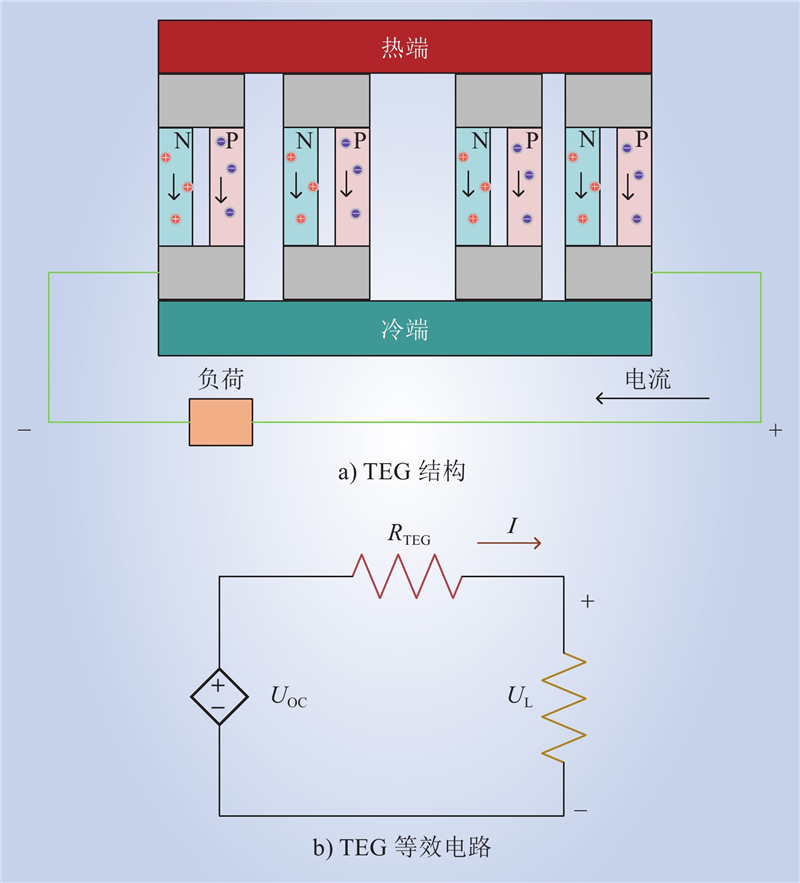
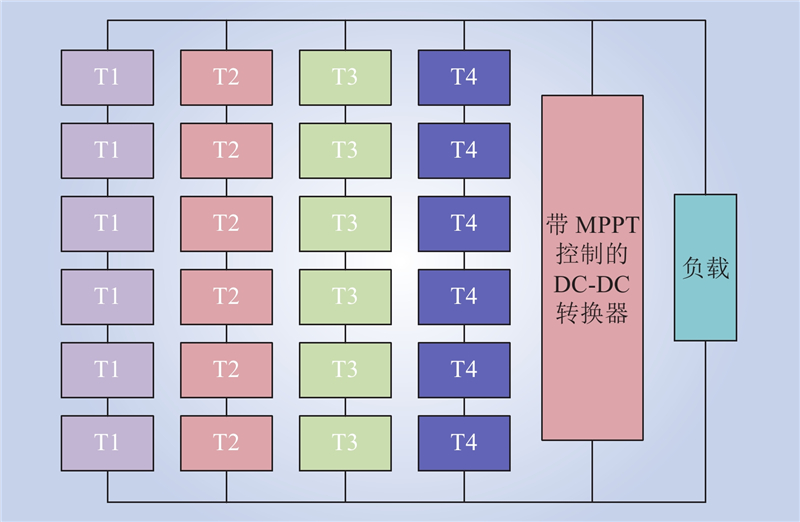
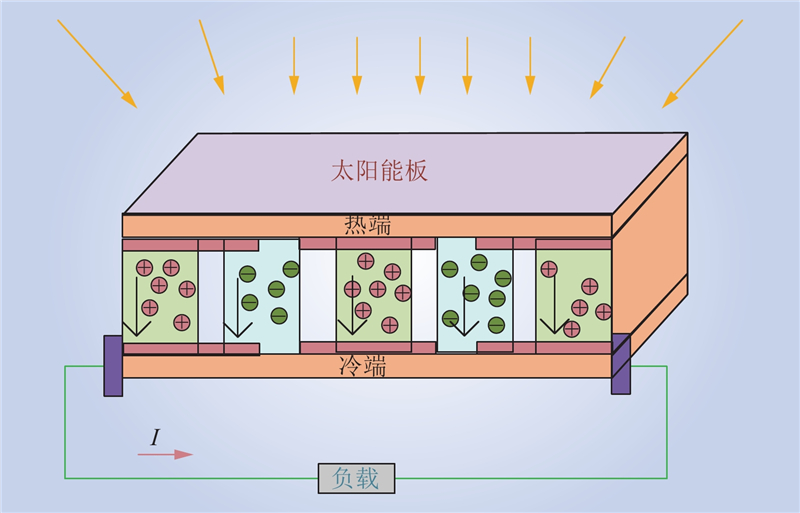
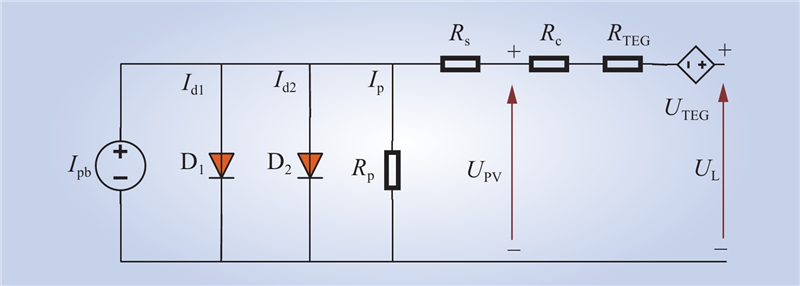
| 1 |
武群丽, 席曼. 基于电力供应链博弈的可再生能源政策效应研究[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (5): 12- 20, 38.
