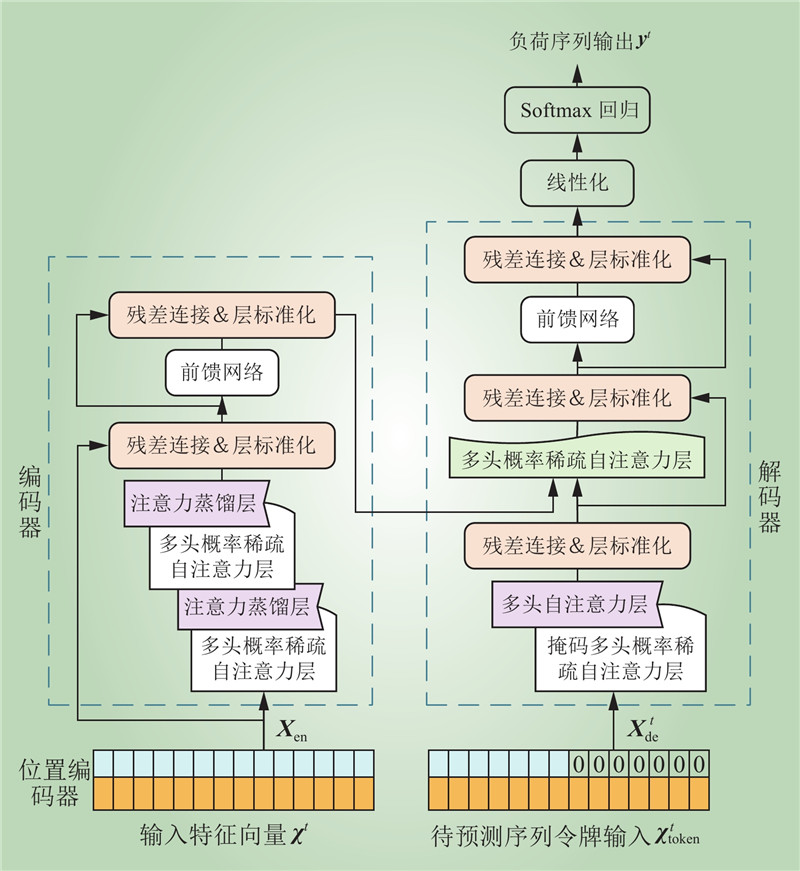
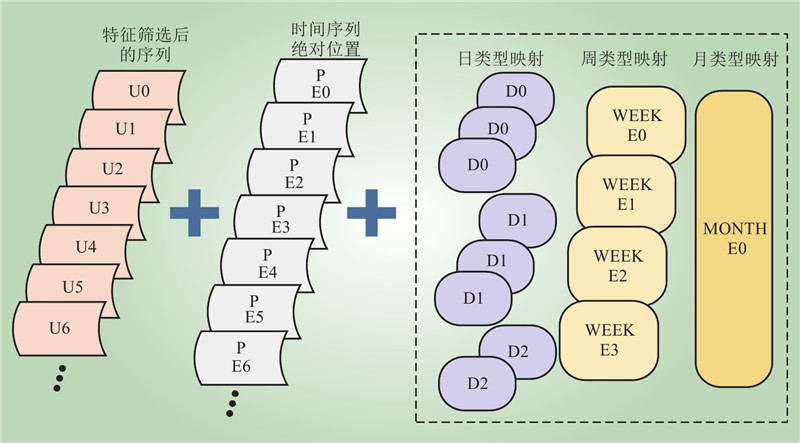
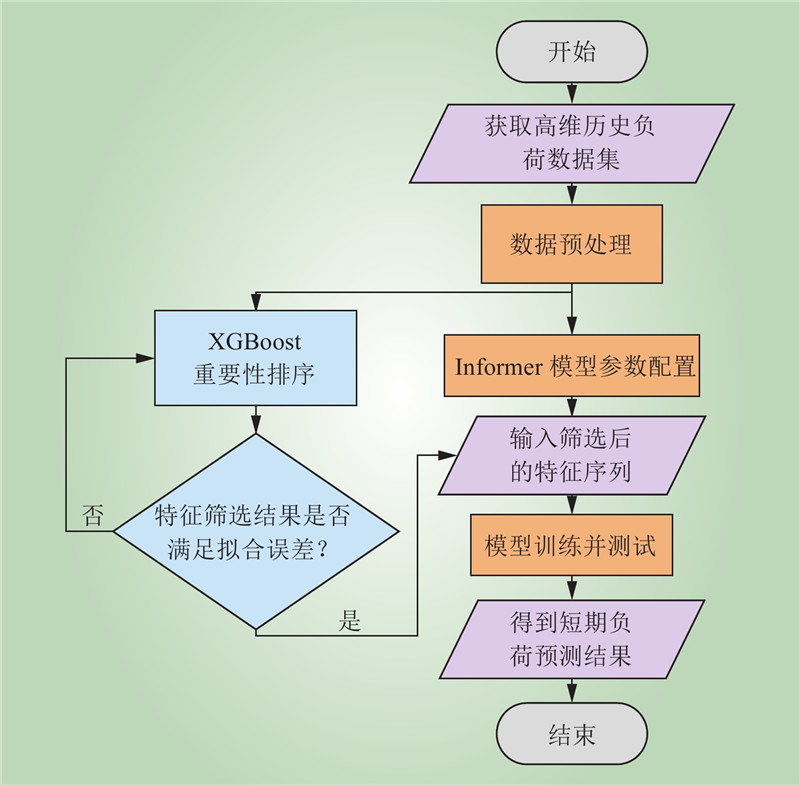
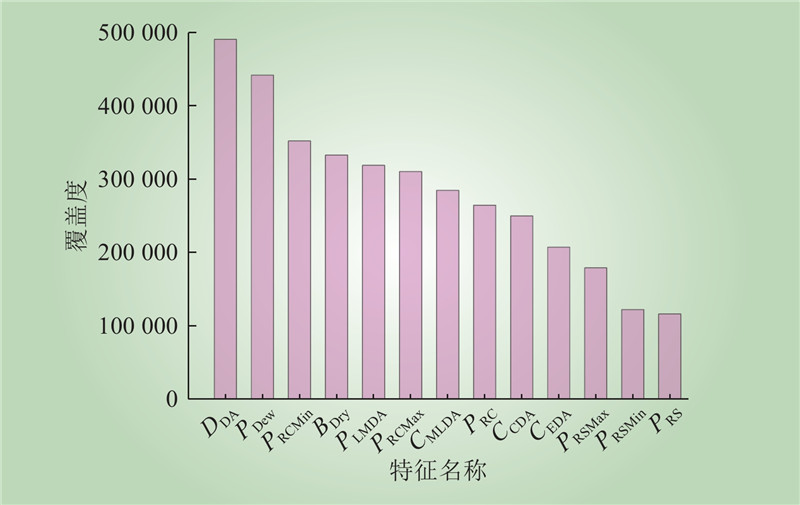
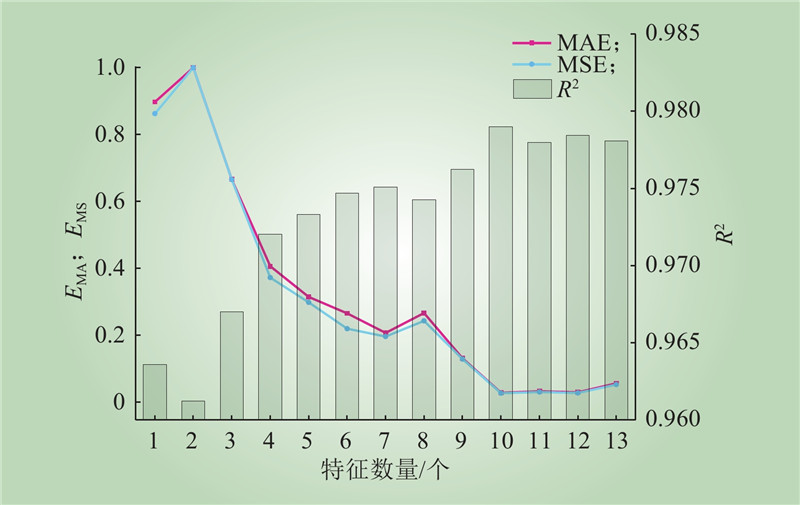
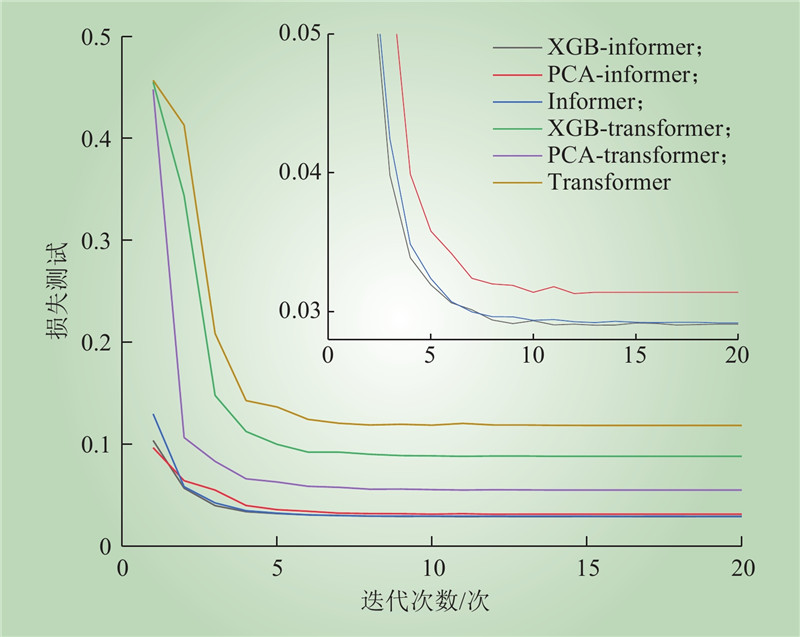
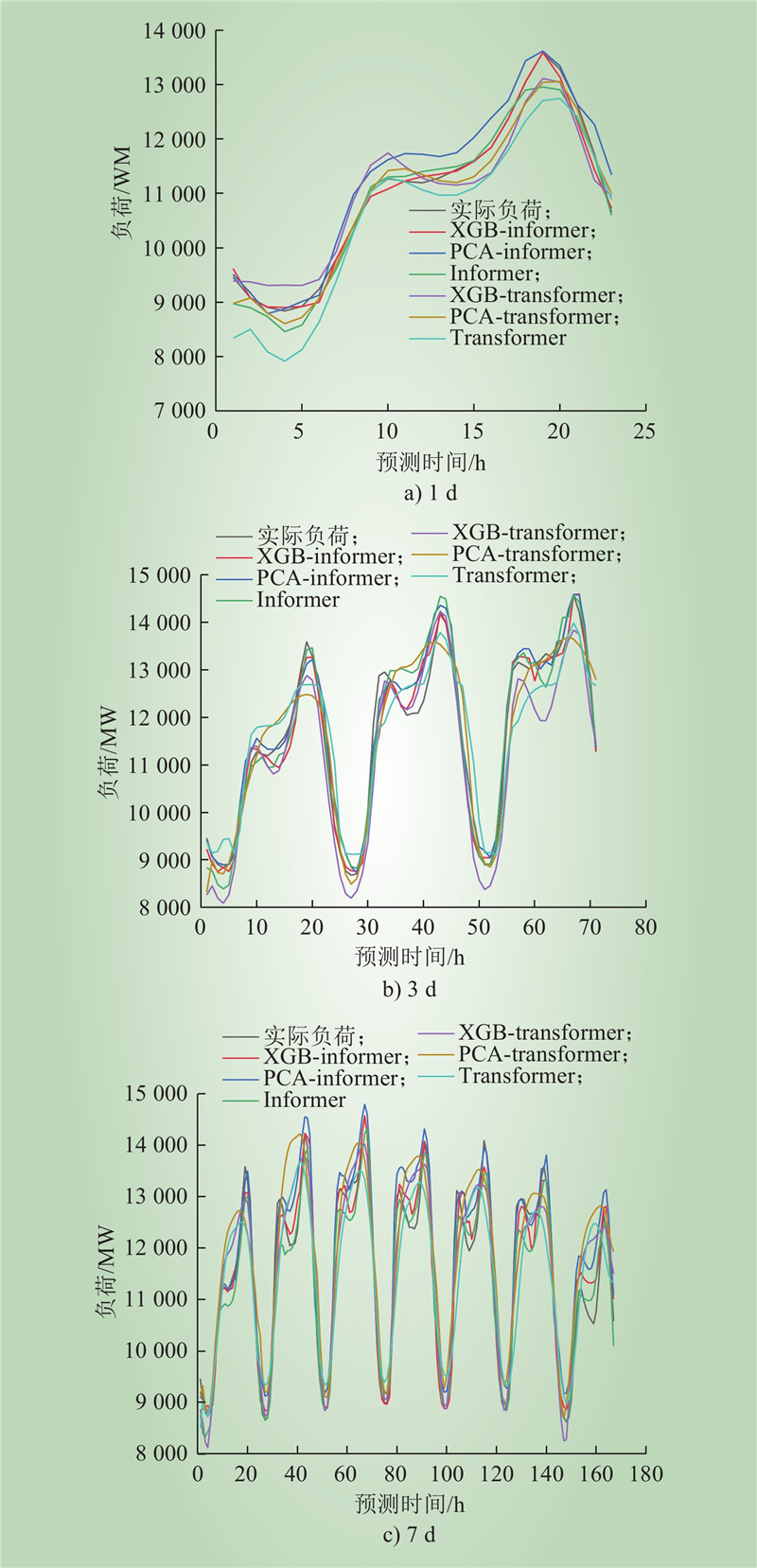
| 1 |
韩富佳, 王晓辉, 乔骥, 等. 基于人工智能技术的新型电力系统负荷预测研究综述[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2023, 43 (22): 8569- 8592.
|
|
