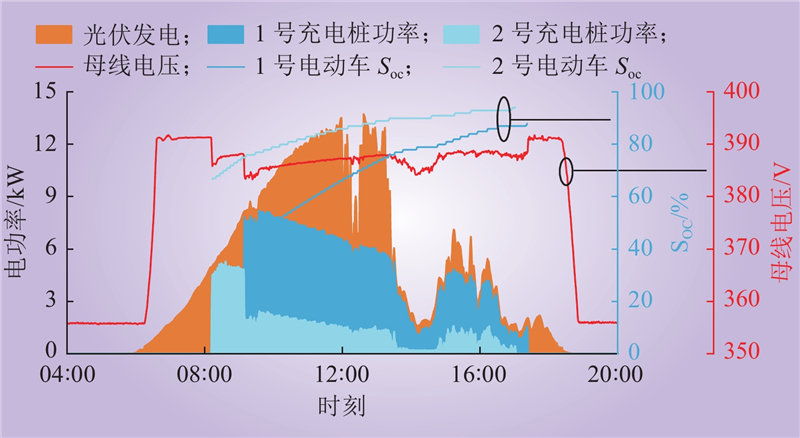
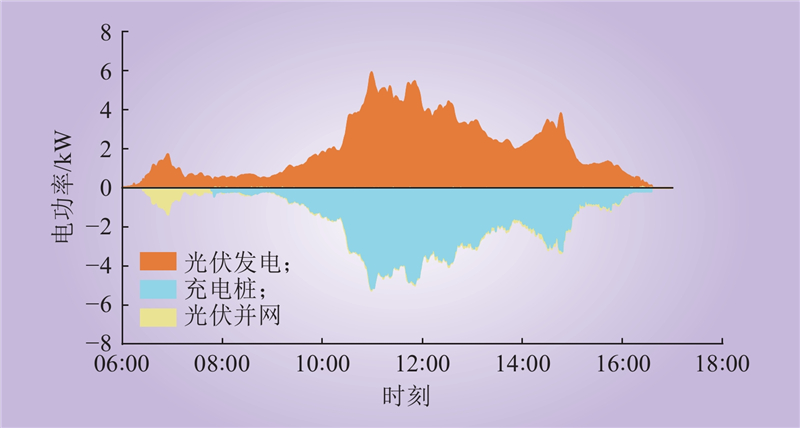
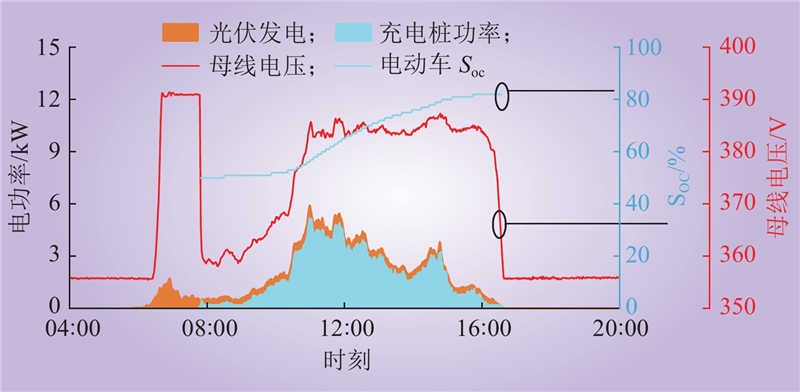
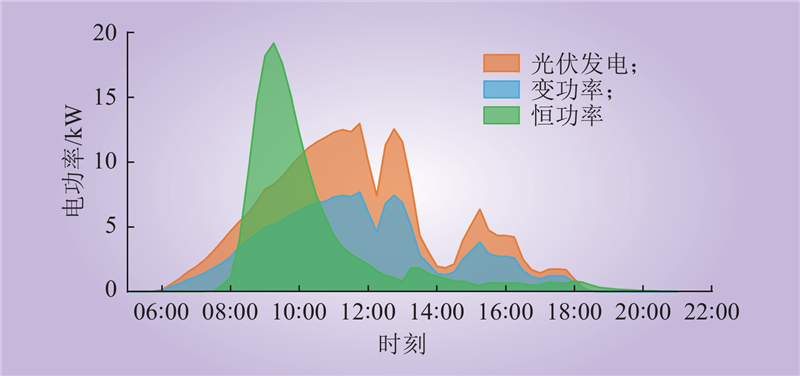
| 1 |
国家发展改革委, 国家能源局. 《关于促进新时代新能源高质量发展的实施方案》[EB/OL]. (2022-05-30)[2023-07-10]. http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2022-05/30/content_5693013.htm.
|
| 2 |
詹天津, 谢玉荣. 国内分布式光伏发展形势分析及思考[J]. 华电技术, 2021, 43 (12): 60- 65.
|
|
ZHAN Tianjin, XIE Yurong. Development status analysis and consideration on domestic distributed PV energy[J]. Huadian Technology, 2021, 43 (12): 60- 65.
|
| 3 |
中国汽车工程学会. 节能与新能源汽车技术路线图2.0[R]. 上海: 中国汽车工程学会, 2020.
|
| 4 |
GARCIA-VILLALOBOS J, ZAMORA I, San MARTIN J I, et al. Plug-in electric vehicles in electric distribution networks: A review of smart charging approaches[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2014, 38, 717- 731.
|
| 5 |
BIRNIE D. Solar-to-vehicle (s2v) systems for powering commuters of the future[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2009, 186 (2): 539- 542.
|
| 6 |
BHATTI A, SALAM Z, AZIZ M, et al. Electric vehicles charging using photovoltaic: Status and technological review[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2016, 54, 34- 47.
