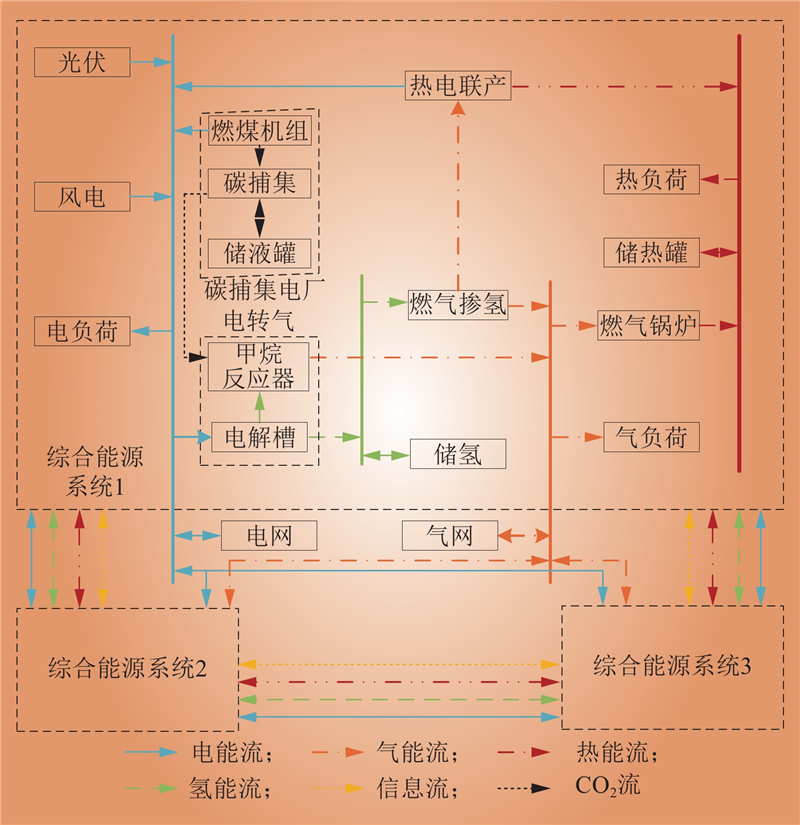
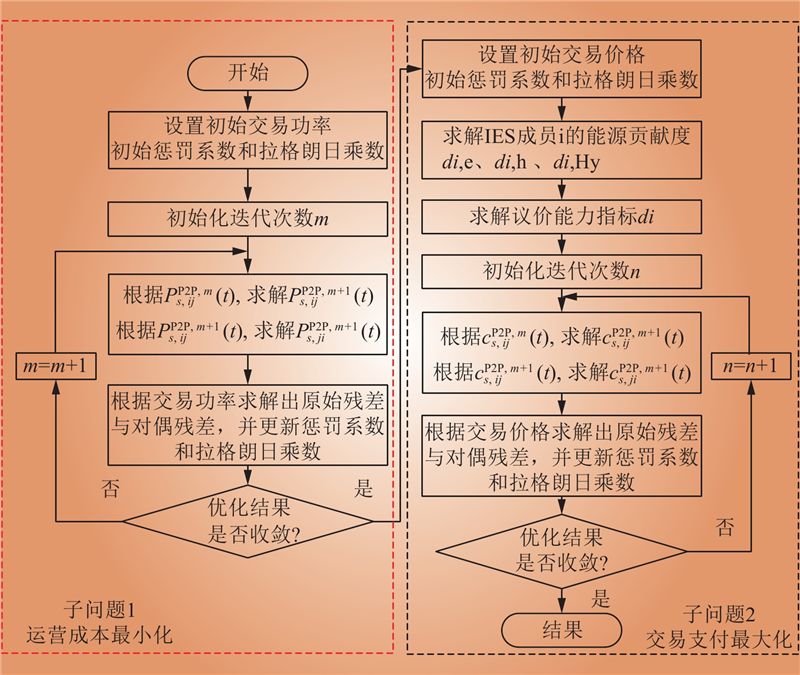
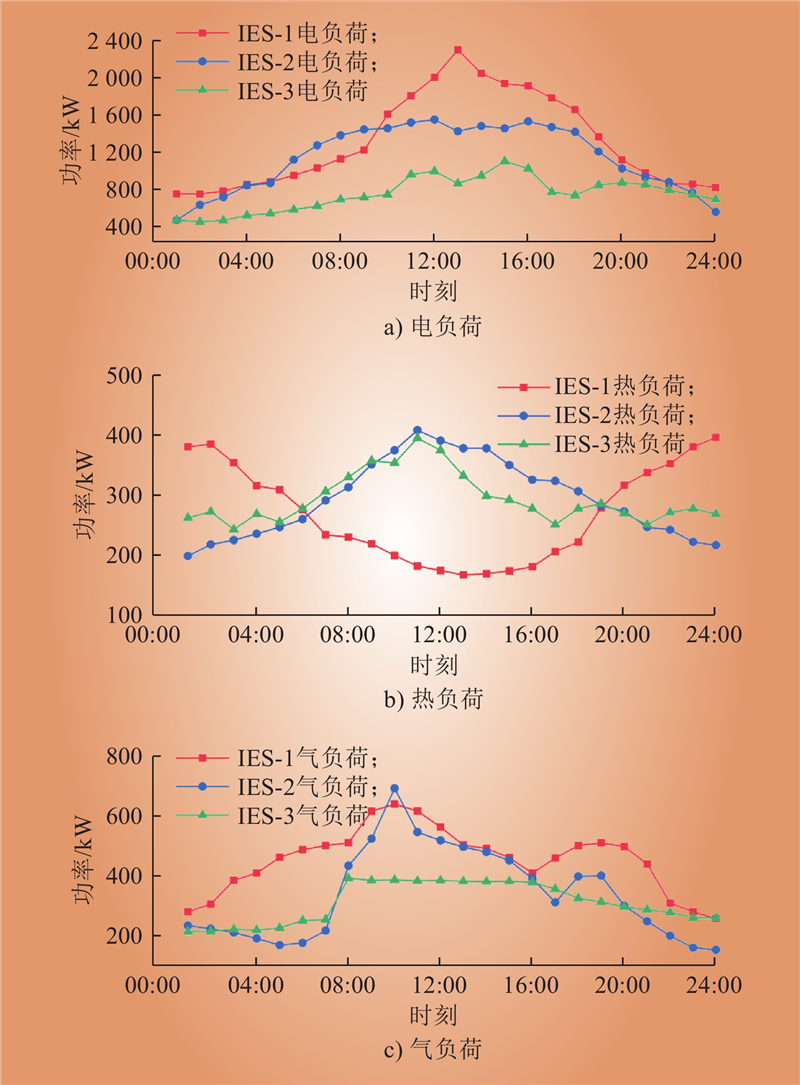
