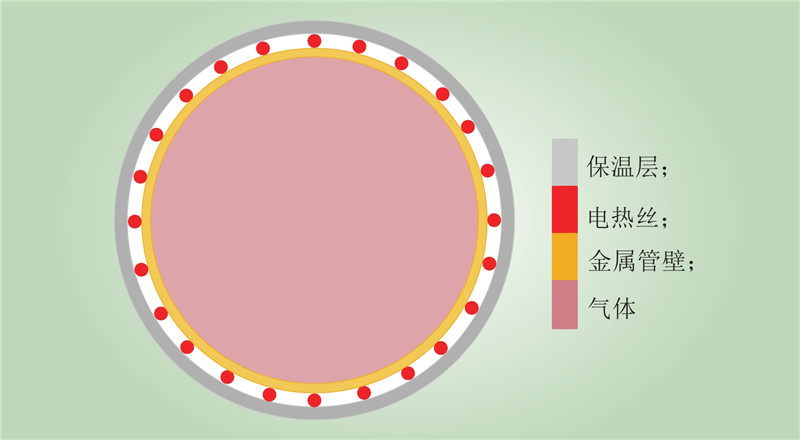
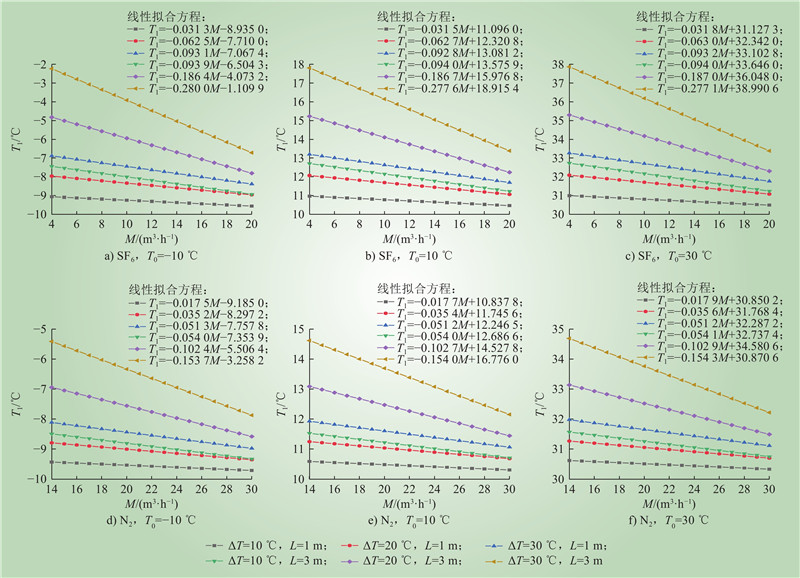
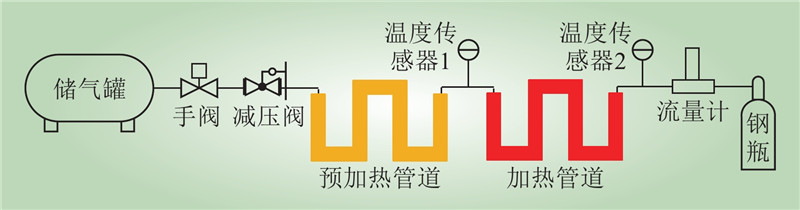
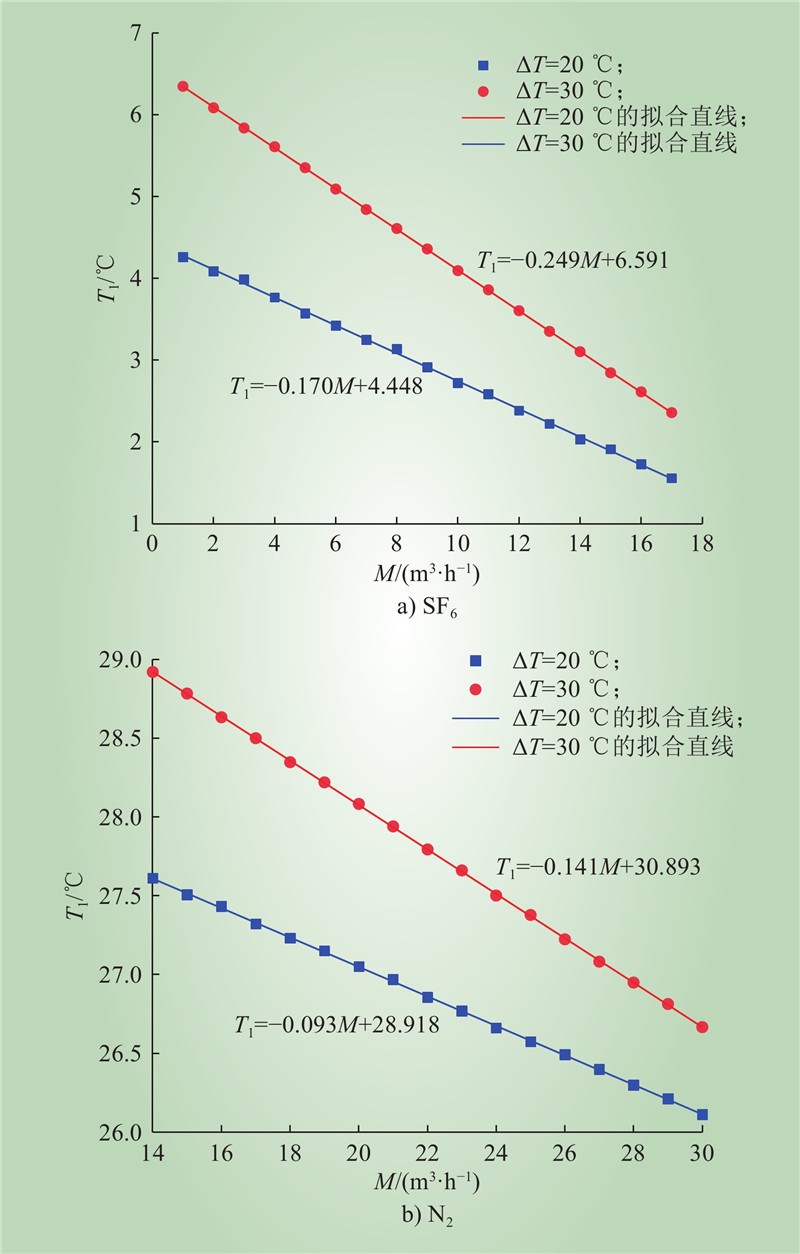
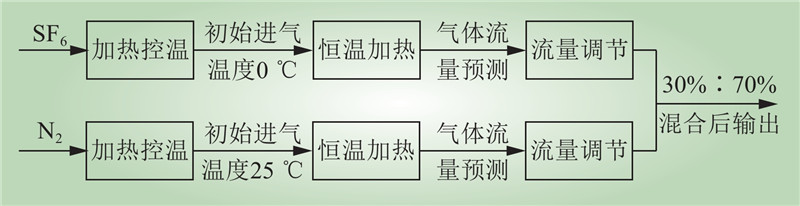
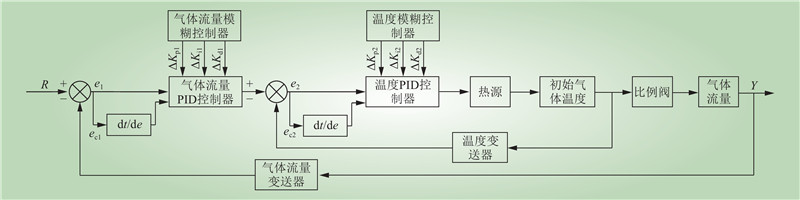
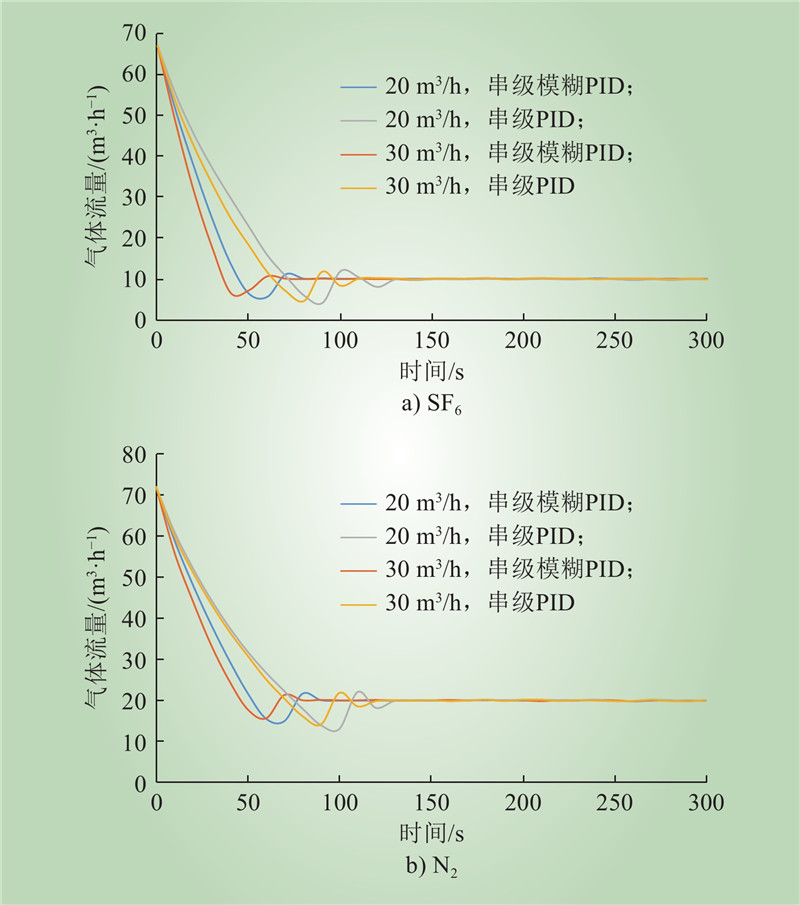
| 1 |
岳嵩, 朱勇, 何龙寿, 等. 基于改进动态电弧模型的GIS快速暂态过电压特性研究[J]. 智慧电力, 2025, 53 (8): 114- 120.
|
|
YUE Song, ZHU Yong, HE Longshou, et al. Research on characteristics of very fast transient overvoltage in GIS based on an improved dynamic arc model[J]. Smart Power, 2025, 53 (8): 114- 120.
|
| 2 |
李峰, 孟圣坤, 陆飞, 等. 基于监督学习的直流偏磁特征分析及评价方法研究[J]. 智慧电力, 2023, 51 (8): 111- 118.
|
|
