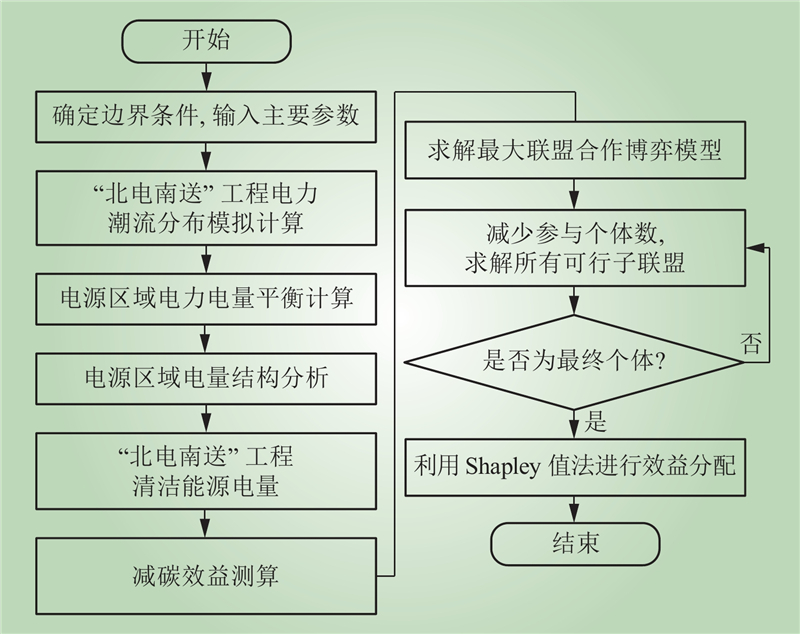
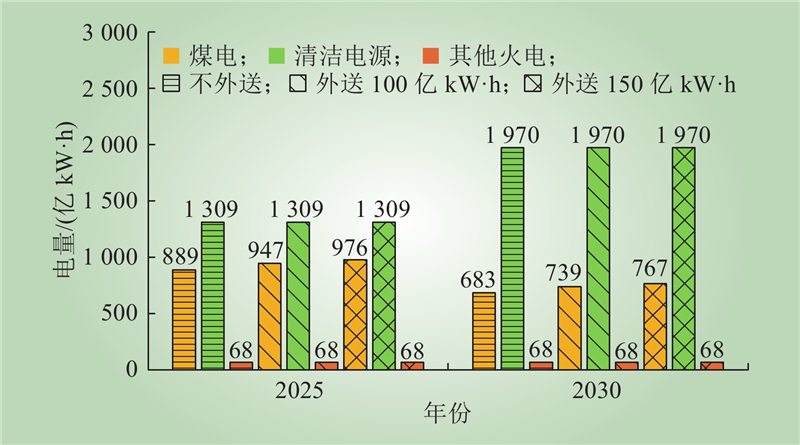
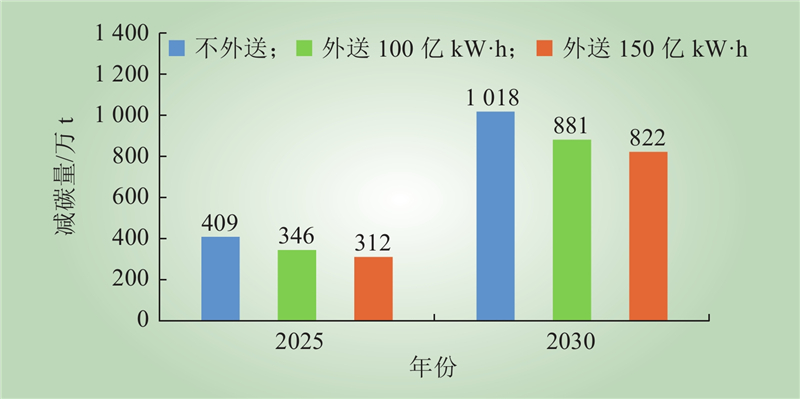
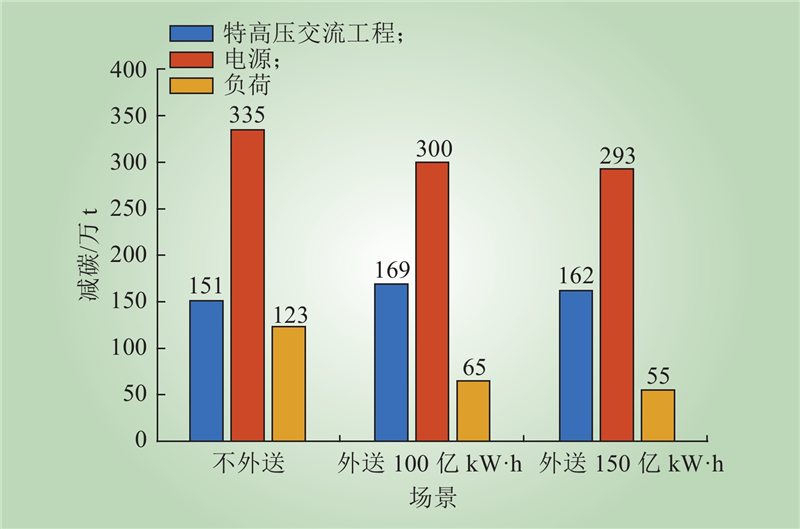
| 1 |
任大伟, 侯金鸣, 肖晋宇, 等. 支撑双碳目标的新型储能发展潜力及路径研究[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (8): 17- 25.
|
|
REN Dawei, HOU Jinming, XIAO Jinyu, et al. Research on development potential and path of new energy storage supporting carbon peak and carbon neutrality[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (8): 17- 25.
|
| 2 |
谭显东, 刘俊, 徐志成, 等. “双碳” 目标下“十四五” 电力供需形势[J]. 中国电力, 2021, 54 (5): 1- 6.
|
|
TAN Xiandong, LIU Jun, XU Zhicheng, et al. Power supply and demand balance during the 14th five-year plan period under the goal of carbon emission peak and carbon neutrality[J]. Electric Power, 2021, 54 (5): 1- 6.
|
| 3 |
陈怡, 田川, 曹颖, 等. 中国电力行业碳排放达峰及减排潜力分析[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2020, 16 (5): 632- 640.
|
|
CHEN Yi, TIAN Chuan, CAO Ying, et al. Research on peaking carbon emissions of power sector in China and the emissions mitigation analysis[J]. Climate Change Research, 2020, 16 (5): 632- 640.
