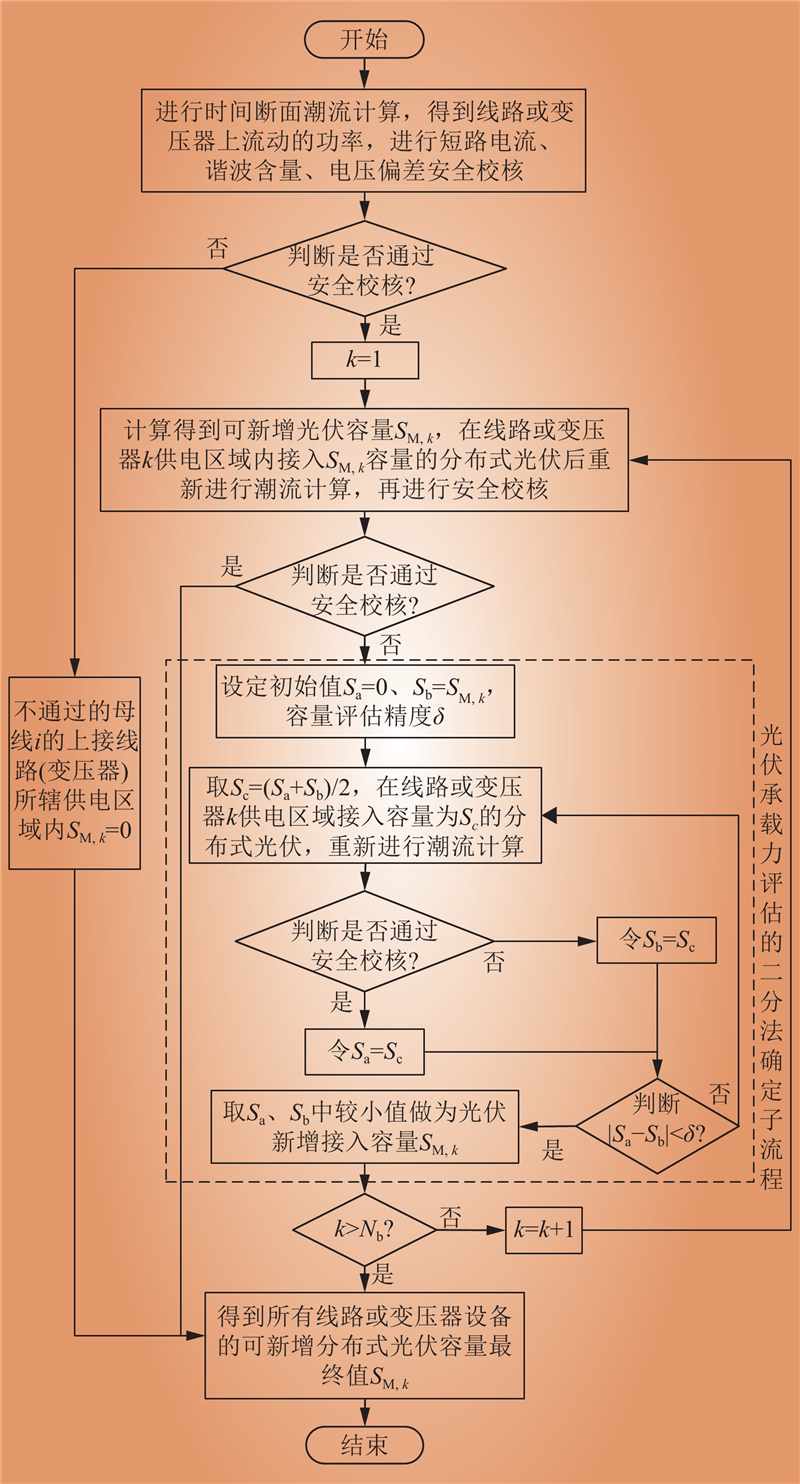
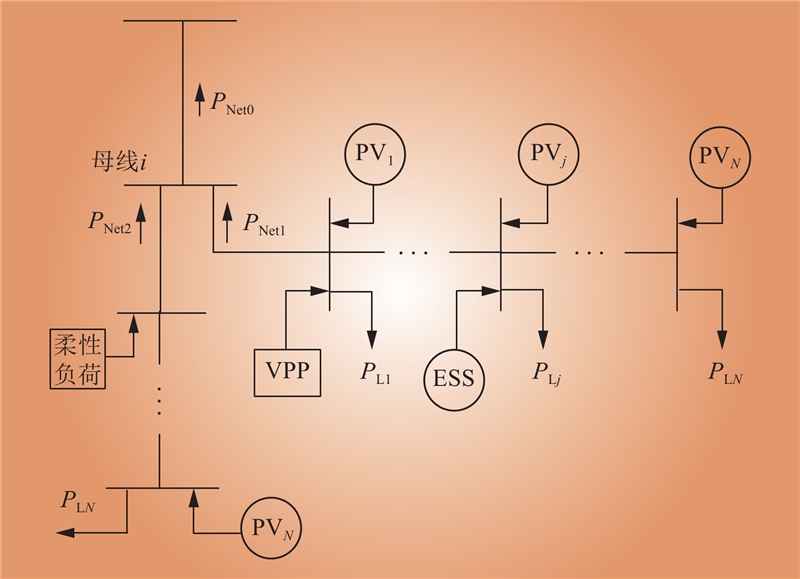
