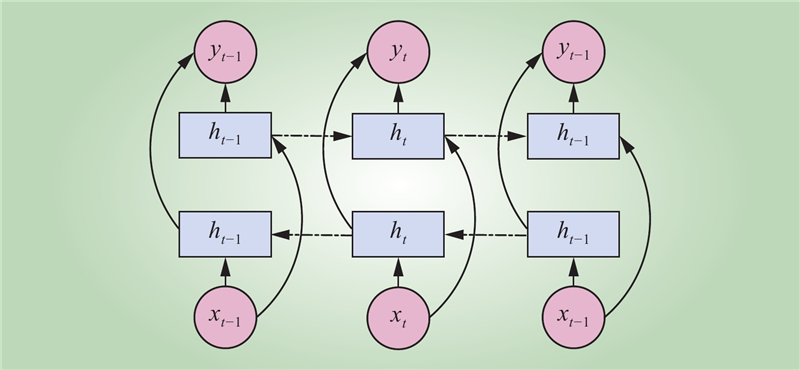
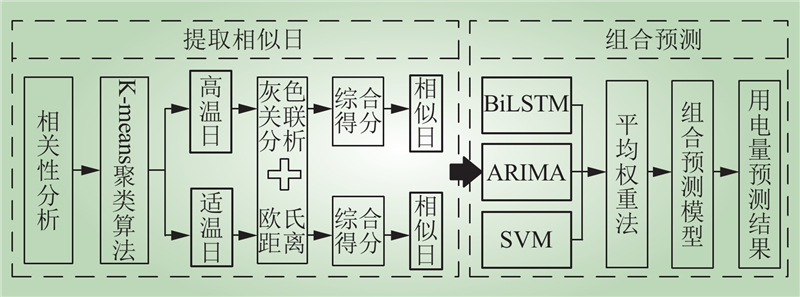
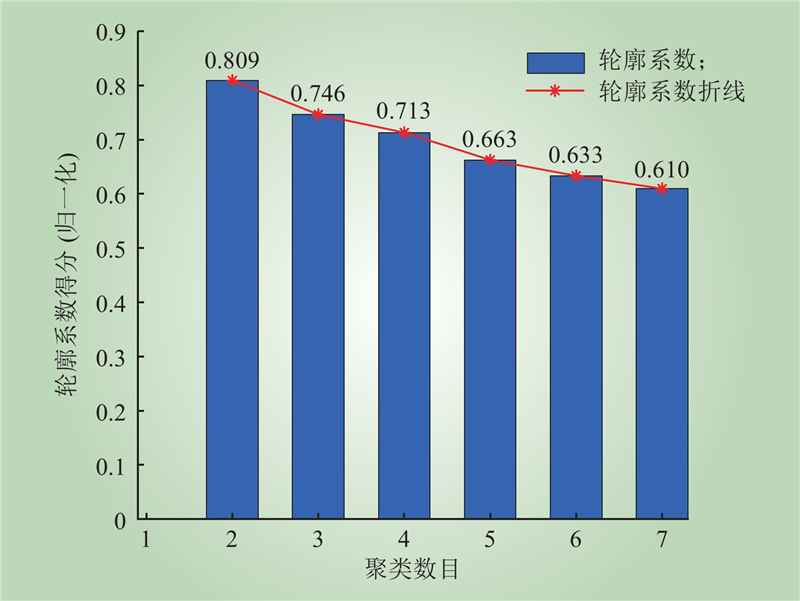
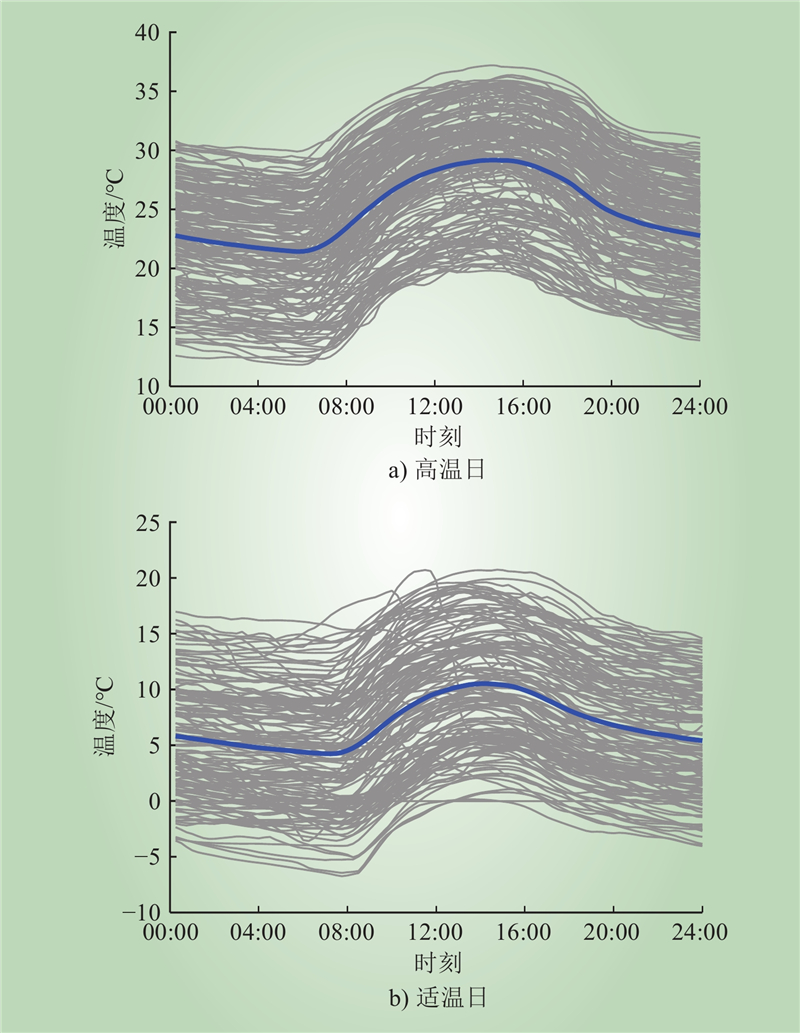
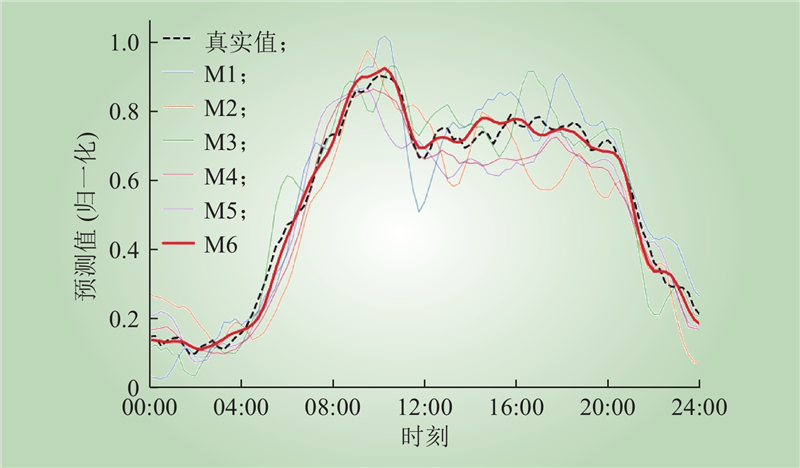
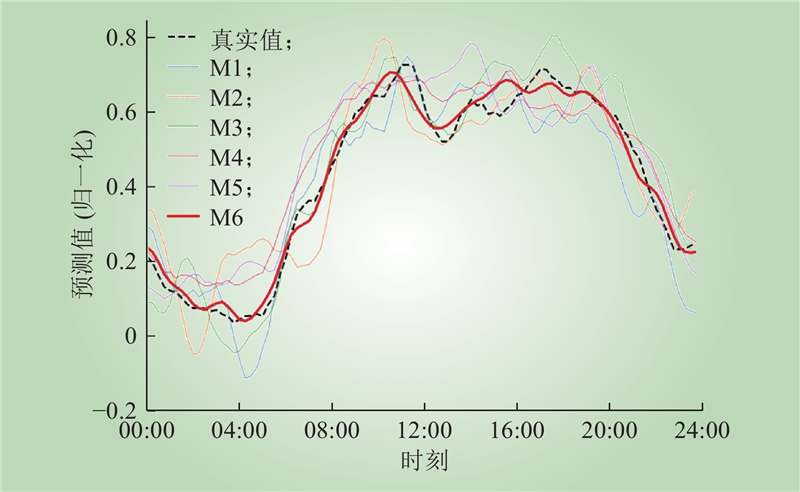