|
| 7 |
QUENTIN H, PEREZ Y. Interactions between electric mobility and photovoltaic generation: a review[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2018, 94, 510- 522.
|
| 8 |
FACHRIZAL R, SHEPERO M, MEER D V D, et al. Smart charging of electric vehicles considering photovoltaic power production and electricity consumption: a review[J]. eTransportation, 2020, 4, 100056.
|
| 9 |
安佳坤, 杨书强, 王涛, 等. 电动汽车聚合下的微能源互联网优化调度策略[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (5): 80- 88.
|
|
AN Jiakun, YANG Shuqiang, WANG Tao, et al. Optimal scheduling strategy for micro energy Internet under electric vehicles aggregation[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (5): 80- 88.
|
| 10 |
RUIZ V, PFRANG A, KRISTON A, et al. A review of international abuse testing standards and regulations for lithium ion batteries in electric and hybrid electric vehicles[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2018, 81, 1427- 1452.
|
| 11 |
清华大学建筑节能研究中心. 中国建筑节能年度发展研究报告-2021-城镇住宅专题[M]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2021.
|
| 12 |
曾伟哲, 曾启林, 黎恒, 等. 基于HPSOGA的多目标电动汽车充电优化[J]. 南方电网技术, 2023, 17 (1): 94- 102, 135.
|
|
ZENG Weizhe, ZENG Qilin, LI Heng, et al. Multi-objective electric vehicle charging optimization based on HPSOGA[J]. Southern Power System Technology, 2023, 17 (1): 94- 102, 135.
|
| 13 |
陈明强, 高健飞, 畅国刚, 等. V2G模式下微网电动汽车有序充电策略研究[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2020, 48 (8): 141- 148.
|
|
CHEN Mingqiang, GAO Jianfei, CHANG Guogang, et al. Research on orderly charging strategy of micro-grid electric vehicles in V2G model[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2020, 48 (8): 141- 148.
|
| 14 |
方胜利, 朱晓亮, 马春艳, 等. 住宅小区电动汽车集群有序充电策略研究[J/OL]. 安徽大学学报(自然科学版): 1–9[2023-10-23]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/34.1063.N.20230506.1744.002.html.
|
|
FANG Shengli, ZHU Xiaoliang, MA Chunyan, et al. Research on orderly charging strategy of electric vehicle cluster in residential area [J/OL]. Journal of Anhui University (Natural Science Edition): 1–9[2023-10-23]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/34.1063.N.20230506.1744.002.html.
|
| 15 |
CHEN X Y, ZHANG H C, XU Z W, et al. Impacts of fleet types and charging modes for electric vehicles on emissions under different penetrations of wind power[J]. Nature Energy, 2018: 413–421.
|
| 16 |
马文彪, 程亮, 陈红坤. 考虑电动汽车有序充电的主动配电网网架规划[J]. 电力科学与技术学报, 2020, 35 (3): 83- 91.
|
|
MA Wenbiao, CHENG Liang, CHEN Hongkun. Framework planning considering coordinated charging of electric vehicles in active distribution networks[J]. Journal of Electric Power Science and Technology, 2020, 35 (3): 83- 91.
|
| 17 |
LI C Z, ZHANG L B, OU Z H, et al. Robust model of electric vehicle charging station location considering renewable energy and storage equipment[J]. Energy, 2021, 238 (6): 121713.
|
| 18 |
陈浩然, 赵晓丽. 考虑分布式光伏发电的电动汽车充电策略研究[J]. 中国管理科学, 2023, 31 (4): 161- 170.
|
|
CHEN Haoran, ZHAO Xiaoli. Research on electric vehicle charging optimization considering distributed photovoltaic power generation[J]. Chinese Journal of Management Science, 2023, 31 (4): 161- 170.
|
| 19 |
党杰, 汤奕, 宁佳, 等. 基于用户意愿和出行规律的电动汽车充电负荷分配策略[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2015, 43 (16): 8- 15.
|
|
DANG Jie, TANG Yi, NING Jia, et al. A strategy for distribution of electric vehicles charging load based on user intention and trip rule[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2015, 43 (16): 8- 15.
|
| 20 |
南斌, 徐成司, 董树锋, 等. 考虑多充电模式的充电桩优化控制策略[J]. 电力工程技术, 2021, 40 (5): 2- 9.
|
|
NAN Bin, XU Chengsi, DONG Shufeng, et al. Optimized control strategy of charging piles considering multiple charging modes[J]. Electric Power Engineering Technology, 2021, 40 (5): 2- 9.
|
| 21 |
陈奇芳, 刘念, 陈征, 等. 考虑充电需求与随机事件的光伏充电站实时运行策略[J]. 电工技术学报, 2016, 31 (18): 142- 150.
|
|
CHEN Qifang, LIU Nian, CHEN Zheng, et al. Real-time operation strategy for PV-based EV charging station considering charging demand and random events[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2016, 31 (18): 142- 150.
|
| 22 |
CHANDRA MAHATO G, RANJAN BISWAL S, ROY CHOUDHURY T, et al. Review of active power control techniques considering the impact of MPPT and FPPT during high PV penetration[J]. Solar Energy, 2023, 251, 404- 419.
|
| 23 |
李雨桐, 郝斌, 童亦斌, 等. 《民用建筑直流配电设计标准》解读[J]. 建筑电气, 2022, 41 (7): 25- 32.
|
|
LI Yutong, HAO Bin, TONG Yibin, et al. Interpretation of design standard for direct current power distribution of civil buildings[J]. Building Electricity, 2022, 41 (7): 25- 32.
|
| 24 |
LIU X C, FU Z, QIU S Y, et al. Building-centric investigation into electric vehicle behavior: a survey-based simulation method for charging system design[J]. Energy, 2023, 271, 127010.
|