|
|
WU Qunli, XI Man. Research on effects of renewable energy policy based on power supply chain game[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (5): 12- 20, 38.
|
| 2 |
许洪华, 邵桂萍, 鄂春良, 等. 我国未来能源系统及能源转型现实路径研究[J]. 发电技术, 2023, 44 (4): 484- 491.
|
|
XU Honghua, SHAO Guiping, E Chunliang, et al. Research on China's future energy system and the realistic path of energy transformation[J]. Power Generation Technology, 2023, 44 (4): 484- 491.
|
| 3 |
MAHIDIN E, HUSIN H, ZAKI N. M, et al. Critical review of the integration of renewable energy sources with various technologies[J]. Protection and Control of Modern Power Systems, 2021, 6 (1): 37- 54.
|
| 4 |
YANG B, WU S, ZHANG H, et al. Wave energy converter array layout optimization: A critical and comprehensive overview[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2022, 167, 112668.
|
| 5 |
董洁,乔建强. “双碳”目标下先进煤炭清洁利用发电技术研究综述,2022,55(8):202-212.[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (8): 202- 212.
|
|
DONG Jie, QIAO Jianqiang. A review on advanced clean coal power generation technology under "Carbon Peaking and Carbon Neutrality" goal[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (8): 202- 212.
|
| 6 |
曹钰, 房磊. “双碳”背景下热电机组-储热联合运行消纳弃风策略[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (10): 142- 149, 160.
|
|
CAO Yu, FANG Lei. Combined operation strategy of CHP unit and heat accumulator for eliminate abandoned wind under "Double Carbon" background[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (10): 142- 149, 160.
|
| 7 |
YANG B, WU S, LI Q, et al. Jellyfish search algorithm based optimal thermoelectric generation array reconfiguration under non-uniform temperature distribution condition[J]. Renewable Energy, 2023, 204, 197- 217.
|
| 8 |
GUCHHAIT P K, BANERJEE A. Stability enhancement of wind energy integrated hybrid system with the help of static synchronous compensator and symbiosis organisms search algorithm[J]. Protection and Control of Modern Power Systems, 2020, 5 (1): 1- 13.
|
| 9 |
王奔, 牛洪海, 徐卫峰, 等. 基于PLC的槽式光热太阳能追踪控制系统的研究与应用[J]. 中国电力, 2020, 53 (11): 185- 194.
|
|
WANG Ben, NIU Honghai, XU Weifeng, et al. Research and application of parabolic sun-tracking system based on PLC[J]. Electric Power, 2020, 53 (11): 185- 194.
|
| 10 |
薛飞, 马鑫, 田蓓, 等. 基于改进蜻蜓算法的光伏全局最大功率追踪[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (2): 131- 137.
|
|
XUE Fei, MA Xin, TIAN Bei, et al. Photovoltaic global maximum power tracking based on improved dragonfly algorithm[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (2): 131- 137.
|
| 11 |
LUND J W, TOTH A N. Direct utilization of geothermal energy 2020 worldwide review[J]. Geothermics, 2021, 90, 101915.
|
| 12 |
李鹏, 信鹏飞, 窦鹏冲, 等. 计及光伏发电最大功率跟踪的光储微电网功率协调控制方法[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2014, 38 (4): 8- 13, 103.
|
|
LI Peng, XIN Pengfei, DOU Pengchong, et al. Power coordinated control of photovoltaic energy-storage system in microgrid under photovoltaic maximum power point tracking condition[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2014, 38 (4): 8- 13, 103.