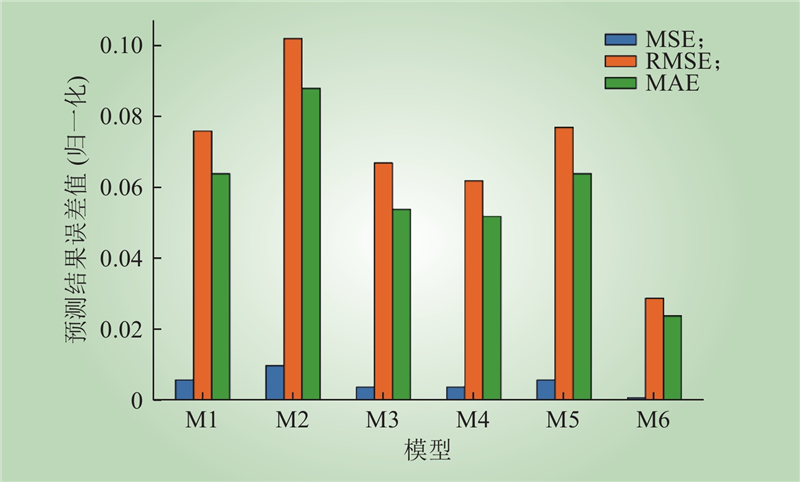
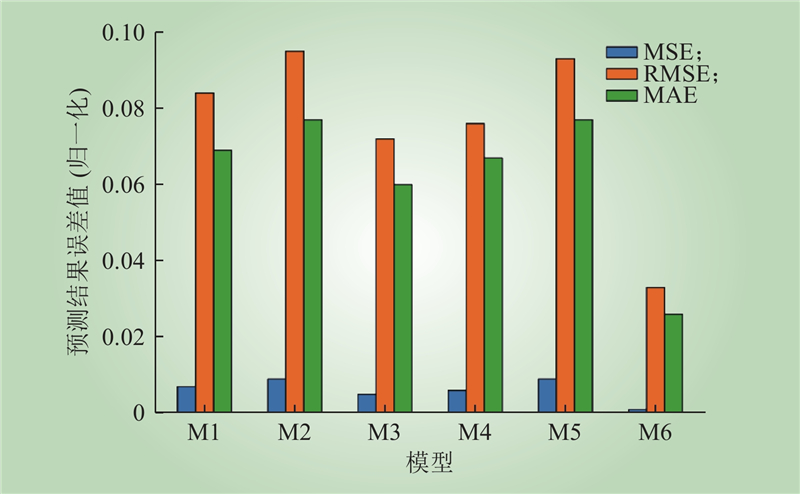
| 1 |
王文坚, 陈飞雄, 林世琦. 新型电力系统下调频容量需求计算与储-荷调频方法研究综述[J]. 智慧电力, 2025, 53 (12): 1- 12.
|
|
WANG Wenjian, CHEN Feixiong, LIN Shiqi. A review of frequency regulation capacity demand calculation and energy storage-load frequency regulation methods in new-type power systems[J]. Smart Power, 2025, 53 (12): 1- 12.
|
| 2 |
杨胡萍, 余阳, 汪超, 等. 基于VMD-CNN-BIGRU的电力系统短期负荷预测[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (10): 71- 76.
