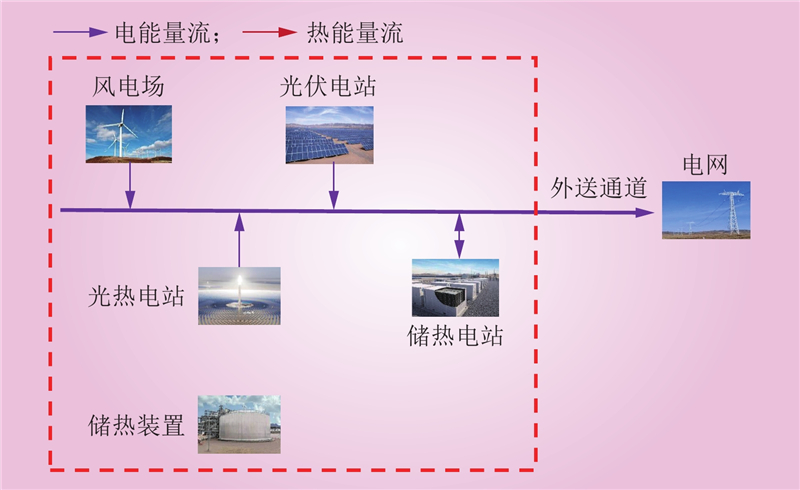
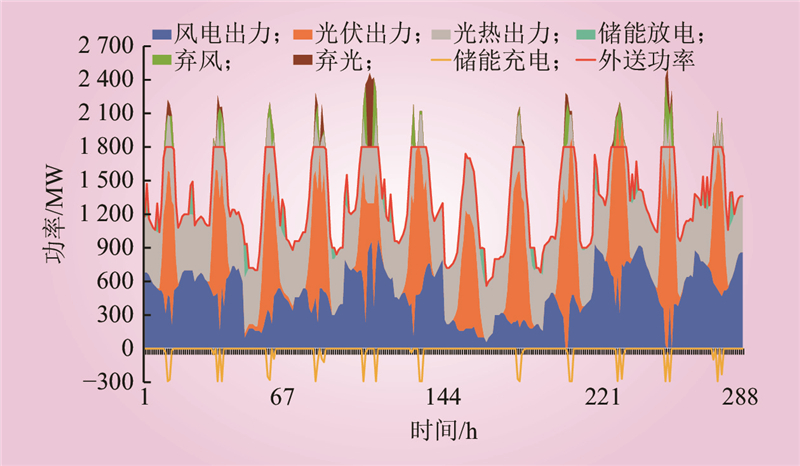
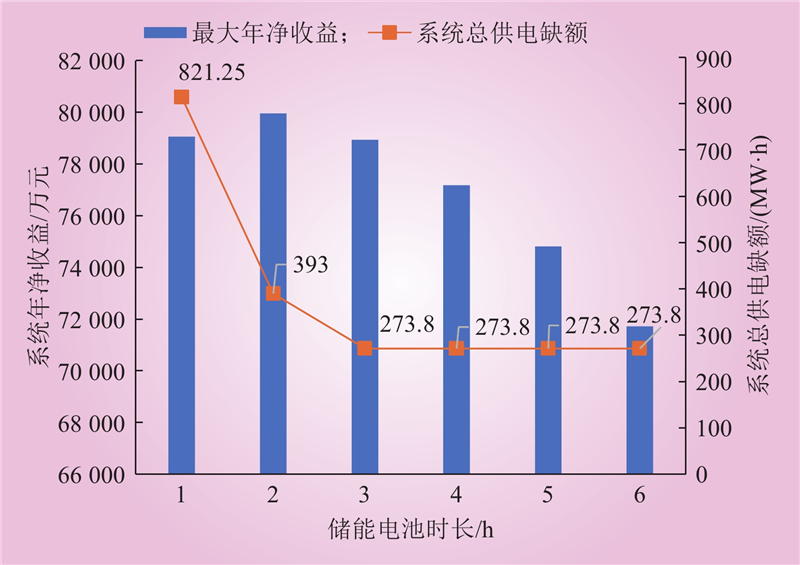
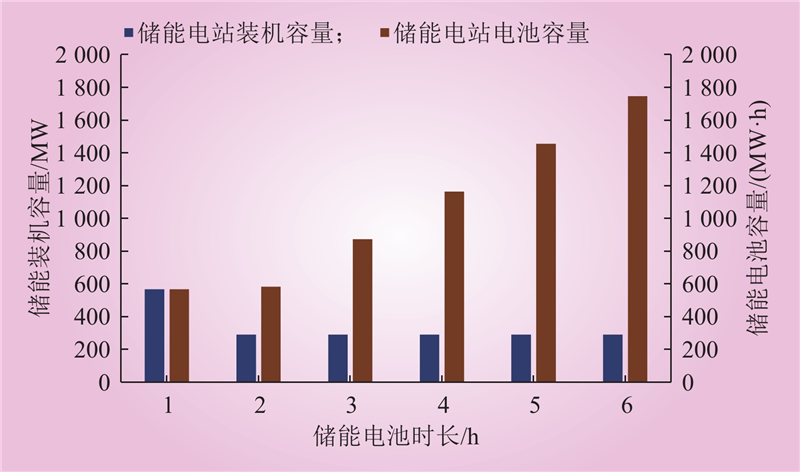
| 1 |
国家能源局. 关于报送“十四五”电力源网荷储一体化和多能互补工作方案的通知[R]. 北京: 国家能源局, 2023.
