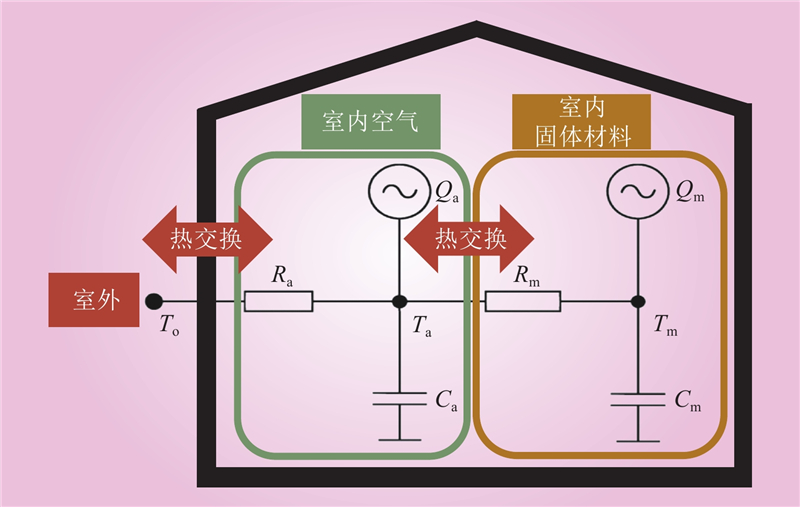
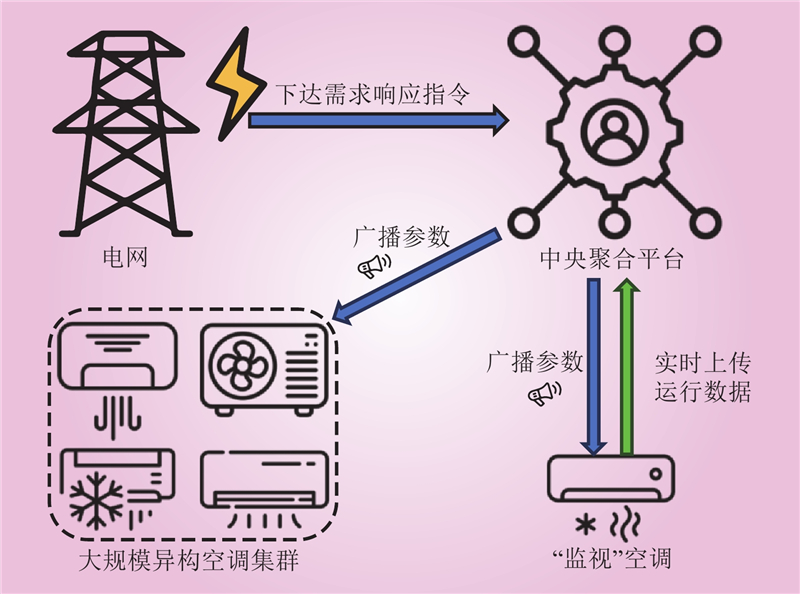
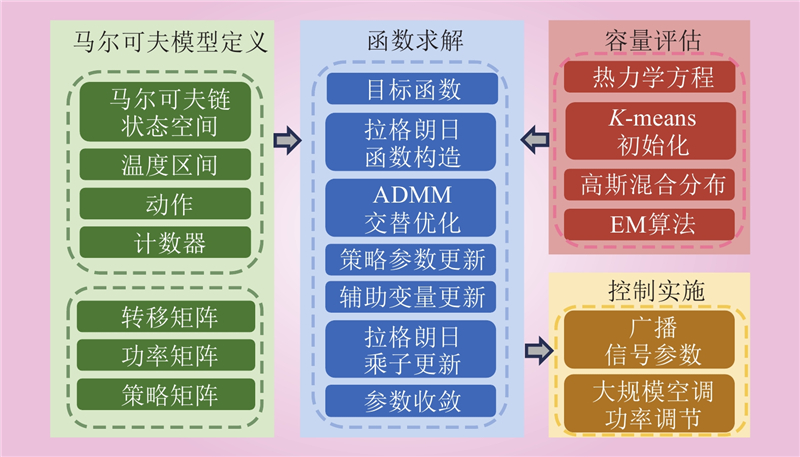
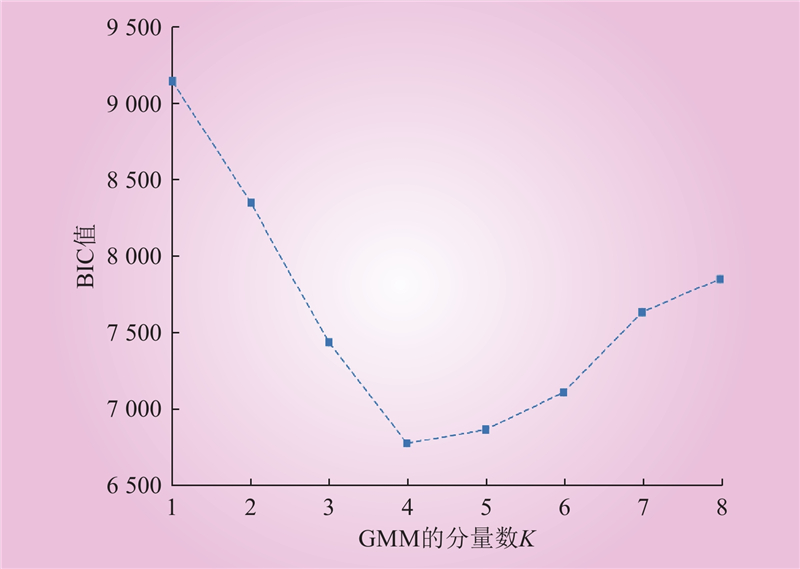