LI Feng, MENG Shengkun, LU Fei, et al. Characteristic analysis and evaluation method of DC magnetic bias based on supervised learning[J]. Smart Power, 2023, 51 (8): 111- 118.
|
| 3 |
和彦淼, 黄印, 颜湘莲, 等. SF6混合气体和环保替代气体设备标准化研究[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (3): 95- 102.
|
|
HE Yanmiao, HUANG Yin, YAN Xianglian, et al. Standardization research on SF6 mixed gas and eco-friendly alternative gas equipment[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (3): 95- 102.
|
| 4 |
朱榜超, 商琼玲, 黄珠羡. 基于SF6气体温度迟滞模型的密度监测失效判定策略[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (5): 200- 210.
|
|
ZHU Bangchao, SHANG Qiongling, HUANG Zhuxian. SF6 gas temperature hysteresis model based density monitoring failure judgement criterion[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (5): 200- 210.
|
| 5 |
张咪, 高克利, 侯华, 等. SF6替代绝缘气体的虚拟筛选与分子设计综述[J]. 高电压技术, 2023, 49 (7): 2816- 2830.
|
|
ZHANG Mi, GAO Keli, HOU Hua, et al. Review on computational screening and molecular design of replacement gases for SF6[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2023, 49 (7): 2816- 2830.
|
| 6 |
马汝括, 董杰, 王雅湉, 等. 基于神经网络的高寒地区CF4和SF6/CF4检测[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (3): 103- 112.
|
|
MA Rukuo, DONG Jie, WANG Yatian, et al. Neural network-based CF4 and SF6/CF4 detection in high altitude and extreme cold regions[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (3): 103- 112.
