| 1 |
王麒翔, 韩震焘, 梁毅. 基于博弈论均衡的风险防控经济调度分析[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (10): 69- 77.
|
|
WANG Qixiang, HAN Zhentao, LIANG Yi. Economic dispatch analysis of risk prevention and control based on game theory equilibrium[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (10): 69- 77.
|
| 2 |
易文飞, 朱卫平, 郑明忠. 计及数据中心和风电不确定性的微电网经济调度[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57(2): 19-26.
|
|
YI Wenfei , ZHU Weiping , ZHENG Mingzhong . Economic dispatch of microgrid considering data center and wind power uncertainty[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57(2): 19-26.
|
| 3 |
陈家兴, 王春玲, 刘春明. 基于改进碳排放流理论的电力系统动态低碳调度方法[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (3): 162- 172.
|
|
CHEN Jiaxing, WANG Chunling, LIU Chunming. Dynamic low-carbon dispatching method of power system based on improved carbon emission flow theory[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (3): 162- 172.
|
| 4 |
赵振宇, 李炘薪. 基于阶梯碳交易的碳捕集电厂-电转气虚拟电厂低碳经济调度[J]. 发电技术, 2023, 44 (6): 769- 780.
|
|
ZHAO Zhenyu, LI Xinxin. Low-carbon economic dispatch based on ladder carbon trading virtual power plant considering carbon capture power plant and power-to-gas[J]. Power Generation Technology, 2023, 44 (6): 769- 780.
|
| 5 |
刘洪波, 高旭升, 刘庸. 基于改进人工鱼群算法的主动配电网日前两阶段优化调度[J]. 广东电力, 2023, 36 (11): 122- 129.
|
|
LIU Hongbo, GAO Xusheng, LIU Yong. Two-stage day-ahead optimal dispatching of active distribution network based on improved artificial fish swarm algorithm[J]. Guangdong Electric Power, 2023, 36 (11): 122- 129.
|
| 6 |
罗其华, 李平, 张少迪. 考虑需求响应和阶梯碳交易的虚拟电厂低碳经济调度[J]. 浙江电力, 2023, 42 (6): 51- 59.
|
|
LUO Qihua, LI Ping, ZHANG Shaodi. Low-carbon and economic scheduling of virtual power plant considering demand response and stepwise carbon trading[J]. Zhejiang Electric Power, 2023, 42 (6): 51- 59.
|
| 7 |
王义军, 孙健淳, 高敏, 等. 考虑含HRD的光热电站和综合需求响应的综合能源系统低碳经济调度[J]. 东北电力大学学报, 2024, 44 (1): 72- 82.
|
|
WANG Yijun, SUN Jianchun, GAO Min, et al. Low-carbon economic dispatch of integrated energy systems considering HRD-containing photovoltaic plants and integrated demand response[J]. Journal of Northeast Electric Power University, 2024, 44 (1): 72- 82.
|
| 8 |
陈耀森, 陈贻颢, 汪枫, 等. 直驱式同步风力发电机组的仿真模拟[J]. 电力科技与环保, 2023, 39 (1): 87- 94.
|
|
CHEN Yaosen, CHEN Yihao, WANG Feng, et al. Modeling and simulation of direct-drive synchronous wind turbine[J]. Electric Power Technology and Environmental Protection, 2023, 39 (1): 87- 94.
|
| 9 |
张洺驿, 黄鹏, 王亚午. 环形介电弹性体发电机的输出特性研究[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45 (3): 517- 526.
|
|
ZHANG Mingyi, HUANG Peng, WANG Yawu. Research on output characteristics of a circular dielectric elastomer generator[J]. Power Generation Technology, 2024, 45 (3): 517- 526.
|
| 10 |
温春雪, 毛健, 王鹏, 等. 基于虚拟同步发电机的构网型光储变流器控制策略研究[J]. 内蒙古电力技术, 2024, 42 (1): 1- 8.
