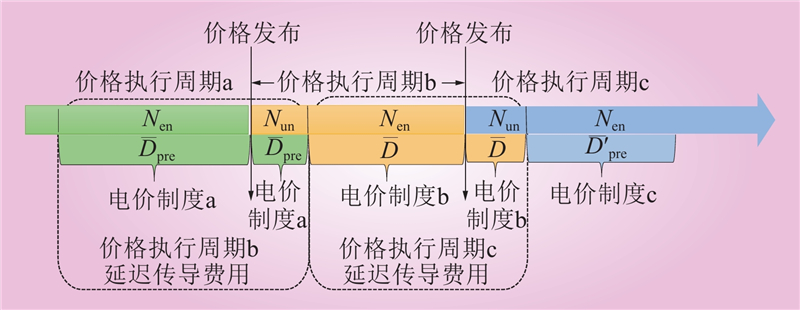
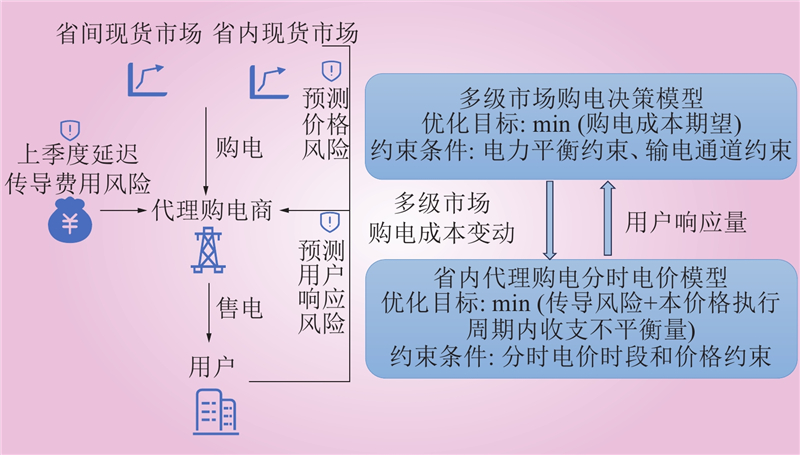
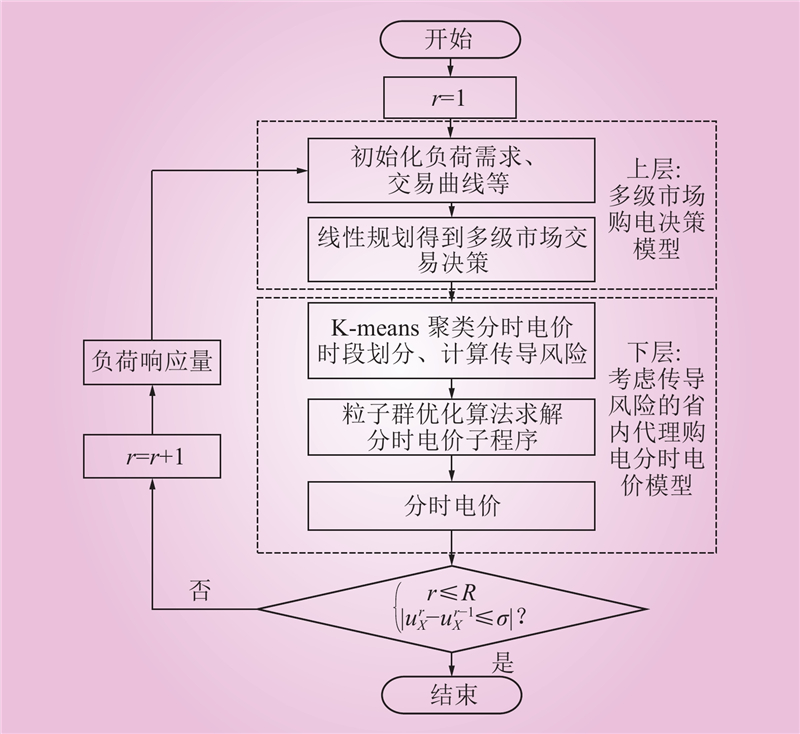
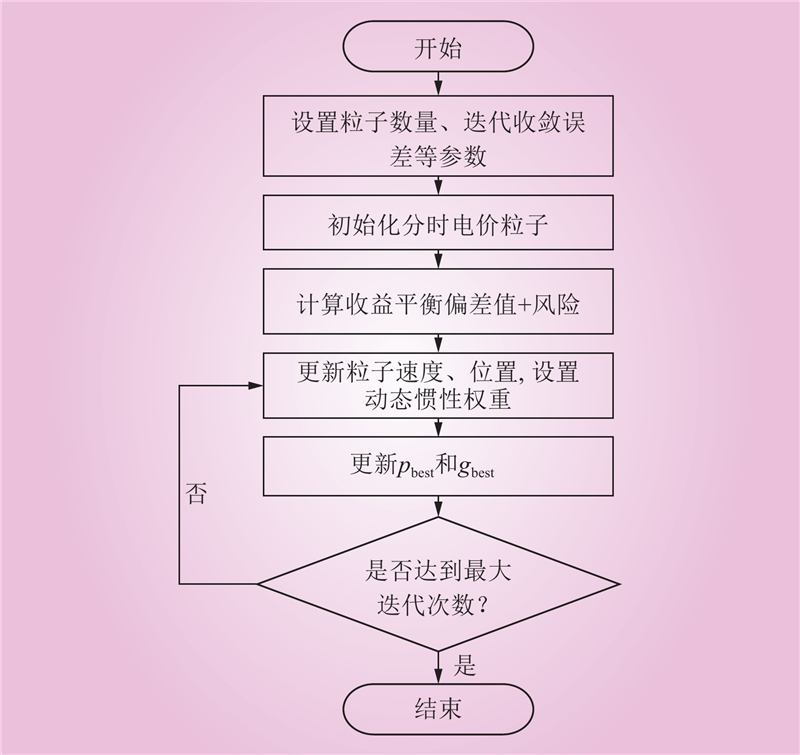
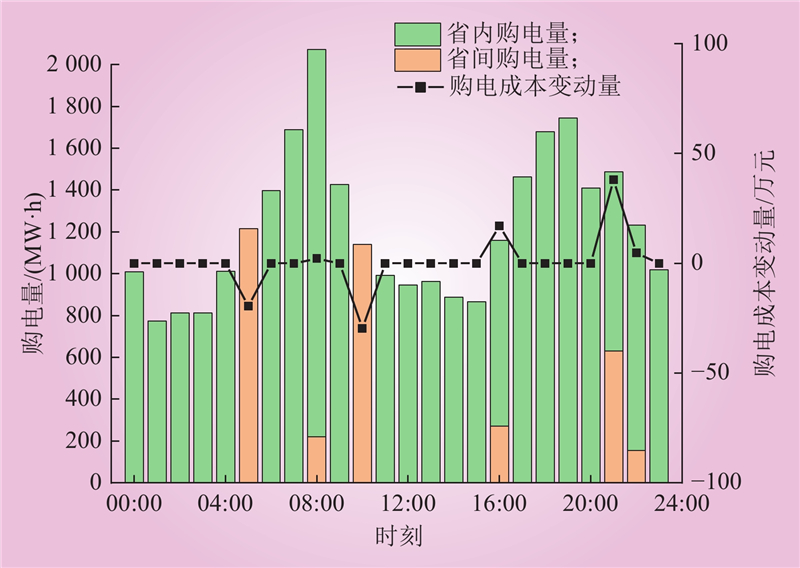
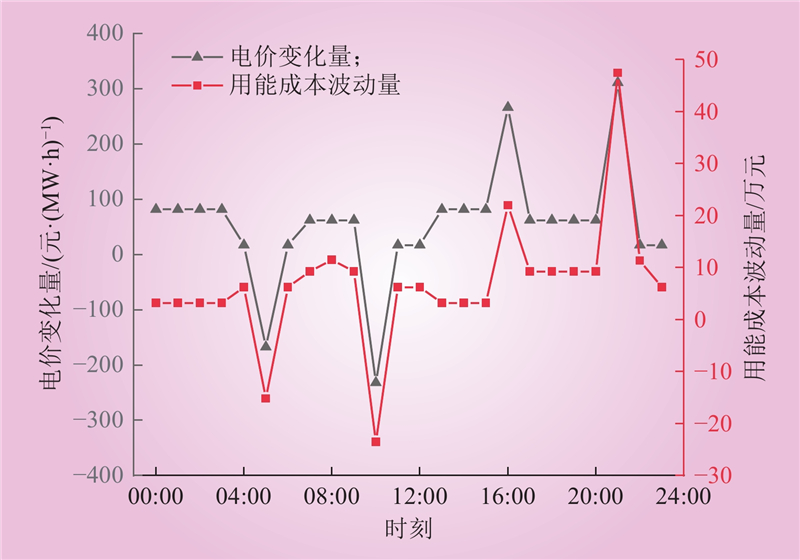
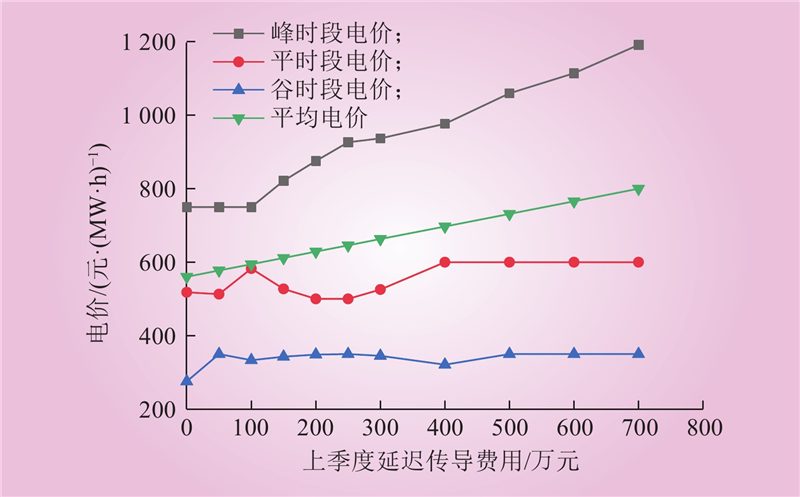
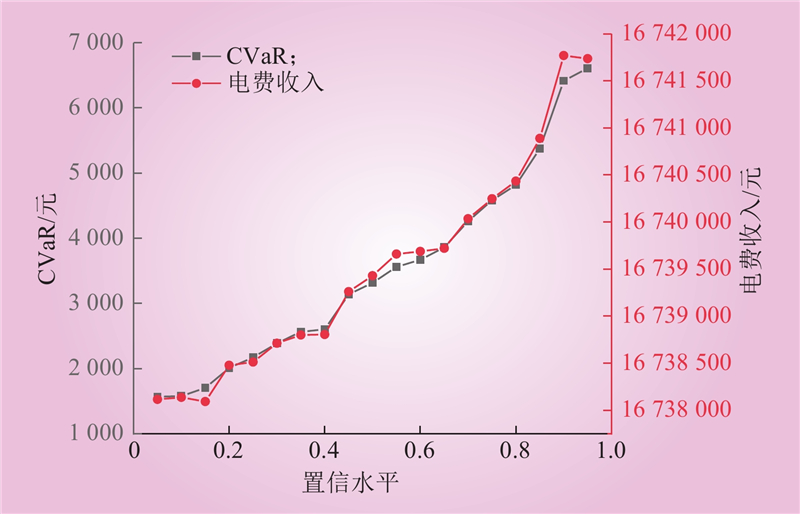
| 1 |
曹婧祎, 何永秀, 周静涵, 等. 基于需求侧响应的不同时间尺度动态分时电价时段优化研究[J]. 电力科学与技术学报, 2024, 39 (6): 242- 250, 268.
|
|
CAO Jingyi, HE Yongxiu, ZHOU Jinghan, et al. Time slot optimization of dynamic time-of-use tariffs under different time scales based on demand side response[J]. Journal of Electric Power Science and Technology, 2024, 39 (6): 242- 250, 268.
|
| 2 |
董雷, 倪佳炜, 张师铭, 等. 基于双重博弈的电价套餐设计方法[J]. 电网技术, 2024, 48 (2): 688- 700.
|
|
DONG Lei, NI Jiawei, ZHANG Shiming, et al. Designing of electricity price package method based on dual game[J]. Power System Technology, 2024, 48 (2): 688- 700.
|
| 3 |
黄剑平, 余欣, 赵东生, 等. 考虑源网荷效益的峰谷电价与峰谷时段双层优化模型[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2024, 44 (6): 217- 224.
|
|
HUANG Jianping, YU Xin, ZHAO Dongsheng, et al. Bi-layer optimization model of peak-valley prices and peak-valley periods considering benefits of source-grid-load[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2024, 44 (6): 217- 224.
|
| 4 |
李骏龙, 尤培培, 张超, 等. 基于双重差分模型的分时电价机制对用电成本的影响分析[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (11): 173- 182.
