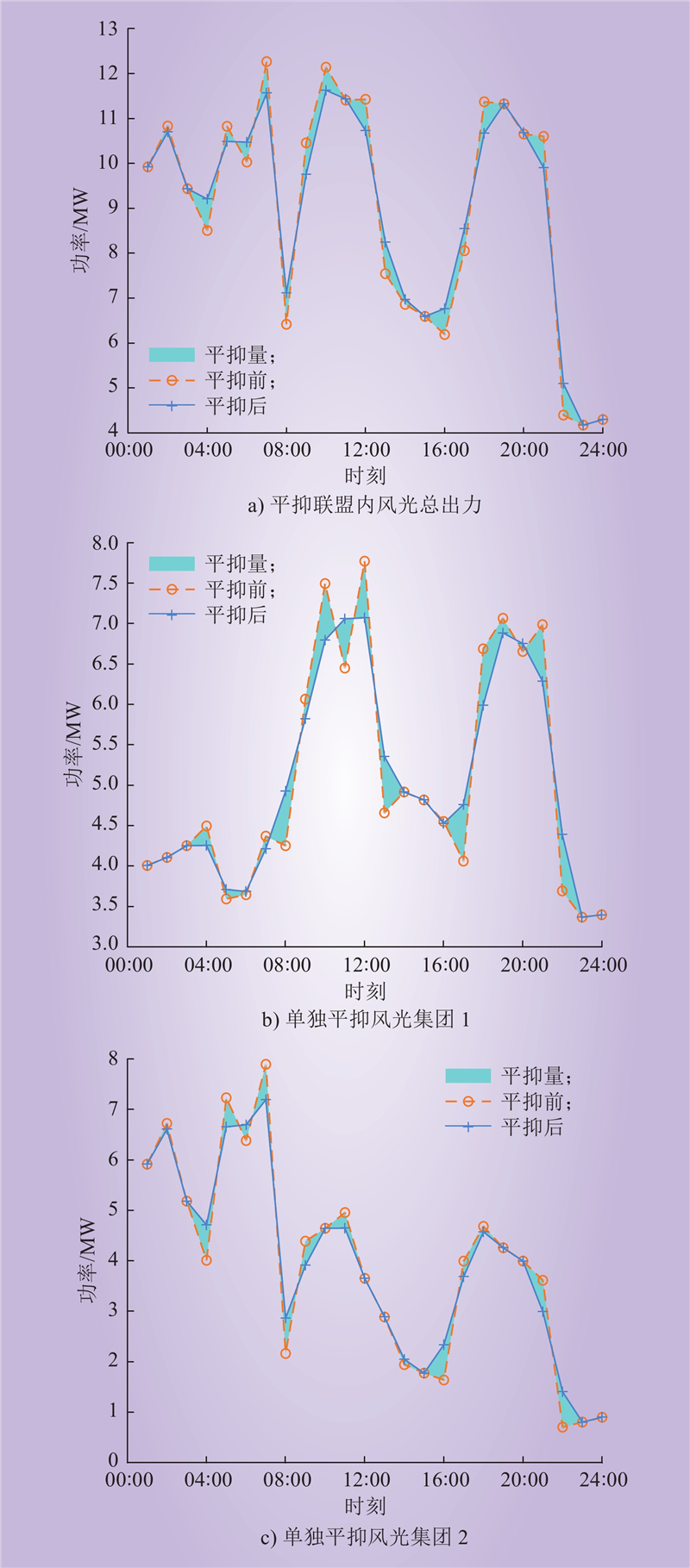
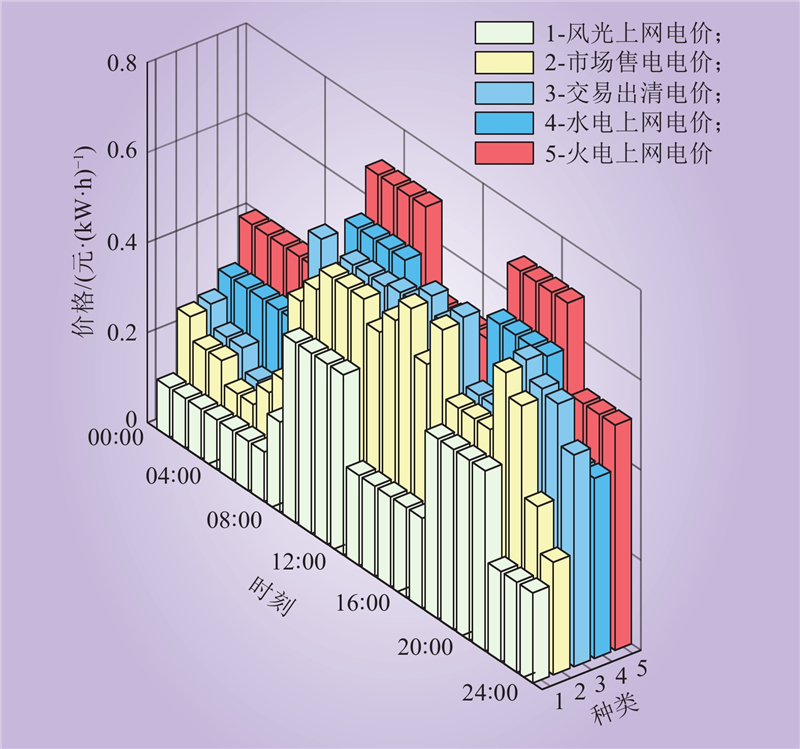
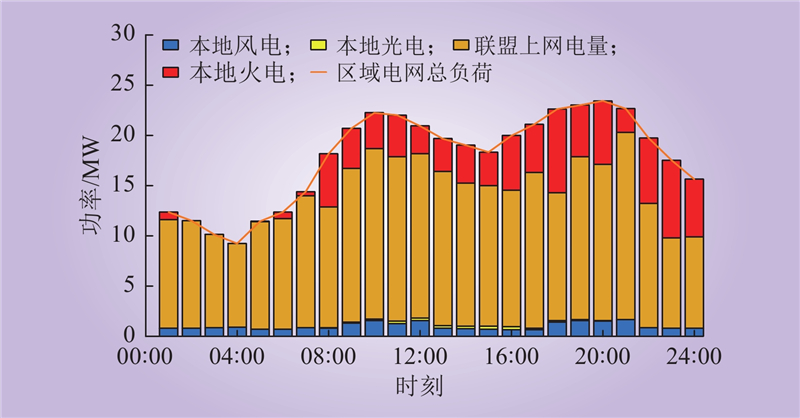
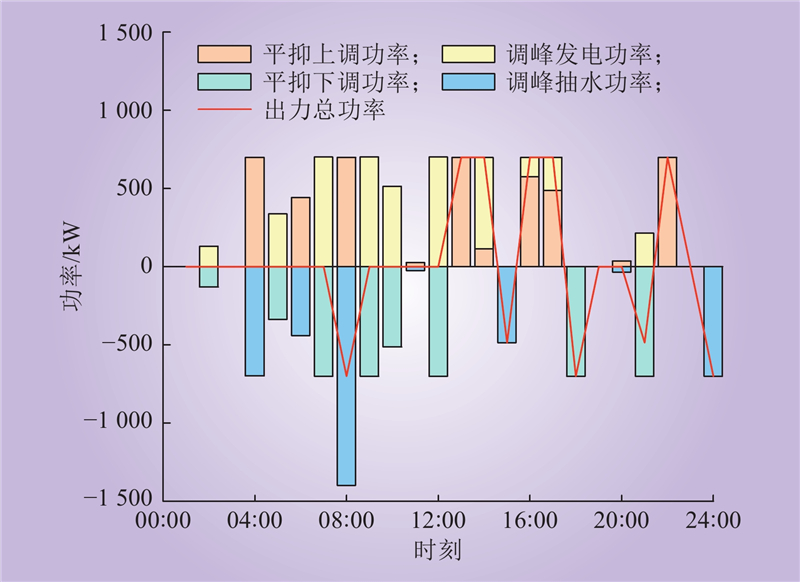
| 1 |
程春田. 碳中和下的水电角色重塑及其关键问题[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2021, 45 (16): 29- 36.
|
|
CHENG Chuntian. Function remolding of hydropower systems for carbon neutral and its key problems[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2021, 45 (16): 29- 36.
|
| 2 |
刘永奇, 陈龙翔, 韩小琪. 能源转型下我国新能源替代的关键问题分析[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2022, 42 (2): 515- 524.
|
|
LIU Yongqi, CHEN Longxiang, HAN Xiaoqi. The key problem analysis on the alternative new energy under the energy transition[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2022, 42 (2): 515- 524.
|
| 3 |
张森林. 新型电力系统中抽水蓄能运营模式及电价形成机制的思考[J]. 中国电力企业管理, 2021, (19): 44- 47.
|
| 4 |
国家发展改革委, 国家能源局, 财政部. “十四五”可再生能源发展规划: 发改能源〔2021〕1445号[EB/OL]. (2021-10-21)[2023-07-30]. http://zfxxgk.nea. gov.cn/2021-10/21/c_1310611148.htm.
|
| 5 |
李飞, 李咸善, 李振兴, 等. 基于梯级水电调节的多能联合发电系统短期优化调度[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2022, 50 (15): 11- 20.
|
|
LI Fei, LI Xianshan, LI Zhenxing, et al. Short-term optimal scheduling of multi-energy combined generation systems based on the regulation of cascade hydropower stations[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2022, 50 (15): 11- 20.
|
| 6 |
周建平, 李世东, 高洁. 新型电力系统中“水储能” 定位与发展前景[J]. 能源, 2022, (4): 60- 65.
|
| 7 |
明波, 成楸语, 黄强, 等. 梯级互补储能对新能源的长期消纳作用分析[J]. 水利学报, 2022, 53 (11): 1280- 1290.