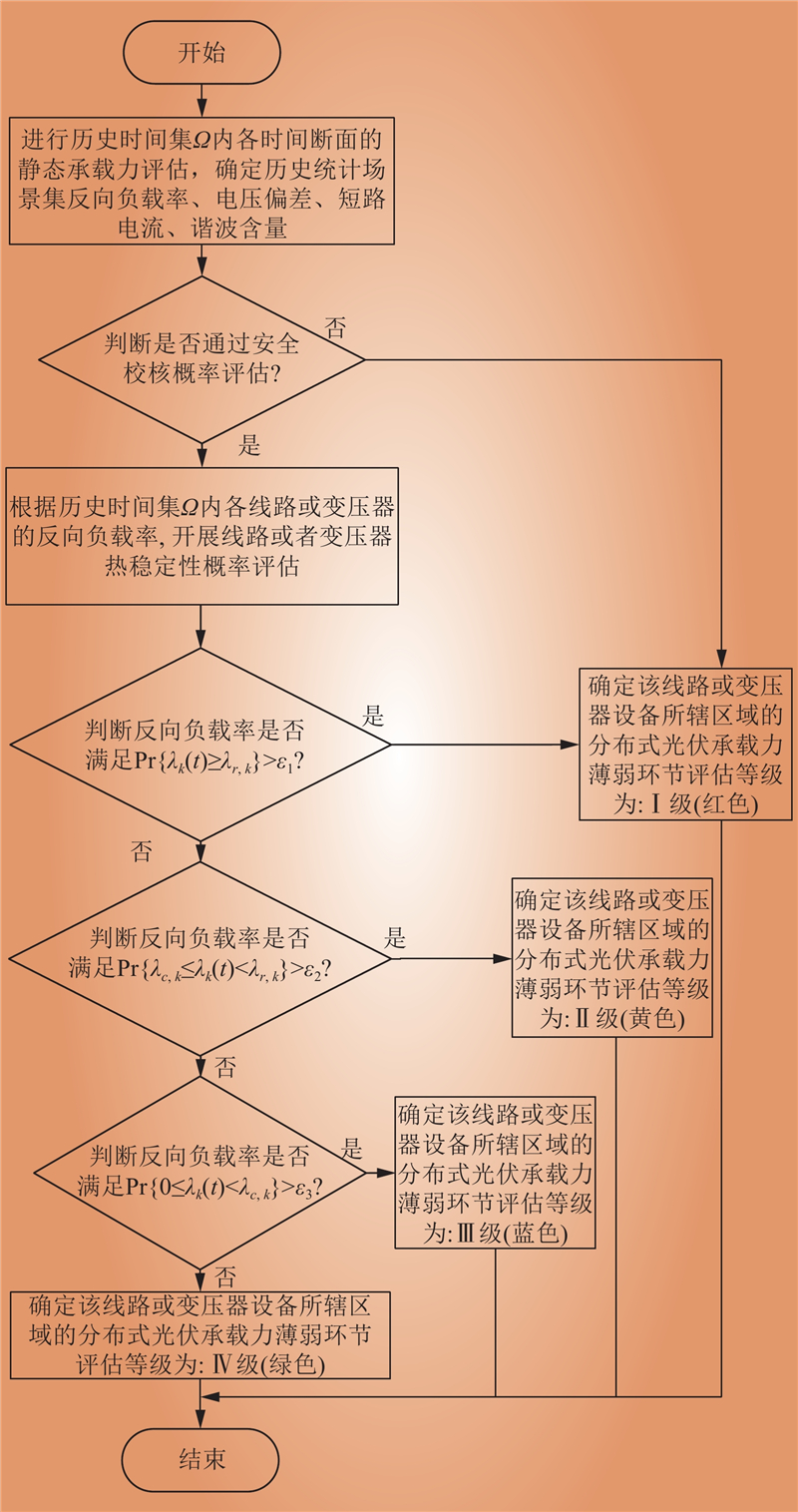
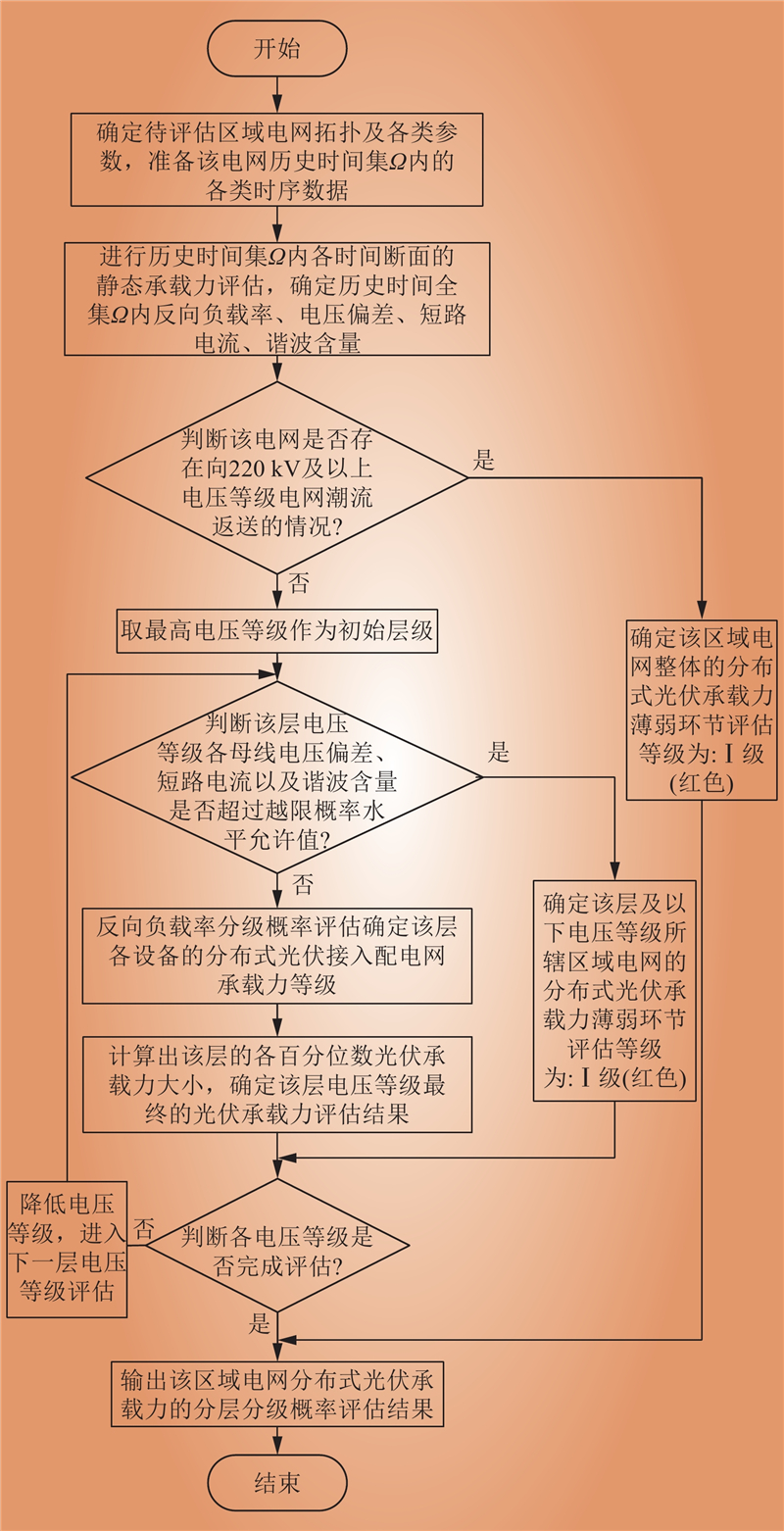
