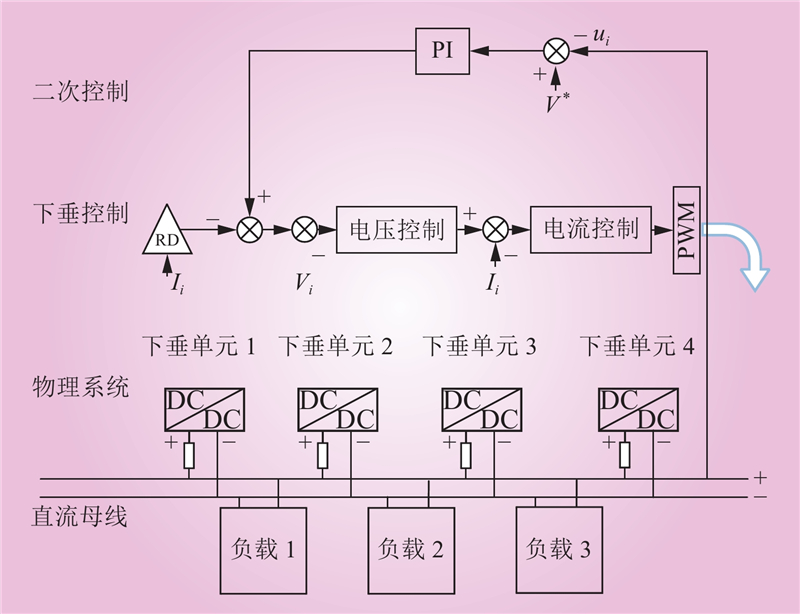
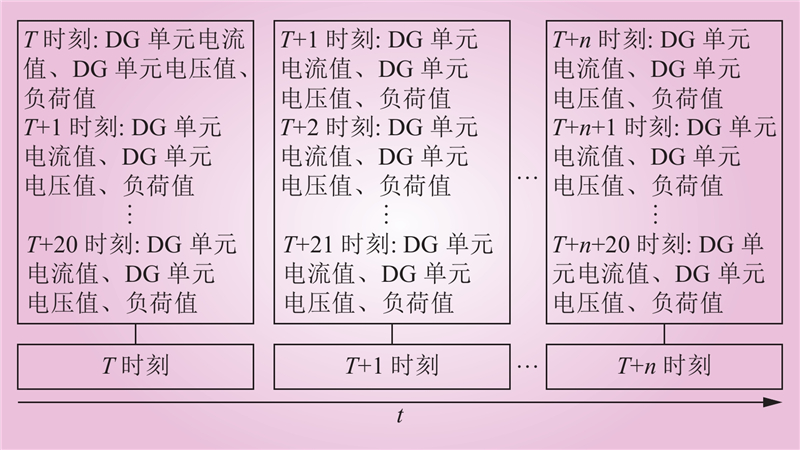
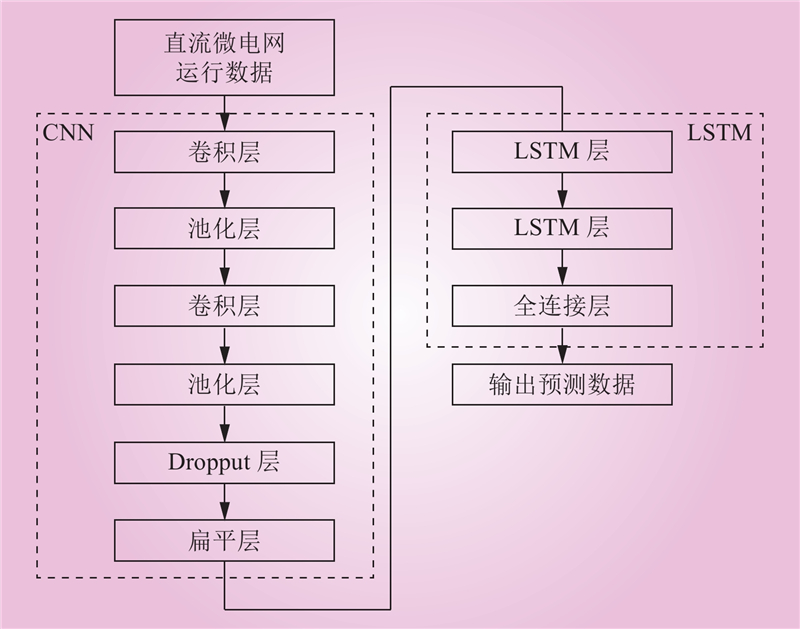
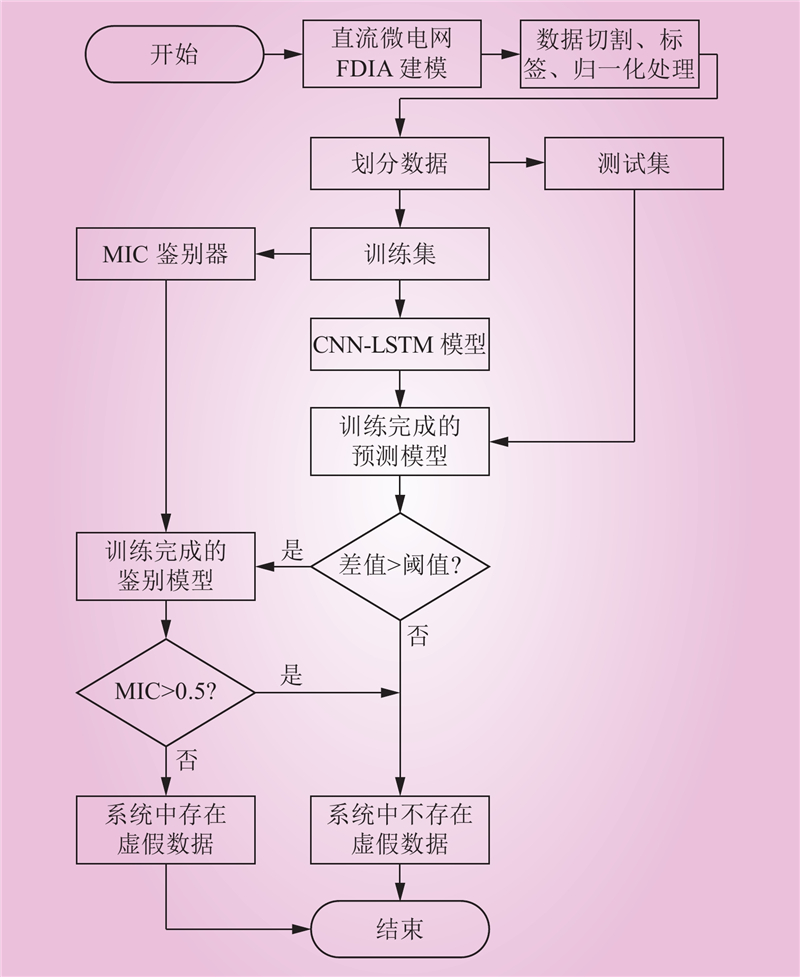
| 1 |
李霞林, 郭力, 王成山, 等. 直流微电网关键技术研究综述[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2016, 36 (1): 2- 17.
|
|
LI Xialin, GUO Li, WANG Chengshan, et al. Key technologies of DC microgrids: an overview[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2016, 36 (1): 2- 17.
|
| 2 |
刘建伟, 李学斌, 刘晓鸥. 有源配电网中分布式电源接入与储能配置[J]. 发电技术, 2022, 43 (3): 476- 484.
|
|
LIU Jianwei, LI Xuebin, LIU Xiaoou. Distributed power access and energy storage configuration in active distribution network[J]. Power Generation Technology, 2022, 43 (3): 476- 484.
|
| 3 |
周杨, 张俊勃. 适用于孤岛微电网的电压型虚拟同步发电机自适应惯性控制与频率恢复控制[J]. 南方电网技术, 2022, 16 (1): 127- 136.
|
|
ZHOU Yang, ZHANG Junbo. Adaptive inertia control and frequency recovery control of voltage-controlled virtual synchronous generators for an isolated microgrid[J]. Southern Power System Technology, 2022, 16 (1): 127- 136.
|
| 4 |
刘骁康, 王燕舞, 肖江文. 环形直流微电网的二次控制与稳定性分析[J]. 控制理论与应用, 2021, 38 (7): 979- 987.
|
|