|
| 4 |
李政, 陈思源, 董文娟, 等. 碳约束条件下电力行业低碳转型路径研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2021, 41 (12): 3987- 4001.
|
|
LI Zheng, CHEN Siyuan, DONG Wenjuan, et al. Low carbon transition pathway of power sector under carbon emission constraints[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2021, 41 (12): 3987- 4001.
|
| 5 |
国家发展改革委环资司召开碳排放核算专家座谈会[J]. 江西建材, 2021(04): 3.
|
| 6 |
李春焕, 曹阿林. 铝电解工业碳排放核算方法[J]. 有色金属(冶炼部分), 2023, (3): 47- 52.
|
|
LI Chunhuan, CAO Alin. Carbon emission accounting methods for aluminum electrolysis industry[J]. Nonferrous Metals (Extractive Metallurgy), 2023, (3): 47- 52.
|
| 7 |
杨本晓, 姜涛, 刘夏青. 基于投入产出法的中国造纸工业碳排放核算[J]. 中国造纸, 2023, 42 (6): 120- 125.
|
|
YANG Benxiao, JIANG Tao, LIU Xiaqing. Carbon emission accounting of China’s paper industry based on the input-output analyses[J]. China Pulp & Paper, 2023, 42 (6): 120- 125.
|
| 8 |
杨本晓, 梁思哲, 刘夏青. 基于投入产出法的中国化石能源加工业碳排放核算[J]. 环境保护, 2023, 51 (S2): 18- 21.
