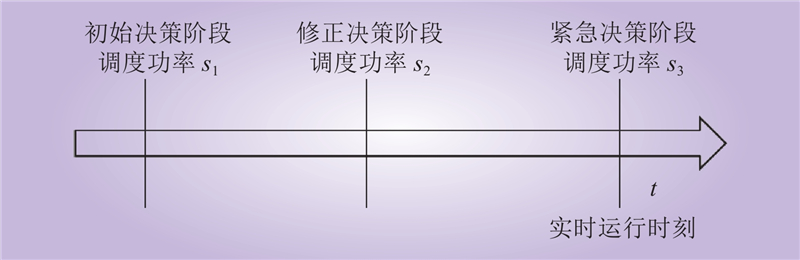
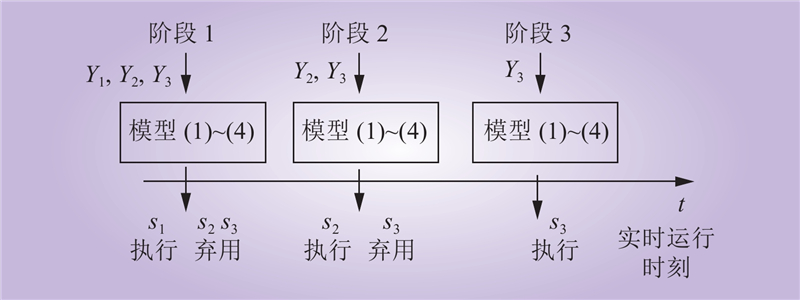
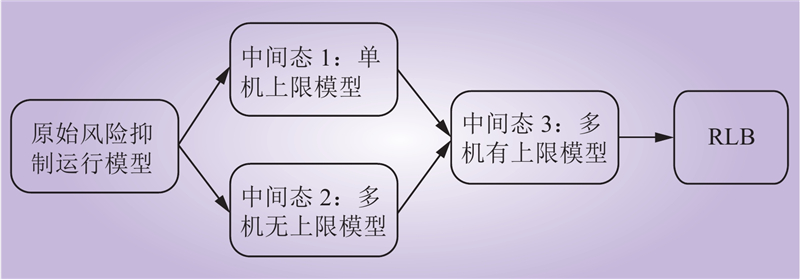
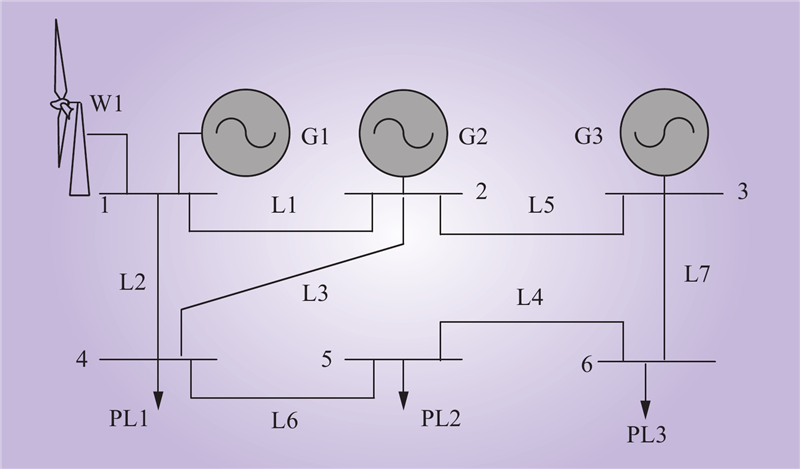
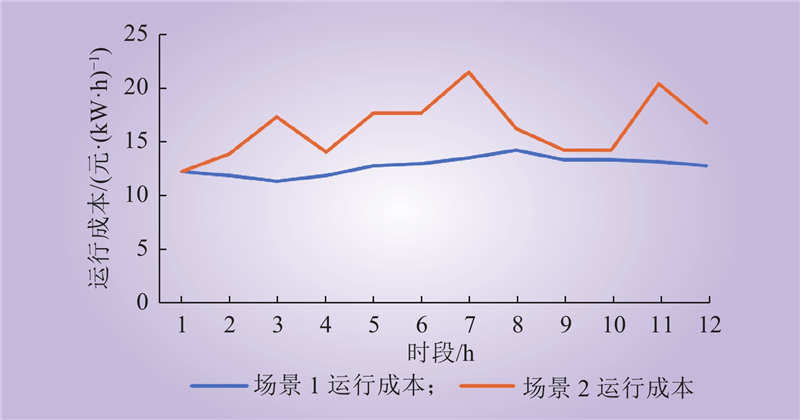
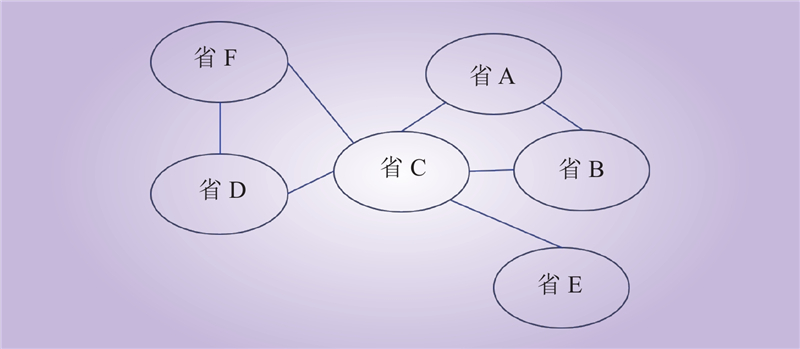
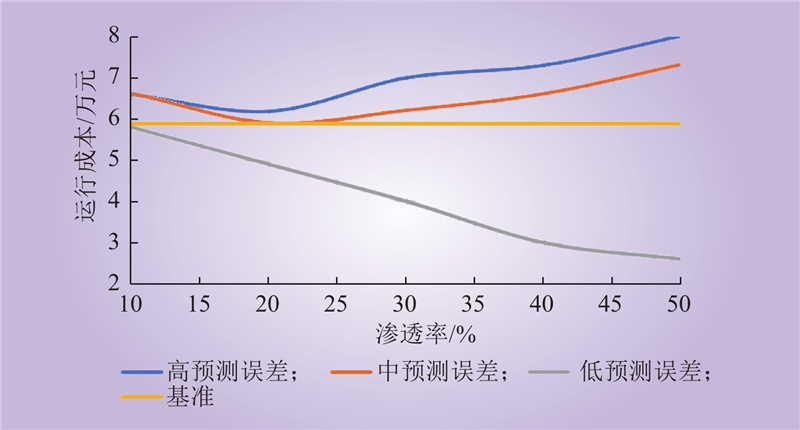
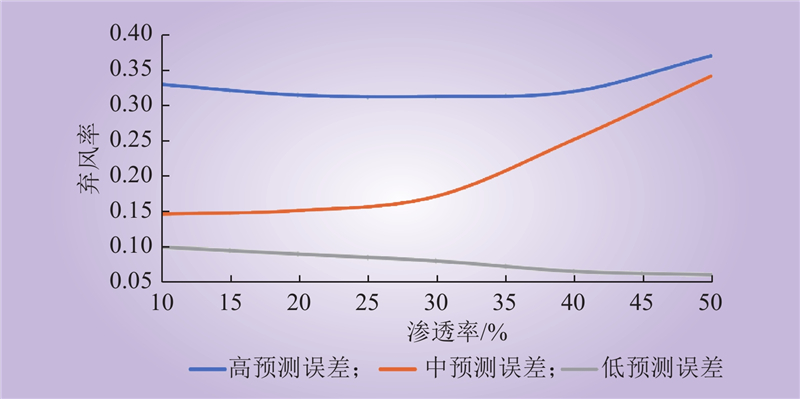
| 1 |
PENG C Y, LEI S B, HOU Y H, et al. Uncertainty management in power system operation[J]. CSEE Journal of Power and Energy Systems, 2015, 1 (1): 28- 35.
DOI
|
| 2 |
李雄威, 王昕, 顾佳伟, 等. 考虑火电深度调峰的风光火储系统日前优化调度[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (1): 1- 7, 48.
|
|
LI Xiongwei, WANG Xin, GU Jiawei, et al. Day-ahead optimal dispatching of wind-solar-thermal power storage system considering deep peak shaving of thermal power[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (1): 1- 7, 48.
|
| 3 |
National Academy of Sciences U. S. A, National Research Council. Disaster resilience: a national imperative[M]. Washington, D.C.: The National Academies Press, 2012.
|
| 4 |
North American Electric Reliability Corporation. High-impact, low-frequency event risk to the North American bulk power system[EB/OL]. (2016-03)[2023-01-06]. http://www.nerc.com/pa/CI/Resources/Documents/HILF%20 Report.pdf.
|
| 5 |
North American Electric Reliability Corporation. Severe impact resilience: considerations and recommendations [EB/OL]. (2016-12) [2023-01-06]. http://www.nerc.com/docs/oc/sirtf/SIRTF_Final_May_9_2012-Board_Accepted.pdf.
|
| 6 |
PANTELI M, MANCARELLA P. Modeling and evaluating the resilience of critical electrical power infrastructure to extreme weather events[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2017, 11 (3): 1733- 1742.