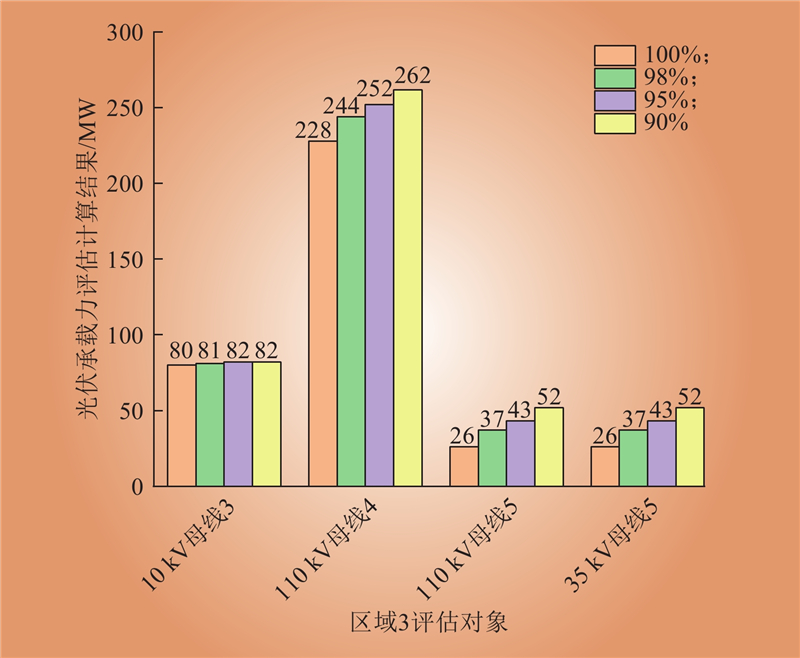
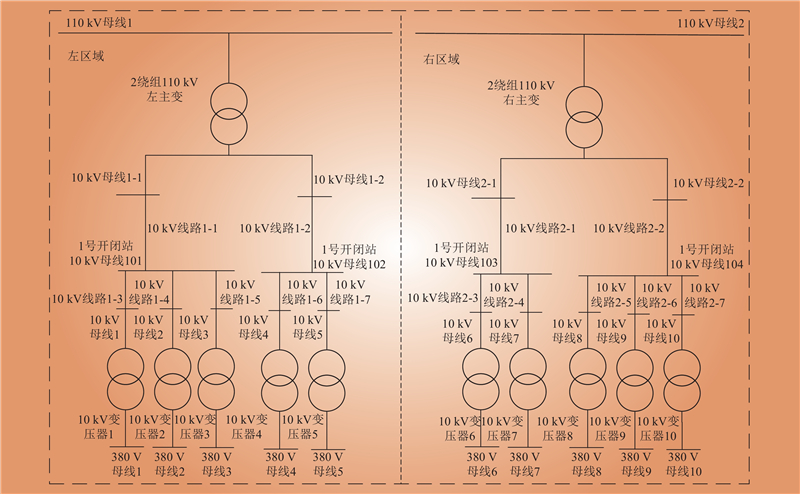