|
|
LI Junlong, YOU Peipei1 ZHANG Chao, et al. Analysis on the effect of time-of-use electricity price on electricity cost based on difference-in-differences model[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (11): 173- 182.
|
| 5 |
黄剑平, 陈皓勇, 钟佳宇, 等. 基于用户成本选择用户范围的分时电价最优策略[J]. 中国电力, 2020, 53 (9): 107- 116.
|
|
HUANG Jianping, CHEN Haoyong, ZHONG Jiayu, et al. Optimal Time-of-use price strategy with selecting customer's range based on cost[J]. Electric Power, 2020, 53 (9): 107- 116.
|
| 6 |
蔡湛, 李泽文, 邹睿奇, 等. 基于负荷转移的售电公司分时电价优化策略[J]. 南方电网技术, 2024, 18 (1): 77- 84.
|
|
CAI Zhan, LI Zewen, ZOU Ruiqi, et al. Optimization strategy of time-of-use electricity price for electricity selling companies based on load transfer[J]. Southern Power System Technology, 2024, 18 (1): 77- 84.
|
| 7 |
刘显茁, 李崇浩, 王皓怀, 等. 新型电力系统环境下电网储能运营机制和成本传导工程应用[J]. 能源与环保, 2024, 46 (3): 178- 183.
|
|
Liu Xianzhuo, Li Chonghao, Wang Haohuai, et al. Research on operation mechanism and cost conduction project application of grid energy storage in new power system environment[J]. China Energy and Environmental Protection, 2024, 46 (3): 178- 183.
|
| 8 |
何凤枝. 电力市场化改革对碳成本传导机制的影响[J]. 低碳世界, 2024, 14 (2): 163- 165.
|
| 9 |
闫豪楠, 赵文会, 刘玮. 考虑新能源参与的售电公司风险管理模型[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2018, 38 (23): 6947- 6954, 7128.
|
|
YAN Haonan, ZHAO Wenhui, LIU Wei. A risk management model of power retailers considering the participation of new energy[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2018, 38 (23): 6947- 6954, 7128.
|
| 10 |
李亚鹏, 赵志鹏, 于申, 等. 计及风险的多尺度电力市场下梯级水电月度发电计划制定方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2020, 40 (8): 2525- 2535.
|
|
LI Yapeng, ZHAO Zhipeng, YU Shen, et al. Risk constrained monthly generation scheduling of cascade hydropower plants in multiple time scale markets[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2020, 40 (8): 2525- 2535.
|
| 11 |
ALMAHDI S, YANG S Y. An adaptive portfolio trading system: a risk-return portfolio optimization using recurrent reinforcement learning with expected maximum drawdown[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2017, 87, 267- 279.
|
| 12 |
胡志林, 陈淳, 朱金吉. 基于CVaR的电网企业代理购电交易模型的研究[J]. 自动化应用, 2023, 64 (6): 195- 198, 201.
|
|
HU Zhilin, CHEN Chun, ZHU Jinji. Research on the model of power purchase agency transactions of power grid enterprises based on CVaR[J]. Automation Application, 2023, 64 (6): 195- 198, 201.
|
| 13 |
黄婧杰, 李金成, 刘科明, 等. 含CVaR及增广ε-约束法的多目标光储充电站容量优化配置[J]. 南方电网技术, 2023, 17 (10): 94- 103.
|
|
HUANG Jingjie, LI Jincheng, LIU Keming, et al. Optimal allocation of multi-objective photovoltaic energy storage charging station capacity with CVaR and augmented ε-constraint method[J]. Southern Power System Technology, 2023, 17 (10): 94- 103.
|
| 14 |
ASENSIO M, CONTRERAS J. Stochastic unit commitment in isolated systems with renewable penetration under CVaR assessment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2016, 7 (3): 1356- 1367.
|
| 15 |
李彦斌, 王佳妮, 肖婷婷, 等. 计及风险的电网企业代理购电中长期分时段滚动交易决策方法[J]. 电网技术, 2023, 47 (10): 4237- 4245.
|
|
LI Yanbin, WANG Jiani, XIAO Tingting, et al. Rolling trading decision methodology of grid companies in time division medium- & long-term electricity market considering risk management[J]. Power System Technology, 2023, 47 (10): 4237- 4245.
|
| 16 |
郭祚刚, 喻磊, 胡洋, 等. 基于合作博弈的综合能源服务商现货市场风险规避策略[J]. 中国电力, 2019, 52 (11): 28- 34.
