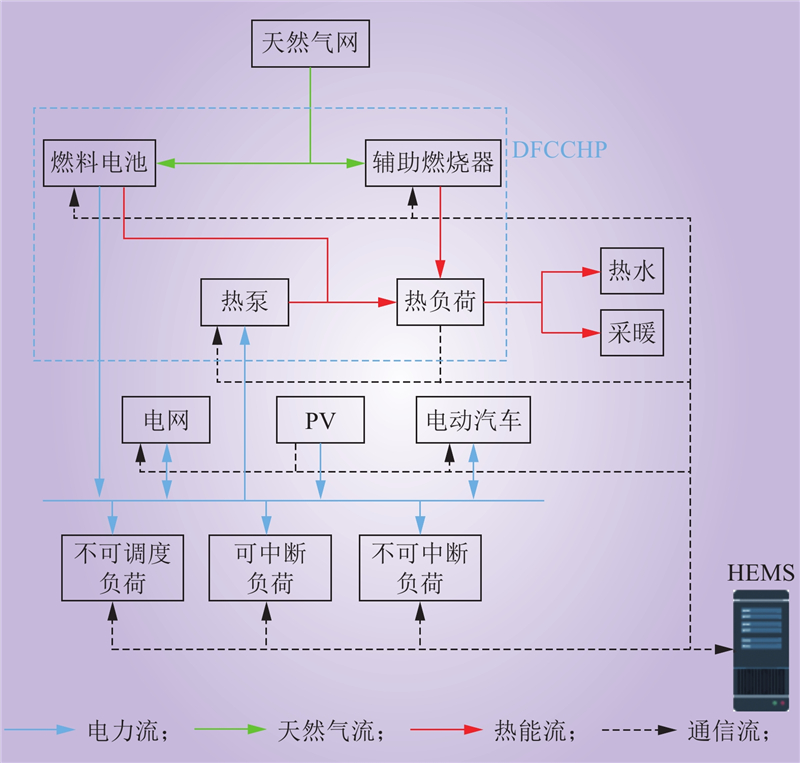
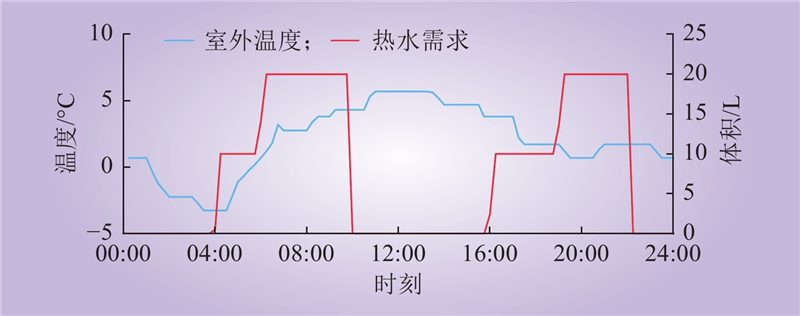
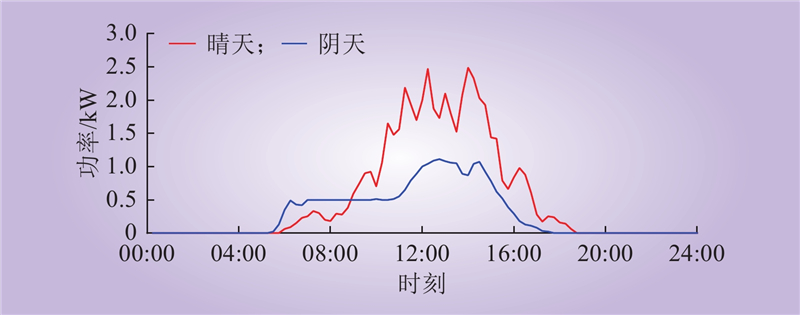
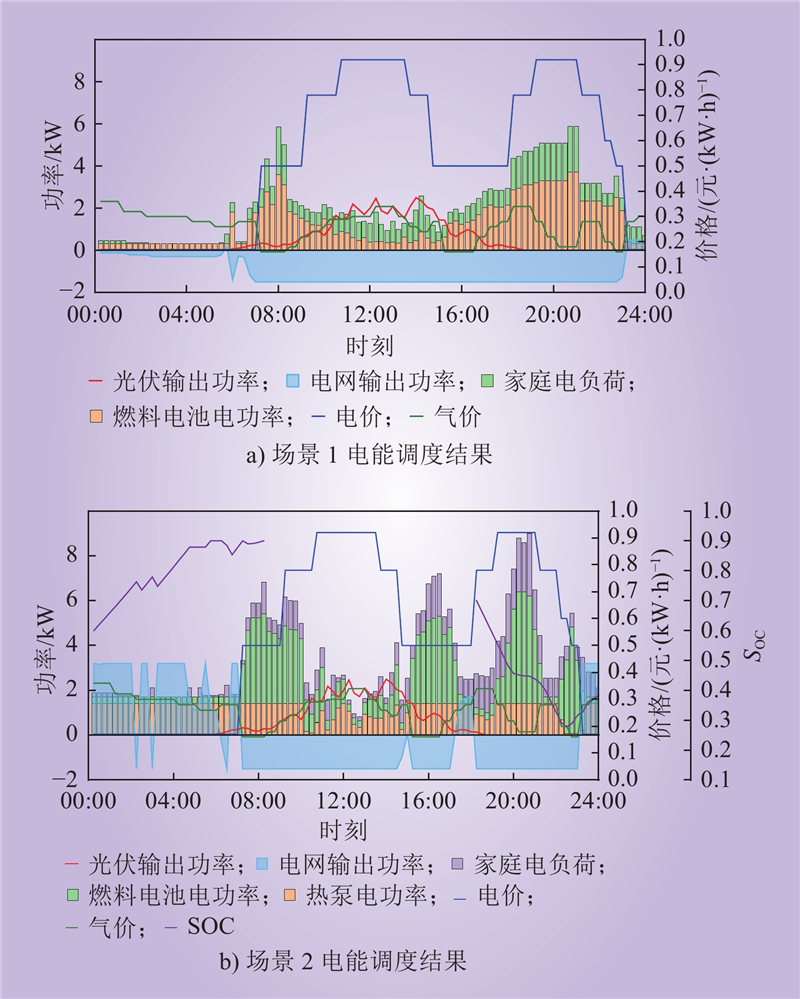
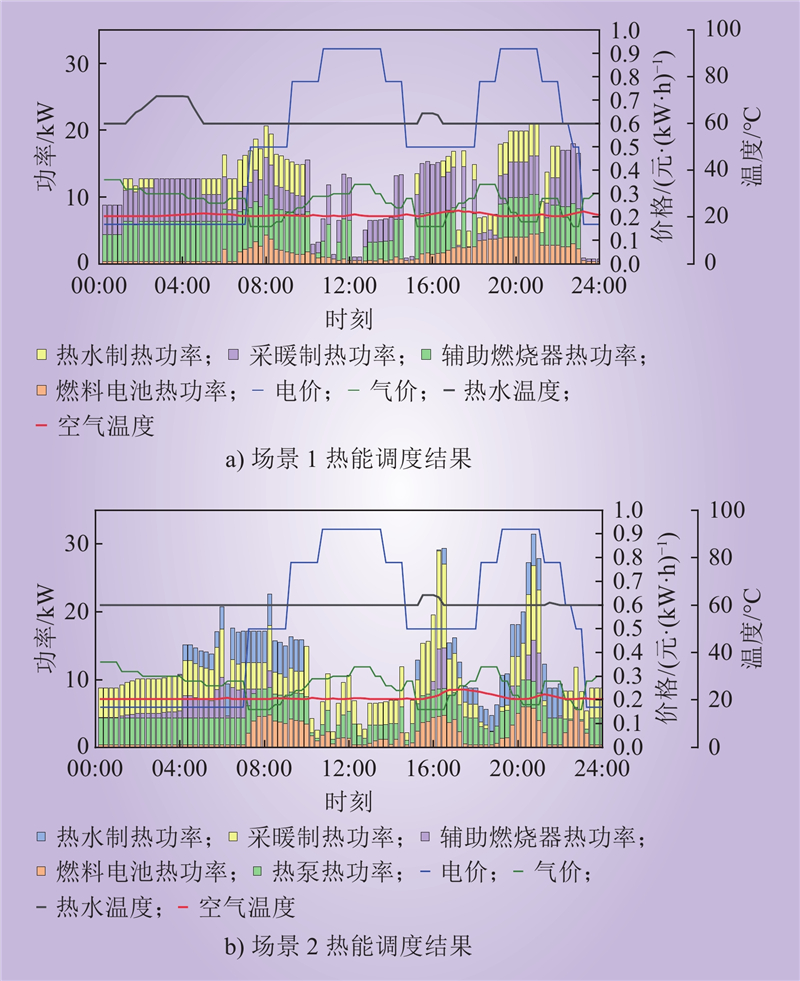
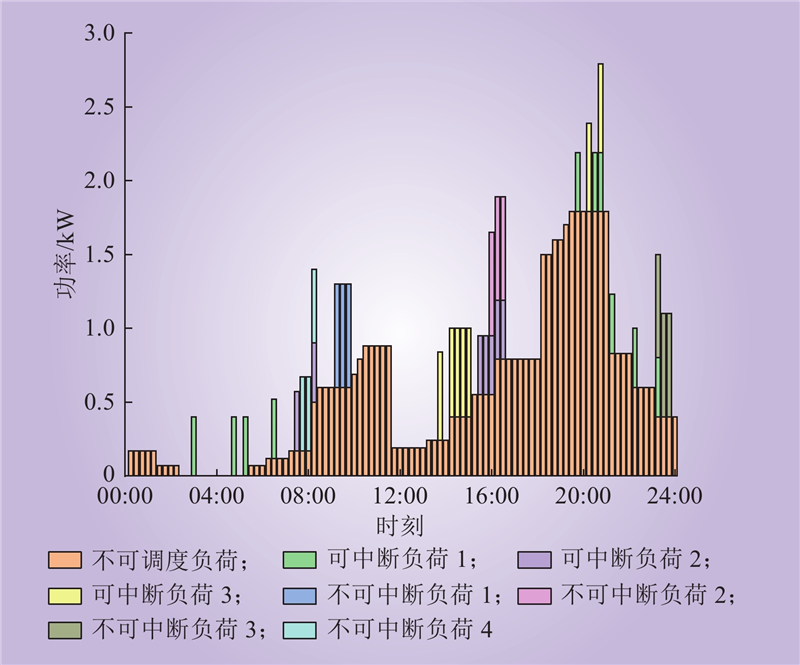
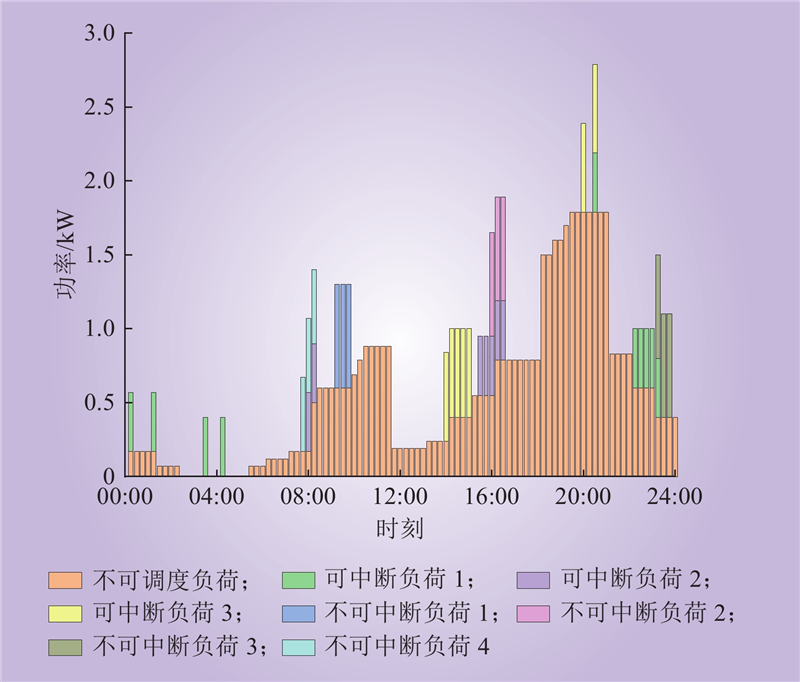
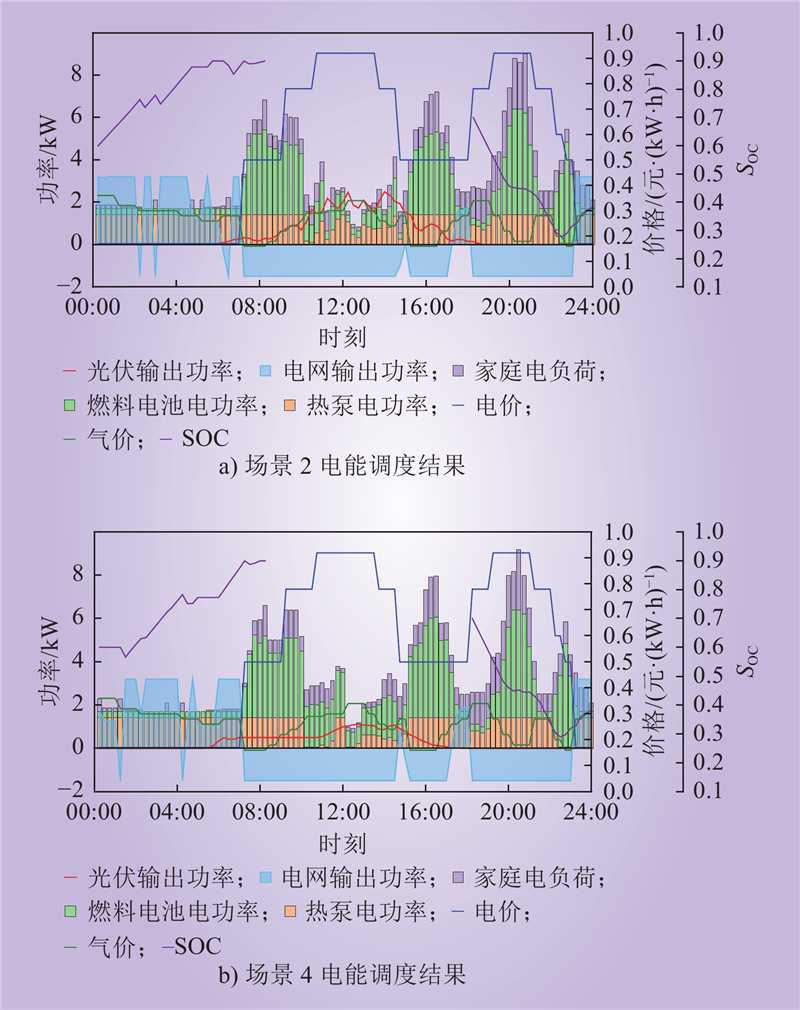
| 1 |
施泉生, 丁建勇, 刘坤, 等. 含电、气、热3种储能的微网综合能源系统经济优化运行[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2019, 39 (8): 269- 276, 293.
|
|
