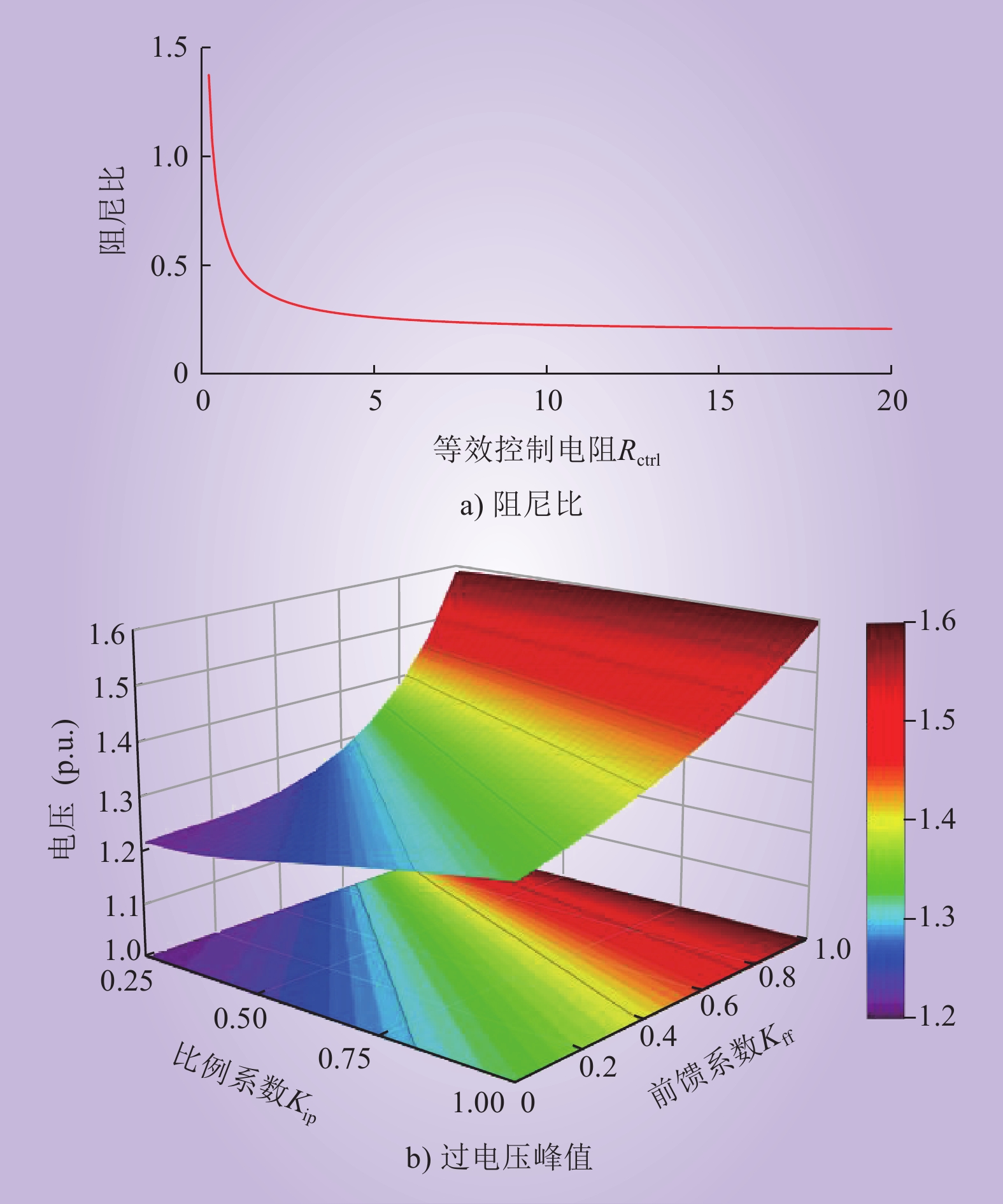
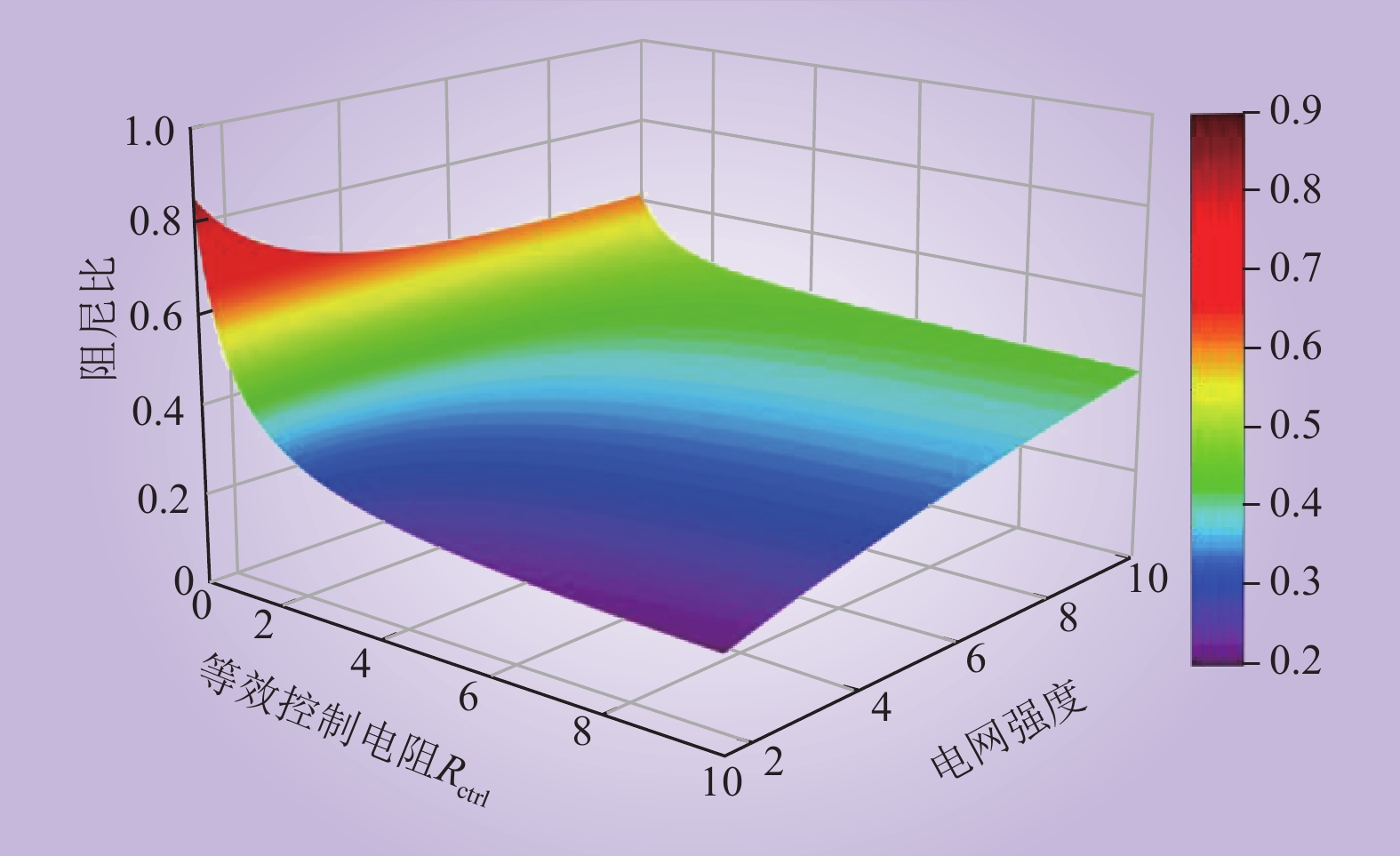
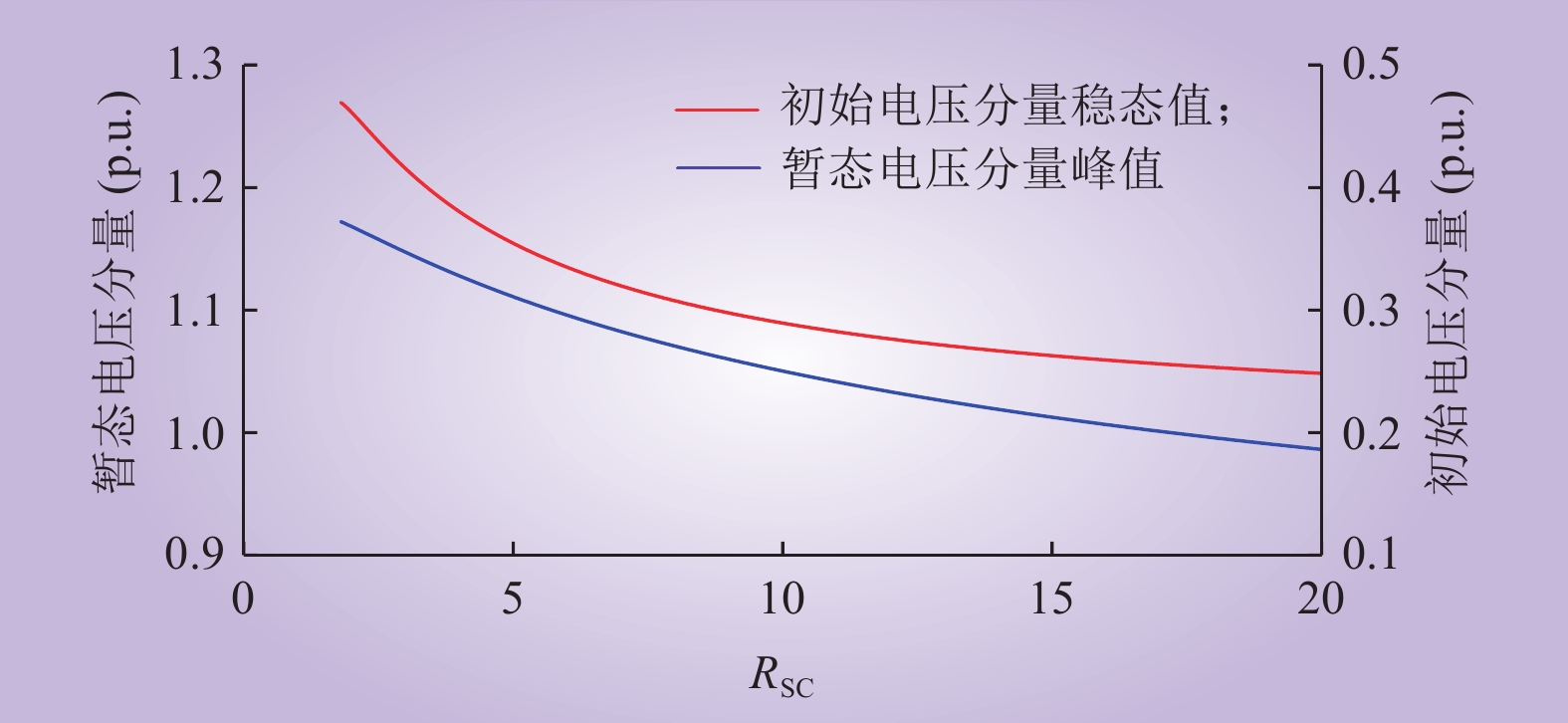
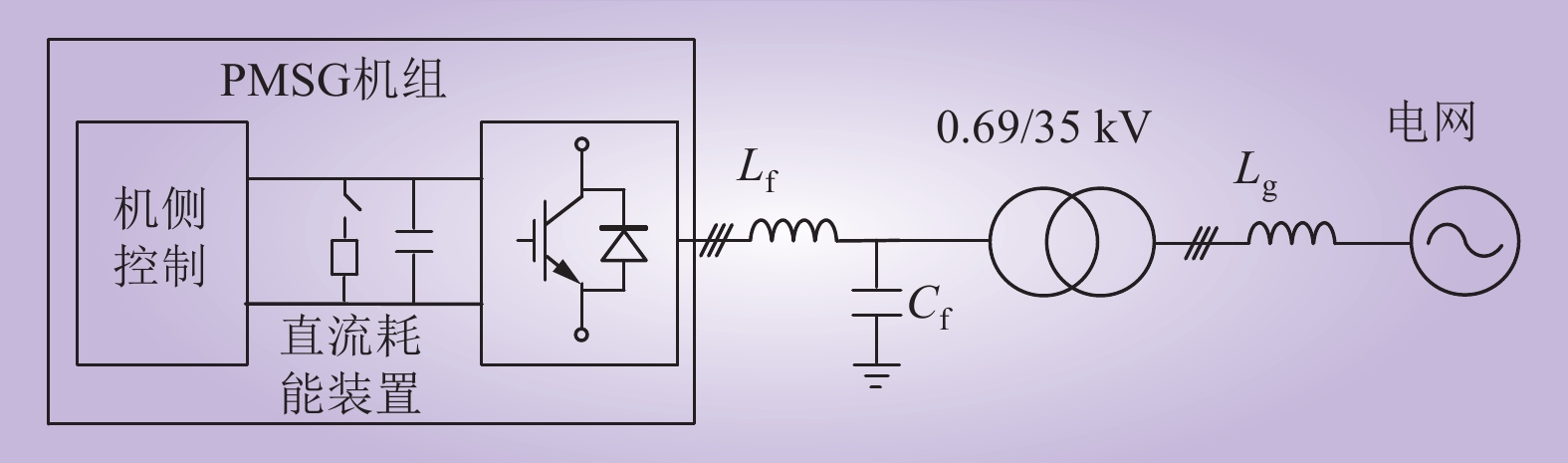
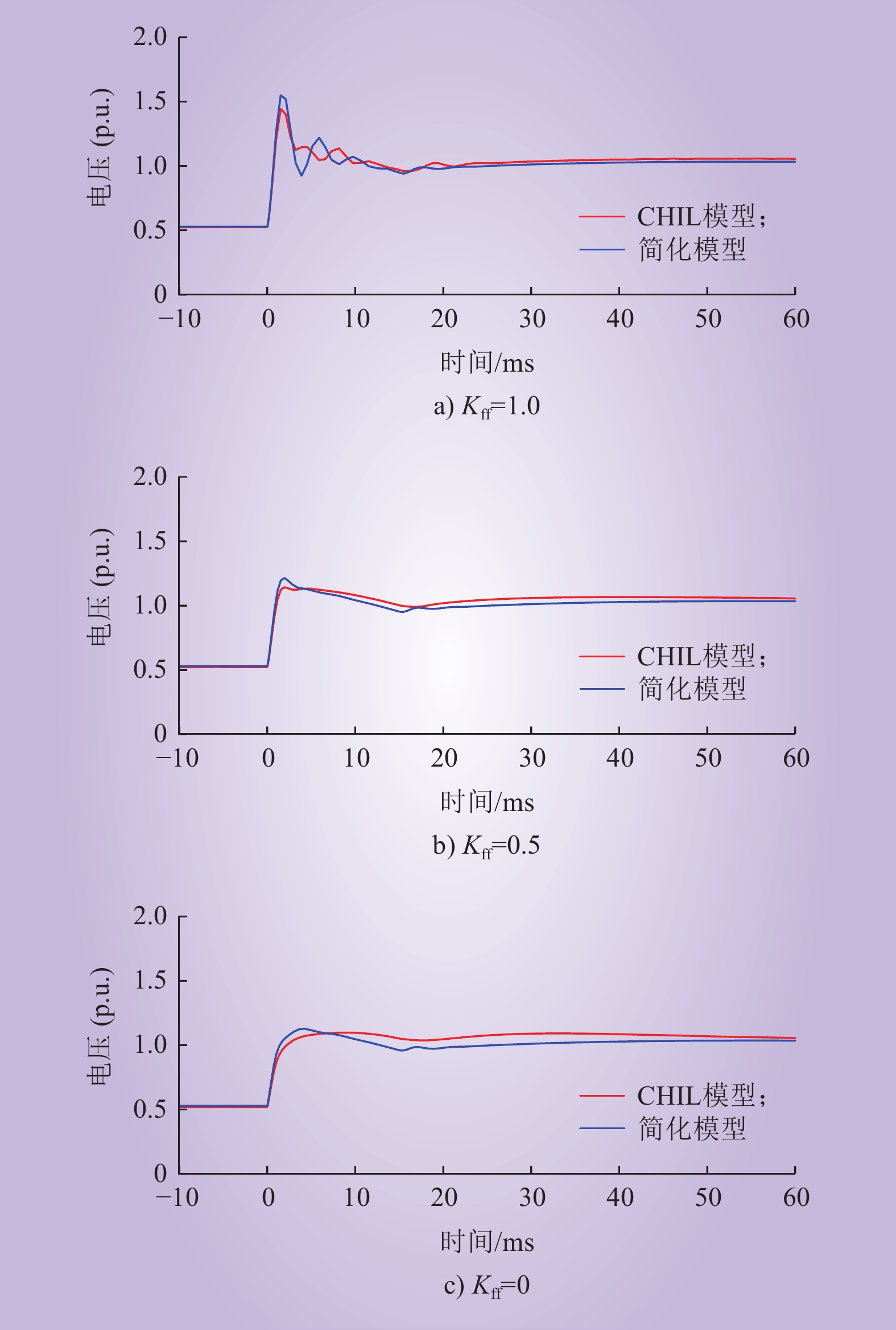
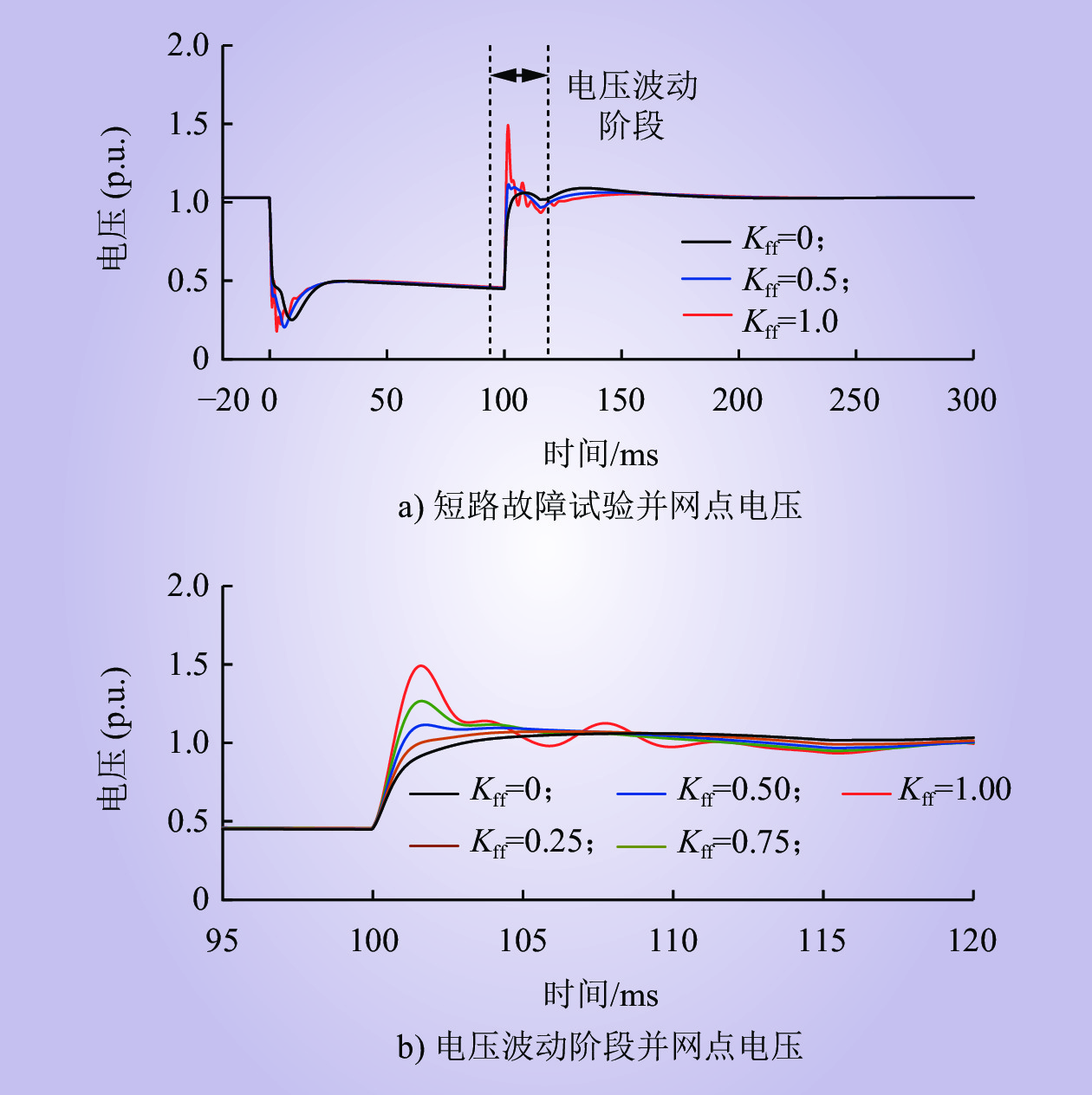
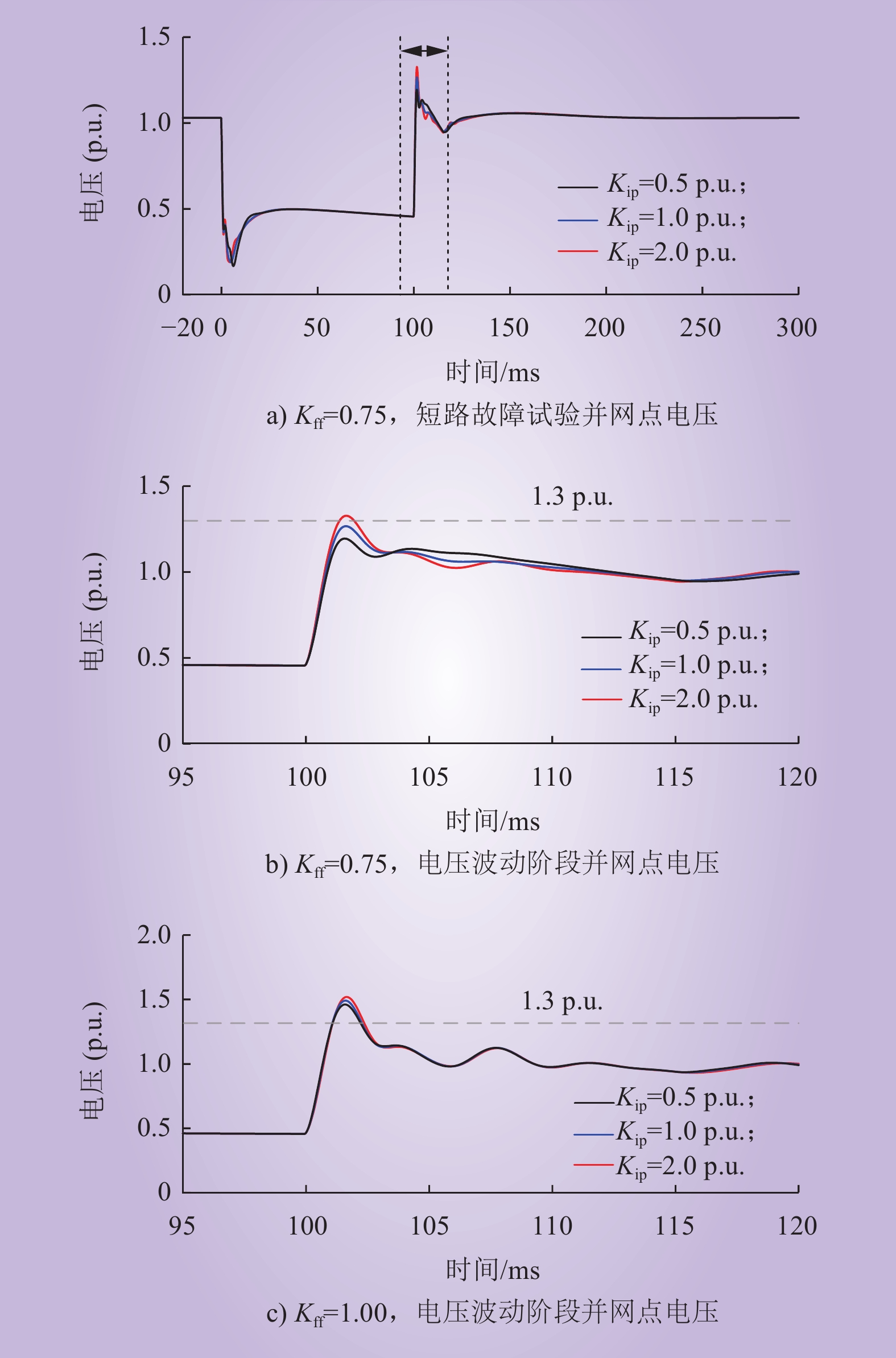
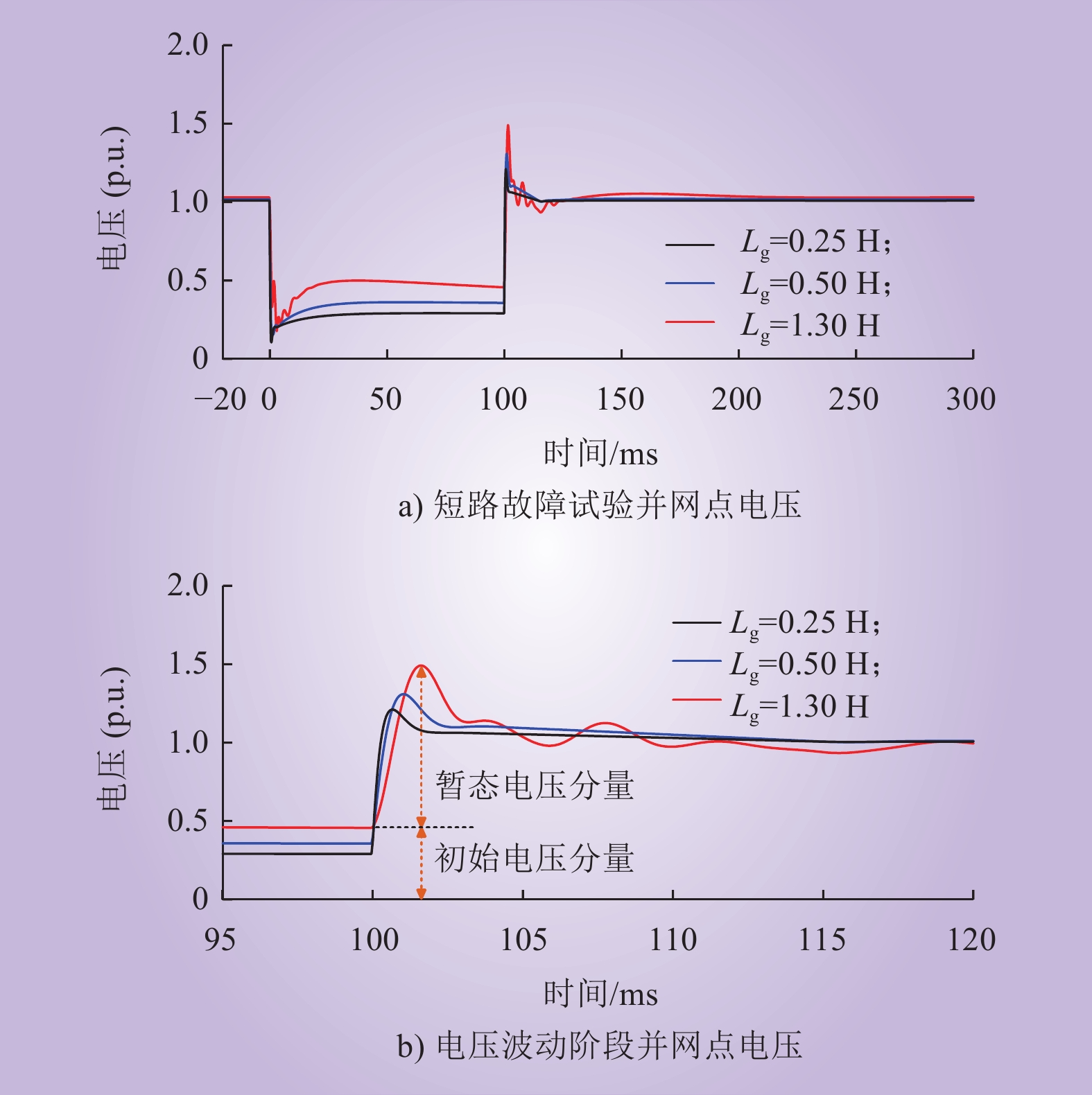
| 1 |
