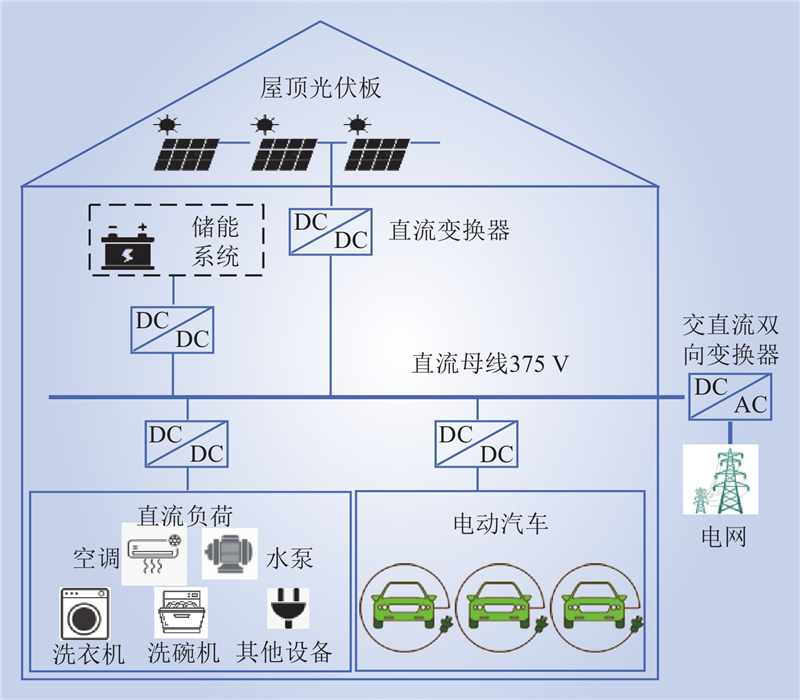
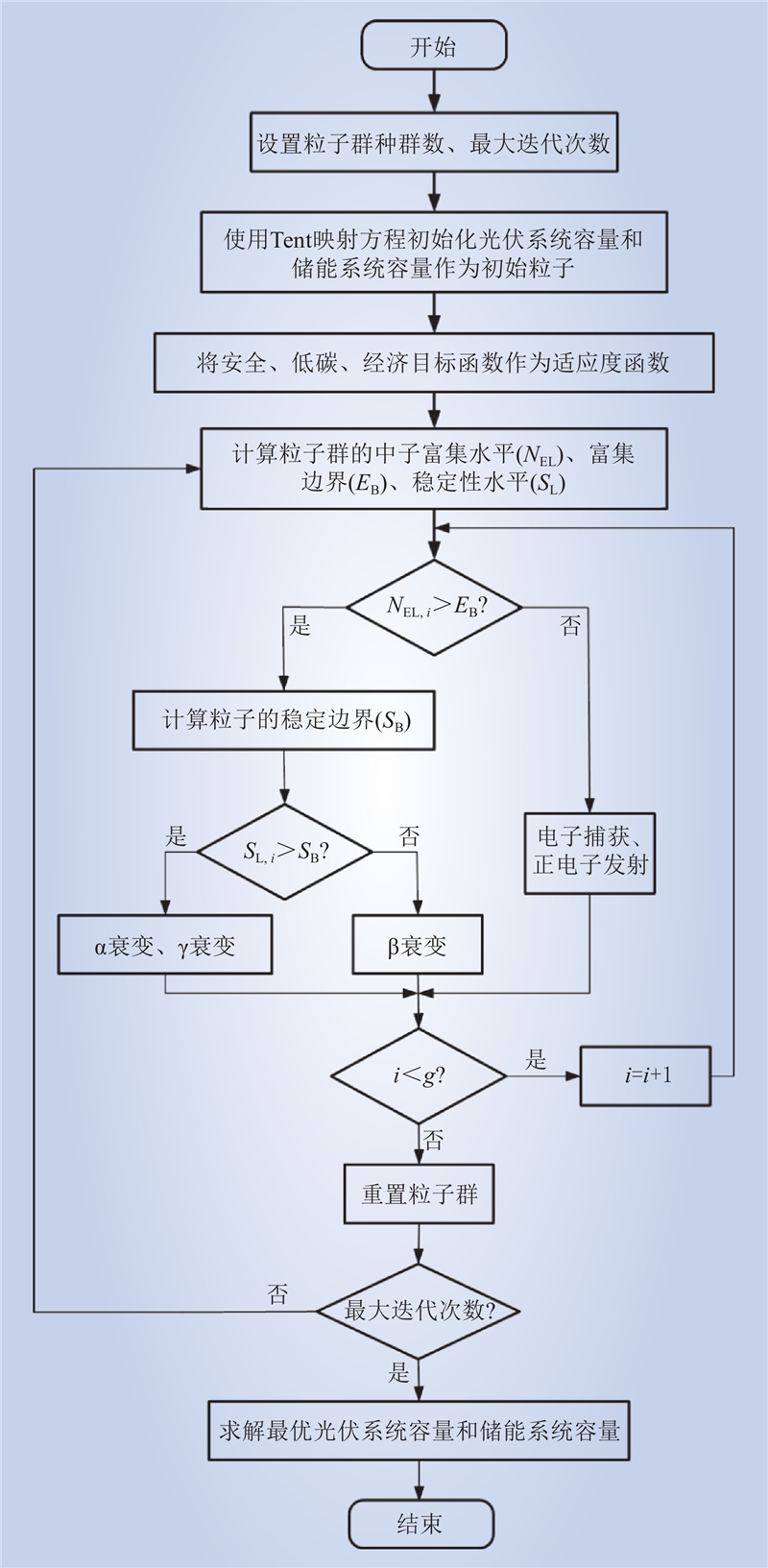
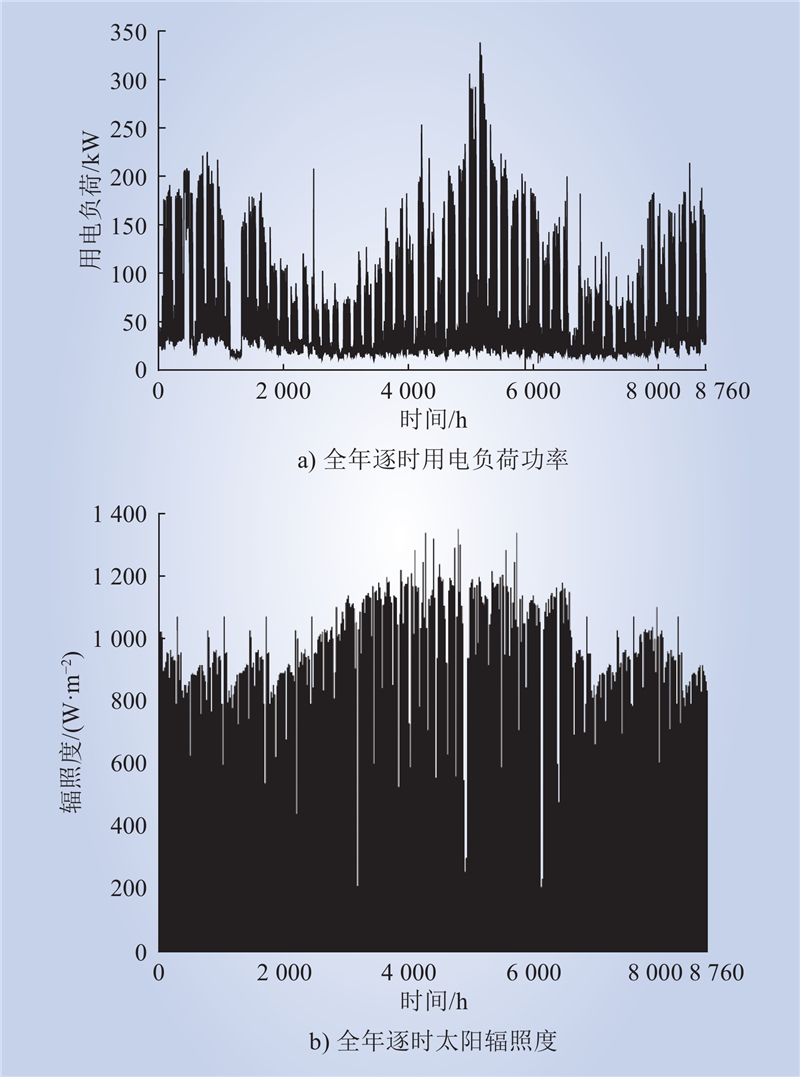
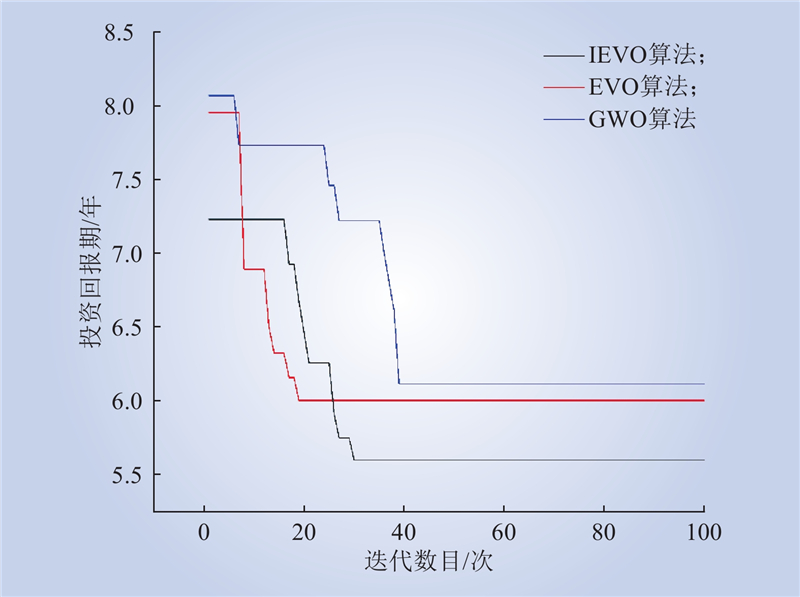
| 1 |
翟苏巍, 李银银, 杜凡, 等. 考虑海量分布式能源接入的配电网分布式无功控制策略[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (8): 138- 144.
|
|
ZHAI Suwei, LI Yinyin, DU Fan, et al. Distributed reactive power control strategy of distribution network considering massive distributed energy access[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (8): 138- 144.
|
| 2 |
王海军, 居蓉蓉, 董颖华. 基于时空关联特征与B-LSTM模型的分布式光伏功率区间预测[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (7): 74- 80.
|
|
WANG Haijun, JU Rongrong, DONG Yinghua. Distributed photovoltaic power interval prediction based on spatio-temporal correlation feature and B-LSTM model[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (7): 74- 80.
|
| 3 |
刘江, 高淑萍, 孙向东, 等. 弱电网下光伏并网逆变器谐振抑制方法综述[J]. 南方电网技术, 2024, 18 (3): 65- 71.
|
|
LIU Jiang, GAO Shuping, SUN Xiangdong, et al. Overview of resonance suppression methods for PV grid-connected inverters in weak grid[J]. Southern Power System Technology, 2024, 18 (3): 65- 71.
|
| 4 |
李泽成, 孙燕盈. 新型电力系统下考虑分布式光伏并网的配电网可靠性评估[J]. 山东电力技术, 2023, 50 (5): 1- 5, 47.
