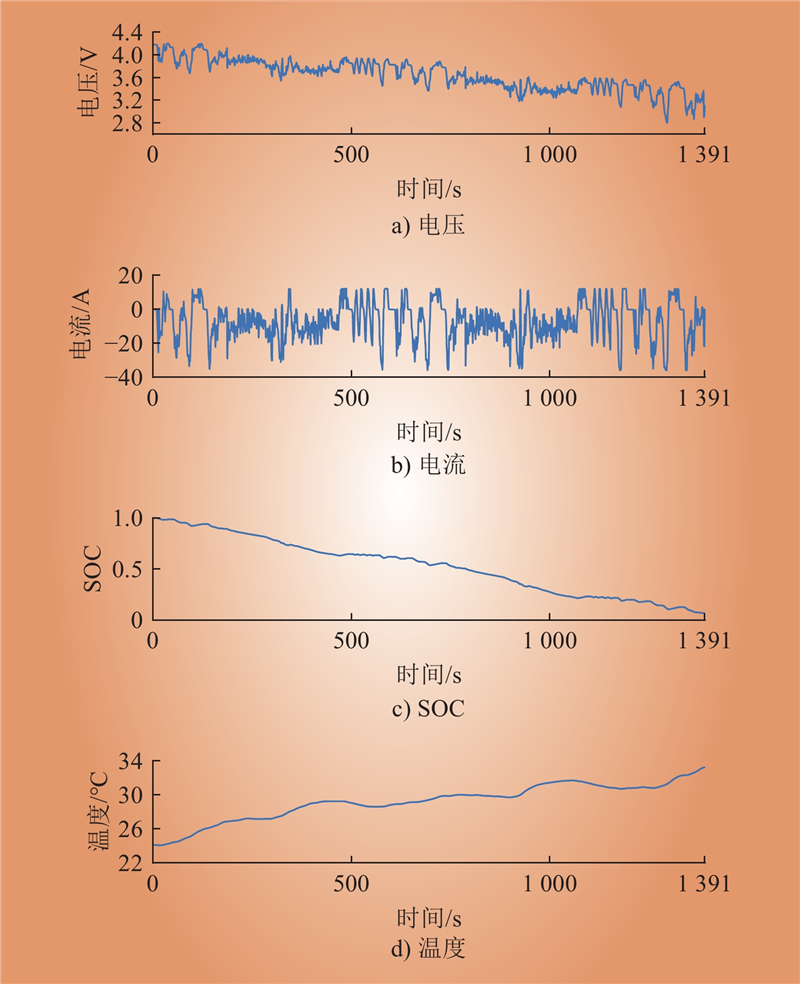
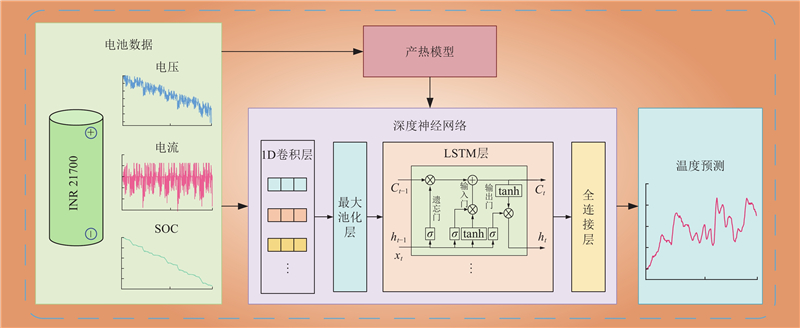
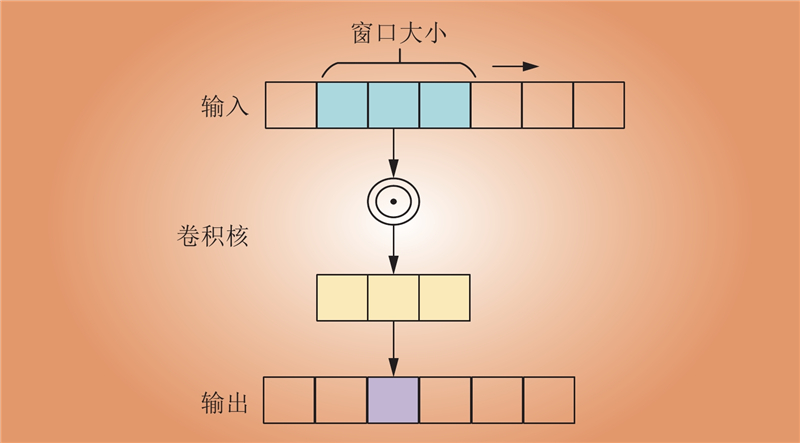
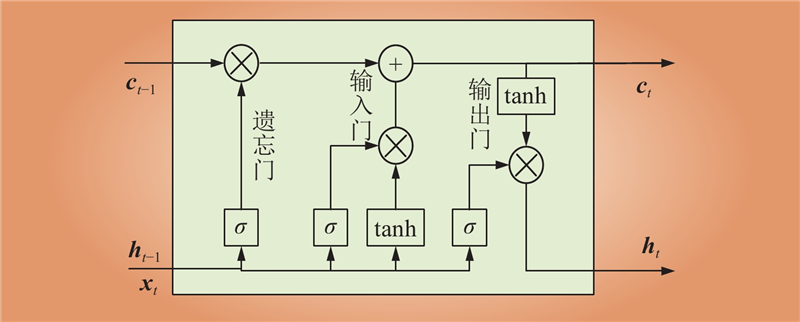