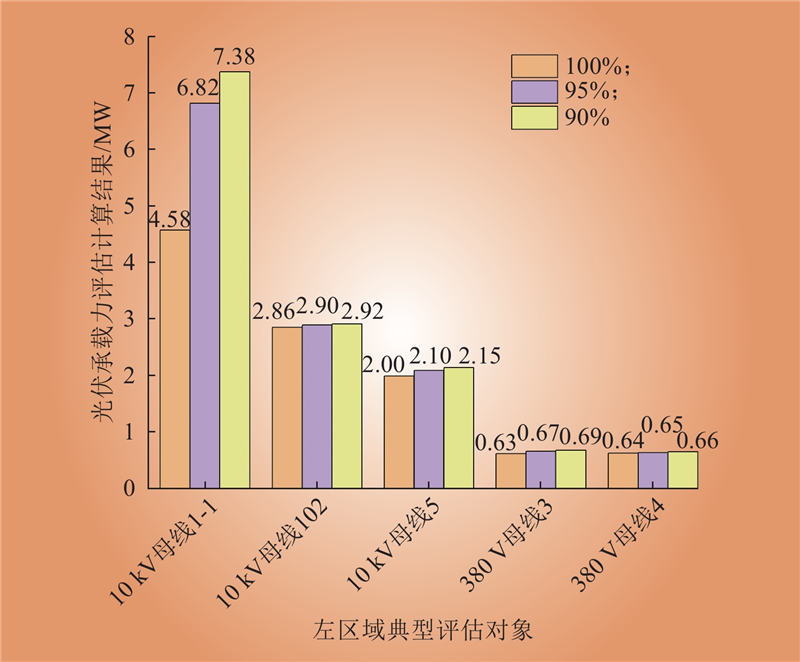
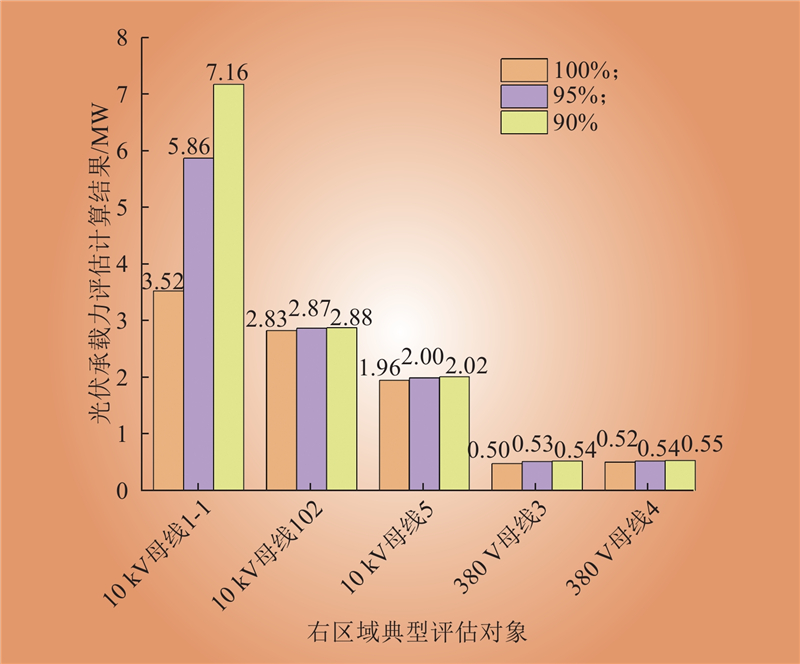
| 1 |
孙通, 张沈习, 曹毅, 等. 计及5G基站可调特性的配电网分布式光伏准入容量鲁棒优化[J]. 中国电力, 2025, 58 (2): 140- 146.