|
|
GUO Zuogang, YU Lei, HU Yang, et al. Research on competition strategy of integrated energy service provider under the pool-based market mechanism[J]. Electric Power, 2019, 52 (11): 28- 34.
|
| 17 |
LI C, XU Y, YU X, et al. Risk-averse energy trading in multienergy microgrids: a two-stage stochastic game approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2017, 13 (5): 2620- 2630.
|
| 18 |
陈黎军, 潘熙, 黄茜, 等. 电网企业代理购电风险及其策略优化研究[J]. 广东电力, 2024, 37 (1): 39- 48.
|
|
CHEN Lijun, PAN Xi, HUANG Qian, et al. Study on electricity purchasing agent service and strategy optimization of power grid enterprises[J]. Guangdong Electric Power, 2024, 37 (1): 39- 48.
|
| 19 |
王博钰, 许小峰, 曹正, 等. 基于多维度风险度量的代理购电多市场交易策略研究[J]. 电网技术, 2025, 49 (3): 1032- 1044.
|
|
WANG Boyu, XU Xiaofeng, CAO Zheng, et al. Research on multi-market trading strategies for agency power purchase based on multi-dimensional risk measurement[J]. Power System Technology, 2025, 49 (3): 1032- 1044.
|
| 20 |
曾丹, 姚建国, 杨胜春, 等. 计及价格型负荷响应不确定性的概率潮流计算[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2015, 39 (20): 66- 71, 97.
|
|
ZENG Dan, YAO Jianguo, YANG Shengchun, et al. Probabilistic load flow calculation considering price-elasticity load uncertainties[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2015, 39 (20): 66- 71, 97.
|
| 21 |
孙博宇, 喻洁, 梅军, 等. 考虑可调负荷集群响应不确定性的联合调度模型[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2016, 44 (23): 61- 67.
|
|
SUN Boyu, YU Jie, MEI Jun, et al. Combined dispatch model of adjustable load clusters considering response uncertainty[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2016, 44 (23): 61- 67.
|
| 22 |
易明月, 童晓阳. 考虑风荷预测误差不确定性的动态经济调度[J]. 电网技术, 2019, 43 (11): 4050- 4057.
|
|
YI Mingyue, TONG Xiaoyang. Dynamic economic dispatch considering uncertainties of wind power and load forecast error[J]. Power System Technology, 2019, 43 (11): 4050- 4057.
|
| 23 |
邢家省, 杨义川, 吴桑. 关于n维正态分布线性函数服从正态分布的证明[J]. 吉首大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 42 (3): 1- 5.
|
|
XING Jiasheng, YANG Yichuan, WU Sang. Proof that n-dimensional normally distributed linear functions obey normal distribution[J]. Journal of Jishou University (Natural Sciences Edition), 2021, 42 (3): 1- 5.
|
| 24 |
张立卓. 两个非独立正态变量的联合分布不服从二维正态分布的示例[J]. 大学数学, 2014, 30 (2): 94- 98.
|
|
ZHANG Lizhuo. Examples on the joint distribution of two non-independent normal variables does not obey two-dimensional normal distribution[J]. College Mathematics, 2014, 30 (2): 94- 98.
|
| 25 |
马燕峰, 范振亚, 刘伟东, 等. 考虑碳权交易和风荷预测误差随机性的环境经济调度[J]. 电网技术, 2016, 40 (2): 412- 418.
|
|
MA Yanfeng, FAN Zhenya, LIU Weidong, et al. Environmental and economic dispatch considering carbon trading credit and randomicity of wind power and load forecast error[J]. Power System Technology, 2016, 40 (2): 412- 418.
|
| 26 |
王子强, 李豹, 杜哲宇, 等. PJM电力市场风险管控措施及对南方区域的建议[J]. 南方电网技术, 2024, 18 (1): 28- 37, 68.
|
|
WANG Ziqiang, LI Bao , DU Zheyu, et al. Risk management and control measures in pjm power market and suggestions for southern region[J]. Southern Power System Technology, 2024, 18 (1): 28- 37, 68.
|
| 27 |
曹祎, 张莉, 郭静, 等. 基于大语言模型的低碳电力市场发展应用前景[J]. 智慧电力, 2024, 52 (2): 8- 16.
|
|
CAO Yi, ZHANG Li, GUO Jing, et al. Prospects for development of low-carbon electricity markets based on large language models[J]. Smart Power, 2024, 52 (2): 8- 16.
|