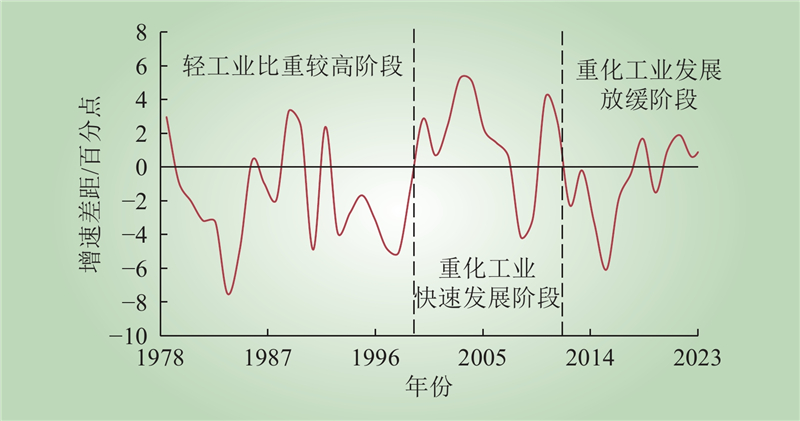
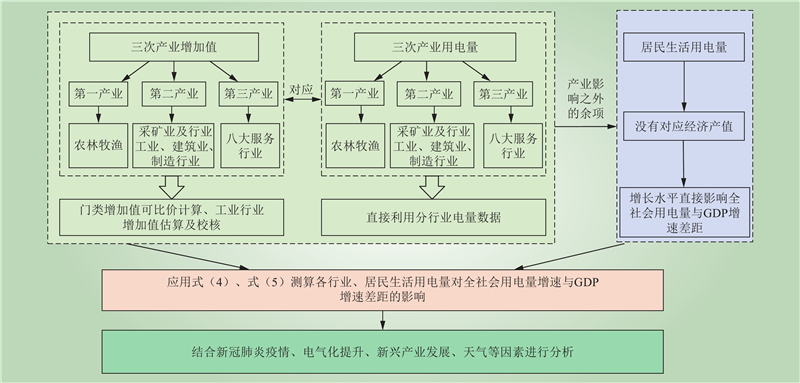
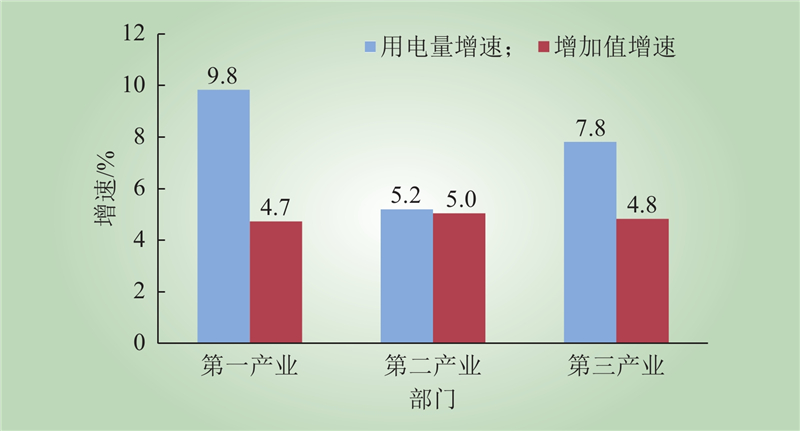
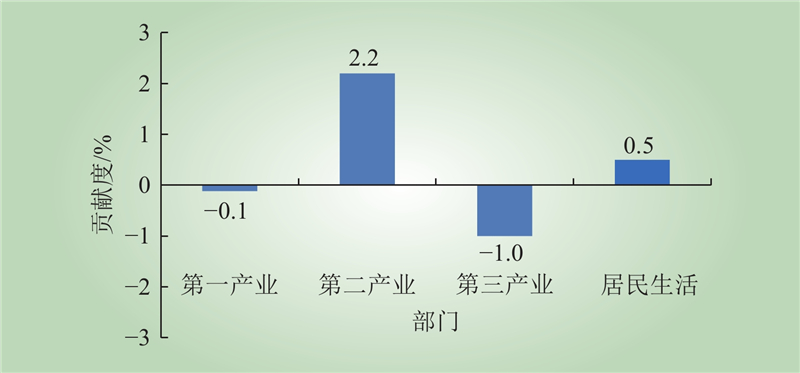
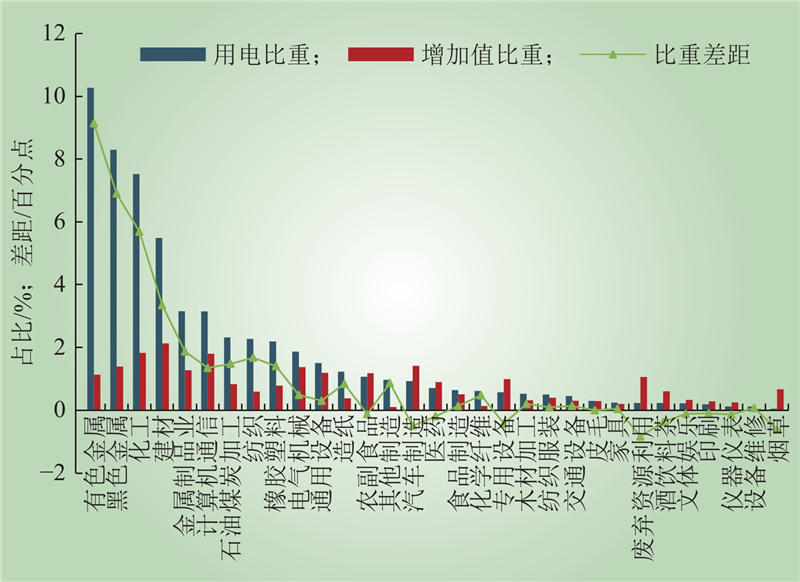
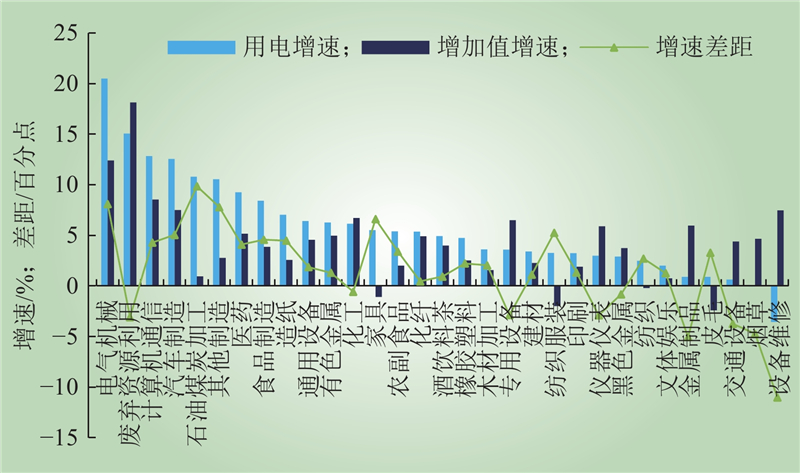
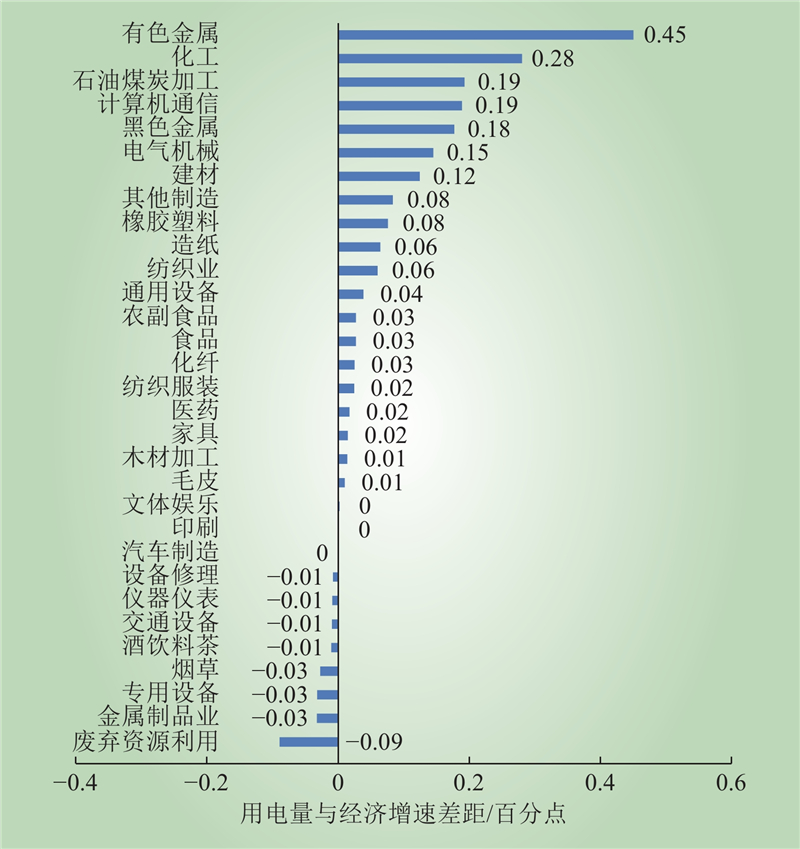
| 1 |
蒋金荷, 姚愉芳. 中国经济增长与电力发展关系的定量分析研究[J]. 数量经济技术经济研究, 2002, 19 (10): 5- 10.
|
| 2 |
袁家海, 丁伟, 胡兆光. 电力消费与中国经济发展的协整与波动分析[J]. 电网技术, 2006, 30 (9): 10- 15.
|
|
YUAN Jiahai, DING Wei, HU Zhaoguang. Analysis on cointegration and co-movement of electricity consumption and economic growth in China[J]. Power System Technology, 2006, 30 (9): 10- 15.
|
| 3 |
张琳, 何炼成, 王俊霞. 电力消费与中国经济增长: 基于中国30省市面板数据的协整检验[J]. 山西财经大学学报, 2008, 30 (12): 18- 21.