|
|
SUN Tong, ZHANG Shenxi, CAO Yi, et al. Robust optimization of hosting capacity of distributed photovoltaics in distribution network considering adjustable characteristics of 5G base station[J]. Electric Power, 2025, 58 (2): 140- 146.
|
| 2 |
分布式电源接入电网承载力评估导则: DL/T 2041—2019[S].
|
|
Guidelines for the evaluation of the carrying capacity of distributed power generation connected to the power grid: DL/T 2041—2019[S].
|
| 3 |
周洋, 黄德志, 李培栋, 等. 考虑平衡端点相位不对称及光伏接入的低压配电网三相潮流模型[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (10): 190- 198.
|
|
ZHOU Yang, HUANG Dezhi, LI Peidong, et al. A three-phase power flow model for low-voltage distribution networks considering balanced bus phase asymmetry and photovoltaic access[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (10): 190- 198.
|
| 4 |
易建波, 胡猛, 王泽宇, 等. 提升光储充电站运行效率的多目标优化配置策略[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2024, 48 (14): 100- 109.
|
|
YI Jianbo, HU Meng, WANG Zeyu, et al. Multi-objective optimal configuration strategy for improving operation efficiency of photovoltaic energy storage charging stations[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2024, 48 (14): 100- 109.
|
| 5 |
呼斯乐, 于源, 王渊, 等. 考虑灵活性分析的典型光伏日出力率曲线提取方法[J]. 内蒙古电力技术, 2024, 42 (3): 20- 27.
|
|
HU Sile, YU Yuan, WANG Yuan, et al. Method for extracting typical PV daily output curves considering flexibility analysis[J]. Inner Mongolia Electric Power, 2024, 42 (3): 20- 27.
|
| 6 |
凡鹏飞, 李宝琴, 侯江伟, 等. 配电网分布式电源经济可承载力评估[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (7): 196- 202.
|
|
FAN Pengfei, LI Baoqin, HOU Jiangwei, et al. Economic capacity assessment of renewables in distribution networks[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (7): 196- 202.
|
| 7 |
康渭滨, 寇明鑫, 张文文, 等. 光伏储能电站不同储能形式经济性对比分析[J]. 电力科技与环保, 2024, 40 (3): 276- 285.
|
|
KANG Weibin, KOU Mingxin, ZHANG Wenwen, et al. Economic comparison analysis of different energy storage forms for photovoltaic energy storage power stations[J]. Electric Power Technology and Environmental Protection, 2024, 40 (3): 276- 285.
|
| 8 |
马成廉, 李闯, 薛冰, 等. 含高比例光伏配电网分区电压协调控制策略[J]. 东北电力大学学报, 2024, 44 (4): 77- 85.
|
|
MA Chenglian, LI Chuang, XUE Bing, et al. Voltage coordination control strategy for zoning in distribution network with high proportion of photovoltaic[J]. Journal of Northeast Electric Power University, 2024, 44 (4): 77- 85.
|
| 9 |
梁志峰, 夏俊荣, 孙檬檬, 等. 数据驱动的配电网分布式光伏承载力评估技术研究[J]. 电网技术, 2020, 44 (7): 2430- 2439.
|
|
LIANG Zhifeng, XIA Junrong, SUN Mengmeng, et al. Data driven assessment of distributed photovoltaic hosting capacity in distribution network[J]. Power System Technology, 2020, 44 (7): 2430- 2439.
|
| 10 |
陈奇芳, 李若凡, 夏明超, 等. 计及多维性能评估的新型配电网光伏选址定容方法[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (10): 172- 178, 207.