|
|
WEN Chunxue, MAO Jian, WANG Peng, et al. Research on control strategy of grid-configured photovoltaic storage converters based on VSG[J]. Inner Mongolia Electric Power, 2024, 42 (1): 1- 8.
|
| 11 |
安军, 周永超, 周毅博, 等. 考虑风荷不确定性的电源无功电压调差系数整定方法研究[J]. 东北电力大学学报, 2023, 43 (4): 30- 38.
|
|
AN Jun, ZHOU Yongchao, ZHOU Yibo, et al. Optimization method for var-voltage adjustment CoefficientConsidering wind power and load uncertainty[J]. Journal of Northeast Electric Power University, 2023, 43 (4): 30- 38.
|
| 12 |
周洋, 黄德志, 李培栋, 等. 考虑平衡端点相位不对称及光伏接入的低压配电网三相潮流模型[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (10): 190- 198.
|
|
ZHOU Yang, HUANG Dezhi, LI Peidong, et al. A three-phase power flow model for low-voltage distribution networks considering balanced bus phase asymmetry and photovoltaic access[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (10): 190- 198.
|
| 13 |
苏立, 毛成, 文贤馗, 等. 变速水力发电机组低电压穿越中机组转速上升率的计算及其影响分析[J]. 电网与清洁能源, 2024, 40 (2): 149- 154.
|
|
SU Li, MAO Cheng, WEN Xiankui, et al. Calculation and impact analysis of unit speed rise rate in low voltage through of variable speed hydropower turbine units[J]. Power System and Clean Energy, 2024, 40 (2): 149- 154.
|
| 14 |
李浩宇, 张春, 吴零晨, 等. 基于改进有限时间一致性的微电网经济优化调度[J]. 电力系统及其自动化学报, 2024, 36 (7): 38- 48.
|
|
LI Haoyu, ZHANG Chun, WU Lingchen, et al. Economic optimal dispatching of microgrid based on improved finite time consistency[J]. Proceedings of the CSU-EPSA, 2024, 36 (7): 38- 48.
|
| 15 |
王隔霞, 王军平. 微电网多目标经济调度的一致性算法[J]. 上海电力大学学报, 2023, 39 (5): 500- 506.
|
|
WANG Gexia, WANG Junping. Consensus based distributed multi-objective algorithms for a micro-grid[J]. Journal of Shanghai University of Electric Power, 2023, 39 (5): 500- 506.
|
| 16 |
江阎, 宋晨辉, 张宁, 等. 考虑多能耦合的虚拟电厂优化运行模型与策略研究[J]. 综合智慧能源, 2025, 47 (1): 34- 41.
|
|
JIANG Yan, SONG Chenhui, ZHANG Ning, et al. Study on optimized operation model and strategy for virtual power plants considering multi-energy coupling[J]. Integrated Intelligent Energy, 2025, 47 (1): 34- 41.
|
| 17 |
ZHANG Z A, CHOW M Y. Convergence analysis of the incremental cost consensus algorithm under different communication network topologies in a smart grid[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2012, 27 (4): 1761- 1768.
|
| 18 |
文淅宇, 朱继忠, 李盛林, 等. 基于时空协同的多数据中心虚拟电厂低碳经济调度策略[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2024, 48 (18): 56- 65.
|
|
WEN Xiyu, ZHU Jizhong, LI Shenglin, et al. Low-carbon economic dispatch for multiple data center virtual power plant based on spatio-temporal collaboration[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2024, 48 (18): 56- 65.
|
| 19 |
刘健, 刘雨鑫, 庄涵羽. 虚拟电厂关键技术及其建设实践[J]. 综合智慧能源, 2023, 45 (6): 59- 65.
|
|
LIU Jian, LIU Yuxin, ZHUANG Hanyu. Key technologies and construction practices of virtual power plants[J]. Integrated Intelligent Energy, 2023, 45 (6): 59- 65.
|
| 20 |
汪进锋, 李金鹏, 许银亮, 等. 考虑不确定性和绿证交易的虚拟电厂与配电网分布式优化[J]. 中国电力, 2025, 58 (4): 21- 30,192.