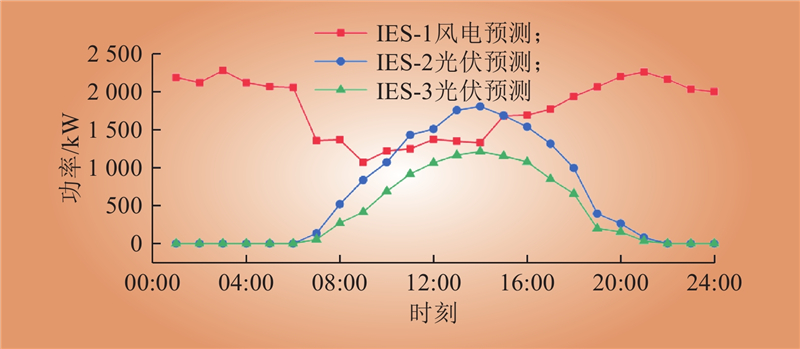
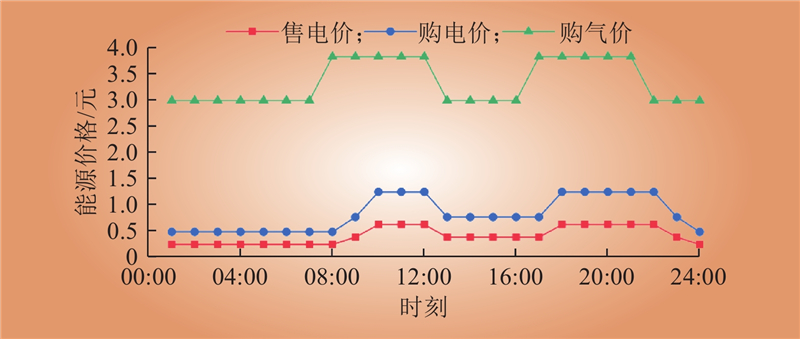
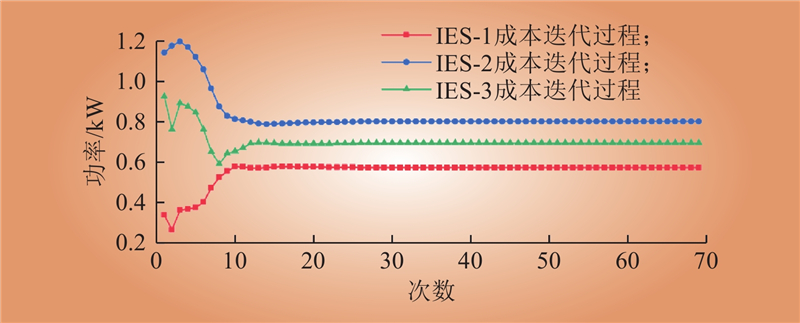