|
|
YANG Huping, YU Yang, WANG Chao, et al. Short-term load forecasting of power system based on VMD-CNN-BIGRU[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (10): 71- 76.
|
| 3 |
孙庆超, 李嘉靓, 江万里, 等. 基于数据驱动时空网络的城市中长期电力负荷预测[J]. 中国电力, 2025, 58 (3): 168- 174.
|
|
SUN Qingchao, LI Jialiang, JIANG Wanli, et al. Mid-long term urban power load forecasting based on data-driven spatio-temporal networks[J]. Electric Power, 2025, 58 (3): 168- 174.
|
| 4 |
李勇, 吴含欣, 李婵虓, 等. 考虑多维气象指标的配电网短期负荷预测[J]. 智慧电力, 2025, 53 (6): 116- 123.
|
|
LI Yong, WU Hanxin, LI Chanxiao, et al. Short-term load forecasting for distribution networks considering multidimensional meteorological indicators[J]. Smart Power, 2025, 53 (6): 116- 123.
|
| 5 |
刘义艳, 李国良, 代杰. 基于VMD-TCN-BiLSTM-Attention的短期电力负荷预测[J]. 智慧电力, 2025, 53 (10): 87- 94.
|
|
LIU Yiyan, LI Guoliang, DAI Jie. Short-term power load forecasting based on VMD-TCN-BiLSTM-attention[J]. Smart Power, 2025, 53 (10): 87- 94.
|
| 6 |
ZHU L, GAO J K, ZHU C Q, et al. Short-term power load forecasting based on spatial-temporal dynamic graph and multi-scale Transformer[J]. Journal of Computational Design and Engineering, 2025, 12 (2): 92- 111.
|
| 7 |
姜东良, 李天昊, 刘文浩. 基于相似日和SAE-DBiLSTM模型的短期电力负荷预测[J]. 电气工程学报, 2022, 17 (4): 240- 249.
|
|
JIANG Dongliang, LI Tianhao, LIU Wenhao. Short-term power load forecasting using similar day and SAE-DBiLSTM model[J]. Journal of Electrical Engineering, 2022, 17 (4): 240- 249.
|
| 8 |
JIANG Q, CHENG Y X, LE H Z, et al. A stacking learning model based on multiple similar days for short-term load forecasting[J]. Mathematics, 2022, 10 (14): 2446.
|
| 9 |
刘明, 尚尚. 基于K_means++聚类与RF_GRU组合模型的电力负荷预测方法研究[J]. 计算机与数字工程, 2024, 52 (6): 1662- 1667, 1702.
|
|
LIU Ming, SHANG Shang. Research on power load forecasting method based on K_means++ clustering and RF_GRU combined model[J]. Computer & Digital Engineering, 2024, 52 (6): 1662- 1667, 1702.
|
| 10 |
祁宇轩, 范俊岩, 吴定会, 等. 基于相似日与BiLSTM组合的短期电力负荷预测[J]. 控制理论与应用, 2024, 41 (12): 2304- 2314.
|
|
QI Yuxuan, FAN Junyan, WU Dinghui, et al. Short term power load forecasting based on the combination of similar days and BiLSTM[J]. Control Theory & Applications, 2024, 41 (12): 2304- 2314.
|
| 11 |
章姝俊, 陆海清, 陈佳玺, 等. 基于多因素相关性分析的气温敏感负荷预测[J]. 浙江电力, 2023, 42 (9): 27- 35.
|
|
ZHANG Shujun, LU Haiqing, CHEN Jiaxi, et al. Research on prediction of temperature-sensitive loads based on multi-factor correlation analysis[J]. Zhejiang Electric Power, 2023, 42 (9): 27- 35.
|
| 12 |
谭诗琪, 范嘉智, 耿欢, 等. 基于LSTM神经网络的多要素用电量动态预测[J]. 农业灾害研究, 2024, 14 (7): 161- 163.