|
|
ZHANG Lin, HE Liancheng, WANG Junxia. Electricity consumption and economic growth in China—based on the 30 provincial panel data co-integration test[J]. Journal of Shanxi Finance and Economics University, 2008, 30 (12): 18- 21.
|
| 4 |
林伯强. 电力消费与中国经济增长: 基于生产函数的研究[J]. 管理世界, 2003, 19 (11): 18- 27.
|
|
LIN Boqiang. Electric consumption and China's economic growth: a study based on production function[J]. Management World, 2003, 19 (11): 18- 27.
|
| 5 |
CHEN S T, KUO H I, CHEN C C. The relationship between GDP and electricity consumption in 10 Asian countries[J]. Energy Policy, 2007, 35 (4): 2611- 2621.
|
| 6 |
刘生龙, 高宇宁, 胡鞍钢. 电力消费与中国经济增长[J]. 产业经济研究, 2014, (3): 71- 80.
|
|
LIU Shenglong, GAO Yuning, HU Angang. Electricity consumption and China's economic growth[J]. Industrial Economics Research, 2014, (3): 71- 80.
|
| 7 |
LIN B Q, WANG Y. Inconsistency of economic growth and electricity consumption in China: a panel VAR approach[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 229, 144- 156.
|
| 8 |
伍萱, 李琼慧. 关于我国电力弹性系数研究[J]. 中国电力企业管理, 2000, (12): 21.
|
| 9 |
郝卫平, 李琼慧, 赵一农. 我国电力弹性系数的现实意义[J]. 中国电力, 2003, 36 (5): 8- 10.
|
|
HAO Weiping, LI Qionghui, ZHAO Yinong. Current significance of electricity elasticity coefficient in China[J]. Electric Power, 2003, 36 (5): 8- 10.
|
| 10 |
单葆国, 张成龙, 王向, 等. 中国电力弹性系数与工业化阶段关系[J]. 中国电力, 2020, 53 (7): 1- 6.