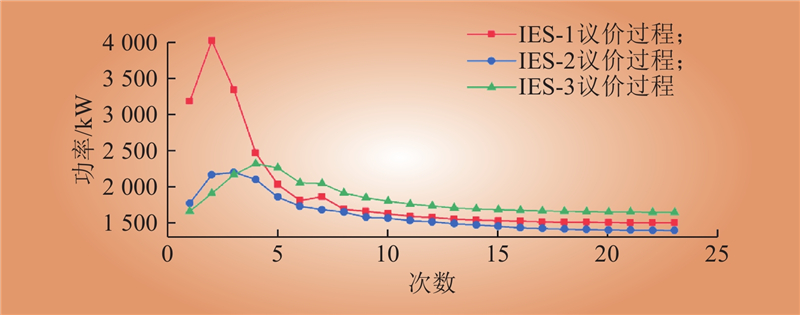
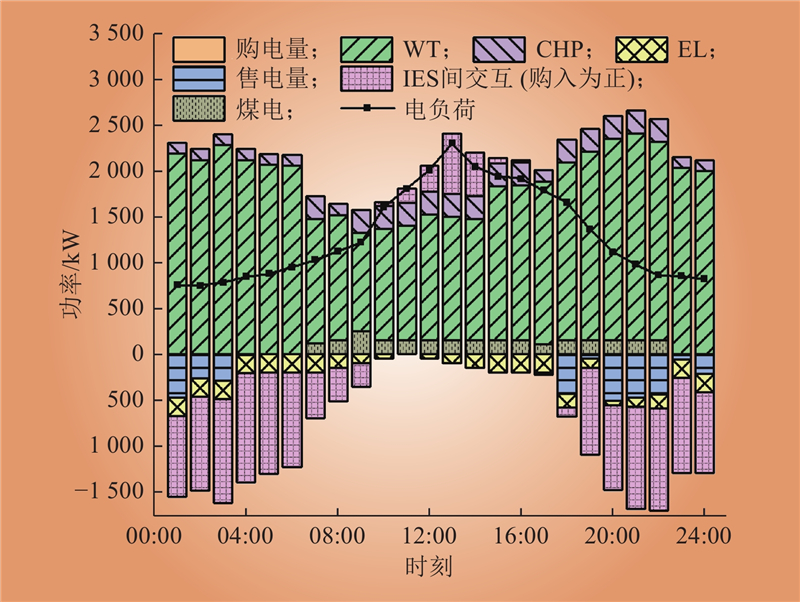
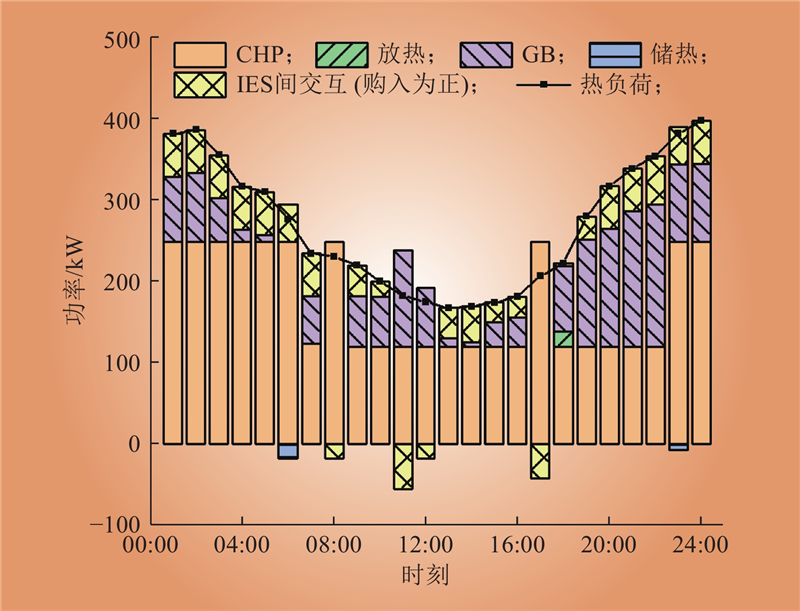