|
|
CHEN Qifang, LI Ruofan, XIA Mingchao, et al. Photovoltaic site selection and capacity determination method for new distribution network considering multidimensional performance evaluation[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (10): 172- 178, 207.
|
| 11 |
刘志文, 董旭柱, 黄豫, 等. 考虑多种约束的分布式电源最大渗透率计算方法[J]. 电力系统及其自动化学报, 2019, 31 (6): 85- 92.
|
|
LIU Zhiwen, DONG Xuzhu, HUANG Yu, et al. Calculation method for maximum penetration of distributed generations considering multiple constraints[J]. Proceedings of the CSU-EPSA, 2019, 31 (6): 85- 92.
|
| 12 |
杨乔丹, 唐岚, 刘乾晖. 考虑分布式光伏的三相不平衡优化方法[J]. 电源技术, 2020, 44 (10): 1522- 1524.
|
|
YANG Qiaodan, TANG Lan, LIU Qianhui. Three phase unbalanced optimization method considering distributed photovoltaic[J]. Chinese Journal of Power Sources, 2020, 44 (10): 1522- 1524.
|
| 13 |
欧阳森, 梁伟斌, 苏为健, 等. 基于电气外特性的大型光伏电站建模及电能质量预评估方法[J]. 电工电能新技术, 2018, 37 (5): 51- 57.
|
|
OUYANG Sen, LIANG Weibin, SU Weijian, et al. Modeling and power quality pre-evaluation method of large photovoltaic power station based on electric external characteristics[J]. Advanced Technology of Electrical Engineering and Energy, 2018, 37 (5): 51- 57.
|
| 14 |
丁琦欣, 覃洪培, 万灿, 等. 基于机会约束规划的配电网分布式光伏承载能力评估[J]. 东北电力大学学报, 2022, 42 (6): 28- 38.
|
|
DING Qixin, QIN Hongpei, WAN Can, et al. Chance-constrained optimization-based distributed photovoltaic hosting capacity assessment of distribution networks[J]. Journal of Northeast Electric Power University, 2022, 42 (6): 28- 38.
|
| 15 |
王利利, 王皓, 任洲洋, 等. 计及灵活资源调节潜力的高压配电网新能源接纳能力评估[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (10): 124- 131.
|
|
WANG Lili, WANG Hao, REN Zhouyang, et al. Evaluation of renewable energy accommodation capacity of high voltage distribution networks considering regulation potential of flexible resources[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (10): 124- 131.
|
| 16 |
李利, 李征, 王文宾, 等. 兼顾经济品质的配电网分布式光伏承载能力评估方法[J]. 燕山大学学报, 2024, 48 (2): 110- 119.
|
|
LI Li, LI Zheng, WANG Wenbin, et al. Evaluation method of distributed photovoltaic hosting capacity of distribution network considering economic quality[J]. Journal of Yanshan University, 2024, 48 (2): 110- 119.
|
| 17 |
段瑶, 高崇, 程苒, 等. 考虑5G基站可调度潜力的配电网分布式光伏最大准入容量评估[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (12): 80- 85, 99.
|
|
DUAN Yao, GAO Chong, CHENG Ran, et al. Evaluation of distributed photovoltaic maximum hosting capacity for distribution network considering dispatchable potential of 5G base station[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (12): 80- 85, 99.
|
| 18 |
屈高强, 王诚良, 靳盘龙, 等. 新型负荷及分布式电源接入配网承载能力综合评估[J]. 电测与仪表, 2019, 56 (19): 37- 45, 113.
|
|
QU Gaoqiang, WANG Chengliang, JIN Panlong, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of carrying capacity in distribution network with new load and distributed generation[J]. Electrical Measurement & Instrumentation, 2019, 56 (19): 37- 45, 113.
|
| 19 |
林沛昕. 面向园区最优用能的分布式光伏及储能容量配置方法[J]. 东北电力大学学报, 2024, 44 (5): 50- 56.
