site selection and capacity planning strategy for power system with high shares of renewables and power electronics[J]. Proceedings of the CSU-EPSA, 2024, 36 (9): 31- 43.
|
| 27 |
吴昊. 计及电网结构和状态的电网关键节点与关键线路的识别研究[D]. 南昌: 南昌大学, 2020.
|
|
WU Hao. Research on the recognition of key nodes and lines in power grid considering power grid structure and state[D]. Nanchang: Nanchang University, 2020.
|