|
|
LI Zecheng, SUN Yanying. Reliability evaluation of distribution network considering flexible grid connection of distributed photovoltaic power generations[J]. Shandong Electric Power, 2023, 50 (5): 1- 5, 47.
|
| 5 |
江亿. 光储直柔: 助力实现零碳电力的新型建筑配电系统[J]. 暖通空调, 2021, 51 (10): 1- 12.
|
|
JIANG Yi. PSDF(photovoltaic, storage, DC, flexible)—a new type of building power distribution system for zero carbon power system[J]. Heating Ventilating & Air Conditioning, 2021, 51 (10): 1- 12.
|
| 6 |
孙冬梅, 康靖, 郝斌, 等. “光储直柔” 建筑案例特征分析及系统设计相关问题探讨[J]. 暖通空调, 2024, 54 (3): 118- 129, 34.
|
|
SUN Dongmei, KANG Jing, HAO Bin, et al. Analysis on characteristics of PEDF (photovoltaic, energy storage, direct current and flexibility) building cases and discussion on related problems of system design[J]. Heating Ventilating & Air Conditioning, 2024, 54 (3): 118- 129, 34.
|
| 7 |
张雷, 肖伟栋, 蒋纯冰, 等. 光伏办公建筑的关键设备容量配置方法[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (3): 152- 159, 169.
|
|
ZHANG Lei, XIAO Weidong, JIANG Chunbing, et al. Capacity allocation method of key equipment in PV system applied in office buildings[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (3): 152- 159, 169.
|
| 8 |
王超, 胡浩, 郑炼, 等. 基于智慧蓄电池的光伏储能系统及其控制策略[J]. 可再生能源, 2022, 40 (4): 506- 512.
|
|
WANG Chao, HU Hao, ZHENG Lian, et al. Photovoltaic energy storage system based on smart battery and its control strategy[J]. Renewable Energy Resources, 2022, 40 (4): 506- 512.
|
| 9 |
NUVVULA R S S, DEVARAJ E, MADURAI ELAVARASAN R, et al. Multi-objective mutation-enabled adaptive local attractor quantum behaved particle swarm optimisation based optimal sizing of hybrid renewable energy system for smart cities in India[J]. Sustainable Energy Technologies and Assessments, 2022, 49, 101689.
|
| 10 |
卢毓东, 陈益. “双碳” 目标下绿色人工智能技术研究综述[J]. 浙江电力, 2023, 42 (10): 45- 56.
|
|
LU Yudong, CHEN Yi. A review of green AI research under carbon peaking and neutrality goals[J]. Zhejiang Electric Power, 2023, 42 (10): 45- 56.
|
| 11 |
宗龙, 赵亚典. 基于光伏建筑一体化的综合能源管控系统设计[J]. 内蒙古电力技术, 2023, 41 (6): 68- 74.
|
|
ZONG Long, ZHAO Yadian. Design of comprehensive energy management and control system based on building integrated photovoltaics[J]. Inner Mongolia Electric Power, 2023, 41 (6): 68- 74.
|
| 12 |
LYU C H, ZHANG Y C, BAI Y L, et al. Inner-outer layer co-optimization of sizing and energy management for renewable energy microgrid with storage[J]. Applied Energy, 2024, 363, 123066.
|
| 13 |
赵才, 张志飞, 陈丹风, 等. 基于改进蜂群算法的微电网优化调度[J]. 电气自动化, 2022, 44 (5): 46- 49.
|
|
ZHAO Cai, ZHANG Zhifei, CHEN Danfeng, et al. Optimal scheduling of microgrid based on improved bee colony algorithm[J]. Electrical Automation, 2022, 44 (5): 46- 49.
|
| 14 |
赵宇明, 郭佩乾, 袁志昌, 等. 建筑直流配用电系统运行控制策略与示范应用[J]. 南方电网技术, 2023, 17 (1): 63- 72.