|
|
TAN Shiqi, FAN Jiazhi, GENG Huan, et al. Dynamic prediction of multi-factor electricity consumption based on LSTM neural network[J]. Agricultural Disaster Research, 2024, 14 (7): 161- 163.
|
| 13 |
吴小涛, 袁晓辉, 毛玉鑫, 等. 基于鹈鹕优化CNN-BiLSTM的电力负荷预测[J]. 水电能源科学, 2024, 42 (8): 209- 212, 172.
|
|
WU Xiaotao, YUAN Xiaohui, MAO Yuxin, et al. Power load prediction based on pelican optimized CNN-BiLSTM[J]. Water Resources and Power, 2024, 42 (8): 209- 212, 172.
|
| 14 |
LIU F, LIANG C. Short-term power load forecasting based on AC-BiLSTM model[J]. Energy Reports, 2024, 11, 1570- 1579.
|
| 15 |
任爽, 杨凯, 商继财, 等. 基于CNN-BiGRU-Attention的短期电力负荷预测[J]. 电气工程学报, 2024, 19 (1): 344- 350.
|
|
REN Shuang, YANG Kai, SHANG Jicai, et al. Short-term power load forecasting based on CNN-BiGRU-attention[J]. Journal of Electrical Engineering, 2024, 19 (1): 344- 350.
|
| 16 |
杨汪洋, 魏云冰, 罗程浩. 基于CVMD-TCN-BiLSTM的短期电力负荷预测[J]. 电气工程学报, 2024, 19 (2): 163- 172.
|
|
YANG Wangyang, WEI Yunbing, LUO Chenghao. Short-term electricity load forecasting based on CVMD-TCN-BiLSTM[J]. Journal of Electrical Engineering, 2024, 19 (2): 163- 172.
|
| 17 |
PENG D G, LIU Y, WANG D H, et al. Multi-energy load forecasting for integrated energy system based on sequence decomposition fusion and factors correlation analysis[J]. Energy, 2024, 308, 132796.
|
| 18 |
YANG Z H, LI J D, WANG H T, et al. An informer model for very short-term power load forecasting[J]. Energies, 2025, 18 (5): 1150.
|
| 19 |
汪繁荣, 梅涛, 卢璐. 基于相似日聚类和VMD-LTWDBO-BiLSTM的短期光伏功率预测[J]. 智慧电力, 2024, 52 (10): 56- 63, 111.
|
|
WANG Fanrong, MEI Tao, LU Lu. Short-term PV power prediction based on similar day clustering with VMD-LTWDBO-BiLSTM[J]. Smart Power, 2024, 52 (10): 56- 63, 111.
|
| 20 |
陈启凡, 丁云飞, 田锟, 等. 基于K-means聚类的BP-DTR的电动汽车短期充电负荷预测[J]. 上海电机学院学报, 2024, 27 (4): 187- 191.
|
|
CHEN Qifan, DING Yunfei, TIAN Kun, et al. Short-term charging load prediction of electric vehicles based on BP-DTR with K-means clustering[J]. Journal of Shanghai Dianji University, 2024, 27 (4): 187- 191.
|
| 21 |
PANG X F, SUN W, LI H B, et al. Short-term power load forecasting based on gray relational analysis and support vector machine optimized by artificial bee colony algorithm[J]. PeerJ Computer Science, 2022, 8, e1108.
|
| 22 |
金丽丽. 基于GRA-SSA-BP神经网络的电力负荷预测方法[J]. 红水河, 2022, 41 (3): 92- 96.
|
|
JIN Lili. Power load forecasting method based on GRA-SSA-BP neural network[J]. Hongshui River, 2022, 41 (3): 92- 96.
|
| 23 |
梁海维, 王阳光, 邓小亮, 等. 基于分段预测及天气相似日选择的区域电网短期负荷预测方法[J]. 湖南电力, 2024, 44 (5): 109- 116.
|
|
LIANG Haiwei, WANG Yangguang, DENG Xiaoliang, et al. Short-term load forecasting method for regional power grid based on segmented prediction and weather similar day selection[J]. Hunan Electric Power, 2024, 44 (5): 109- 116.