|
|
YANG Benxiao, LIANG Sizhe, LIU Xiaqing. Carbon emissions in the Chinese fossil energy industries based on input output analyses[J]. Environmental Protection, 2023, 51 (S2): 18- 21.
|
| 9 |
李春焕, 曹阿林. 氧化铝工业碳排放核算方法[J]. 有色金属(冶炼部分), 2023, (5): 26- 31, 91.
|
|
LI Chunhuan, CAO Alin. Carbon emission accounting methods of alumina industry[J]. Nonferrous Metals (Extractive Metallurgy), 2023, (5): 26- 31, 91.
|
| 10 |
朱振兴. 燃煤电厂碳排放的核算方法对比分析[J]. 中国资源综合利用, 2023, 41 (4): 165- 167.
|
|
ZHU Zhenxing. Comparative analysis of accounting methods for carbon emissions from coal-fired power plants[J]. China Resources Comprehensive Utilization, 2023, 41 (4): 165- 167.
|
| 11 |
张宁, 李姚旺, 黄俊辉, 等. 电力系统全环节碳计量方法与碳表系统[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2023, 47 (9): 2- 12.
|
|
ZHANG Ning, LI Yaowang, HUANG Junhui, et al. Carbon measurement method and carbon meter system for whole chain of power system[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2023, 47 (9): 2- 12.
|
| 12 |
汪超群, 陈懿, 文福拴, 等. 电力系统碳排放流理论改进与完善[J]. 电网技术, 2022, 46 (5): 1683- 1693.
|
|
WANG Chaoqun, CHEN Yi, WEN Fushuan, et al. Improvement and perfection of carbon emission flow theory in power systems[J]. Power System Technology, 2022, 46 (5): 1683- 1693.
|
| 13 |
段力勇, 李方勇, 王庆红, 等. 电网企业碳排放核算与配额分配方法研究[J]. 能源与环保, 2018, 40 (12): 127- 131.
|
|
DUAN Liyong, LI Fangyong, WANG Qinghong, et al. Study on carbon emission quantification and quota allocation methods of power grid enterprise[J]. China Energy and Environmental Protection, 2018, 40 (12): 127- 131.
|
| 14 |
SUN Y L, KANG C Q, XIA Q, et al. Analysis of transmission expansion planning considering consumption-based carbon emission accounting[J]. Applied Energy, 2017, 193, 232- 242.
|
| 15 |
田欣, 陈来军, 李笑竹, 等. 基于主从博弈和改进Shapley值的分布式光伏社区共享储能优化运行策略[J]. 电网技术, 2023, 47 (6): 2252- 2261.
|
|
TIAN Xin, CHEN Laijun, LI Xiaozhu, et al. Optimal scheduling for energy storage sharing among communities with photovoltaic resource based on stackelberg game and improved shapley value[J]. Power System Technology, 2023, 47 (6): 2252- 2261.
|
| 16 |
蒋从伟, 欧庆和, 吴仲超, 等. 基于联盟博弈的多微网共享储能联合配置与优化[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (12): 11- 21.
|
|
JIANG Congwei, OU Qinghe, WU Zhongchao, et al. Joint configuration and optimization of multi-microgrid shared energy storage based on coalition game[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (12): 11- 21.
|
| 17 |
张爱国, 霍晓谦, 李佳佳, 等. 基于Shapley值法的再生水回用利益分配机制研究[J]. 水电能源科学, 2022, 40 (4): 58- 61.
|
|
ZHANG Aiguo, HUO Xiaoqian, LI Jiajia, et al. Study on benefit allocation mechanism of reclaimed water reuse based on shapley value method[J]. Water Resources and Power, 2022, 40 (4): 58- 61.
|
| 18 |
刘振亚. 中国特高压交流输电技术创新[J]. 电网技术, 2013, 37 (3): 567- 574.
|
|
LIU Zhenya. Innovation of UHVAC transmission technology in China[J]. Power System Technology, 2013, 37 (3): 567- 574.
|
| 19 |
徐菁, 李妍, 刘一鸣, 等. 基于相对靶心度的区域电网低碳发展潜力评估[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2023, 43 (4): 1281- 1290.