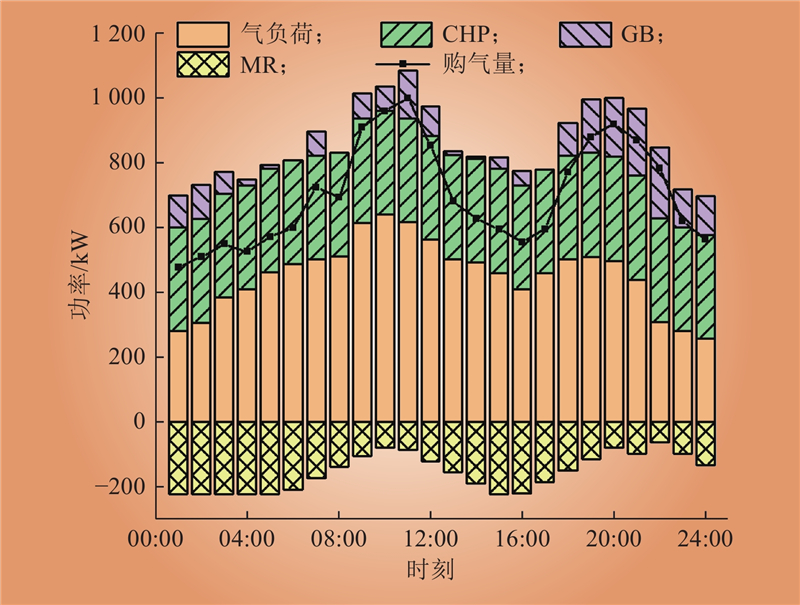
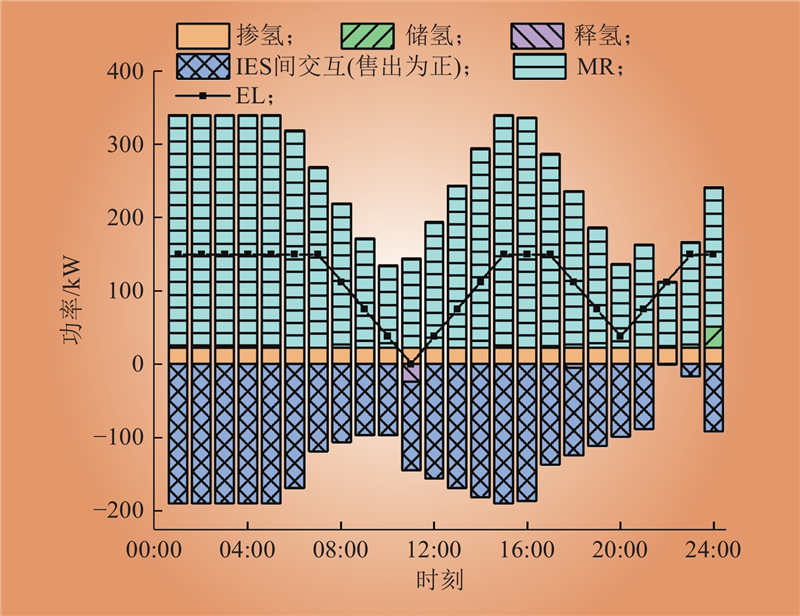
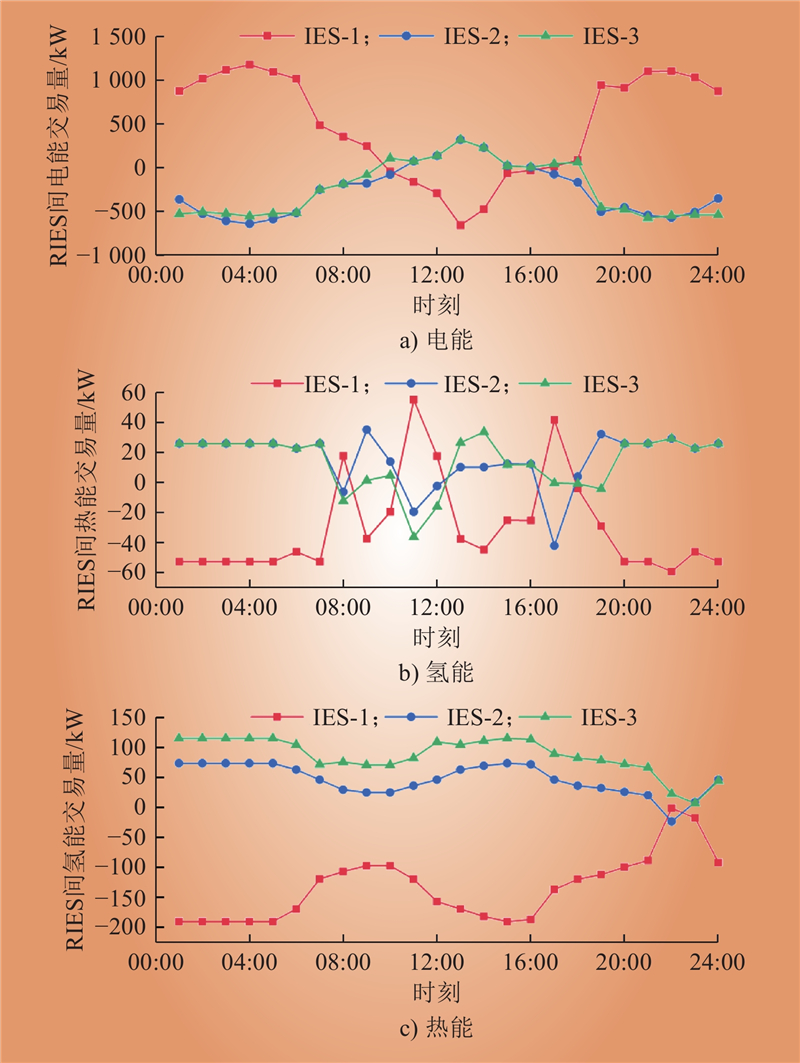