DOI
|
| 7 |
ARAB A, KHODAEI A, KHATOR S K, et al. Stochastic pre-hurricane restoration planning for electric power systems infrastructure[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2015, 6 (2): 1046- 1054.
DOI
|
| 8 |
CHEN G, LU E, PENG C Y, et al. Coordinating preventive strategies and restoration under extreme weather conditions[J]. Journal of Power and Energy Engineering, 2015, 3 (4): 313- 318.
DOI
|
| 9 |
REED D A, KAPUR K C, CHRISTIE R D. Methodology for assessing the resilience of networked infrastructure[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2009, 3 (2): 174- 180.
DOI
|
| 10 |
俞拙非, 刘菲, 刘瑞环, 等. 面向配电网弹性提升的源网荷灵活资源优化研究综述及展望[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (4): 132- 144.
|
|
YU Zhuofei, LIU Fei, LIU Ruihuan, et al. Resilience-oriented optimization of source-grid-load flexible resources in distribution systems: review and prospect[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (4): 132- 144.
|
| 11 |
陈磊, 邓欣怡, 陈红坤, 等. 电力系统韧性评估与提升研究综述[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2022, 50 (13): 11- 22.
DOI
|
|
CHEN Lei, DENG Xinyi, CHEN Hongkun, et al. Review of the assessment and improvement of power system resilience[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2022, 50 (13): 11- 22.
DOI
|
| 12 |
赵军, 张敏, 张世锋, 等. 计及碳交易和新能源不确定性的多微电网合作运行优化策略[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (5): 62- 71.
|
|
ZHAO Jun, ZHANG Min, ZHANG Shifeng, et al. Optimization strategy of multi-microgrid cooperative operation considering carbon trading and renewable energy uncertainties[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (5): 62- 71.
|
| 13 |
谭俊丰, 杨苹, 张凡, 等. 考虑能量-辅助服务下的园区综合能源系统多时间尺度优化模型[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (10): 100- 111.
|
|
TAN Junfeng, YANG Ping, ZHANG Fan, et al. Multi-time scale optimization dispatch model of integrated energy system considering energy-auxiliary services[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (10): 100- 111.
|
| 14 |
余帆, 牛洪海, 李兵, 等. 计及源荷双侧不确定性的全可再生能源系统日前经济调度[J]. 中国电力, 2020, 53 (12): 101- 109.
|
|
YU Fan, NIU Honghai, LI Bing, et al. Economic dispatch of fully renewable energy system considering uncertainty of both energy source and load[J]. Electric Power, 2020, 53 (12): 101- 109.
|
| 15 |
VARAIYA P P, WU F F, BIALEK J W. Smart operation of smart grid: risk-limiting dispatch[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2011, 99 (1): 40- 57.
DOI
|
| 16 |
PENG C Y, HOU Y H, YU N P, et al. Risk-limiting unit commitment in smart grid with intelligent periphery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2017, 32 (6): 4696- 4707.
|
| 17 |
BOYD S, VANDENBERGHE L. Convex Optimization[M]. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press, 2004.
|
| 18 |
张虹, 闫贺, 申鑫, 等. 面向能源社区能量管理的配网产消者分布式优化调度[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2022, 42 (12): 4449- 4459.
|
|
ZHANG Hong, YAN He, SHEN Xin, et al. Distributed optimal scheduling for prosumer in distribution network for energy community energy management[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2022, 42 (12): 4449- 4459.
|
| 19 |
赵冬梅, 王浩翔, 陶然. 基于改进交替方向乘子法的输配电网分散协调鲁棒优化调度模型[J]. 电网技术, 2023, 47 (3): 1138- 1151.
|
|
ZHAO Dongmei, WANG Haoxiang, TAO Ran. Decentralized coordination robust optimal scheduling model for transmission and distribution networks based on improved alternating direction method of multipliers[J]. Power System Technology, 2023, 47 (3): 1138- 1151.
|