HAN Fujia, WANG Xiaohui, QIAO Ji, et al. Review on artificial intelligence based load forecasting research for the new-type power system[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2023, 43 (22): 8569- 8592.
|
| 2 |
陈宋宋, 王阳, 周颖, 等. 基于客户用电数据的多时空维度负荷预测综述[J]. 电网与清洁能源, 2023, 39 (12): 28- 40.
|
|
CHEN Songsong, WANG Yang, ZHOU Ying, et al. A review of multi-time-space load forecasting based on customer electricity consumption data[J]. Power System and Clean Energy, 2023, 39 (12): 28- 40.
|
| 3 |
杨佳泽, 王灿, 王增平. 新型电力系统背景下的智能负荷预测算法研究综述[J]. 华北电力大学学报(自然科学版), 2025, 52 (3): 54- 67.
|
|
YANG Jiaze, WANG Can, WANG Zengping. Review on intelligent load forecasting algorithms for the new-type power system[J]. Journal of North China Electric Power University (Natural Science Edition), 2025, 52 (3): 54- 67.
|
| 4 |
朱明, 夏宇栋, 常凯, 等. 基于粒子群优化算法的空调负荷灰箱模型辨识[J]. 电力科学与技术学报, 2023, 38 (04): 214- 221.
|
|
ZHU Ming, XIA Yudong, CHANG Kai, et al. Identification of grey box model for air conditioning load based on particleswarm optimization algorithm[J]. Journal of Electric Power Science and Technology, 2023, 38 (04): 214- 221.
|
| 5 |
刘杰, 从兰美, 夏远洋, 等. 基于DBO-VMD和IWOA-BILSTM神经网络组合模型的短期电力负荷预测[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2024, 52 (8): 123- 133.