《新型电力系统发展蓝皮书》编写组. 新型电力系统发展蓝皮书[M]. 北京: 中国电力出版社, 2023.
|
| 2 |
王伟胜, 李光辉, 何国庆, 等. 面向新型电力系统的新能源并网控制挑战与展望[J]. 新型电力系统, 2023, (2): 145- 160.
|
|
WANG Weisheng, LI Guanghui, HE Guoqing, et al. Challenges and prospects of grid connection control of renewable energy for new power systems[J]. New Type Power Systems, 2023, (2): 145- 160.
|
| 3 |
秦世耀, 齐琛, 李少林, 等. 电压源型构网风电机组研究现状及展望[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2023, 43 (4): 1314- 1334.
|
|
QIN Shiyao, QI Chen, LI Shaolin, et al. Review of the voltage-source grid forming wind turbine[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2023, 43 (4): 1314- 1334.
|
| 4 |
刘辉, 王阔. 新能源低电压穿越无功电流对暂态电压安全约束的影响[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (2): 152- 158.
|
|
LIU Hui, WANG Kuo. LVRT reactive current index of renewable units based on the constraints of transient voltage[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (2): 152- 158.
|
| 5 |
WANG W S, LI G H, GUO J B. Large-scale renewable energy transmission by HVDC: challenges and proposals[J]. Engineering, 2022, 19, 252- 267.
|
| 6 |