|
|
LIN Peixin. Distributed photovoltaic and energy storage capacity allocation method for the optimal use of energy in the park[J]. Journal of Northeast Electric Power University, 2024, 44 (5): 50- 56.
|
| 20 |
王文倬, 谢丁, 谢醉冰, 等. 考虑集群划分的分布式光伏无功电压控制策略[J]. 浙江电力, 2024, 43 (7): 64- 75.
|
|
WANG Wenzhuo, XIE Ding, XIE Zuibing, et al. A reactive voltage control strategy for distributed PV based on cluster segmentation[J]. Zhejiang Electric Power, 2024, 43 (7): 64- 75.
|
| 21 |
NIU H N, YANG L, ZHAO J X, et al. Flexible-regulation resources planning for distribution networks with a high penetration of renewable energy[J]. IET Generation, Transmission & Distribution, 2018, 12(18): 4099-4107.
|
| 22 |
王振国, 康丽莉, 李特, 等. 浙江沿海地区台风灾害风险区域划分研究[J]. 浙江电力, 2024, 43 (3): 28- 37.
|
|
WANG Zhenguo, KANG Lili, LI Te, et al. A study on typhoon disaster risk zoning in Zhejiang coastal areas[J]. Zhejiang Electric Power, 2024, 43 (3): 28- 37.
|
| 23 |
继雅, 刘嘉丽, 张伟, 等. 电力用户碳排放指标评价体系与方法[J]. 内蒙古电力技术, 2024, 42 (5): 44- 51.
|
|
JI Ya, LIU Jiali, ZHANG Wei, et al. Evaluation system and method for carbon emission indicators of electricity users[J]. Inner Mongolia Electric Power, 2024, 42 (5): 44- 51.
|
| 24 |
杨彪, 颜伟, 莫静山. 考虑源荷功率随机性和相关性的主导节点选择与无功分区方法[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2021, 45 (11): 61- 67.
|
|
YANG Biao, YAN Wei, MO Jingshan. Pilot-bus selection and network partitioning method considering randomness and correlation of source-load power[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2021, 45 (11): 61- 67.
|
| 25 |
杨军, 王楠楠, 王江, 等. 基于潮流追踪的有源配电网碳排放流分析方法[J]. 浙江电力, 2024, 43 (6): 80- 87.
|
|
YANG Jun, WANG Nannan, WANG Jiang, et al. A method for carbon emission flow analysis in active distribution networks based on power flow tracking[J]. Zhejiang Electric Power, 2024, 43 (6): 80- 87.
|
| 26 |
朱朝阳, 景栋盛, 李荷婷, 等. 多源数据驱动的中低压配电网通用拓扑辨识框架[J]. 中国电力, 2025, 58 (5): 137- 143.
|
|
ZHU Chaoyang, JING Dongsheng, LI Heting, et al. A topology identification framework for medium and low voltage distribution networks driven by multiple source data[J]. Electric Power, 2025, 58 (5): 137- 143.
|
| 27 |
范仲鸣, 纪陵, 张晓瑞. 配电系统电力设备数字孪生底座系统设计[J]. 综合智慧能源, 2023, 45 (3): 50- 56.
|
|
FAN Zhongming, JI Ling, ZHANG Xiaorui. Design of a base system for power equipment in a distribution system based on digital twin[J]. Integrated Intelligent Energy, 2023, 45 (3): 50- 56.
|
| 28 |
王奎, 余梦, 张海静, 等. 面向光伏消纳和冰蓄冷空调群低碳需求响应的新型配电系统多时间尺度优化策略[J]. 发电技术, 2025, 46 (2): 284- 295.
|
|
WANG Kui, YU Meng, ZHANG Haijing, et al. Multi-time scale optimization strategy for new distribution system oriented to photovoltaic consumption and low carbon demand response of ice storage air conditioning groups[J]. Power Generation Technology, 2025, 46 (2): 284- 295.
|