|
|
LIU Jie, CONG Lanmei, XIA Yuanyang, et al. Short-term power load prediction based on DBO-VMD and an IWOA-BILSTMneural network combination model[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2024, 52 (8): 123- 133.
|
| 6 |
邓皓云, 陈卓. 基于EEMD-IWOA-TCN的电网短期负荷预测[J]. 电力信息与通信技术, 2024, 22 (1): 70- 76.
|
|
DENG Haoyun, CHEN Zhuo. Short-term load forecasting of power gird based on EEMD-IWOA-TCN[J]. Electric Power Information and Communication Technology, 2024, 22 (1): 70- 76.
|
| 7 |
张大海, 孙锴, 和敬涵. 基于相似日与多模型融合的短期负荷预测[J]. 电网技术, 2023, 47 (5): 1961- 1970.
|
|
ZHANG Dahai, SUN Kai, HE Jinghan. Short-term load forecasting based on similar day and multi-model fusion[J]. Power System Technology, 2023, 47 (5): 1961- 1970.
|
| 8 |
苗磊, 李擎, 蒋原, 等. 深度学习在电力系统预测中的应用[J]. 工程科学学报, 2023, 45 (4): 663- 672.
|
|
MIAO Lei, LI Qing, JIANG Yuan, et al. A survey of power system prediction based on deep learning[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2023, 45 (4): 663- 672.
|
| 9 |
沈赋, 刘思蕊, 徐潇源, 等. 基于多尺度特征提取的IES多元负荷短期联合预测[J]. 高电压技术, 2024, 50 (7): 2918- 2930.
|
|
SHEN Fu, LIU Sirui, XU Xiaoyuan, et al. Multi-load short-term joint forecasting of integrated energy system based on multi-scale feature extraction[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2024, 50 (7): 2918- 2930.
|
| 10 |
邵必林, 纪丹阳. 基于VMD-SE的电力负荷分量的多特征短期预测[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (4): 162- 170.
|
|
SHAO Bilin, JI Danyang. Multi-feature short-term prediction of power load components based on VMD-SE[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (4): 162- 170.
|
| 11 |
VASWANI A, SHAZEER N, PARMAR N, et al. Attention is all you need[J]. arXiv: 1706.03762.
|
| 12 |
吴军英, 路欣, 刘宏, 等. 基于Spearman-GCN-GRU模型的超短期多区域电力负荷预测[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (6): 131- 140.
|
|
WU Junying, LU Xin, LIU Hong, et al. Ultra-short-term multi-region power load forecasting based on Spearman-GCN-GRU model[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (6): 131- 140.
|
| 13 |
方娜, 余俊杰, 李俊晓, 等. 基于CNN-BIGRU-ATTENTION的短期电力负荷预测[J]. 计算机仿真, 2022, 39 (2): 40- 44, 82.
|
|
FANG Na, YU Junjie, LI Junxiao, et al. Short-term power load forecasting based on CNN-BIGRU-ATTENTION[J]. Computer Simulation, 2022, 39 (2): 40- 44, 82.
|
| 14 |
王宇飞, 杜桐, 边伟国, 等. 基于DTW K-medoids与VMD-多分支神经网络的多用户短期负荷预测[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (6): 121- 130.
|
|
WANG Yufei, DU Tong, BIAN Weiguo, et al. Short-term load forecasting based on DTW K-medoids and VMD multi-branch neural network for multiple users[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (6): 121- 130.
|
| 15 |
钟吴君, 李培强, 涂春鸣. 基于EEMD-CBAM-Bi LSTM的牵引负荷超短期预测[J]. 电工技术学报, 2024, 39 (21): 6850- 6864.
|
|
ZHONG Wujun, LI Peiqiang, TU Chunming. Traction load ultra-short-term forecasting framework based on EEMD-CBAM-BiLSTM[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2024, 39 (21): 6850- 6864.
|
| 16 |
杨胡萍, 余阳, 汪超, 等. 基于VMD-CNN-BIGRU的电力系统短期负荷预测[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (10): 71- 76.