于思奇, 孙大卫, 吴林林, 等. 新能源汇集系统短路故障清除后的暂态过电压机理[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2023, 43 (9): 179- 185.
|
|
YU Siqi, SUN Dawei, WU Linlin, et al. Transient overvoltage mechanism after short circuit fault removal of renewable energy collection system[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2023, 43 (9): 179- 185.
|
| 7 |
赵溶溶, 柯德平, 孙元章, 等. 考虑直流闭锁暂态过电压约束的送端电网换流站高效无功规划[J]. 南方电网技术, 2022, 16 (7): 10- 21.
|
|
ZHAO Rongrong, KE Deping, SUN Yuanzhang, et al. Efficient reactive power planning of converter station in HVDC sending system considering HVDC blocking transient overvoltage constraint[J]. Southern Power System Technology, 2022, 16 (7): 10- 21.
|
| 8 |
郄朝辉, 李兆伟, 王维洲, 等. 直流闭锁故障下风电并网功率和直流输送功率的耦合关系分析[J]. 中国电力, 2021, 54 (6): 175- 182.
|
|
QIE Zhaohui, LI Zhaowei, WANG Weizhou, et al. Coupling relationship between wind power grid-connected power and DC transmission power with DC block fault[J]. Electric Power, 2021, 54 (6): 175- 182.
|
| 9 |
秦世耀, 姜蓉蓉, 刘晋, 等. UHVDC闭锁引发风电场暂态过电压分析及HVRT协调控制[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2020, 40 (6): 63- 69, 1–4.