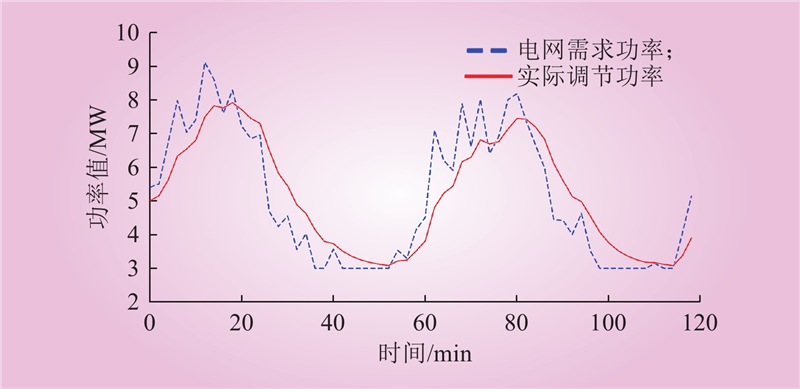
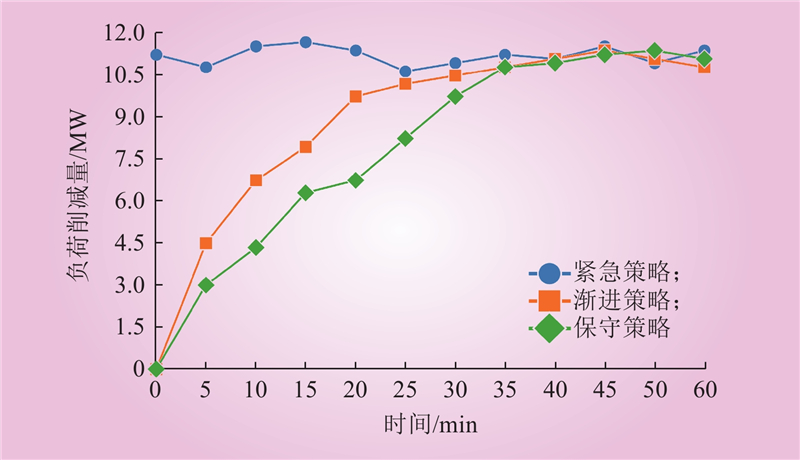
| 1 |
左强, 李波, 杨世海. 大规模空调负荷参与新能源电力系统调频的无模型自适应控制方法[J]. 电力科学与技术学报, 2023, 38 (2): 224- 231.