|
|
MING Bo, CHENG Qiuyu, HUANG Qiang, et al. Analysis of long-term consumption effects of cascade complementary energy storage on new energies[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2022, 53 (11): 1280- 1290.
|
| 8 |
JU C, DING T, JIA W H, et al. Two-stage robust unit commitment with the cascade hydropower stations retrofitted with pump stations[J]. Applied Energy, 2023, 334, 120675.
|
| 9 |
ZHANG J T, CHENG C T, YU S, et al. Chance-constrained co-optimization for day-ahead generation and reserve scheduling of cascade hydropower–variable renewable energy hybrid systems[J]. Applied Energy, 2022, 324, 119732.
|
| 10 |
桑林卫, 卫璇, 许银亮, 等. 抽水蓄能助力风光稳定外送的最佳配置策略[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (12): 86- 90,123.
|
|
SANG Linwei, WEI Xuan, XU Yinliang, et al. The optimal allocation strategy of pumped storage for the collaborative operation with wind/solar generation[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (12): 86- 90,123.
|
| 11 |
陈汉雄. 水风互补四川清洁能源外送优化[J]. 中国电力, 2017, 50 (9): 37- 43.
|
|
CHEN Hanxiong. Optimizing Sichuan clean energy delivery by hydro/wind power complementation[J]. Electric Power, 2017, 50 (9): 37- 43.
|
| 12 |
郑伟民, 但扬清, 王晨轩, 等. 计及风-光-水-火多能协同的电网可再生能源消纳能力评估[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (12): 248- 254.
|
|
ZHENG Weimin, DAN Yangqing, WANG Chenxuan, et al. Evaluation of renewable energy consumption capacity in power grid considering the synergistic effect of wind-photovoltaic-hydro-thermal power[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (12): 248- 254.
|
| 13 |
肖欣, 周渝慧, 何时有, 等. 含流域梯级水电的水火风互补发电系统联合运行优化[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2018, 38 (2): 100- 108.
|
|
XIAO Xin, ZHOU Yuhui, HE Shiyou, et al. Optimal joint operation of hydro-thermal-wind hybrid power system with cascaded hydro power[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2018, 38 (2): 100- 108.
|
| 14 |
段佳南, 谢俊, 冯丽娜, 等. 基于合作博弈论的风–光–水–氢多主体能源系统增益分配策略[J]. 电网技术, 2022, 46 (5): 1703- 1712.
|
|
DUAN Jianan, XIE Jun, FENG Lina, et al. Synergistic gains allocation for multi-stakeholder wind-solar-hydro-hydrogen energy system based on cooperative game theory[J]. Power System Technology, 2022, 46 (5): 1703- 1712.
|
| 15 |
李咸善, 杨拯, 李飞, 等. 基于梯级水电调节的风光水联盟与区域电网联合运行优化调度策略[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2023, 43 (6): 2234- 2248.
|
|
LI Xianshan, YANG Zheng, LI Fei, et al. Optimization scheduling strategy for joint operation of wind-solar-water power alliance and regional power grid based on cascade hydropower regulation[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2023, 43 (6): 2234- 2248.
|
| 16 |
程瑜, 胡紫豪, 王婕. 基于分布式交易的集群多能系统运行优化[J]. 电工技术学报, 2022, 37 (S1): 116- 125.
|
|
CHENG Yu, HU Zihao, WANG Jie. Operation optimization of multi-energy system based on distributed transaction[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2022, 37 (S1): 116- 125.
|
| 17 |
刘志坚, 余宸昕, 梁宁, 等. 考虑碳排放金融市场的风-氢-火多能耦合系统交易模型[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2023, 43 (5): 138- 144.
|
|
LIU Zhijian, YU Chenxin, LIANG Ning, et al. Trading model of wind-hydrogen-fire coupled energy system considering carbon emission financial market[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2023, 43 (5): 138- 144.
|
| 18 |
CUI S C, WANG Y W, SHI Y, et al. Community energy cooperation with the presence of cheating behaviors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2021, 12 (1): 561- 573.
|
| 19 |
国家发展改革委. 关于进一步完善抽水蓄能价格形成机制的意见: 发改价格〔2021〕633号[EB/OL]. (2021-05-08)[2023-07-30].https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/2021-05/08/content_5605367.htm.
|
| 20 |
李咸善, 解仕杰, 方子健, 等. 多微电网共享储能的优化配置及其成本分摊[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2021, 41 (10): 44- 51.
|
|
LI Xianshan, XIE Shijie, FANG Zijian, et al. Optimal configuration of shared energy storage for multi-microgrid and its cost allocation[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2021, 41 (10): 44- 51.
|
| 21 |
李咸善, 方子健, 李飞, 等. 含多微电网租赁共享储能的配电网博弈优化调度[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2022, 42 (18): 6611- 6625.
|
|
LI Xianshan, FANG Zijian, LI Fei, et al. Game-based optimal dispatching strategy for distribution network with multiple microgrids leasing shared energy storage[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2022, 42 (18): 6611- 6625.
|