|
| 2 |
文云峰, 杨伟峰, 汪荣华, 等. 构建100%可再生能源电力系统述评与展望[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2020, 40 (6): 1843- 1856.
|
|
WEN Yunfeng, YANG Weifeng, WANG Ronghua. Review and prospect of toward 100% renewable energy power systems[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2020, 40 (6): 1843- 1856.
|
| 3 |
HAN Z X, FANG D B, YANG P W, et al. Cooperative mechanisms for multi-energy complementarity in the electricity spot market[J]. Energy economics, 2023, 127: 107108.
|
| 4 |
潘尔生, 李晖, 肖晋宇, 等. 考虑大范围多种类能源互补的中国西部清洁能源开发外送研究[J]. 中国电力, 2018, 51 (9): 158- 164.
|
|
PAN Ersheng, LI Hui, XIAO Jinyu, et al. Research on the development and transmission of clean energy in western china considering wide range coordination of multi-energy[J]. Electric Power, 2018, 51 (9): 158- 164.
|
| 5 |
熊文, 刘育权, 苏万煌, 等. 考虑多能互补的区域综合能源系统多种储能优化配置[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2019, 39 (1): 118- 126.
|
|
XIONG Wen, LIU Yuquan, SU Wanhuang, et al. Optimal configuration of multi-energy storage in regional integrated energy system considering multi-energy complementation[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2019, 39 (1): 118- 126.
|
| 6 |
付文龙, 卓庆澳, 吴月超等. 多能互补提供频率支撑的储能容量分布鲁棒规划方法[J]. 电网技术, 2024, 48 (1): 282- 297.
|
|
FU Wenlong, ZHUO Qingao, WU Yuechao, et al. Distributed robust planning for energy storage capacity with multi-energy complementarity providing frequency support[J]. Power system technology, 2024, 48 (1): 282- 297.
|
| 7 |
ZHU Z, ZHANG D, MISCHKE P, et al. Electricity generation costs of concentrated solar power technologies in China based on operational plants[J]. Energy, 2015, 89, 65- 74.
|
| 8 |
刘永前, 梁超, 阎洁, 等. 风-光电站中储能系统混合最优配置及其经济性研究[J]. 中国电力, 2020, 53 (12): 143- 150.
|
|
LIU Yongqian, LIANG Chao, YAN Jie, et al. Optimal configuration and economic study of hybrid energy storage system in wind and solar power plants[J]. Electric Power, 2020, 53 (12): 143- 150.
|
| 9 |
杜尔顺, 张宁, 康重庆, 等. 太阳能光热发电并网运行及优化规划研究综述与展望[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2016, 36 (21): 5765- 5775.
|
|
DU Ershun, ZHANG Ning, KANG Chongqing, et al. Reviews and prospects of the operation and planning optimization for grid integrated concentrating solar power[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2016, 36 (21): 5765- 5775.
|
| 10 |
屈小云, 吴鸣, 李奇等. 多能互补综合能源系统综合评价研究进展综述[J]. 中国电力, 2021, 54 (11): 153- 163.
|
|
QU Xiaoyun, WU Ming, LI Qi, et al. Review on comprehensive evaluation of multi-energy complementary integrated energy systems[J]. Electric power, 2021, 54 (11): 153- 163.
|
| 11 |
QI Y C, HU W, DONG Y, et al. Optimal configuration of concentrating solar power in multi energy power systems with an improved variational autoencoder[J]. Applied Energy, 2020, 274, 115124.
|
| 12 |
王永利, 向皓, 郭璐, 等. 面向多能互补的分布式光伏与电氢混合储能规划优化研究[J]. 电网技术, 2024, 48 (2): 564- 576.
|
|
WANG Yongli, XIANG Hao, GUO Lu, et al. Research on planning optimization of distributed photovoltaic and electro-hydrogen hybrid energy storage for multi-energy complementarity[J]. Power System Technology, 2024, 48 (2): 564- 576.
|
| 13 |
STARKE A R, CARDENIL J M, Escobar R, et al. Multi-objective optimization of hybrid CSP+PV system using genetic algorithm[J]. Energy, 2018, 147, 490- 503.
|
| 14 |
ZHANG X J, ELIA CAMPANA P, BI X J, et al. Capacity configuration of a hydro-wind-solar-storage bundling system with transmission constraints of the receiving-end power grid and its techno-economic evaluation[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2022, 270: 116177.