|
| 13 |
HÜBNER S, ECK M, STILLER C, et al. Techno-economic heat transfer optimization of large scale latent heat energy storage systems in solar thermal power plants[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2016, 98, 483- 491.
|
| 14 |
LU F L, ZHU Y, PAN M Z, et al. Thermodynamic, economic, and environmental analysis of new combined power and space cooling system for waste heat recovery in waste-to-energy plant[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2020, 226, 113511.
|
| 15 |
王立舒, 白龙, 房俊龙, 等. 基于双曲正切函数的光伏/温差自适应MPPT控制策略研究[J]. 农业工程学报, 2021, 37 (16): 184- 191.
|
|
WANG Lishu, BAI Long, FANG Junlong, et al. Self-adaptive photovoltaic/temperature difference MPPT control strategy based on hyperbolic tangent function[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2021, 37 (16): 184- 191.
|
| 16 |
CALISE F, CAPPIELLO F L, D'ACCADIA M D, et al. Smart grid energy district based on the integration of electric vehicles and combined heat and power generation[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2021, 234 (8): 113932.
|
| 17 |
LI K W, GARRISON G, MOORE M, et al. An expandable thermoelectric power generator and the experimental studies on power output[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2020, 160, 120205.
|
| 18 |
CHEN M, LUND H, ROSENDAHL L A, et al. Energy efficiency analysis and impact evaluation of the application of thermoelectric power cycle to today's CHP systems[J]. Applied Energy, 2021, 87 (4): 1231- 1238.
|
| 19 |
TORRECILLA M C, MONTECUCCO A, SIVITER, J, et al. Novel model and maximum power tracking algorithm for thermoelectric generators operated under constant heat flux[J]. Applied Energy, 2019, 256, 113930.
|
| 20 |
韩鹏, 李银红, 何璇, 等. 结合量子粒子群算法的光伏多峰最大功率点跟踪改进方法[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2016, 40 (23): 101- 108.
|
|
HAN Peng, LI Yinhong, HE Xuan, et al. Improved maximum power point tracking method for photovoltaic multi-peak based on quantum-behaved particle swarm optimization algorithm[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2016, 40 (23): 101- 108.
|
| 21 |
REZK H, ELTAMALY A M. A comprehensive comparison of different MPPT techniques for photovoltaic systems[J]. Solar Energy, 2015, 112 (2): 1- 11.
|
| 22 |
殷明慧, 蒯狄正, 李群, 等. 风机最大功率点跟踪的失效现象[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2011, 31 (18): 40- 47.
|
|
YIN Minghui, KUAI Dizheng, LI Qun, et al. A phenomenon of maximum power point tracking invalidity of wind turbines[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2011, 31 (18): 40- 47.
|
| 23 |
MUZATHIK A M, LANKA S. Photovoltaic modules operating temperature estimation using a simple correlation[J]. International Journal of Energy Engineering, 2014, 4 (4): 151.
|
| 24 |
BALATO M, COSTANZO L, LO SCHIAVO A, et al. Optimization of both perturb & observe and open circuit voltage MPPT techniques for resonant piezoelectric vibration harvesters feeding bridge rectifiers[J]. Sensors and Actuators A Physical, 2018, 278: 85-97.
|
| 25 |
REZK H, FATHY A, ABDELAZIZ A Y. A comparison of different global MPPT techniques based on meta-heuristic algorithms for photovoltaic system subjected to partial shading condition[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2017, 74, 377- 386.
|
| 26 |
ZAKI DIAB A A, REZK H. Global MPPT based on flower pollination and differential evolution algorithms to mitigate partial shading in building integrated PV system[J]. Solar Energy, 2017, 157, 171- 186.
|
| 27 |
MOHAMED M A, ZAKI DIAB A A, REZK H. Partial shading mitigation of PV systems via different meta-heuristic techniques[J]. Renewable Energy, 2019, 130: 1159–1175.
|
| 28 |
FARIS H, MAFARJA M M, HEIDARI A A, et al. An efficient binary salp swarm algorithm with crossover scheme for feature selection problems[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2018, 154, 43- 67.
|
| 29 |
EL-FERGANY A. Extracting optimal parameters of PEM fuel cells using salp swarm optimizer[J]. Renewable Energy, 2018, 119, 641- 648.
|
| 30 |
JATELY V, ARORA S. Development of a dual-tracking technique for extracting maximum power from PV systems under rapidly changing environmental conditions[J]. Energy, 2017, 133, 557- 571.
|
| 31 |
LI X S, WEN H Q, HU Y H, et al. Modified beta algorithm for GMPPT and partial shading detection in photovoltaic systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2018, 33 (3): 2172- 2186.
|