|
|
XU Jing, LI Yan, LIU Yiming, et al. Assessment of low-carbon development potential of regional power grid based on relative off-targets distance[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2023, 43 (4): 1281- 1290.
|
| 20 |
王梓珺, 王承民, 谢宁. 基于柔性计算的高比例新能源环境下的电力电量平衡[J]. 智慧电力, 2021, 49 (8): 15- 22.
|
|
WANG Zijun, WANG Chengmin, XIE Ning. Electric power and energy balance based on flexible computing in energy Internet with high proportion of new energy[J]. Smart Power, 2021, 49 (8): 15- 22.
|
| 21 |
朱俊澎, 施凯杰, 李强, 等. 考虑输电网潮流约束的时序生产模拟及新能源消纳能力评估[J]. 电网技术, 2022, 46 (5): 1947- 1955.
|
|
ZHU Junpeng, SHI Kaijie, LI Qiang, et al. Time series production simulation and renewable energy accommodation capacity evaluation considering transmission network power flow constraints[J]. Power System Technology, 2022, 46 (5): 1947- 1955.
|
| 22 |
高澈, 牛东晓, 马明, 等. 大规模新能源区域互联消纳能力分析及综合评价方法研究[J]. 中国电力, 2017, 50 (7): 56- 63.
|
|
GAO Che, NIU Dongxiao, MA Ming, et al. Accommodating capability analysis and comprehensive assessment method of large-scale new energy areas interconnected[J]. Electric Power, 2017, 50 (7): 56- 63.
|
| 23 |
李湃, 王伟胜, 黄越辉, 等. 大规模新能源基地经特高压直流送出系统中长期运行方式优化方法[J]. 电网技术, 2023, 47 (1): 31- 44.
|
|
LI Pai, WANG Weisheng, HUANG Yuehui, et al. Method on optimization of medium and long term operation modes of large-scale renewable energy power base through UHVDC system[J]. Power System Technology, 2023, 47 (1): 31- 44.
|
| 24 |
赵书强, 索璕, 许朝阳, 等. 考虑断面约束的多能源电力系统时序性生产模拟[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2021, 41 (7): 1- 6.
|
|
ZHAO Shuqiang, SUO Xun, XU Zhaoyang, et al. Time series production simulation of multi-energy power system considering section constraints[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2021, 41 (7): 1- 6.
|
| 25 |
刘文霞, 王丽娜, 张帅, 等. 基于合作博弈论的日前自备电厂与风电发电权交易模型[J]. 电网技术, 2022, 46 (7): 2647- 2658.
|
|
LIU Wenxia, WANG Lina, ZHANG Shuai, et al. Cooperation game theory-based model for trading of power generation rights between former captive power plants and wind power[J]. Power System Technology, 2022, 46 (7): 2647- 2658.
|
| 26 |
陶良彦, 王丽, 齐晓霞, 等. 武器装备体系贡献率评估灰色Shapley值模型[J]. 中国管理科学, 2024, 32 (4): 89- 96.
|
|
TAO Liangyan, WANG Li, QI Xiaoxia, et al. Grey Shapley value model for evaluating the contribution rate of weapon and Equipment Systems[J]. Chinese Management Science, 2024, 32 (4): 89- 96.
|
| 27 |
陈岑, 武传涛, 康慨, 等. 基于改进Owen值法的分布式储能双层合作博弈优化策略[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2022, 42 (11): 3924- 3936.
|
|
CHEN Cen, WU Chuantao, KANG Kai, et al. Optimal strategy of distributed energy storage two-layer cooperative game based on improved owen-value method[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2022, 42 (11): 3924- 3936.
|
| 28 |
王永利, 刘振, 薛露, 等. 基于多主体博弈的综合能源系统运行优化方法[J]. 控制理论与应用, 2022, 39 (3): 499- 508.
|
|
WANG Yongli, LIU Zhen, XUE Lu, et al. Optimization method of integrated energy system operation based on multi-body game[J]. Control Theory & Applications, 2022, 39 (3): 499- 508.
|