|
|
WANG Jinfeng, LI Jinpeng, XU Yinliang, et al. Distributed optimization for VPP and distribution network operation considering uncertainty and green certificate market[J]. Electric Power, 2025, 58 (4): 21- 30,192.
|
| 21 |
王愿, 李彦斌, 宋明浩, 等. 计及多重不确定性和时间相关性的虚拟电厂参与碳-绿证协同交易优化调度[J]. 电网技术, 2024, 48 (12): 4938- 4947.
|
|
WANG Yuan, LI Yanbin, SONG Minghao, et al. Optimal scheduling of virtual power plant participating in carbon-green certificates collaborative trading considering multiple uncertainties and time correlations[J]. Power System Technology, 2024, 48 (12): 4938- 4947.
|
| 22 |
宋懿洋, 申萌均, 王剑晓, 等. 基于多参数规划的虚拟电厂边际成本函数解析表征方法[J]. 电网技术, 2025, 49 (3): 879- 888.
|
|
SONG Yiyang, SHEN Mengjun, WANG Jianxiao, et al. Analytical characterization of marginal cost function for virtual power plants based on multi-parametric programming[J]. Power System Technology, 2025, 49 (3): 879- 888.
|
| 23 |
左伟林, 秦晓辉, 许彦平, 等. 基于图论的碳流网络分布和路径追踪算法研究[J]. 电网技术, 2025, 49 (4): 1305- 1315.
|
|
ZUO Weilin, QIN Xiaohui, XU Yanping, et al. Carbon flow network distribution and path tracing algorithm based on graph theory[J]. Power System Technology, 2025, 49 (4): 1305- 1315.
|
| 24 |