|
| 15 |
ZHANG H Y, LIAO K, YANG J W, et al. Frequency-constrained expansion planning for wind and photovoltaic power in wind-photovoltaic-hydro-thermal multi-power system[J]. Applied Energy, 2024, 356: 122401.
|
| 16 |
HUANG W J, ZHANG N, YANG J W, et al. Optimal configuration planning of multi-energy systems considering distributed renewable energy[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2019, 10 (2): 1452- 1464.
|
| 17 |
寇凌峰, 季宇, 吴鸣等. 多能互补系统全寿命周期优化配置方法[J]. 中国电力, 2020, 53 (12): 75- 82.
|
|
KOU Lingfeng, JI Yu, WU Ming, et al. Optimal configuration of multi-energy complementary system considering full life cycle[J]. Electric Power, 2020, 53 (12): 75- 82.
|
| 18 |
刘树桦, 王建学, 李清涛. 多能互补复合电站的优化配置及其在系统电源规划中的应用[J]. 电网技术, 2021, 45 (8): 3006- 3015.
|
|
LIU Shuhua, WANG Jianxue, LI Qingtao, et al. Optimal configuration of multi-energy complementary composite power plant and its application in generation expansion planning[J]. Power System Technology, 2021, 45 (8): 3006- 3015.
|
| 19 |
崔杨, 于世鹏, 王学斌, 等. 考虑系统调峰需求与光热电站收益平衡的储热容量优化配置[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2023, 43 (22): 8745- 8754.
|
|
CUI Yang, YU Shipeng, WANG Xuebin, et al. Optimal configuration of heat storage capacity considering the balance between system peak shaving demand and concentrating solar power plant revenue[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2023, 43 (22): 8745- 8754.
|
| 20 |
邵志芳, 张东强. 基于合约负荷曲线的多能互补电力系统容量优化配置[J]. 电网技术, 2021, 45 (5): 1757- 1767.
|
|
SHAO Zhifang, ZHANG Dongqiang. Capacity configuration optimization of multi-energy complementary power system based on contract load curve[J]. Power System Technology, 2021, 45 (5): 1757- 1767.
|
| 21 |
史昭娣, 王伟胜, 黄越辉, 等. 多能互补发电系统储电和储热容量分层优化规划方法[J]. 电网技术, 2020, 44 (9): 3263- 3271.
|
|
SHI Zhaodi, WANG Weisheng, HUANG Yuehui, et al. Hierarchical optimization planning for electrical energy storage and heat storage capacity planning in multi-energy complementary generation system[J]. Power System Technology, 2020, 44 (9): 3263- 3271.
|
| 22 |
安源, 郑申印, 苏瑞, 等. 风光水储多能互补发电系统双层优化研究[J]. 太阳能学报, 2023, 44 (12): 510- 517.
|
|
AN Yuan, ZHENG Shenyin, SU Rui. Research on two-layer optimization of wind-solar-water-storage multi-energy complementary power generation system[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2023, 44 (12): 510- 517.
|
| 23 |
LI Z Y, SHAHIDEHPOUR M. Privacy-preserving collaborative operation of networked microgrids with the local utility grid based on enhanced benders decomposition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2020, 11 (3): 2638- 2651.
|
| 24 |
ZHU Z A, WANG L L, WANG X, et al. Complementary operations of multi-renewable energy systems with pumped storage[J]. CSEE Journal of Power and Energy Systems, 2023, 9 (5): 1866- 1880.
|
| 25 |
ZHANG H X, LU Z X, HU W, et al. Coordinated optimal operation of hydro–wind–solar integrated systems[J]. Applied Energy, 2019, 242, 883- 896.
|
| 26 |
孙志媛, 彭博雅, 孙艳. 考虑多能互补的电力电量平衡优化调度策略[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (1): 115- 122.
|
|
SUN Zhiyuan, PENG Boya, SUN Yan. Optimal dispatch strategy of power and electricity balance based on multi-energy complementation[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (1): 115- 122.
|
| 27 |
叶林, 屈晓旭, 么艳香, 等. 风光水多能互补发电系统日内时间尺度运行特性分析[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2018, 42 (4): 158- 164.
|
|
YE Lin, QU Xiaoxu, YAO Yanxiang, et al. Analysis on intraday operation characteristics of hybrid wind-solar-hydro power generation system[J]. Automation of Electric Power System, 2018, 42 (4): 158- 164.
|
| 28 |
KLEINERT T, LABBÉ M, LJUBIĆ I, et al. A survey on mixed-integer programming techniques in bilevel optimization[J]. EURO Journal on Computational Optimization, 2021, 9, 100007.
|
| 29 |
AUGUSTO A A, DO COUTTO FILHO M B, DE SOUZA J C S, et al. Branch-and-bound guided search for critical elements in state estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2019, 34 (3): 2292- 2301.
|
| 30 |
HE C, LV Y F, MARTINI H, et al. A branch-and-bound approach for estimating covering functionals of convex bodies[J]. Journal of Optimization Theory and Applications, 2023, 196 (3): 1036- 1055.
|