|
| 7 |
闫超, 林悦德, 梁伟杰, 等. 基于气体流向的SF6充气装置的研制及应用[J]. 电工技术, 2020, (7): 99- 100.
|
|
YAN Chao, LIN Yuede, LIANG Weijie, et al. Development and application of SF6 inflating device based on gas flow direction[J]. Electric Engineering, 2020, (7): 99- 100.
|
| 8 |
姚钊泓, 陈翔, 林宏达, 等. 一种SF6快速充气装置的设计与应用[J]. 自动化应用, 2024, (4): 107- 109.
|
|
YAO Zhaohong, CHEN Xiang, LIN Hongda, et al. Design and application of an SF6 rapid inflation device[J]. Automation Application, 2024, (4): 107- 109.
|
| 9 |
国家能源局. 六氟化硫混合绝缘气体充补气技术规范: DL/T 2243—2021[S]. 北京: 中国电力出版社, 2021.
|
|
National Energy Bureau of the People's Republic of China. Specification for filling and supplying of SF6 gas mixture: DL/T 2243—2021[S]. Beijing: China Electric Power Press, 2021.
|
| 10 |
周倩, 柯锟, 张晓星, 等. 基于SF6混合气体绝缘性能的设备补气策略研究[J]. 电力工程技术, 2021, 40 (4): 175- 181.
|
|
ZHOU Qian, KE Kun, ZHANG Xiaoxing, et al. Air supply strategy of equipment based on SF6 mixed gas insulation performance[J]. Electric Power Engineering Technology, 2021, 40 (4): 175- 181.
|
| 11 |
周朕蕊, 韩冬, 赵明月, 等. SF6替代气体分解特性的研究综述[J]. 电工技术学报, 2020, 35 (23): 4998- 5014.
|
|
ZHOU Zhenrui, HAN Dong, ZHAO Mingyue, et al. Review on decomposition characteristics of SF6 alternative gases[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2020, 35 (23): 4998- 5014.
|
| 12 |
马凤翔, 朱峰, 袁小芳, 等. 混合气体绝缘设备充、补气技术研究[J]. 安徽电气工程职业技术学院学报, 2019, 24 (1): 53- 58.
|
|
MA Fengxiang, ZHU Feng, YUAN Xiaofang, et al. Research on gas filling and supplying technology of mixed gas insulation equipment[J]. Journal of Anhui Electrical Engineering Professional Technique College, 2019, 24 (1): 53- 58.
|
| 13 |
董杰, 杨博, 伊国鑫, 等. 电力环保型混合绝缘气体配气方法优化[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (6): 102- 109.
|
|
DONG Jie, YANG Bo, YI Guoxin, et al. Distribution optimization method for power environment-friendly mixed insulation gas[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (6): 102- 109.
|
| 14 |
王战. 半导体工艺气体管道加热控制系统及控制方法研究[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2021.
|
|
WANG Zhan. Research on heating control system and control method of gas pipeline of semiconductor process[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2021.
|
| 15 |
冯忠园. 柔性管道加热系统优化及温度控制方法研究[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2023.
|
|
FENG Zhongyuan. Research on optimization and temperature control method of flexible pipe heating system[D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2023.
|
| 16 |
王战, 高长水. 基于模糊广义预测控制的管道加热系统温度控制[J]. 机械制造与自动化, 2022, 51 (3): 229- 231.
|
|
WANG Zhan, GAO Changshui. Temperature control of pipeline heating system based on fuzzy generalized predictive control[J]. Machine Building & Automation, 2022, 51 (3): 229- 231.
|
| 17 |
孙勇, 吕全, 马宁, 等. 加热与常温输送在役原油管道对调运行投产技术[J]. 油气储运, 2024, 43 (2): 232- 239.
|
|
SUN Yong, LV Quan, MA Ning, et al. Commissioning technology for switching operation between in-service crude oil pipelines for heated and normal-temperature transmission[J]. Oil & Gas Storage and Transportation, 2024, 43 (2): 232- 239.