孙冬川, 孙亮, 孔令乾, 等. 基于深度强化学习的多能虚拟电厂优化调度[J]. 东北电力大学学报, 2024, 44 (3): 102- 111.
|
|
SUN Dongchuan, SUN Liang, KONG Lingqian, et al. Deep reinforcement learning-based optimal scheduling for multi-energy virtual power plant[J]. Journal of Northeast Electric Power University, 2024, 44 (3): 102- 111.
|
| 25 |
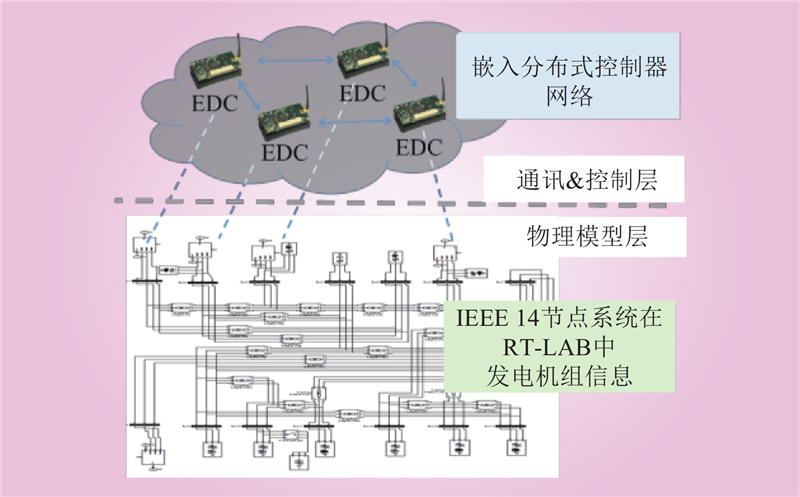
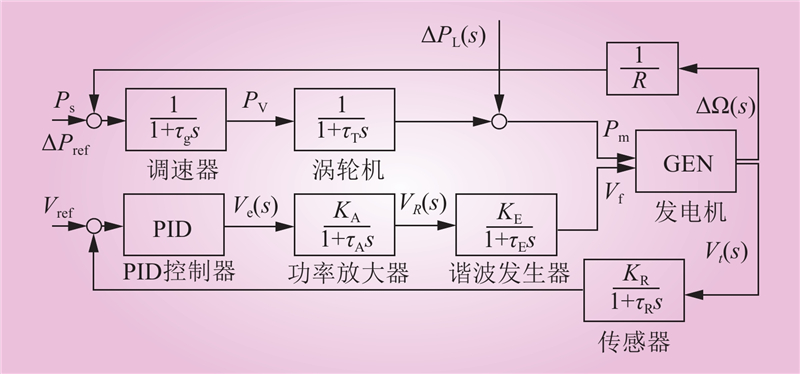
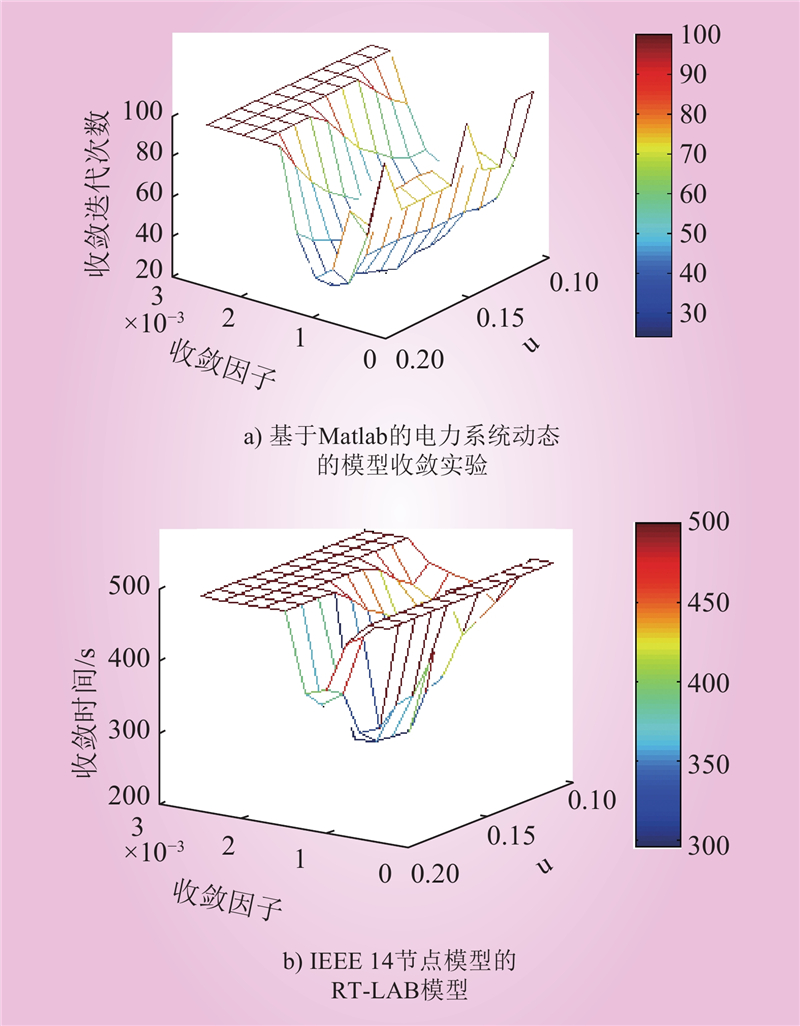
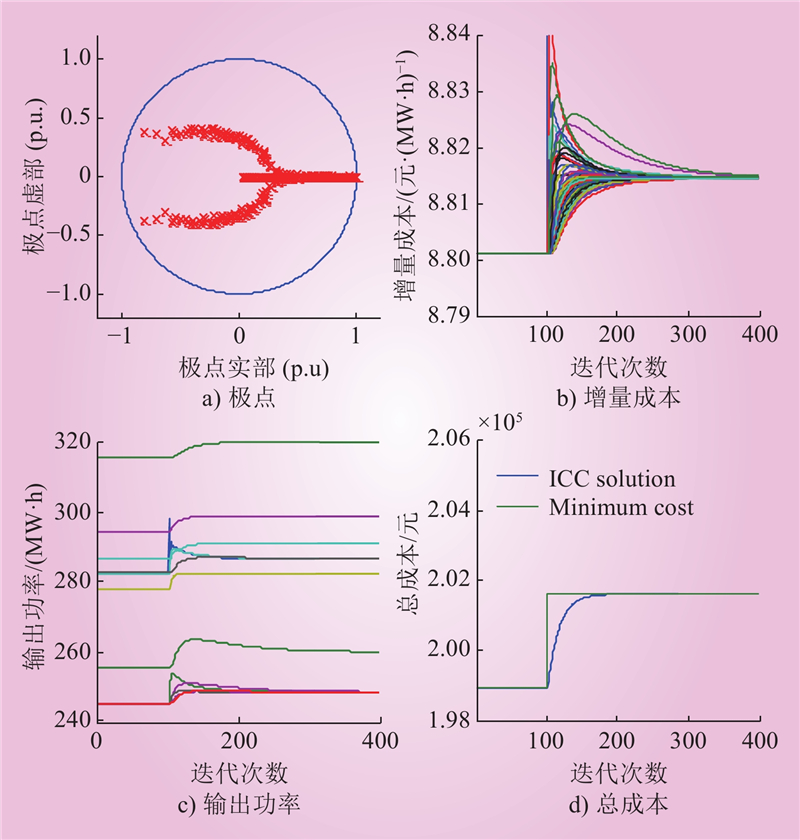
夏仕伟, 高晨祥, 孙昱昊, 等. 含多种限流设备的柔性直流电网RT-LAB实时仿真建模[J]. 中国电力, 2021, 54 (10): 28- 37.
|
|
XIA Shiwei, GAO Chenxiang, SUN Yuhao, et al. Real-time modeling and simulation of flexible DC grid with various types of current limiting devices based on RT-LAB[J]. Electric Power, 2021, 54 (10): 28- 37.
|
| 26 |
WANG Y Q, WU Q H, WANG Y, et al. Consensus algorithm for multiple quadrotor systems under fixed and switching topologies[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2013, 24 (5): 818- 827.
|
| 27 |
KHATANA V, SALAPAKA M V. Noise resilient distributed average consensus over directed graphs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal and Information Processing Over Networks, 2023, 9, 770- 785.
|
| 28 |