|
|
ZHAO Yuming, GUO Peiqian, YUAN Zhichang, et al. Operation control strategy and demonstration application of DC building distribution and utilization system[J]. Southern Power System Technology, 2023, 17 (1): 63- 72.
|
| 15 |
王扬, 路菲, 李骥, 等. 基于综合优化目标的低碳园区能源系统规划配置[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (4): 14- 24.
|
|
WANG Yang, LU Fei, LI Ji, et al. Multi-energy system planning and configuration study for low-carbon parks based on comprehensive optimization objectives[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (4): 14- 24.
|
| 16 |
陈东海, 马旭, 王波, 等. 基于多阶段注意力机制的建筑空调负荷预测方法[J]. 浙江电力, 2023, 42 (10): 57- 64.
|
|
CHEN Donghai, MA Xu, WANG Bo, et al. A load forecasting method for building air conditioning based on multi-stage attention mechanism[J]. Zhejiang Electric Power, 2023, 42 (10): 57- 64.
|
| 17 |
孙婉玉, 蒋天茁, 付强, 等. 谷电储能供暖系统优化设计方法[J]. 电力科技与环保, 2024, 40 (3): 286- 295.
|
|
SUN Wanyu, JIANG Tianzhuo, FU Qiang, et al. Optimization design method of valley power energy storage heating system[J]. Electric Power Technology and Environmental Protection, 2024, 40 (3): 286- 295.
|
| 18 |
潘雨情, 祁兵, 李彬. 新能源园区零碳评价指标体系研究[J]. 内蒙古电力技术, 2023, 41 (5): 12- 18.
|
|
PAN Yuqing, QI Bing, LI Bin. Research on zero carbon evaluation index system for new energy parks[J]. Inner Mongolia Electric Power, 2023, 41 (5): 12- 18.
|
| 19 |
吴俊, 庞波, 方鑫, 等. 建筑整合式太阳能微型聚光器集热性能测试与分析[J]. 东北电力大学学报, 2022, 42 (2): 26- 32.
|
|
WU Jun, PANG Bo, FANG Xin, et al. Experimental performance of a building-integrated linear FresnelMicro-concentrator[J]. Journal of Northeast Electric Power University, 2022, 42 (2): 26- 32.
|
| 20 |
蒋棹骏, 向月, 谈竹奎, 等. 计及需求响应的高比例清洁能源园区储能容量优化配置[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (12): 147- 155, 163.
|
|
JIANG Zhaojun, XIANG Yue, TAN Zhukui, et al. Optimal allocation of energy storage capacity in high proportion clean energy parks considering demand response[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (12): 147- 155, 163.
|
| 21 |
潘忠志, 孔宁, 王燕涛. 改进新能源消纳的配电网资源优化配置研究[J]. 东北电力大学学报, 2023, 43 (6): 71- 78.
|
|
PAN Zhongzhi, KONG Ning, WANG Yantao. Joint optimal allocation method of energy-load-storage in power SupplyArea to improve new energy consumption capacity[J]. Journal of Northeast Electric Power University, 2023, 43 (6): 71- 78.
|
| 22 |
赵斌, 梁告, 姜孟浩, 等. 光储系统并网功率波动平抑及储能优化配置[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45 (3): 423- 433.
|
|
ZHAO Bin, LIANG Gao, JIANG Menghao, et al. Grid-connected power fluctuation suppression and energy storage optimization configuration of photovoltaic-energy storage system[J]. Power Generation Technology, 2024, 45 (3): 423- 433.
|
| 23 |
杨锡勇, 张仰飞, 林纲, 等. 考虑需求响应的源-荷-储多时间尺度协同优化调度策略[J]. 发电技术, 2023, 44 (2): 253- 260.
|
|
YANG Xiyong, ZHANG Yangfei, LIN Gang, et al. Multi-time scale collaborative optimal scheduling strategy for source-load-storage considering demand response[J]. Power Generation Technology, 2023, 44 (2): 253- 260.
|