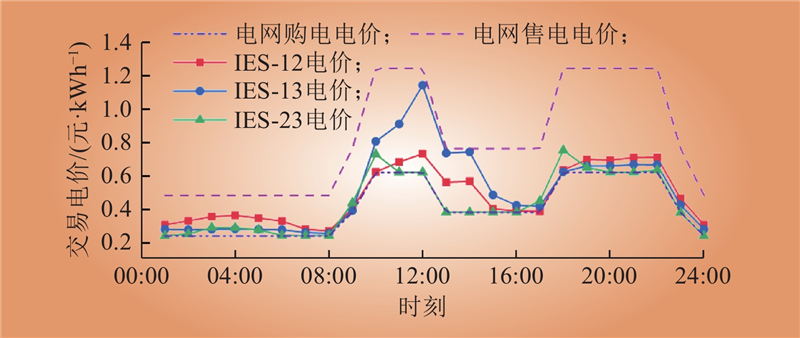
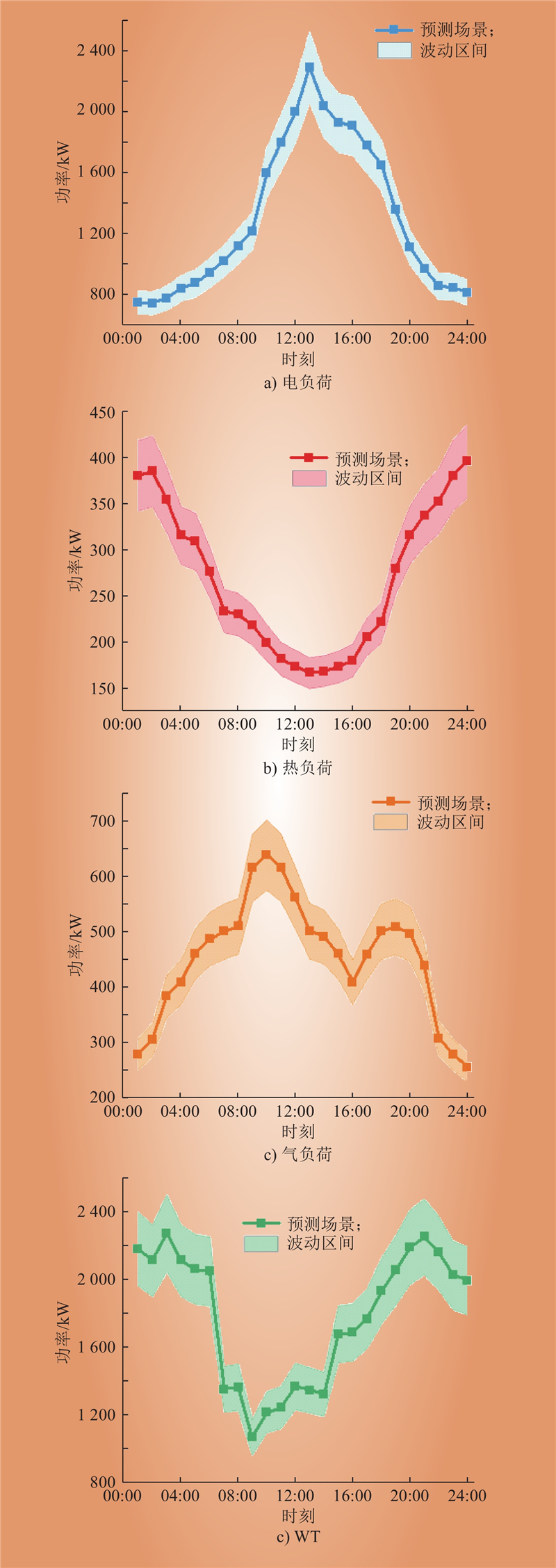
| 1 |
中国经济时报社, 国家电网发布碳达峰碳中和行动方案[N]. 中国经济报, 2021-03-24(4).
