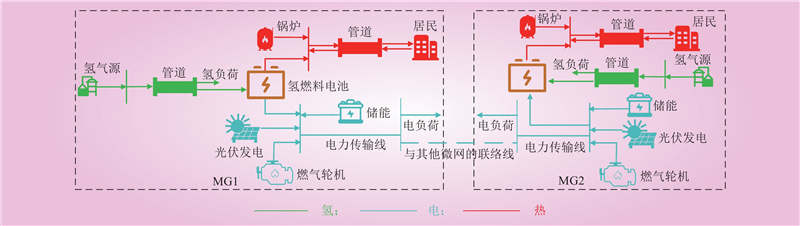
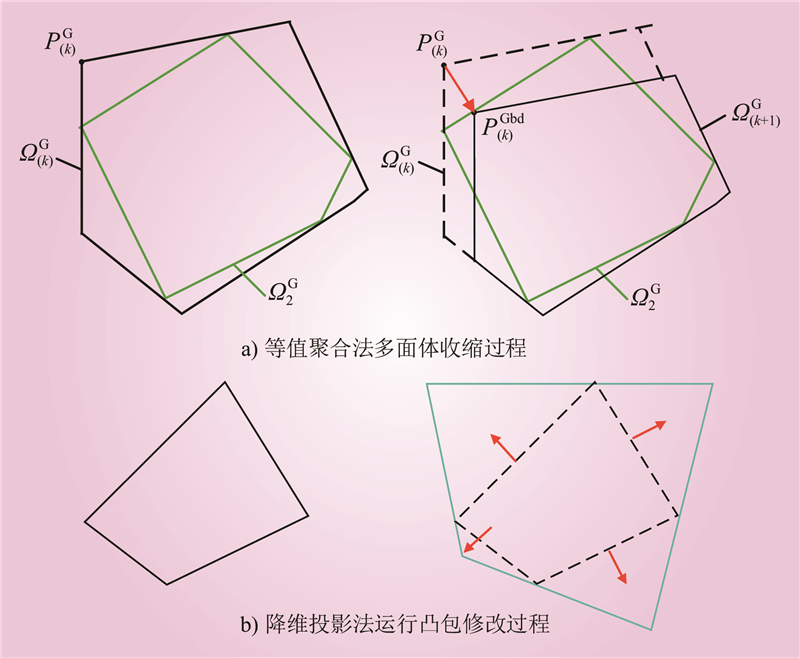
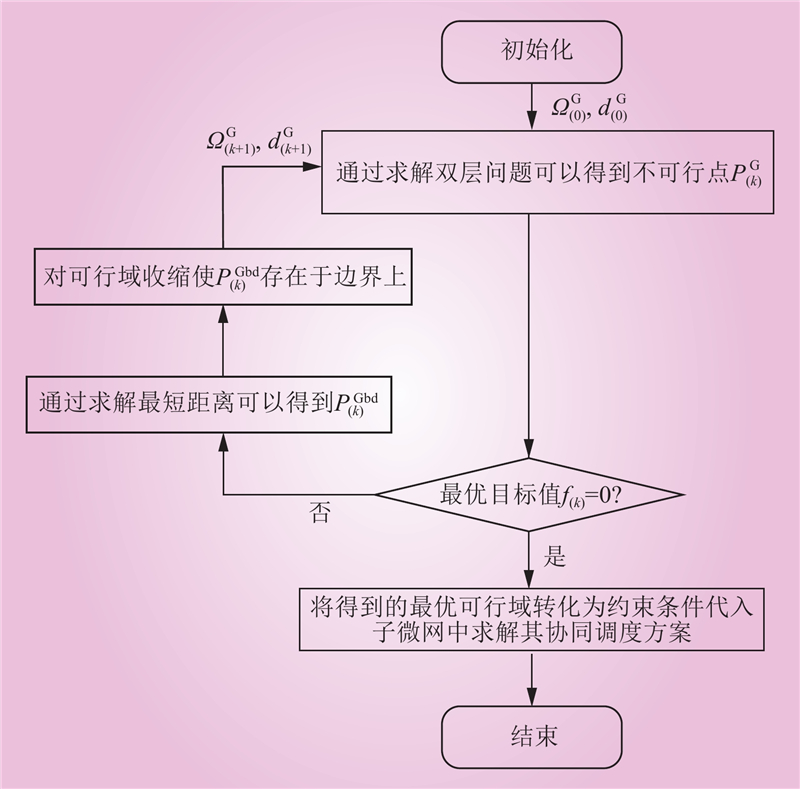
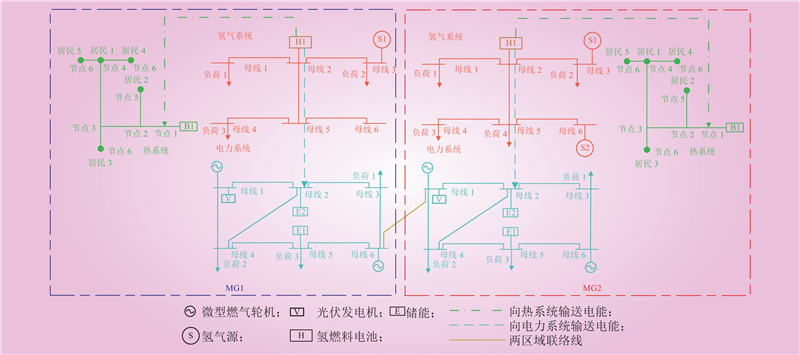
| 1 |
张丝钰, 张宁, 代红才, 等. 可再生能源电解水制氢系统规划优化与生产模拟[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (4): 52- 60.
|
|
ZHANG Siyu, ZHANG Ning, DAI Hongcai, et al. Optimization and simulation on hydrogen production system using water electrolysis powered by renewable energy[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (4): 52- 60.
|
| 2 |
徐连兵. 我国氢能源利用前景与发展战略研究[J]. 洁净煤技术, 2022, 28 (9): 1- 10.
|
|
XU Lianbing. Research on the prospect and development strategy of hydrogen energy in China[J]. Clean Coal Technology, 2022, 28 (9): 1- 10.
|
| 3 |
LI J R, LIN J, SONG Y H, et al. Operation optimization of power to hydrogen and heat (P2HH) in ADN coordinated with the district heating network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Sustainable Energy, 2019, 10 (4): 1672- 1683.
|
| 4 |
邓卜元, 袁至, 李骥. 考虑氢储能的富氧燃烧碳捕集电厂热电联合优化调度[J]. 中国电力, 2025, 58 (4): 159- 169.
|
|
DENG Buyuan, YUAN Zhi, LI Ji. Optimized coordinated scheduling of oxy-fuel combustion carbon capture combined heat and power plant considering hydrogen energy storage[J]. Electric Power, 2025, 58 (4): 159- 169.
|
| 5 |
URBANUCCI L, TESTI D. Optimal integrated sizing and operation of a CHP system with Monte Carlo risk analysis for long-term uncertainty in energy demands[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2018, 157, 307- 316.
|
| 6 |
张雨檬, 李鑫, 王宁玲, 等. 计及多重不确定性的氢-电耦合热电联供系统配置优化[J]. 太阳能学报, 2025, 46 (9): 399- 407.
|
|
ZHANG Yumeng, LI Xin, WANG Ningling, et al. Optimization of hydrogen-electric coupled combined heat and power system with multiple uncertainties[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2025, 46 (9): 399- 407.
|
| 7 |
张继红, 阚圣钧, 化玉伟, 等. 基于氢气储能的热电联供微电网容量优化配置[J]. 太阳能学报, 2022, 43 (6): 428- 434.
|
|
ZHANG Jihong, KAN Shengjun, HUA Yuwei, et al. Capacity optimization of chp microgrid based on hydrogen energy storage[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2022, 43 (6): 428- 434.