|
| 24 |
王晓东, 李清, 付德义, 等. 基于卷积双向长短期记忆网络的风电机组传动系统疲劳载荷预测[J]. 中国电力, 2025, 58 (4): 90- 97.
|
|
WANG Xiaodong, LI Qing, FU Deyi, et al. Fatigue load prediction of wind turbine drive train based on CNN-BiLSTM[J]. Electric Power, 2025, 58 (4): 90- 97.
|
| 25 |
吴辉, 邹子威, 肖丰明, 等. 基于BiLSTM与自注意力机制生成对抗网络的GSA防护方法[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (9): 61- 70.
|
|
WU Hui, ZOU Ziwei, XIAO Fengming, et al. Defense method for smart grid GPS spoofing attack based on BiLSTM and self-attention mechanism generative adversarial network[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (9): 61- 70.
|
| 26 |
高芷蓉, 杨杉, 喻希, 等. 基于CNN-BiLSTM-Attention的电力系统虚假数据注入攻击检测[J]. 智慧电力, 2025, 53 (4): 103- 111.
|
|
GAO Zhirong, YANG Shan, YU Xi, et al. False data injection attack detection in power systems based on CNN-BiLSTM-attention[J]. Smart Power, 2025, 53 (4): 103- 111.
|
| 27 |
田书欣, 韩雪. 基于正交小波变换的LSTM-ARIMA海上风速组合预测模型[J]. 智慧电力, 2023, 51 (7): 39- 43, 50.
|
|
TIAN Shuxin, HAN Xue. LSTM-ARIMA offshore wind speed combined prediction model based on orthogonal wavelet transform[J]. Smart Power, 2023, 51 (7): 39- 43, 50.
|
| 28 |
ZHOU R Y, ZHANG X C. Short-term power load forecasting based on ARIMA-LSTM[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2024, 2803 (1): 012002.
|
| 29 |
王晨, 李又轩, 吴其琦, 等. 基于SVM-STL-LSTM的区域短期电力负荷预测研究[J]. 水电能源科学, 2024, 42 (4): 215- 218.
|
|
WANG Chen, LI Youxuan, WU Qiqi, et al. Research on regional short-term load forecasting based on SVM-STL-LSTM[J]. Water Resources and Power, 2024, 42 (4): 215- 218.
|
| 30 |
WANG Z X, KU Y Y, LIU J. The power load forecasting model of combined SaDE-ELM and FA-CAWOA-SVM based on CSSA[J]. IEEE Access, 2024, 12, 41870- 41882.
|
| 31 |
李鹏, 罗湘淳, 孟庆伟, 等. 基于Spearman相关性阈值寻优和VMD-LSTM的用户级综合能源系统超短期负荷预测[J]. 全球能源互联网, 2024, 7 (4): 406- 420.
|
|
LI Peng, LUO Xiangchun, MENG Qingwei, et al. Ultra short-term load forecasting of user level integrated energy system based on spearman threshold optimization and variational mode decomposition and long short-term memory[J]. Journal of Global Energy Interconnection, 2024, 7 (4): 406- 420.
|
| 32 |
郑巧兰, 林燕薇, 王景周. P值大小不等价于差异或相关性大小[J]. 数理医药学杂志, 2024, 37 (3): 158- 163.
|
|
ZHENG Qiaolan, LIN Yanwei, WANG Jingzhou. The size of P value does not equal to the magnitude of difference or correlation[J]. Journal of Mathematical Medicine, 2024, 37 (3): 158- 163.
|
| 33 |
王宇飞, 杜桐, 边伟国, 等. 基于DTW K-medoids与VMD-多分支神经网络的多用户短期负荷预测[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (6): 121- 130.
|
|
WANG Yufei, DU Tong, BIAN Weiguo, et al. Short-term load forecasting based on DTW K-medoids and VMD multi-branch neural network for multiple users[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (6): 121- 130.
|