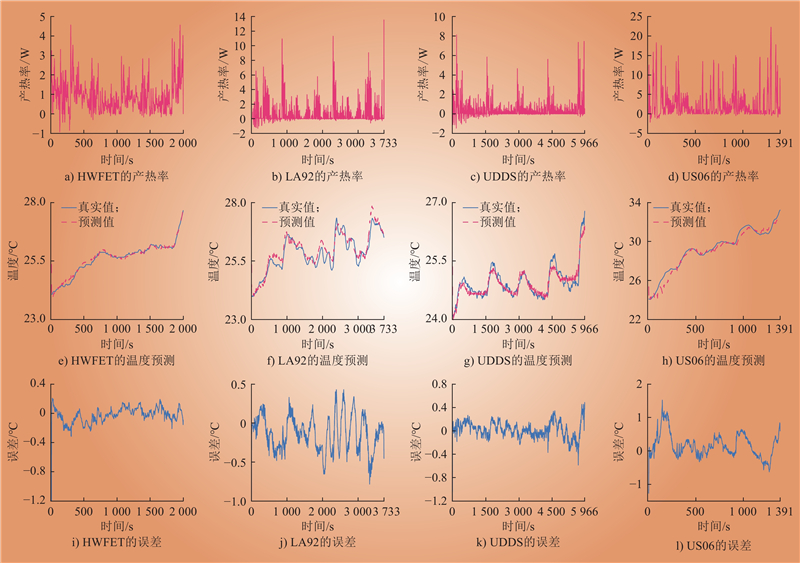
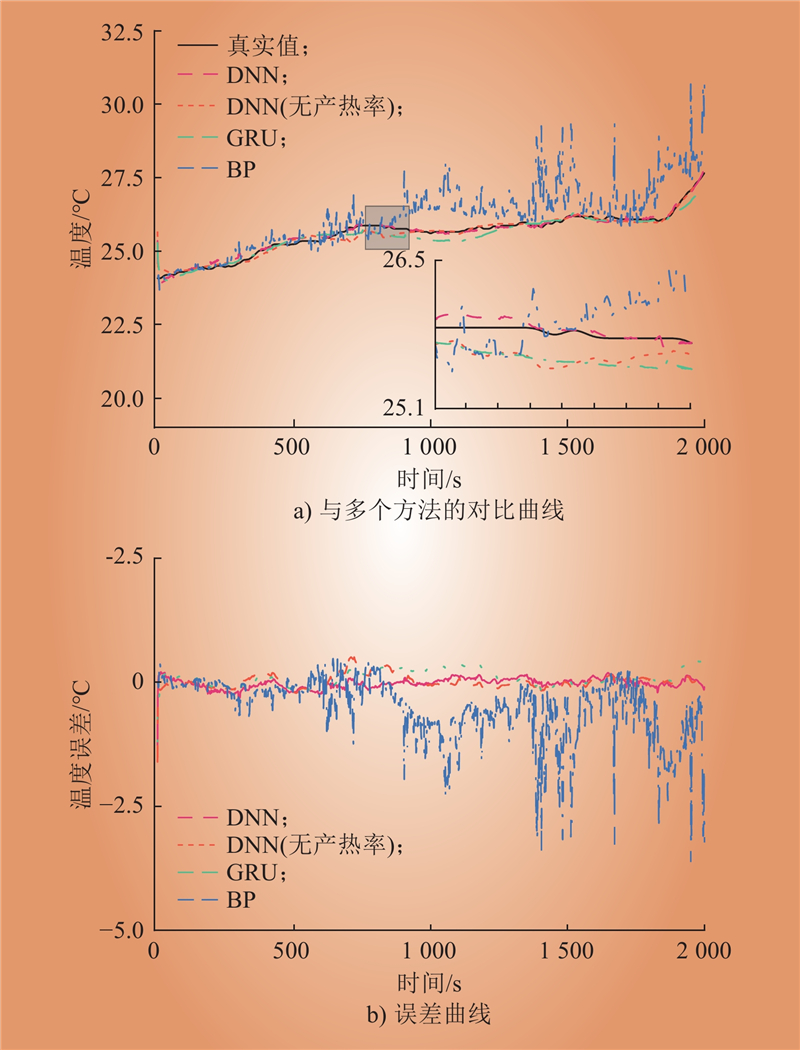
| 1 |
张媛, 夏向阳, 岳家辉, 等. 基于电池簇放电电量的电池堆不一致性在线监测方法[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (7): 207- 215,227.