|
|
YANG Huping, YU Yang, WANG Chao, et al. Short-term load forecasting of power system based on VMD-CNN-BIGRU[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (10): 71- 76.
|
| 17 |
葛亚明, 仇晨光, 谢丽荣, 等. 基于K-means聚类与LSTM模型的多能源耦合电力负荷预测[J]. 现代电力, 2025, 42 (2): 369- 376.
|
|
GE Yaming, QIU Chenguang, XIE Lirong, et al. Research on multi-energy coupled power load prediction based on K-means clustering and LSTM model[J]. Modern Electric Power, 2025, 42 (2): 369- 376.
|
| 18 |
郝文斌, 孟志高, 张勇, 等. 基于SOM特征聚类及RBF神经网络的电力负荷预测方法研究[J]. 电力需求侧管理, 2024, 26 (2): 49- 54.
|
|
HAO Wenbin, MENG Zhigao, ZHANG Yong, et al. Research on power load forecasting method based on feature clustering of SOM and RBF neural network[J]. Power Demand Side Management, 2024, 26 (2): 49- 54.
|
| 19 |
冉启武, 张宇航. 基于模态分解及GRU-XGBoost短期电力负荷预测[J]. 电网与清洁能源, 2024, 40 (4): 18- 27, 34.
|
|
RAN Qiwu, ZHANG Yuhang. Short-term power load forecasting based on modal decomposition and GRU-XGBoost[J]. Power System and Clean Energy, 2024, 40 (4): 18- 27, 34.
|
| 20 |
刘明, 尚尚. 基于K_means++聚类与RF_GRU组合模型的电力负荷预测方法研究[J]. 计算机与数字工程, 2024, 52 (6): 1662- 1667, 1702.
|
|
LIU Ming, SHANG Shang. Research on power load forecasting method based on K_means++ clustering and RF_GRU combined model[J]. Computer & Digital Engineering, 2024, 52 (6): 1662- 1667, 1702.
|
| 21 |
张峻凯, 胡旭光, 刘要博, 等. 基于动态关联图注意力网络的虚拟电厂居民短期负荷预测[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2024, 48 (21): 120- 128.
|
|
ZHANG Junkai, HU Xuguang, LIU Yaobo, et al. Short-term residential load forecasting based on dynamic association graph attention networks for virtual power plant[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2024, 48 (21): 120- 128.
|
| 22 |
李甲祎, 赵兵, 刘宣, 等. 基于DWT-Informer的台区短期负荷预测[J]. 电测与仪表, 2024, 61 (3): 160- 166, 191.
|
|
LI Jiayi, ZHAO Bing, LIU Xuan, et al. Short-term substation load forecasting based on DWT-Informer model[J]. Electrical Measurement & Instrumentation, 2024, 61 (3): 160- 166, 191.
|
| 23 |
石卓见, 冉启武, 徐福聪. 基于聚合二次模态分解及Informer的短期负荷预测[J]. 电网技术, 2024, 48 (6): 2574- 2583.
|
|
SHI Zhuojian, RAN Qiwu, XU Fucong. Short-term load forecasting based on aggregated secondary decomposition and informer[J]. Power System Technology, 2024, 48 (6): 2574- 2583.
|
| 24 |
任晟岐, 宋伟. 基于GGInformer模型的多维时间序列特征提取与预测研究[J]. 计算机工程与科学, 2024, 46 (4): 590- 598.
|
|
REN Shengqi, SONG Wei. Feature extraction and prediction of multidimensional time series based on GGInformer model[J]. Computer Engineering & Science, 2024, 46 (4): 590- 598.
|
| 25 |
CHEN T Q, GUESTRIN C. XGBoost: a scalable tree boosting system[C]//Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. San Francisco California USA. ACM, 2016: 785-794.
|
| 26 |
ZHOU H Y, ZHANG S H, PENG J Q, et al. Informer: beyond efficient transformer for long sequence time-series forecasting[J]. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2021, 35 (12): 11106- 11115.
|