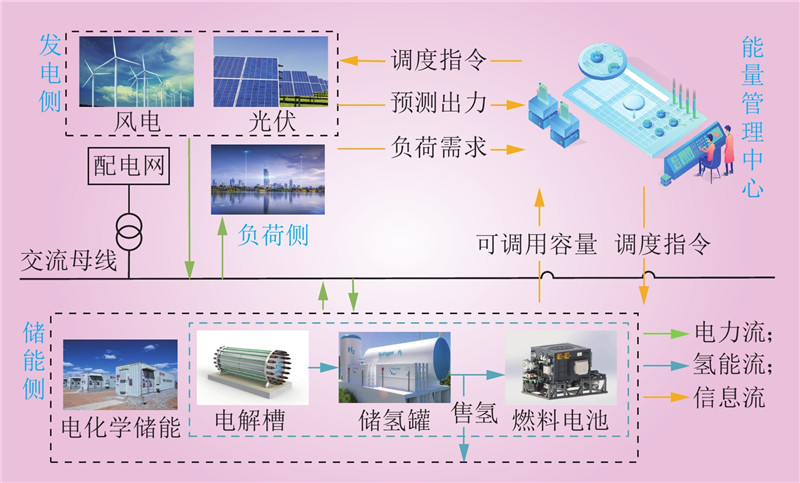
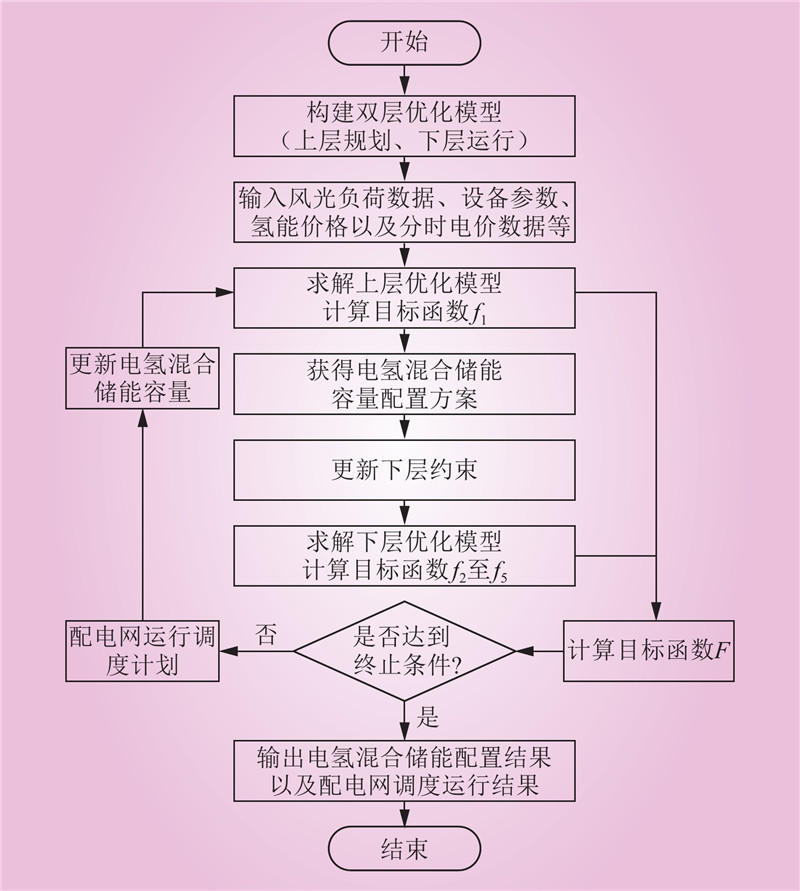
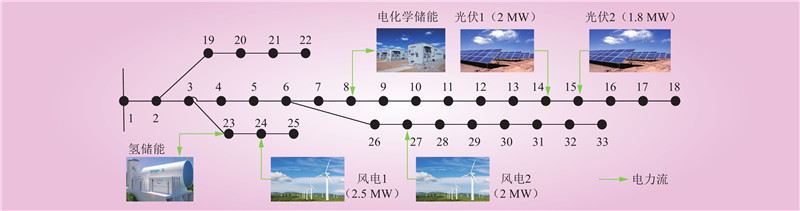
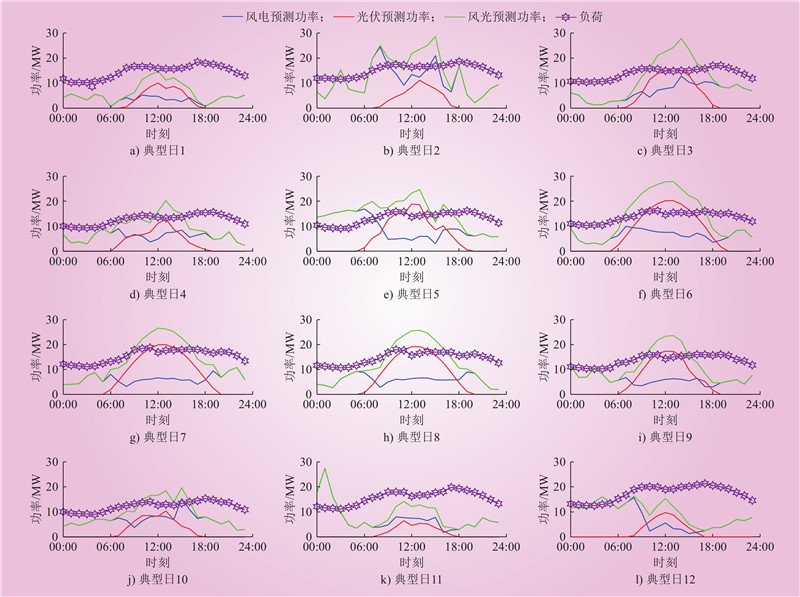
| 1 |
徐文韬, 米阳, 蔡鹏程, 等. 基于机会约束规划的含多微网主动配电网分布式优化管理[J]. 电力建设, 2024, 45 (11): 1- 13.
|
|
XU Wentao, MI Yang, CAI Pengcheng, et al. Distributed optimization management for active distribution networks with multiple microgrids based on chance-constrained programming[J]. Electric Power Construction, 2024, 45 (11): 1- 13.
|
| 2 |
YANG S X, WANG X F, XU J Y, et al. Distribution network adaptability assessment considering distributed PV "reverse power flow" behavior - a case study in Beijing[J]. Energy, 2023, 275, 127497.
|
| 3 |
孙国强, 殷岩岩, 卫志农, 等. 基于深度确定性策略梯度的主动配电网有功-无功协调优化调度[J]. 电力建设, 2023, 44 (11): 33- 42.
|
|
SUN Guoqiang, YIN Yanyan, WEI Zhinong, et al. Coordinated optimal dispatch of active and reactive power in active distribution networks using deep deterministic strategy gradient[J]. Electric Power Construction, 2023, 44 (11): 33- 42.
|
| 4 |
郭文凯, 王果, 闵永智. 计及阶梯式碳交易的牵引供电系统混合储能容量配置[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2025, 60 (3): 550- 560.
|
|
GUO Wenkai, WANG Guo, MIN Yongzhi. Hybrid energy storage capacity configuration for traction power supply systems considering ladder-type carbon trading mechanism[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2025, 60 (3): 550- 560.