|
|
SHAN Baoguo, ZHANG Chenglong, WANG Xiang, et al. Relationship between electricity elasticity coefficient and industrialization stage in China[J]. Electric Power, 2020, 53 (7): 1- 6.
|
| 11 |
欧阳昌裕. 正确对待电力弹性系数法: 电力需求预测思考[J]. 中国电力企业管理, 2000, (12): 22- 23.
|
| 12 |
林卫斌, 苏剑, 施发启. 经济增长、能耗强度与电力消费: 用电量与GDP增长率背离的原因探析[J]. 经济科学, 2010, (5): 15- 22.
|
| 13 |
肖宏伟. 用电量与经济增长“短期背离” 的原因分析[J]. 宏观经济管理, 2015, (6): 27- 29.
|
| 14 |
王保安. 从用电量铁路货运量的波动看结构调整的积极变化[N]. 人民日报, 2015-10-08(10).
|
| 15 |
谭显东, 单葆国, 吴姗姗, 等. 经济新常态下中国全社会用电量与GDP增速差距研究[J]. 中国电力, 2017, 50 (12): 5- 9.
|
|
TAN Xiandong, SHAN Baoguo, WU Shanshan, et al. Study on the difference between China's total electricity consumption and economic growth under the new normal[J]. Electric Power, 2017, 50 (12): 5- 9.
|
| 16 |
南方能源观察. 我国电力消费增长缘何高于经济增长?[EB/OL](2024-01-22)[2024-05-10]. https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/9Zy7eegVSq5jmU7Tq4P4jQ.
|
| 17 |
雪涛宏观笔记. 破解用电量持续高增之谜[EB/OL] (2024-03-31)[2024-05-10]. https://www.gelonghui.com/p/714449.
|
| 18 |
单葆国, 李江涛, 谭显东, 等. 经济转型时期电力弹性系数应用[J]. 中国电力, 2017, 50 (12): 1- 4.
|
|
SHAN Baoguo, LI Jiangtao, TAN Xiandong, et al. The application of electricity elasticity coefficient during economic transition period[J]. Electric Power, 2017, 50 (12): 1- 4.
|
| 19 |
国家统计局. 中国第三产业统计年鉴-2023[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2023.
|
| 20 |
国家统计局国民经济核算司. 2020年中国投人产出表[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2022年.
|
| 21 |
何蕾. 中国工业行业产能利用率测度研究: 基于面板协整的方法[J]. 产业经济研究, 2015, (2): 90- 99.
|
|
HE Lei. Measuring capacity utilization in China's industries: a panel cointegration method[J]. Industrial Economics Research, 2015, (2): 90- 99.
|
| 22 |
卢梅, 王科. 中国工业两位数行业经济能源环境数据估算[J]. 环境经济研究, 2019, 4 (4): 28- 46.
|
|
LU Mei, WANG Ke. Economic, energy and environmental data estimation of China's two-digit industrial sectors[J]. Journal of Environmental Economics, 2019, 4 (4): 28- 46.
|
| 23 |
李婧婧, 郝悦, 朱祎, 等. 全球新冠肺炎疫情下中国对外贸易和出口替代效应研究[J]. 调研世界, 2023, (3): 41- 51.
|
|
LI Jingjing, HAO Yue, ZHU Yi, et al. Research on China's foreign trade and export substitution effect under the influence of global COVID-19[J]. The World of Survey and Research, 2023, (3): 41- 51.
|
| 24 |
薛万磊, 温权, 单葆国. 降温负荷分析方法研究[J]. 能源技术经济, 2011, 23 (11): 37- 40.
|
|
XUE Wanlei, WEN Quan, SHAN Baoguo. Study on the analytical method of power load for cooling[J]. Energy Technology and Economics, 2011, 23 (11): 37- 40.
|
| 25 |
United Nations. World Population Prospects: The 2024 Revision [R]. 2024.
|
| 26 |
蔡昉, 都阳. 人口与劳动绿皮书: 中国人口与劳动问题报告No. 24 [M]. 北京: 社会科学文献出版社, 2023年.
|