LIU Xiaokang, WANG Yanwu, XIAO Jiangwen. Secondary control and stability analysis of ring-bus DC microgrids[J]. Control Theory & Applications, 2021, 38 (7): 979- 987.
|
| 5 |
LAI J G, LU X Q, YU X H, et al. Distributed voltage regulation for cyber-physical microgrids with coupling delays and slow switching topologies[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2020, 50 (1): 100- 110.
|
| 6 |
王波, 张占营, 张霄, 等. 直流微电网分布式储能系统精确电流分配策略[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (8): 96- 103, 112.
|
|
WANG Bo, ZHANG Zhanying, ZHANG Xiao, et al. Accurate current sharing strategy for distributed energy storage system in DC microgrids[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (8): 96- 103, 112.
|
| 7 |
阳育德, 蓝水岚, 覃智君, 等. 电力信息物理融合系统的网络-物理协同攻击[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2020, 40 (2): 97- 103.
|
|
YANG Yude, LAN Shuilan, QIN Zhijun, et al. Coordinated cyber-physical attacks of cyber-physical power system[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2020, 40 (2): 97- 103.
|
| 8 |
韩丽芳, 胡博文, 杨军, 等. 基于攻击预测的电力CPS安全风险评估[J]. 中国电力, 2019, 52 (1): 48- 56.