|
|
China Economic Times. State Grid of China releases action plan for carbon peaking and carbon neutrality[N]. China Economic Times, 2021-03-24(4).
|
| 2 |
马成元, 陈皓勇, 肖东亮. 考虑碳约束的新型电力系统跨区域优化调度研究[J]. 智慧电力, 2024, 52 (6): 38- 45.
|
|
MA Chengyuan, CHEN Haoyong, XIAO Dongliang. Cross-region optimal dispatch of new power system considering carbon constraints[J]. Smart Power, 2024, 52 (6): 38- 45.
|
| 3 |
李家桐, 谢宁, 王承民, 等. 基于CHP机组碳排放分析的综合能源系统低碳调度优化方法[J]. 智慧电力, 2024, 52 (6): 31- 37, 83.
|
|
LI Jiatong, XIE Ning, WANG Chengmin, et al. Low-carbon dispatch optimization method for integrated energy system based on carbon emission analysis of CHP units[J]. Smart Power, 2024, 52 (6): 31- 37, 83.
|
| 4 |
王凌云, 徐健哲, 李世春, 等. 考虑电-气-热需求响应和阶梯式碳交易的综合能源系统低碳经济调度[J]. 智慧电力, 2022, 50 (9): 45- 52.
|
|
WANG Lingyun, XU Jianzhe, LI Shichun, et al. Low carbon economic dispatch of integrated energy system considering electricity-gas-heat demand response and tiered carbon trading[J]. Smart Power, 2022, 50 (9): 45- 52.
|
| 5 |
李振坤, 游胜苒, 李景岳, 等. 计及动态定价机制和需求响应的社区综合能源系统优化运行[J]. 智慧电力, 2025, 53 (9): 56- 63.
|
|
LI Zhenkun, YOU Shengran, LI Jingyue, et al. Optimized operation of community integrated energy systems considering dynamic pricing mechanism and demand response[J]. Smart Power, 2025, 53 (9): 56- 63.
|
| 6 |
舒征宇, 方曼琴, 李黄强, 等. 计及季节性碳排的综合能源系统经济优化调度[J]. 智慧电力, 2025, 53 (9): 37- 47.
|
|
SHU Zhengyu, FANG Manqin, LI Huangqiang, et al. Economic optimal scheduling of integrated energy systems considering seasonal carbon emissions[J]. Smart Power, 2025, 53 (9): 37- 47.
|
| 7 |
宋晓通, 陈佳琪, 师芊芊. 多主体博弈背景下的综合能源微网优化调度[J]. 高电压技术, 2023, 49 (8): 3163- 3178.
|
|
SONG Xiaotong, CHEN Jiaqi, SHI Qianqian. Optimal scheduling of integrated energy microgrid under the background of multi-agent game[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2023, 49 (8): 3163- 3178.
|
| 8 |
WANG H, WANG C L, ZHAO L, et al. Multi-micro-grid main body electric heating double-layer sharing strategy based on Nash game[J]. Electronics, 2023, 12 (1): 214.
|
| 9 |
DING J Y, GAO C W, SONG M, et al. Optimal operation of multi-agent electricity-heat-hydrogen sharing in integrated energy system based on Nash bargaining[J]. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 2023, 148, 108930.
|
| 10 |
王辉, 吴作辉, 李欣, 等. 含租赁共享储能的多微网与配电网的双层能量交易策略[J]. 电测与仪表, 2025, 62 (6): 24- 34.
|
|
WANG Hui, WU Zuohui, LI Xin, et al. Double-layer energy transaction strategy of multi-microgrids and distribution network with leased shared energy storage[J]. Electrical Measurement & Instrumentation, 2025, 62 (6): 24- 34.