SHI Quansheng, DING Jianyong, LIU Kun, et al. Economic optimal operation of microgrid integrated energy system with electricity, gas and heat storage[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2019, 39 (8): 269- 276, 293.
|
| 2 |
SAIDU A M, MUHAMMAD A, IMRAN G, et al. Systematic review analysis on smart building: challenges and opportunities[J]. Sustainability, 2022, 14 (5): 3009.
|
| 3 |
金炼, 张亚君, 杨尚恒, 等. 家庭用微型热电联产技术[J]. 现代化工, 2012, 32 (5): 6- 9, 15.
|
|
JIN Lian, ZHANG Yajun, YANG Shangheng, et al. Micro-combined heat and power technology for household use[J]. Modern Chemical Industry, 2012, 32 (5): 6- 9, 15.
|
| 4 |
李岩学, 高伟俊, 张晓易, 等. 日本零能耗住宅及智能化家庭能源管理系统应用现状研究[J]. 中外能源, 2019, 24 (10): 89- 97.
|
|
LI Yanxue, GAO Weijun, ZHANG Xiaoyi, et al. Zero energy house in Japan and the application of smart home energy management system[J]. Sino-Global Energy, 2019, 24 (10): 89- 97.
|
| 5 |
蔡钦钦, 杨晓华, 朱永强. 楼宇能量管理系统的光伏消纳与储能调度研究[J]. 电力建设, 2020, 41 (1): 23- 31.
|
|
CAI Qinqin, YANG Xiaohua, ZHU Yongqiang. Research on photovoltaic accommodation and energy storage scheduling of building energy management system[J]. Electric Power Construction, 2020, 41 (1): 23- 31.
|
| 6 |
HUANG Y T, ZHANG J J, MO Y J, et al. A hybrid optimization approach for residential energy management[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8, 225201- 225209.
|
| 7 |
张华一, 文福拴, 张璨, 等. 计及舒适度的家庭能源中心运行优化模型[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2016, 40 (20): 32- 39.