|
| 8 |
孙璐瑶, 陈来军, 熊宇峰, 等. 考虑光热集热单元的氢储能热电联供综合能源系统容量优化配置[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2023, 43 (12): 70- 76.
|
|
SUN Luyao, CHEN Laijun, XIONG Yufeng, et al. Capacity optimization configuration of hydrogen energy storage cogeneration integrated energy system considering photothermal collector module[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2023, 43 (12): 70- 76.
|
| 9 |
陈燚, 何山, 谢少华, 等. 基于合作博弈的风-光-电氢微网容量配置[J]. 太阳能学报, 2024, 45 (2): 395- 405.
|
|
CHEN Yi, HE Shan, XIE Shaohua, et al. Capacity configuration of wind-photovoltaic-electric hydrogen microgrid based on cooperative game[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2024, 45 (2): 395- 405.
|
| 10 |
陈铭宏天, 耿江海, 赵雨泽, 等. 基于两阶段随机优化的电氢耦合微电网周运行策略[J]. 中国电力, 2025, 58 (5): 82- 90.
|
|
CHEN Minghongtian, GENG Jianghai, ZHAO Yuze, et al. Two-stage stochastic optimization based weekly operation strategy for electric-hydrogen coupled microgrid[J]. Electric Power, 2025, 58 (5): 82- 90.
|
| 11 |
刘铠诚, 王松岑, 何桂雄, 等. 家庭用户燃料电池热电联供系统能量管理策略及配置优化[J]. 综合智慧能源, 2025, 47 (10): 77- 87.
|
|
LIU Kaicheng, WANG Songcen, HE Guixiong, et al. Energy management strategy and configuration optimization of fuel cell combined heat and power system for household consumers[J]. Integrated Intelligent Energy, 2025, 47 (10): 77- 87.
|
| 12 |
滕云, 孙鹏, 罗桓桓, 等. 计及电热混合储能的多源微网自治优化运行模型[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2019, 39 (18): 5316- 5324, 5578.
|
|
TENG Yun, SUN Peng, LUO Huanhuan, et al. Autonomous optimization operation model for multi-source microgrid considering electrothermal hybrid energy storage[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2019, 39 (18): 5316- 5324, 5578.
|
| 13 |
吕振宇, 丁磊, 吴在军, 等. 考虑电-氢-热多能互补的微网多目标优化配置[J]. 电力工程技术, 2024, 43 (2): 11- 20.
|
|
LYU Zhenyu, DING Lei, WU Zaijun, et al. Multi-objective optimization configuration of microgrid considering electricity-hydrogen-heat multi-energy complementation[J]. Electric Power Engineering Technology, 2024, 43 (2): 11- 20.
|
| 14 |
房超运, 杨昆, 柴瑞环. 分时电价下含电动汽车的微电网群双层多目标优化调度[J]. 电力科学与技术学报, 2024, 39 (1): 124- 133.
|
|
FANG Chaoyun, YANG Kun, CHAI Ruihuan. Two-layer multi-objective optimal dispatching of microgrid group with electricvehicles under time-of-use electricity prices[J]. Journal of Electric Power Science and Technology, 2024, 39 (1): 124- 133.
|
| 15 |
田海东, 何山, 艾纯玉, 等. 计及能源交易下基于纳什议价模型的多微网合作博弈运行优化策略[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2024, 52 (6): 29- 41.
|
|
TIAN Haidong, HE Shan, AI Chunyu, et al. Optimization strategy for cooperative game operation of multi-microgrids based on the Nashbargaining model considering energy trading[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2024, 52 (6): 29- 41.
|
| 16 |
荆江平, 李晨, 孙勇, 等. 基于点对点交易与储能循环寿命约束的多微网综合能源系统能量共享优化[J]. 电力信息与通信技术, 2024, 22 (9): 8- 17.
|
|
JING Jiangping, LI Chen, SUN Yong, et al. Optimization of energy sharing in multi-microgrid integrated energy systems based on peer-to-peer trading and energy storage cycle life constraints[J]. Electric Power Information and Communication Technology, 2024, 22 (9): 8- 17.