|
| 11 |
刘可真, 董敏, 杨春昊, 等. 基于纳什谈判的智能园区P2P电能交易优化运行[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2023, 43 (5): 45- 53.
|
|
LIU Kezhen, DONG Min, YANG Chunhao, et al. Optimal operation of P2P electric power trading in smart park based on Nash negotiation[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2023, 43 (5): 45- 53.
|
| 12 |
于浩, 沈运帷, 林顺富, 等. 考虑用户心理的商业楼宇集群能量共享优化策略[J]. 电网技术, 2022, 46 (11): 4423- 4436.
|
|
YU Hao, SHEN Yunwei, LIN Shunfu, et al. Optimization strategies for energy sharing in commercial building clusters considering user psychology[J]. Power System Technology, 2022, 46 (11): 4423- 4436.
|
| 13 |
CHEN J, TANG Z Y, HUANG Y, et al. Asymmetric Nash bargaining-based cooperative energy trading of multi-park integrated energy system under carbon trading mechanism[J]. Electric Power Systems Research, 2024, 228, 110033.
|
| 14 |
ZHANG W W, WANG W Q, FAN X C, et al. Low-carbon optimal operation strategy of multi-park integrated energy system considering multi-energy sharing trading mechanism and asymmetric Nash bargaining[J]. Energy Reports, 2023, 10, 255- 284.
|
| 15 |
杨阳, 杨东泰, 张超群, 等. 双碳背景下火电厂低碳化改造技术路径及经济分析[J]. 电力科技与环保, 2025, 41 (1): 13- 26.
|
|
YANG Yang, YANG Dongtai, ZHANG Chaoqun, et al. Tech-economic and carbon emissions analysis of net zero emissions technologies under the background of carbon peaking and carbon neutrality[J]. Electric Power Technology and Environmental Protection, 2025, 41 (1): 13- 26.
|
| 16 |
宋晓通, 李文博, 周京华, 等. 碳交易机制下计及P2G及负荷柔性特征的低碳经济调度[J]. 电测与仪表, 2025, 62 (4): 34- 43, 112.
|
|
SONG Xiaotong, LI Wenbo, ZHOU Jinghua, et al. Low-carbon economic dispatch considering P2G and load flexibility characteristic under carbon trading mechanism[J]. Electrical Measurement & Instrumentation, 2025, 62 (4): 34- 43, 112.
|
| 17 |
康重庆, 季震, 陈启鑫. 碳捕集电厂灵活运行方法评述与展望[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2012, 36 (6): 1- 10.
|
|
KANG Chongqing, JI Zhen, CHEN Qixin. Review and prospects of flexible operation of carbon capture power plants[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2012, 36 (6): 1- 10.
|
| 18 |
陈启鑫, 康重庆, 夏清. 碳捕集电厂的运行机制研究与调峰效益分析[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2010, 30 (7): 22- 28.
|
|
CHEN Qixin, KANG Chongqing, XIA Qing. Operation mechanism and peak-load shaving effects of carbon-capture power plant[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2010, 30 (7): 22- 28.
|
| 19 |
张程, 曾崟琳, 匡宇. 考虑需求响应和碳捕集电厂灵活运行方式的综合能源系统调度[J]. 智慧电力, 2024, 52 (9): 88- 95.
|
|
ZHANG Cheng, ZENG Yinlin, KUANG Yu. Integrated energy system scheduling considering demand response and flexible operation of carbon capture power plant[J]. Smart Power, 2024, 52 (9): 88- 95.
|
| 20 |
袁桂丽, 张睿, 赵洵, 等. 含碳捕集机组的虚拟电厂热电联合随机优化调度[J]. 太阳能学报, 2024, 45 (12): 627- 636.
|
|
YUAN Guili, ZHANG Rui, ZHAO Xun, et al. Stochastic optimal dispatch of combined heat and power in virtual power plant with carbon capture units[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2024, 45 (12): 627- 636.
|
| 21 |
ROSEN M A, KOOHI-FAYEGH S. The prospects for hydrogen as an energy carrier: an overview of hydrogen energy and hydrogen energy systems[J]. Energy, Ecology and Environment, 2016, 1 (1): 10- 29.
|
| 22 |
樊伟杰, 崔双喜, 李浩博. 考虑两阶段P2G和燃气掺氢的综合能源系统双层优化调度[J]. 电测与仪表, 2025, 62 (2): 16- 25.