|
|
ZUO Qiang, LI Bo, YANG Shihai. Model-free adaptive frequency control of renewable energy power systems withparticipation of large-scale air conditioner loads[J]. Journal of Electric Power Science and Technology, 2023, 38 (2): 224- 231.
|
| 2 |
徐玉婷, 田世明, 陈宋宋, 等. 基于LSTM的居民负荷预测及其可调节潜力分析[J]. 电力信息与通信技术, 2023, 21 (5): 1- 8.
|
|
XU Yuting, TIAN Shiming, CHEN Songsong, et al. Resident load forecasting based on LSTM and its adjustable potential analysis[J]. Electric Power Information and Communication Technology, 2023, 21 (5): 1- 8.
|
| 3 |
史媛, 周浩, 张俊娜, 等. 双碳背景下的用户负荷主动优化方法研究[J]. 电力信息与通信技术, 2023, 21 (5): 25- 32.
|
|
SHI Yuan, ZHOU Hao, ZHANG Junnan, et al. Research on user load active optimization method under dual carbon background[J]. Electric Power Information and Communication Technology, 2023, 21 (5): 25- 32.
|
| 4 |
刘广生, 李成鑫, 侯治吉, 等. 计及用户舒适度的空调负荷可调节能力评估及响应策略[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2023, 47 (21): 58- 66.
|
|
LIU Guangsheng, LI Chengxin, HOU Zhiji, et al. Evaluation of adjustable capacity and response strategy for air conditioning load considering comfort of customers[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2023, 47 (21): 58- 66.
|
| 5 |
张智刚, 康重庆. 碳中和目标下构建新型电力系统的挑战与展望[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2022, 42 (8): 2806- 2819.
|
|
ZHANG Zhigang, KANG Chongqing. Challenges and prospects for constructing the new-type power system towards a carbon neutrality future[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2022, 42 (8): 2806- 2819.
|
| 6 |
王朋, 张迪, 张勇军, 等. 新型电力系统数智化关键技术应用研究与展望[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2025, 53 (6): 175- 187.
|
|
WANG Peng, ZHANG Di, ZHANG Yongjun, et al. Research and prospects for key digital-intelligent technology applications in new power systems[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2025, 53 (6): 175- 187.
|
| 7 |
唐志辉, 张欣, 宁艺飞, 等. 基于联盟链技术的商业建筑转供电主体需求响应策略[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (12): 109- 119.
|
|
TANG Zhihui, ZHANG Xin, NING Yifei, et al. Demand response strategy for commercial building power supply conversion entities based on alliance chain technology[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (12): 109- 119.
|
| 8 |
任帅, 肖楚鹏, 梁新龙, 等. 计及虚拟电厂内需求侧灵活性资源的实时电价和V2G协调优化调度策略[J]. 电力信息与通信技术, 2024, 22 (8): 27- 36.
|
|
REN Shuai, XIAO Chupeng, LIANG Xinlong, et al. The real-time electricity price and V2G coordinated optimal scheduling strategy considering demand-side flexibility resources in VPP[J]. Electric Power Information and Communication Technology, 2024, 22 (8): 27- 36.
|
| 9 |
李思维, 许中平, 于龙, 等. 计及电动汽车和温控负荷集群的负荷控制用户组合优化方法[J]. 中国电力, 2025, 58 (3): 86- 97.