|
|
QIN Shiyao, JIANG Rongrong, LIU Jin, et al. Transient overvoltage analysis of wind farm with UHVDC block and HVRT coordinated control[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2020, 40 (6): 63- 69, 1–4.
|
| 10 |
周文俊, 曹毅, 李杰, 等. 考虑风电场调控裕度的风火打捆直流外送系统无功电压紧急控制策略[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (4): 77- 87.
|
|
ZHOU Wenjun, CAO Yi, LI Jie, et al. Reactive voltage emergency control strategy of wind-thermal-bundled DC transmission system considering wind farm regulation margin[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (4): 77- 87.
|
| 11 |
梁伟, 吴林林, 赖启平, 等. 风电直流送出系统送端交流故障下风机过电压研究[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (4): 28- 37.
|
|
LIANG Wei, WU Linlin, LAI Qiping, et al. Study on overvoltage of wind farm under AC fault at sending end of HVDC transmission system[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (4): 28- 37.
|
| 12 |
孙大卫, 吴林林, 刘辉, 等. 弱电网直驱风机低电压穿越特性及其对机端暂态电压的影响[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2021, 41 (14): 4777- 4786.
|
|
SUN Dawei, WU Linlin, LIU Hui, et al. Effect of the low voltage ride through characteristics on PMSG terminal transient voltage in weakly-synchronized gird[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2021, 41 (14): 4777- 4786.
|
| 13 |
徐潜, 王彤, 王增平. 计及锁相环和电流内环暂态过程的逆变型电源故障电流解析方法[J]. 电网技术, 2024, 48 (6): 2603- 2612.
|
|
XU Qian, WANG Tong, WANG Zengping. Fault current analysis method of inverter-interfaced renewable energy sources with PLL and current inner loop transient processes[J]. Power System Technology, 2024, 48 (6): 2603- 2612.
|
| 14 |
赵博元, 路晨, 陈磊, 等. 锁相环动态对切换延迟导致的暂态过电压的影响[J]. 电网技术, 2025, 49 (1): 284- 294.
|
|
ZHAO Boyuan, LU Chen, CHEN Lei, et al. impact of phase-locked loop dynamics on transient over-voltage in VSC due to switching delays[J]. Power System Technology, 2025, 49 (1): 284- 294.
|
| 15 |
刘其辉, 闫佳颖, 吴勇, 等. 计及锁相误差的双馈风电并网系统暂态过电压特性与抑制[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2023, 47 (11): 165- 173.
|
|
LIU Qihui, YAN Jiaying, WU Yong, et al. Characteristics and suppression of transient overvoltage for DFIG wind power grid-connected system considering phase locking error[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2023, 47 (11): 165- 173.
|
| 16 |
何国庆, 王伟胜, 刘纯, 等. 风电基地经特高压直流送出系统换相失败故障(一): 送端风电机组暂态无功电压建模[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2022, 42 (12): 4391- 4405.
|
|
HE Guoqing, WANG Weisheng, LIU Chun, et al. Commutation failure of UHVDC system for wind farm integration(part Ⅰ): transient reactive power and voltage modeling of wind powers in sending terminal grid[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2022, 42 (12): 4391- 4405.
|
| 17 |
年珩, 金萧, 李光辉. 特高压直流换相失败对送端电网风机暂态无功特性的影响分析[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2020, 40 (13): 4111- 4122.
|
|
NIAN Heng, JIN Xiao, LI Guanghui. Influence of UHV DC commutation failure on the transient reactive power characteristics of wind turbines in sending terminal grid[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2020, 40 (13): 4111- 4122.
|
| 18 |
金一丁, 贺静波, 李光辉, 等. 风电基地经特高压直流送出系统换相失败故障(二): 送端风电机组暂态无功电压特性与作用机理分析[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2022, 42 (13): 4738- 4749.
|
|
JIN Yiding, HE Jingbo, LI Guanghui, et al. Commutation failure of UHVDC system for wind farm integration(part Ⅱ): characteristics and mechanism analysis of transient reactive power and voltage of wind powers in sending terminal grid[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2022, 42 (13): 4738- 4749.
|
| 19 |
李光辉, 王伟胜, 何国庆, 等. 风电基地经特高压直流送出系统换相失败故障(三): 送端风电机组暂态过电压抑制措施[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2022, 42 (14): 5079- 5089.
|
|
LI Guanghui, WANG Weisheng, HE Guoqing, et al. Commutation failure of UHVDC system for wind farm integration(part Ⅲ): transient overvoltage suppression measures of wind powers in sending terminal grid[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2022, 42 (14): 5079- 5089.
|