|
| 18 |
万军. 热输原油管道总传热系数的研究及应用[J]. 管道技术与设备, 2022, (5): 15- 18.
|
|
WAN Jun. Research and application of total heat transfer coefficient of heating crude oil pipeline[J]. Pipeline Technique and Equipment, 2022, (5): 15- 18.
|
| 19 |
郑伟龙. 12 kV开关柜温度场分析及优化设计[D]. 厦门: 厦门理工学院, 2021.
|
|
ZHENG Weilong. Temperature field analysis and optimization design of 12 kV switchgear[D]. Xiamen: Xiamen University of Technology, 2021.
|
| 20 |
周娟, 林加顺, 吴乃豪, 等. 一种联合PID控制与扩展卡尔曼滤波的磷酸铁锂电池荷电状态估算方法[J]. 电网技术, 2023, 47 (4): 1623- 1632.
|
|
ZHOU Juan, LIN Jiashun, WU Naihao, et al. State of charge estimation for LiFeO4 battery combining PID control and extended Kalman filter[J]. Power System Technology, 2023, 47 (4): 1623- 1632.
|
| 21 |
冯陈, 刘朝爽, 吴春旺, 等. 抽水蓄能机组新型变工况自适应模糊控制策略[J]. 电网技术, 2024, 48 (7): 2815- 2822.
|
|
FENG Chen, LIU Chaoshuang, WU Chunwang, et al. Innovative adaptive fuzzy control strategy for pumped storage units under variable operating conditions[J]. Power System Technology, 2024, 48 (7): 2815- 2822.
|
| 22 |
张建新, 江出阳, 苏寅生, 等. 一种基于Prony分析的水电机组调速器PID参数切换方法[J]. 南方电网技术, 2019, 13 (12): 60- 66, 84.
|
|
ZHANG Jianxin, JIANG Chuyang, SU Yinsheng, et al. A PID parameter switching method based on prony analysis for hydropower unit governor[J]. Southern Power System Technology, 2019, 13 (12): 60- 66, 84.
|
| 23 |
王育飞, 程伟, 薛花, 等. 基于串级PI-(1+PD)算法的含飞轮储能互联电网AGC控制器设计[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2023, 51 (14): 127- 138.
|
|
WANG Yufei, CHENG Wei, XUE Hua, et al. Controller design of an AGC based on a cascade PI-(1+PD) algorithm for an interconnected power grid with flywheel energy storage[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2023, 51 (14): 127- 138.
|
| 24 |
李建林, 梁策, 曾飞, 等. 基于级联式模糊控制的电氢耦合直流微网能量管理策略研究[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2024, 52 (18): 87- 100.
|
|
LI Jianlin, LIANG Ce, ZENG Fei, et al. An energy management strategy for an electricity-hydrogen coupled DC microgrid based on cascade fuzzy control[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2024, 52 (18): 87- 100.
|
| 25 |
杨帆, 杨平, 彭道刚. 检定炉炉温的阶跃响应试验建模与MCP-PID实时控制[J]. 电力科学与技术学报, 2020, 35 (6): 187- 193.
|
|
YANG Fan, YANG Ping, PENG Daogang. Step response modeling of calibrated furnace temperature and its MCP-PID real-time control[J]. Journal of Electric Power Science and Technology, 2020, 35 (6): 187- 193.
|
| 26 |
杨永辉, 谢丽蓉, 李佳明, 等. 基于模糊控制的储能参与一次调频综合控制策略[J]. 智慧电力, 2023, 51 (4): 38- 45.
|
|
YANG Yonghui, XIE Lirong, LI Jiaming, et al. Integrated control strategy of energy storage participating in primary frequency regulation based on fuzzy control[J]. Smart Power, 2023, 51 (4): 38- 45.
|
| 27 |
冀炳晖, 茅健, 钱波. 基于遗传算法-模糊PID的双喷头FDM型3D打印机温度控制方法[J]. 工程设计学报, 2024, 31 (2): 151- 159.
|
|
JI Binghui, MAO Jian, QIAN Bo. Temperature control method for dual-nozzle FDM 3D printer based on genetic algorithm-fuzzy PID[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering Design, 2024, 31 (2): 151- 159.
|