|
|
LI Siwei, XU Zhongping, YU Long, et al. A load control user combinatorial optimization method considering electric vehicle and temperature-controlled load clusters[J]. Electric Power, 2025, 58 (3): 86- 97.
|
| 10 |
张冲标, 高博, 漆淘懿, 等. 基于变频空调的虚拟储能建模与控制[J]. 电力科学与技术学报, 2023, 38 (4): 240- 249.
|
|
ZHANG Chongbiao, GAO Bo, QI Taoyi, et al. Modelling and control of virtual energy storage based on the inverter air conditioner[J]. Journal of Electric Power Science and Technology, 2023, 38 (4): 240- 249.
|
| 11 |
张钦, 王锡凡, 王建学, 等. 电力市场下需求响应研究综述[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2008, 32 (3): 97- 106.
|
|
ZHANG Qin, WANG Xifan, WANG Jianxue, et al. Survey of demand response research in deregulated electricity markets[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2008, 32 (3): 97- 106.
|
| 12 |
吴桐, 惠红勋, 张洪财. 商业建筑空调系统参与城市电网负荷调控综述[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (7): 1- 11.
|
|
WU Tong, HUI Hongxun, ZHANG Hongcai. Review of commercial air conditioners for participating in urban grid regulation[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (7): 1- 11.
|
| 13 |
周颖, 龚桃荣, 陈宋宋, 等. 面向新型电力负荷管理的分层分区动态调控架构展望[J]. 电力信息与通信技术, 2023, 21 (4): 51- 58.
|
|
ZHOU Ying, YAO Taorong, CHEN Songsong, et al. Prospect of hierarchical and partitioned dynamic regulation architecture for new power load management[J]. Electric Power Information and Communication Technology, 2023, 21 (4): 51- 58.
|
| 14 |
张梦悦, 余涛, 潘振宁, 等. 基于数据驱动知识显式嵌入的配电网最优需求响应策略[J]. 电力信息与通信技术, 2024, 22 (1): 14- 21.
|
|
ZHANG Mengyue, YU Tao, PAN Zhenning, et al. Optimal demand response strategy for distribution network based on data-driven knowledge explicit embedding[J]. Electric Power Information and Communication Technology, 2024, 22 (1): 14- 21.
|
| 15 |
张俊成, 黎敏, 刘志文, 等. 配电网用户侧多类型柔性资源调节能力评估方法[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (9): 96- 103, 119.
|
|
ZHANG Juncheng, LI Min, LIU Zhiwen, et al. An evaluation method for multi-type flexible resource regulation capability on the user side of distribution networks[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (9): 96- 103, 119.
|
| 16 |
仪忠凯, 侯朗博, 徐英, 等. 市场环境下灵活性资源虚拟电厂聚合调控关键技术综述[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (12): 82- 96.
|
|
YI Zhongkai, HOU Langbo, XU Ying, et al. Aggregation and operation key technology of virtual power plant with flexible resources in electricity market environment: review[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (12): 82- 96.
|
| 17 |
程林, 万宇翔, 张放, 等. 基于负荷聚合商业务的空调服务运作模式及控制策略[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2018, 42 (18): 8- 16.
|
|
CHENG Lin, WAN Yuxiang, ZHANG Fang, et al. Operation mode and control strategy for air-conditioning service based on business of load aggregator[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2018, 42 (18): 8- 16.
|
| 18 |
HUI H X, DING Y, SONG Y H, et al. Modeling and control of flexible loads for frequency regulation services considering compensation of communication latency and detection error[J]. Applied Energy, 2019, 250, 161- 174.
|
| 19 |
许竞, 赵铁军, 高小刚, 等. 高比例新能源电力系统调节资源灵活性不足风险分析[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (11): 129- 138.
|
|
XU Jing, ZHAO Tiejun, GAO Xiaogang, et al. Risk analysis of insufficient flexibility from regulation resources in high proportion renewable energy power systems[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (11): 129- 138.