|
|
ZHANG Huayi, WEN Fushuan, ZHANG Can, et al. Operation optimization model of home energy hubs considering comfort level of customers[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2016, 40 (20): 32- 39.
|
| 8 |
YAO L, TEO J C. Optimization of power dispatch with load scheduling for domestic fuel cell-based combined heat and power system[J]. IEEE Access, 2022, 10, 5968- 5979.
|
| 9 |
ABDELAAL G, GILANY M I, ELSHAHED M, et al. Integration of electric vehicles in home energy management considering urgent charging and battery degradation[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9, 47713- 47730.
|
| 10 |
贾雁冰, 杨阳方, 刘继春, 等. 售用双方协同优化的家庭柔性负荷管理策略[J]. 电网技术, 2019, 43 (4): 1430- 1438.
|
|
JIA Yanbing, YANG Yangfang, LIU Jichun, et al. Management strategy for domestic flexible load to achieve retailer-user coordinated optimization[J]. Power System Technology, 2019, 43 (4): 1430- 1438.
|
| 11 |
林俐, 顾嘉, 王铃. 面向风电消纳的考虑热网特性及热舒适度弹性的电热联合优化调度[J]. 电网技术, 2019, 43 (10): 3648- 3661.
|
|
LIN Li, GU Jia, WANG Ling. Optimal dispatching of combined heat-power system considering characteristics of thermal network and thermal comfort elasticity for wind power accommodation[J]. Power System Technology, 2019, 43 (10): 3648- 3661.
|
| 12 |
文明, 胡资斌, 龙乙林, 等. 考虑碳排放惩罚因子的综合能源系统优化规划[J]. 电力科学与技术学报, 2021, 36 (3): 11- 18.
|
|
WEN Ming, HU Zibin, LONG Yilin, et al. Optimal planning of integrated energy system considering carbon emission penalty factor[J]. Journal of Electric Power Science and Technology, 2021, 36 (3): 11- 18.
|
| 13 |
MALINA R M. Thermal comfort: analysis and applications in environmental engineering by P. O. Fanger[J]. Human Biology, 1973, 45, 116- 117.
|
| 14 |
LEITÃO J, GIL P, RIBEIRO B, et al. A survey on home energy management[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8, 5699- 5722.
|
| 15 |
ANVARI-MOGHADDAM A, MONSEF H, RAHIMI-KIAN A. Optimal smart home energy management considering energy saving and a comfortable lifestyle[C]//2016 IEEE Power and Energy Society General Meeting (PESGM). Boston, MA, USA. IEEE, 2016: 1.
|
| 16 |
陈维荣, 冉韵早, 韩莹, 等. 考虑两阶段P2G的区域综合能源系统优化调度[J/OL]. 西南交通大学学报: 1–9[2023-09-27]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/51.1277.U.20211230.0937.002.html.
|
|
CHEN Weirong, RAN Yunzao, HAN Ying, et al. Optimal scheduling of regional integrated energy systems under two-stage P2G[J/OL]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University: 1–9[2023-09-27]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/51.1277.U.20211230.0937.002.html.
|
| 17 |
安佳坤, 杨书强, 王涛, 等. 电动汽车聚合下的微能源互联网优化调度策略[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (5): 80- 88.
|
|
AN Jiakun, YANG Shuqiang, WANG Tao, et al. Optimal scheduling strategy for micro energy Internet under electric vehicles aggregation[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (5): 80- 88.
|
| 18 |
叶宇剑, 袁泉, 汤奕. 面向双碳目标的交通网-电网耦合网络中电动汽车负荷低碳优化方法[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (5): 72- 79.
|
|
YE Yujian, YUAN Quan, TANG Yi. Electric vehicle charging demand low carbon optimization in traffic-grid coupling networks towards "dual carbon" goal[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (5): 72- 79.
|
| 19 |
康继光, 琚洁华, 赵艳敏, 等. 计及能源社区产消者的综合能源系统优化方法[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (11): 206- 216.
|
|
KANG Jiguang, JU Jiehua, ZHAO Yanmin et al. Integrated energy system optimization considering energy communities with prosumers[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (11): 206- 216.
|
| 20 |
张涛, 刘伉, 陶然, 等. 计及热媒流率和热损耗不确定性的综合能源系统优化调度[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (4): 146- 155.
|
|
ZHANG Tao, LIU Kang, TAO Ran, et al. Optimal scheduling of integrated energy system considering uncertainty of heat medium flow rate and heating network loss[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (4): 146- 155.
|