|
| 5 |
刘秋华, 王明康, 杨圣城. 基于全寿命周期内经济收益最大化的退役电池储能容量配置方法研究[J]. 太阳能学报, 2024, 45 (7): 143- 152.
|
|
LIU Qiuhua, WANG Mingkang, YANG Shengcheng. Research on configuration method of energy storage capacity for retired batteries based on maximizing economic benefits throughout life cycle[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2024, 45 (7): 143- 152.
|
| 6 |
毛志宇, 李培强, 马德鑫, 等. 基于风功率波动平抑的复合储能两次功率分配容量配置方法研究[J]. 电网技术, 2023, 47 (10): 4111- 4123.
|
|
MAO Zhiyu, LI Peiqiang, MA Dexin, et al. Double power allocation of capacity configuration of compound energy storage based on wind power smoothing[J]. Power System Technology, 2023, 47 (10): 4111- 4123.
|
| 7 |
米阳, 王沛林, 周杰, 等. 基于电力系统分区惯量估计的储能容量配置策略[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2024, 44 (7): 13- 20.
|
|
MI Yang, WANG Peilin, ZHOU Jie, et al. Energy storage capacity configuration strategy based on partitioned inertia estimation of power system[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2024, 44 (7): 13- 20.
|
| 8 |
张震霄, 年珩, 李培, 等. 储能型统一电能质量调节器电压补偿能力分析及提升方法[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2022, 46 (23): 151- 159.
|
|
ZHANG Zhenxiao, NIAN Heng, LI Pei, et al. Voltage compensation capability analysis and improvement method for unified power quality conditioner with energy storage[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2022, 46 (23): 151- 159.