|
| 17 |
康田园, 刘科研, 贾东梨, 等. 计及分布式电源出力不确定性的虚拟电厂鲁棒优化调度[J]. 电力信息与通信技术, 2024, 22 (2): 16- 24.
|
|
KANG Tianyuan, LIU Keyan, JIA Dongli, et al. Robust optimal scheduling of virtual power plant considering output uncertainty of distributed generation[J]. Electric Power Information and Communication Technology, 2024, 22 (2): 16- 24.
|
| 18 |
段麟奇, 贾燕冰, 黄亮, 等. 含多类型电解槽模块的电-氢-热综合能源系统优化策略[J/OL]. 上海交通大学学报, 2025: 1–17. (2025-05-29). https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.16183/j.cnki.jsjtu.2025.050.
|
|
DUAN Linqi, JIA Yanbing, HUANG Liang, et al. Optimisation strategy for an integrated electric-hydrogen-thermal energy system with multiple types of electrolyser modules[J/OL]. Journal of Shanghai Jiaotong University, 2025: 1–17. (2025-05-29). https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.16183/j.cnki.jsjtu.2025.050.
|
| 19 |
HAN P F, XU X Y, YAN Z, et al. Dual-layer model predictive control-based scheduling of integrated electricity-hydrogen-heat microgrid[J]. IET Renewable Power Generation, 2024, 18 (S1): 4638- 4649.
|
| 20 |
邢家维, 程艳, 孙树敏, 等. 计及负荷运行风险的电氢热耦合微电网区域零碳优化调度技术[J]. 山东电力技术, 2025, 52 (1): 38- 45.
|
|
XING Jiawei, CHENG Yan, SUN Shumin, et al. Zero carbon optimization scheduling technology for electric hydrogen thermal coupling microgrid regions considering load operation risks[J]. Shandong Electric Power, 2025, 52 (1): 38- 45.
|
| 21 |
郭佳, 潘磊, 苏莽, 等. 基于改进RWCE算法的海岛微电网双层优化方法[J]. 能源研究与信息, 2024, 40 (4): 203- 212.
|
|
GUO Jia, PAN Lei, SU Mang, et al. Double-layer optimization of island micro-grid based on improved RWCE algorithm[J]. Energy Research and Information, 2024, 40 (4): 203- 212.
|
| 22 |
刘权, 钟剑, 陈晨, 等. 基于压缩空气储能的电-热综合能源系统两阶段弹性提升策略[J/OL]. 电网技术, 2025: 1–18. (2025-05-09). https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.13335/j.1000-3673.pst.2025.0010.
|
|
LIU Quan, ZHONG Jian, CHEN Chen, et al. Two-stage resilience enhancement strategy for integrated electricity-heat energy system based on compressed air energy storage[J/OL]. Power System Technology, 2025: 1–18. (2025-05-09). https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.13335/j.1000-3673.pst.2025.0010.
|
| 23 |
王世萱, 朱武. 含冰蓄冷空调的CCHP微电网优化调度[J]. 上海电力大学学报, 2021, 37 (1): 37- 43.
|
|
WANG Shixuan, ZHU Wu. Optimal scheduling of CCHP micro-grid with ice storage air-conditioning[J]. Journal of Shanghai University of Electric Power, 2021, 37 (1): 37- 43.
|
| 24 |
李佩杰, 陆镛, 白晓清, 等. 基于交替方向乘子法的动态经济调度分散式优化[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2015, 35 (10): 2428- 2435.
|
|
LI Peijie, LU Yong, BAI Xiaoqing, et al. Decentralized optimization for dynamic economic dispatch based on alternating direction method of multipliers[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2015, 35 (10): 2428- 2435.
|
| 25 |
严嘉鑫, 范宏, 贾庆山, 等. 计及共享氢储能和虚拟储能的多园区综合能源系统协同规划[J]. 智慧电力, 2025, 53 (6): 10- 18.