|
|
ZHANG Yuan, XIA Xiangyang, YUE Jiahui, et al. Remaining useful life prediction and state of health estimation of lithium-Ion batteries based on voltage data segment hybrid model[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (7): 207- 215,227.
|
| 2 |
刘周斌, 朱涛, 姜巍, 等. 储能锂离子电池包冷却系统的数值模拟与结构优化[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (10): 202- 210.
|
|
LIU Zhoubin, ZHU Tao, JIANG Wei, et al. Simulation analysis and structure optimization of cooling system for energy storage lithium-ion battery pack[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (10): 202- 210.
|
| 3 |
WASEEM M, AHMAD M, PARVEEN A, et al. Battery technologies and functionality of battery management system for EVs: Current status, key challenges, and future prospectives[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2023, 580, 233349.
|
| 4 |
杜伟兮, 周子牛, 鲁金科, 等. 基于电化学阻抗谱的锂离子电池内部温度监测方法综述[J]. 广东电力, 2023, 36 (8): 27- 38.
|
|
DU Weixi, ZHOU Ziniu, LU Jinke, et al. Review of internal temperature monitoring methods for lithium-ion batteries based on electrochemical impedance spectroscopy[J]. Guangdong Electric Power, 2023, 36 (8): 27- 38.
|
| 5 |
林甲深. 考虑温度影响的锂离子电池放电容量不确定度评定[J]. 电源技术, 2023, 47 (5): 635- 638.
|
|
LIN Jiashen. Uncertainty evaluation of discharge capacity of lithium ion battery considering temperature effect[J]. Chinese Journal of Power Sources, 2023, 47 (5): 635- 638.
|
| 6 |
EL FALLAH S, KHARBACH J, HAMMOUCH Z, et al. State of charge estimation of an electric vehicle’s battery using Deep Neural Networks: Simulation and experimental results[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2023, 62, 106904.
|
| 7 |
赵珈卉, 田立亭, 程林. 锂离子电池状态估计与剩余寿命预测方法综述[J]. 发电技术, 2023, 44 (1): 1- 17.
|
|
ZHAO Jiahui, TIAN Liting, CHENG lin. Review on state estimation and remaining useful life prediction methods for lithium-ion battery[J]. Power Generation Technology, 2023, 44 (1): 1- 17.
|
| 8 |
黎冲, 王成辉, 王高, 等. 基于数据驱动的锂离子电池健康状态估计技术[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (8): 73- 86, 95.
|
|
LI Chong, WANG Chenghui, WANG Gao, et al. Technology of lithium-ion battery state-of-health assessment based on data-driven[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (8): 73- 86, 95.
|
| 9 |
ZHENG Y S, CHE Y H, HU X S, et al. Thermal state monitoring of lithium-ion batteries: Progress, challenges, and opportunities[J]. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science, 2024, 100, 101120.
|
| 10 |
周炜航, 叶青, 叶蕾, 等. 锂离子电池内温度场健康状态分布式光纤原位监测技术研究[J]. 中国激光, 2020, 47 (12): 154- 163.
|
|
ZHOU Weihang, YE Qing, YE Lei, et al. Distributed optical fiber in situ monitoring technology for a healthy temperature field in lithium ion batteries[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2020, 47 (12): 154- 163.