|
|
FAN Weijie, CUI Shuangxi, LI Haobo. Double-layer optimal scheduling of integrated energy system considering two-stage P2G and gas hydrogen doping[J]. Electrical Measurement & Instrumentation, 2025, 62 (2): 16- 25.
|
| 23 |
王汝田, 杨凌, 王秀云. 计及碳捕集电厂与电制氢的综合能源系统低碳优化运行[J]. 电气工程学报, 2024, 19 (4): 368- 376.
|
|
WANG Rutian, YANG Ling, WANG Xiuyun. Low carbon optimal operation of integrated energy system considering carbon capture power plant and electrolytic hydrogen[J]. Journal of Electrical Engineering, 2024, 19 (4): 368- 376.
|
| 24 |
李江南, 程韧俐, 周保荣, 等. 含碳捕集及电转氢设备的低碳园区综合能源系统随机优化调度[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (5): 149- 156.
|
|
LI Jiangnan, CHENG Renli, ZHOU Baorong, et al. Stochastic optimal of integrated energy system in low-carbon parks considering carbon capture storage and power to hydrogen[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (5): 149- 156.
|
| 25 |
刘妍, 胡志坚, 陈锦鹏, 等. 含碳捕集电厂与氢能多元利用的综合能源系统低碳经济调度[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2024, 48 (1): 31- 40.
|
|
LIU Yan, HU Zhijian, CHEN Jinpeng, et al. Low-carbon economic dispatch of integrated energy system considering carbon capture power plant and multi-utilization of hydrogen energy[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2024, 48 (1): 31- 40.
|
| 26 |
万庆祝, 闵现娟, 于佳松, 等. 需求响应下的电制氢多模式利用综合能源系统优化调度[J]. 供用电, 2024, 41 (12): 81- 92.
|
|
WAN Qingzhu, MIN Xianjuan, YU Jiasong, et al. Optimized scheduling for an integrated energy system with multi-modal utilization of electric hydrogen production under demand response[J]. Distribution & Utilization, 2024, 41 (12): 81- 92.
|
| 27 |
崔杨, 管彦琦, 李佳宇, 等. 考虑碳捕集机组与氢储能系统协调运行的源荷储低碳经济调度[J]. 电网技术, 2024, 48 (6): 2307- 2316.
|
|
CUI Yang, GUAN Yanqi, LI Jiayu, et al. Source-load-storage low-carbon economic dispatching considering coordinated operation of carbon capture unit and hydrogen energy storage system[J]. Power System Technology, 2024, 48 (6): 2307- 2316.
|
| 28 |
王辉, 周珂锐, 吴作辉, 等. 含电转气和碳捕集耦合的综合能源系统多时间尺度优化调度[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (8): 214- 226.
|
|
WANG Hui, ZHOU Kerui, WU Zuohui, et al. Multi-time scale optimal scheduling of integrated energy system coupling power-to-gas and carbon capture system[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (8): 214- 226.
|
| 29 |
陈彬彬, 孙宏斌, 尹冠雄, 等. 综合能源系统分析的统一能路理论(二): 水路与热路[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2020, 40 (7): 2133- 2142, 2393.
|
|
CHEN Binbin, SUN Hongbin, YIN Guanxiong, et al. Energy circuit theory of integrated energy system analysis(II): hydraulic circuit and thermal circuit[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2020, 40 (7): 2133- 2142, 2393.
|
| 30 |
陈彬彬, 孙宏斌, 陈瑜玮, 等. 综合能源系统分析的统一能路理论(一): 气路[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2020, 40 (2): 436- 444.
|
|
CHEN Binbin, SUN Hongbin, CHEN Yuwei, et al. Energy circuit theory of integrated energy system analysis (I): gaseous circuit[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2020, 40 (2): 436- 444.
|
| 31 |
翟江, 周孝信, 李亚楼, 等. 综合能源系统天然气管道压力和流量的控制方案研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2022, 42 (11): 3911- 3924.
|
|
ZHAI Jiang, ZHOU Xiaoxin, LI Yalou, et al. Research on control strategy of pressure and flow of natural gas pipeline in integrated energy system[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2022, 42 (11): 3911- 3924.
|
| 32 |
国家能源局. 国家发展改革委国家能源局关于印发新能源微电网示范项目名单的通知[EB/OL]. (2017-05-05) [2025-04-07]. https://zfxxgk.nea.gov.cn/auto87/201705/t20170511_2789.htm.
|
| 33 |
国网江苏省电力有限公司电力科学研究院. 综合能源系统关键技术与典型案例[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2021-12-01.
|