胡景成, 范耘豪, 朱同, 等. 基于同态加密的综合能源系统完全分布式低碳经济调度[J]. 中国电力, 2025, 58 (2): 164- 175.
|
|
HU Jingcheng, FAN Yunhao, ZHU Tong, et al. Distributed low-carbon economic dispatch for integrated energy system based on homomorphic encryption[J]. Electric Power, 2025, 58 (2): 164- 175.
|
| 29 |
胡程平, 范明, 刘艾旺, 等. 考虑云储能的多区互联综合能源系统规划[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45 (4): 641- 650.
|
|
HU Chengping, FAN Ming, LIU Aiwang, et al. Multi-area interconnected integrated energy system planning considering cloud energy storage[J]. Power Generation Technology, 2024, 45 (4): 641- 650.
|
| 30 |
伏绍鑫, 张路, 唐翰峰, 等. 考虑柔性电热负荷的区域综合能源系统低碳经济调度[J]. 电力科技与环保, 2023, 39 (5): 417- 428.
|
|
FU Shaoxin, ZHANG Lu, TANG Hanfeng, et al. Low-carbon economic dispatch of community integrated energy system considering flexible electric heating load[J]. Electric Power Technology and Environmental Protection, 2023, 39 (5): 417- 428.
|
| 31 |
陈思勤, 朱伊囡, 李晓辰, 等. 基于双层规划的碳减排配煤优化方法研究[J]. 发电技术, 2023, 44 (2): 155- 162.
|
|
CHEN Siqin, ZHU Yinan, LI Xiaochen, et al. Research on optimization method of coal blending for carbon emission reduction based on bi-level programming[J]. Power Generation Technology, 2023, 44 (2): 155- 162.
|