|
| 9 |
武晓朦, 孙安磊, 李晨晨, 等. 考虑风电出力波动性的混合储能双层优化配置[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2024, 24 (24): 10313- 10320.
|
|
WU Xiaomeng, SUN Anlei, LI Chenchen, et al. Hybrid energy storage double-layer optimal configuration considering wind power output volatility[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2024, 24 (24): 10313- 10320.
|
| 10 |
李金中, 徐斌, 李喆, 等. 基于COA算法和PSO-GSA算法的储能优化与调控方法[J]. 供用电, 2025, 42 (6): 40- 47.
|
|
LI Jinzhong, XU Bin, LI Zhe, et al. Energy storage optimization and regulation and control methods based on COA and PSO-GSA algorithms[J]. Distribution & Utilization, 2025, 42 (6): 40- 47.
|
| 11 |
DUAN F D, BU X Z. A new cloud-stochastic framework for optimized deployment of hydrogen storage in distribution network integrated with renewable energy considering hydrogen-based demand response[J]. Energy, 2025, 316, 134483.
|
| 12 |
方石磊, 杨志淳, 闵怀东, 等. 高比例光伏下考虑移动储能接入的柔性配电网协调优化策略[J]. 供用电, 2025, 42 (5): 61- 71.
|
|
FANG Shilei, YANG Zhichun, MIN Huaidong, et al. Coordinated optimization strategy of flexible distribution network considering mobile energy storage system integration under high proportion photovoltaic[J]. Distribution & Utilization, 2025, 42 (5): 61- 71.
|
| 13 |
袁铁江, 郭建华, 杨紫娟, 等. 平抑风电波动的电-氢混合储能容量优化配置[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2024, 44 (4): 1397- 1406.
|
|
YUAN Tiejiang, GUO Jianhua, YANG Zijuan, et al. Optimal allocation of power electric-hydrogen hybrid energy storage of stabilizing wind power fluctuation[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2024, 44 (4): 1397- 1406.
|
| 14 |
卢子敬, 李子寿, 郭相国, 等. 基于多目标人工蜂鸟算法的电-氢混合储能系统最优配置[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (7): 33- 42.
|
|
LU Zijing, LI Zishou, GUO Xiangguo, et al. Optimal configuration of electricity-hydrogen hybrid energy storage system based on multi-objective artificial hummingbird algorithm[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (7): 33- 42.
|
| 15 |
陈铭宏天, 耿江海, 赵雨泽, 等. 基于两阶段随机优化的电氢耦合微电网周运行策略[J]. 中国电力, 2025, 58 (5): 82- 90.
|
|
CHEN Minghongtian, GENG Jianghai, ZHAO Yuze, et al. Two-stage stochastic optimization based weekly operation strategy for electric-hydrogen coupled microgrid[J]. Electric Power, 2025, 58 (5): 82- 90.
|
| 16 |
胡伟, 杨硕. 考虑配电网脆弱性的储能双层优化配置模型[J]. 智慧电力, 2024, 52 (6): 1- 8.
|
|
HU Wei, YANG Shuo. Dual-tiered optimization configuration model for energy storage considering distribution network vulnerability[J]. Smart Power, 2024, 52 (6): 1- 8.
|
| 17 |
李湃, 卢慧, 李驰, 等. 多能互补发电系统电/热储能容量双层优化配置方法[J]. 中国电力, 2025, 58 (3): 55- 64.
|
|
LI Pai, LU Hui, LI Chi, et al. Bi-level capacity optimization for battery/thermal energy storage system in multi-energy complementary power generation system[J]. Electric Power, 2025, 58 (3): 55- 64.
|
| 18 |
国家发展和改革委员会. 关于新形势下配电网高质量发展的指导意见(发改能源〔2024〕187号) [EB/OL]. (2024-03-01)[2025-09-10]. https://www.ndrc.gov.cn/xxgk/zcfb/tz/202403/t20240301_1364313.html.
|
| 19 |
国家能源局. 国家能源局关于印发《配电网高质量发展行动实施方案(2024—2027年)》的通知(国能发电力〔2024〕59号)[EB/OL]. (2024-08-02)[2025-09-10]. https://zfxxgk.nea.gov.cn/2024-08/02/c_1310784260.htm.
|
| 20 |
刘忠, 黄彦铭, 朱光明, 等. 含风-光-电氢混合储能的多微电网系统容量优化配置方法[J]. 发电技术, 2025, 46 (2): 240- 251.