|
|
HAN Lifang, HU Bowen, YANG Jun, et al. A new security risk assessment method for cyber physical power system based on attack prediction[J]. Electric Power, 2019, 52 (1): 48- 56.
|
| 9 |
陈郁林, 齐冬莲, 李真鸣, 等. 虚假数据注入攻击下的微电网分布式协同控制[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2021, 45 (5): 97- 103.
|
|
CHEN Yulin, QI Donglian, LI Zhenming, et al. Distributed cooperative control of microgrid under false data injection attacks[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2021, 45 (5): 97- 103.
|
| 10 |
何耀, 周聪, 郑凌月, 等. 基于扩展卡尔曼滤波的虚假数据攻击检测方法[J]. 中国电力, 2017, 50 (10): 35- 40.
|
|
HE Yao, ZHOU Cong, ZHENG Lingyue, et al. Detection method against false data injection attack based on extended Kalman filter[J]. Electric Power, 2017, 50 (10): 35- 40.
|
| 11 |
ALI B O, JOHNSON TAYLOR T, ALI D. Detection of false-data injection attacks in cyber-physical DC microgrids[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2017, 13 (5): 2693- 2703.
|
| 12 |
王琦, 李梦雅, 汤奕, 等. 电力信息物理系统网络攻击与防御研究综述(一)建模与评估[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2019, 43 (9): 9- 21.
|
|
WANG Qi, LI Mengya, TANG Yi, et al. A review on research of cyber-attacks and defense in cyber physical power systems part one modelling and evaluation[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2019, 43 (9): 9- 21.
|
| 13 |
GALLO A J, TURAN M S, BOEM F, et al. A distributed cyber-attack detection scheme with application to DC microgrids[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2020, 65 (9): 3800- 3815.
|
| 14 |
郭方洪, 郑祥康, 邓超, 等. 直流微电网无界虚假数据注入网络攻击检测与系统恢复方法[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2023, 47 (2): 146- 153.
|
|
GUO Fanghong, ZHENG Xiangkang, DENG Chao, et al. Detection and system recovery method against unbounded false data injection network attack on DC microgrid[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2023, 47 (2): 146- 153.
|
| 15 |
HABIBI M R, BAGHAEE H R, DRAGICEVIC T, et al. Detection of false data injection cyber-attacks in DC microgrids based on recurrent neural networks[J]. IEEE Journal of Emerging and Selected Topics in Power Electronics, 2021, 9 (5): 5294- 5310.
|
| 16 |
HABIBI M R , BAGHAEE H R , DRAGICEVIC T , et al. False data injection cyber-attacks mitigation in parallel DC/DC converters based on artificial neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 2020, PP(99): 1–5.
|
| 17 |
陈亮, 王震, 王刚. 深度学习框架下LSTM网络在短期电力负荷预测中的应用[J]. 电力信息与通信技术, 2017, 15 (5): 8- 11.
|
|
CHEN Liang, WANG Zhen, WANG Gang. Application of LSTM networks in short-term power load forecasting under the deep learning framework[J]. Electric Power Information and Communication Technology, 2017, 15 (5): 8- 11.
|
| 18 |
陈卓, 孙龙祥. 基于深度学习LSTM网络的短期电力负荷预测方法[J]. 电子技术, 2018, 47 (1): 39- 41.
|
|
CHEN Zhuo, SUN Longxiang. Short-term electrical load forecasting based on deep learning LSTM networks[J]. Electronic Technology, 2018, 47 (1): 39- 41.
|
| 19 |
陈铁, 张治藩, 李咸善, 等. 基于混合模态分解和LSTM-CNN的变压器油中溶解气体浓度预测[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (1): 132- 141.
|
|
CHEN Tie, ZHANG Zhifan, LI Xianshan, et al. Prediction of dissolved gas concentration in transformer oil based on hybrid mode decomposition and LSTM-CNN[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (1): 132- 141.
|
| 20 |
GUO F H, XU Q W, WEN C Y, et al. Distributed secondary control for power allocation and voltage restoration in islanded DC microgrids[J]. IEEE Transactions on Sustainable Energy, 2018, 9 (4): 1857- 1869.
|
| 21 |
陆继翔, 张琪培, 杨志宏, 等. 基于CNN-LSTM混合神经网络模型的短期负荷预测方法[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2019, 43 (8): 131- 137.
|
|
LU Jixiang, ZHANG Qipei, YANG Zhihong, et al. Short-term load forecasting method based on CNN-LSTM hybrid neural network model[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2019, 43 (8): 131- 137.
|
| 22 |
ZUO S, ALTUN T, LEWIS F L, et al. Distributed resilient secondary control of DC microgrids against unbounded attacks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2020, 11 (5): 3850- 3859.
|
| 23 |
DENG C, GUO F H, WEN C Y, et al. Distributed resilient secondary control for DC microgrids against heterogeneous communication delays and DoS attacks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2022, 69 (11): 11560- 11568.
|