|
| 20 |
党东升, 韩松, 周珏, 等. 需求响应参与系统调峰研究综述[J]. 电力需求侧管理, 2017, 19 (5): 13- 17.
|
|
DANG Dongsheng, HAN Song, ZHOU Jue, et al. Review of demand response participating in power system peak shifting[J]. Power Demand Side Management, 2017, 19 (5): 13- 17.
|
| 21 |
YU P P, ZHANG H C, SONG Y H, et al. District cooling system control for providing operating reserve based on safe deep reinforcement learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2024, 39 (1): 40- 52.
|
| 22 |
HUI H X, YU P P, ZHANG H C, et al. Regulation capacity evaluation of large-scale residential air conditioners for improving flexibility of urban power systems[J]. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 2022, 142, 108269.
|
| 23 |
WANG Z Y, YU P P, ZHANG H C. Privacy-preserving regulation capacity evaluation for HVAC systems in heterogeneous buildings based on federated learning and transfer learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2023, 14 (5): 3535- 3549.
|
| 24 |
王蓓蓓, 胡晓青, 顾伟扬, 等. 分层控制架构下大规模空调负荷参与调峰的分散式协同控制策略[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2019, 39 (12): 3514- 3528.
|
|
WANG Beibei, HU Xiaoqing, GU Weiyang, et al. Hierarchical control architecture and decentralized cooperative control strategy for large scale air conditioning load participating in peak load regulation[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2019, 39 (12): 3514- 3528.
|
| 25 |
王成山, 刘梦璇, 陆宁. 采用居民温控负荷控制的微网联络线功率波动平滑方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2012, 32 (25): 36- 43, 8.
|
|
WANG Chengshan, LIU Mengxuan, LU Ning. A Tie-line power smoothing method for microgrid using residential thermostatically-controlled loads[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2012, 32 (25): 36- 43, 8.
|
| 26 |
姚垚, 张沛超. 基于市场控制的空调负荷参与平抑微网联络线功率波动的方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2018, 38 (3): 782- 791.
|
|
YAO Yao, ZHANG Peichao. A market-based control method for air conditioner loads to smooth microgrid Tie-line power fluctuation[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2018, 38 (3): 782- 791.
|
| 27 |
CHENG L M, BAO Y Q. A day-ahead scheduling of large-scale thermostatically controlled loads model considering second-order equivalent thermal parameters model[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8, 102321- 102334.
|
| 28 |
王婷, 刘潇, 武媚, 等. 大规模空调负荷聚合建模及跟踪控制方案研究[J]. 电力需求侧管理, 2020, 22 (6): 51- 56.
|
|
WANG Ting, LIU Xiao, WU Mei, et al. Research on load aggregation modeling and tracking control scheme for large scale air conditioning[J]. Power Demand Side Management, 2020, 22 (6): 51- 56.
|
| 29 |
BAO Y Q, YAO Z L, WU X H. Thermal parameters estimation of air conditioners based on reduced order equivalent thermal parameters model[J]. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 2023, 151, 109149.
|
| 30 |
HUI H X, YU P P, ZHANG H C, et al. Regulation capacity evaluation of large-scale heterogeneous residential air conditioning loads[C]//2021 IEEE Sustainable Power and Energy Conference (iSPEC). Nanjing, China. IEEE, 2022: 2505–2510.
|
| 31 |
SAMMAKNEJAD N, ZHAO Y J, HUANG B. A review of the Expectation Maximization algorithm in data-driven process identification[J]. Journal of Process Control, 2019, 73, 123- 136.
|
| 32 |
IEŠMANTAS T, ALZBUTAS R. Bayesian assessment of electrical power transmission grid outage risk[J]. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 2014, 58, 85- 90.
|
| 33 |
CHEN Y F, TAN P G, LI M, et al. K-means clustering method based on nearest-neighbor density matrix for customer electricity behavior analysis[J]. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 2024, 161, 110165.
|