|
|
LIU Zhong, HUANG Yanming, ZHU Guangming, et al. Optimal capacity configuration method for multi-microgrid system utilizing wind-solar-electric-hydrogen hybrid energy storage[J]. Power Generation Technology, 2025, 46 (2): 240- 251.
|
| 21 |
闫群民, 李召, 马永翔, 等. 考虑综合经济性的风光配电网储能优化配置[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2024, 24 (12): 5014- 5022.
|
|
YAN Qunmin, LI Zhao, MA Yongxiang, et al. Consider the optimal configuration of energy storage in wind-solar distribution networks with comprehensive economy[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2024, 24 (12): 5014- 5022.
|
| 22 |
彭钢, 寇启龙, 方涛, 等. 考虑新能源消纳率的主动配电网储能优化配置策略[J]. 浙江电力, 2025, 44 (1): 84- 94.
|
|
PENG Gang, KOU Qilong, FANG Tao, et al. An optimal strategy for energy storage allocation in active distribution networks considering new energy consumption rates[J]. Zhejiang Electric Power, 2025, 44 (1): 84- 94.
|
| 23 |
ZHANG T M, WANG X, PARISIO A. A corrective control framework for mitigating voltage fluctuations and congestion in distribution networks with high renewable energy penetration[J]. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 2025, 165, 110508.
|
| 24 |
杜帅, 贾黎明, 李真娣, 等. “光伏-储能”耦合参与调峰的配电网运行优化配置[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13 (5): 1741- 1743.
|
|
DU Shuai, JIA Liming, LI Zhendi, et al. Optimization configuration of distribution network operation with "photovoltaic energy storage" coupling participation in peak shaving[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13 (5): 1741- 1743.
|
| 25 |
李响, 武海潮, 王文雪, 等. 基于电网承载能力的新能源并网适应性评估[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2023, 43 (S1): 107- 113.
|
|
LI Xiang, WU Haichao, WANG Wenxue, et al. Adaptability assessment of new energy connected to the power grid based on the carrying capacity[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2023, 43 (S1): 107- 113.
|
| 26 |
刘志文, 李岩, 邵冲, 等. 考虑柔性资源协同互动的配电网灵活性评估方法[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (10): 158- 165.
|
|
LIU Zhiwen, LI Yan, SHAO Chong, et al. Distribution network flexibility evaluation method considering collaborative interaction of flexible resources[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (10): 158- 165.
|
| 27 |
郭久亿, 刘洋, 郭焱林, 等. 不同典型用户侧储能配置评估与运行优化模型[J]. 电网技术, 2020, 44 (11): 4245- 4254.
|
|
GUO Jiuyi, LIU Yang, GUO Yanlin, et al. Configuration evaluation and operation optimization model of energy storage in different typical user-side[J]. Power System Technology, 2020, 44 (11): 4245- 4254.
|
| 28 |
李明, 尹文良, 李勇康, 等. 多源耦合不确定性下含电氢储能的微电网低碳容量优化配置研究[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2025, 14 (5): 1969- 1981.
|
|
LI Ming, YIN Wenliang, LI Yongkang, et al. Low-carbon capacity optimal configuration of microgrid with hydrogen energy storage under multi-source coupling uncertainties[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2025, 14 (5): 1969- 1981.
|
| 29 |
河北省发展和改革委员会. 河北省组织开展电网企业代理购电工作实施方案(冀发改能价〔2021〕1626号)[EB/OL]. (2021-11-23)[2025-09-10]. http://www.he.sgcc.com.cn/html/main/col466/2024-07/17/20240717224048613298204_1.html.
|
| 30 |
河北省发展和改革委员会. 河北省发展和改革委员会关于进一步完善冀北电网工商业及其他用户分时电价政策的通知(冀发改能价[2023]1711号)[EB/OL]. (2023-12-13)[2025-09-10]. https://hbdrc.hebei.gov.cn/xxgk_2232/zc/wzcwj/202312/t20231214_107025.html.
|
| 31 |
夏佳伟, 张一帆, 雷浩, 等. 考虑高效氢能利用和碳捕集的综合能源系统低碳优化调度[J]. 电力建设, 2024, 45 (12): 100- 111.
|
|
XIA Jiawei, ZHANG Yifan, LEI Hao, et al. Low-carbon economic dispatch of integrated energy system considering efficient hydrogen utilization and carbon capture equipment[J]. Electric Power Construction, 2024, 45 (12): 100- 111.
|