|
| 11 |
范文杰, 徐广昊, 于泊宁, 等. 基于电化学阻抗谱的锂离子电池内部温度在线估计方法研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2021, 41 (9): 3283- 3293.
|
|
FAN Wenjie, XU Guanghao, YU Boning, et al. On-line estimation method for internal temperature of lithium-ion battery based on electrochemical impedance spectroscopy[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2021, 41 (9): 3283- 3293.
|
| 12 |
熊瑞, 李幸港. 基于双卡尔曼滤波算法的动力电池内部温度估计[J]. 机械工程学报, 2020, 56 (14): 146- 151.
|
|
XIONG Rui, LI Xinggang. Battery internal temperature estimation method through double extended Kalman filtering algorithm[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2020, 56 (14): 146- 151.
|
| 13 |
谢家乐, 李增超, 王光, 等. 基于电热耦合效应的18650锂离子电池内外温度预测模型[J]. 机械工程学报, 2023, 59 (16): 342- 352.
|
|
XIE JiaLe, LI Zengchao, WANG Guang, et al. Internal and external temperature prediction models for 18650 li-ion battery based on electrical-thermal coupled effects[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2023, 59 (16): 342- 352.
|
| 14 |
FENG F, TENG S L, LIU K L, et al. Co-estimation of lithium-ion battery state of charge and state of temperature based on a hybrid electrochemical-thermal-neural-network model[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2020, 455, 227935.
|
| 15 |
HUSSEIN A A, CHEHADE A A. Robust artificial neural network-based models for accurate surface temperature estimation of batteries[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 2020, 56 (5): 5269- 5278.
|
| 16 |
KLEINER J, STUCKENBERGER M, KOMSIYSKA L, et al. Real-time core temperature prediction of prismatic automotive lithium-ion battery cells based on artificial neural networks[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2021, 39, 102588.
|
| 17 |
YAO Q, LU D D C, LEI G. A surface temperature estimation method for lithium-ion battery using enhanced GRU-RNN[J]. IEEE Transactions on Transportation Electrification, 2023, 9 (1): 1103- 1112.
|
| 18 |
闫志远, 孙桓五, 刘世闯, 等. 一种基于GRU的氢燃料重卡汽车工况下锂离子电池温度预测模型[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2024, 44 (6): 2330- 2339.
|
|
YAN Zhiyuan, SUN Huanwu, LIU Shichuang, et al. A GRU based temperature prediction model of lithium-ion battery for hydrogen fuel heavy truck under operating conditions[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2024, 44 (6): 2330- 2339.
|
| 19 |
ZHENG F D, XING Y J, JIANG J C, et al. Influence of different open circuit voltage tests on state of charge online estimation for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Applied Energy, 2016, 183, 513- 525.
|
| 20 |
周飞燕, 金林鹏, 董军. 卷积神经网络研究综述[J]. 计算机学报, 2017, 40 (6): 1229- 1251.
|
|
ZHOU Feiyan, JIN Linpeng, DONG Jun. Review of convolutional neural network[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2017, 40 (6): 1229- 1251.
|
| 21 |
ZHU S, HE C N, ZHAO N Q, et al. Data-driven analysis on thermal effects and temperature changes of lithium-ion battery[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2021, 482, 228983.
|
| 22 |
杨丽, 吴雨茜, 王俊丽等. 循环神经网络研究综述[J]. 计算机应用, 2018, 38 (S2): 1- 6, 26.
|
|
YANG Li, WU Yuqian, WANG Junli, et al. Research on recurrent neural network[J]. Journal of computer applications, 2018, 38 (S2): 1- 6, 26.
|
| 23 |
常禧龙, 梁琨, 李文涛. 深度学习优化器进展综述[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2024, 60 (7): 1- 12.
|
|
CHANG Xilong, LIANG Kun, LI Wentao. Review of development of deep learning optimizer[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2024, 60 (7): 1- 12.
|
| 24 |
WEI J W, DONG G Z, CHEN Z H. Lyapunov-based thermal fault diagnosis of cylindrical lithium-ion batteries[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2020, 67 (6): 4670- 4679.
|
| 25 |
隋全武. 基于人工神经网络的锂离子电池组温度预测[J]. 小型内燃机与车辆技术, 2018, 47 (3): 71- 73.
|
|
SUI Quanwu. Temperature prediction of lithium-ion batteries based on artificial neural networks[J]. Small Internal Combustion Engine and Vehicle Technique, 2018, 47 (3): 71- 73.
|