|
|
YAN Jiaxin, FAN Hong, JIA Qingshan, et al. Collaborative planning of multi-park integrated energy systems considering shared hydrogen energy storage and virtual energy storage[J]. Smart Power, 2025, 53 (6): 10- 18.
|
| 26 |
李明, 尹文良, 李勇康, 等. 多源耦合不确定性下含电氢储能的微电网低碳容量优化配置研究[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2025, 14 (5): 1969- 1981.
|
|
LI Ming, YIN Wenliang, LI Yongkang, et al. Low-carbon capacity optimal configuration of microgrid with hydrogen energy storage under multi-source coupling uncertainties[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2025, 14 (5): 1969- 1981.
|
| 27 |
高扬, 贺兴, 艾芊. 基于数字孪生驱动的智慧微电网多智能体协调优化控制策略[J]. 电网技术, 2021, 45 (7): 2483- 2491.
|
|
GAO Yang, HE Xing, AI Qian. Multi agent coordinated optimal control strategy for smart microgrid based on digital twin drive[J]. Power System Technology, 2021, 45 (7): 2483- 2491.
|
| 28 |
曹猛, 解超, 尹纯亚, 等. 计及源荷不确定性的多综合能源微网协同优化运行策略[J]. 电网与清洁能源, 2025, 41 (3): 112- 124.
|
|
CAO Meng, XIE Chao, YIN Chunya, et al. Co-optimized operation strategy for multiple integrated energy microgrids considering source-load uncertainty[J]. Power System and Clean Energy, 2025, 41 (3): 112- 124.
|
| 29 |
陈乐飞, 朱自伟, 王凯, 等. 基于混合博弈的配电网与多综合能源微网优化运行[J]. 电网技术, 2023, 47 (6): 2229- 2243.
|
|
CHEN Lefei, ZHU Ziwei, WANG Kai, et al. Optimal operation of distribution networks and multiple integrated energy microgrids based on mixed game theory[J]. Power System Technology, 2023, 47 (6): 2229- 2243.
|
| 30 |
宋晓通, 陈佳琪, 师芊芊. 多主体博弈背景下的综合能源微网优化调度[J]. 高电压技术, 2023, 49 (8): 3163- 3178.
|
|
SONG Xiaotong, CHEN Jiaqi, SHI Qianqian. Optimal scheduling of integrated energy microgrid under the background of multi-agent game[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2023, 49 (8): 3163- 3178.
|
| 31 |
TAN Z F, ZHONG H W, WANG J X, et al. Enforcing intra-regional constraints in Tie-line scheduling: a projection-based framework[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2019, 34 (6): 4751- 4761.
|
| 32 |
冯昌森, 李邗邺, 汤飞霞, 等. 考虑配电系统拓扑变化的电压控制深度强化学习方法[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2025, 45 (8): 156- 163.
|
|
FENG Changsen, LI Hanye, TANG Feixia, et al. Deep reinforcement learning method for voltage control consideringtopology change of distribution system[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2025, 45 (8): 156- 163.
|
| 33 |
沈赋, 张宇涛, 王健, 等. 基于改进随机响应面法的电-气-热区域综合能源系统概率能量流计算[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2025, 53 (5): 69- 81.
|
|
SHEN Fu, ZHANG Yutao, WANG Jian, et al. Probabilistic energy flow calculation for regional integrated electricity-gas-heat energy systems based on an improved stochastic response surface method[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2025, 53 (5): 69- 81.
|
| 34 |
YAN M Y, GAN W, ZHOU Y, et al. Projection method for blockchain-enabled non-iterative decentralized management in integrated natural gas-electric systems and its application in digital twin modelling[J]. Applied Energy, 2022, 311, 118645.
|
| 35 |
彭弘毅, 晏鸣宇, 周奕佳. 基于降维投影的氢-电综合能源系统最优潮流[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2025, 49 (7): 169- 178.
|
|
PENG Hongyi, YAN Mingyu, ZHOU Yijia. Optimal power flow of integrated hydrogen-electricity energy system based on reduced-dimension projection[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2025, 49 (7): 169- 178.
|