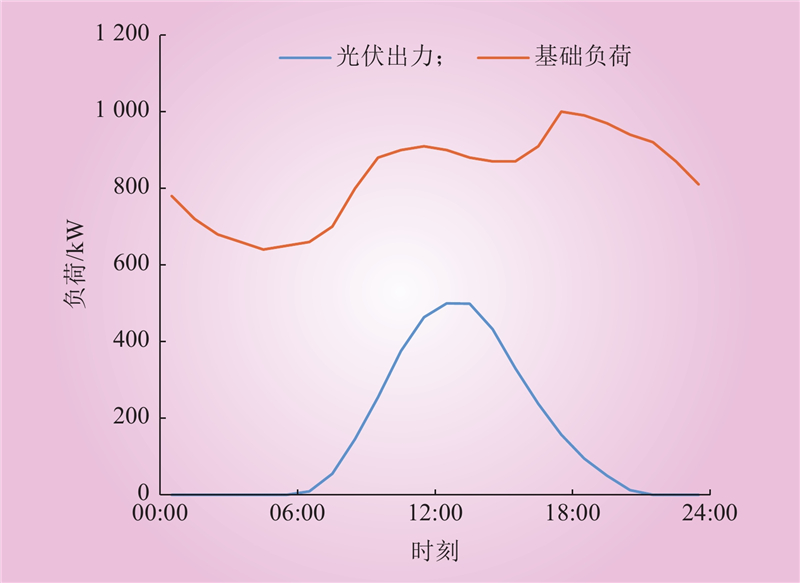
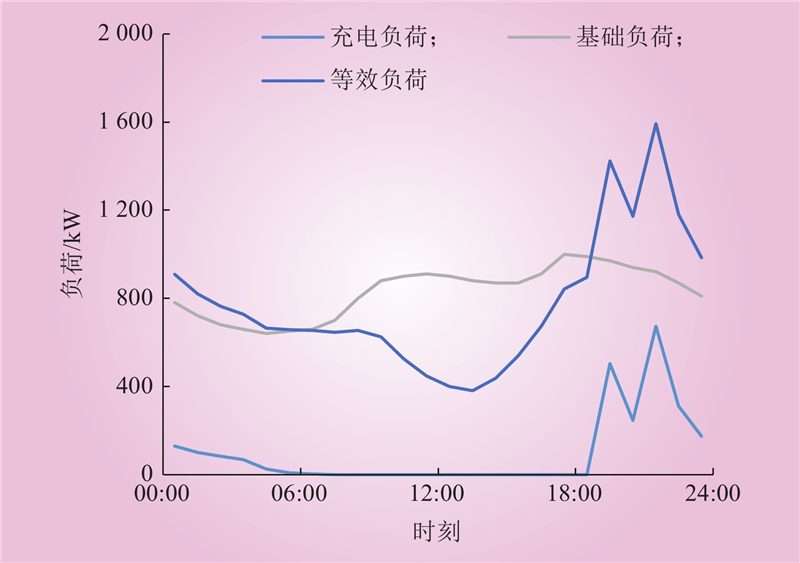
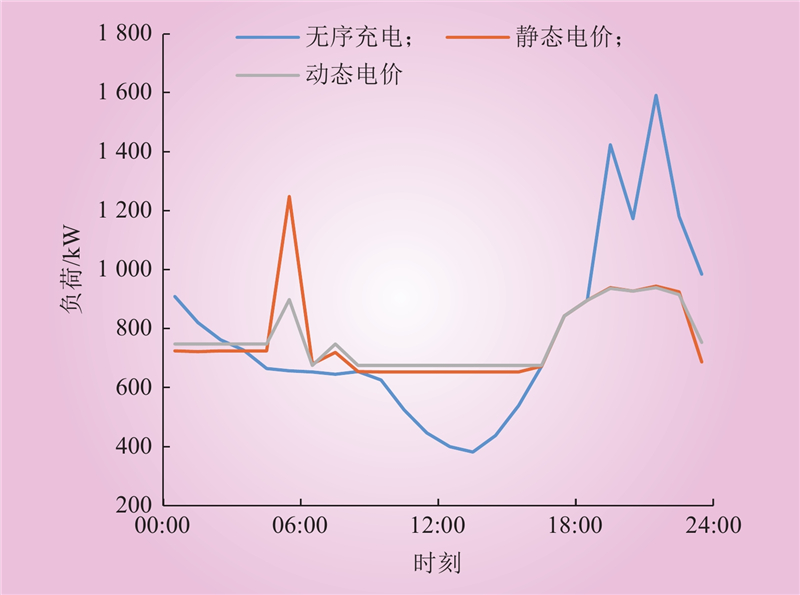
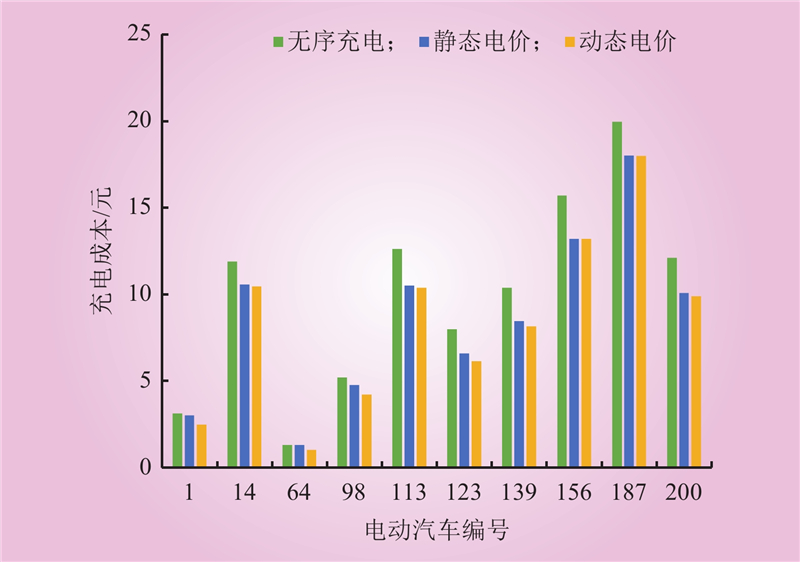
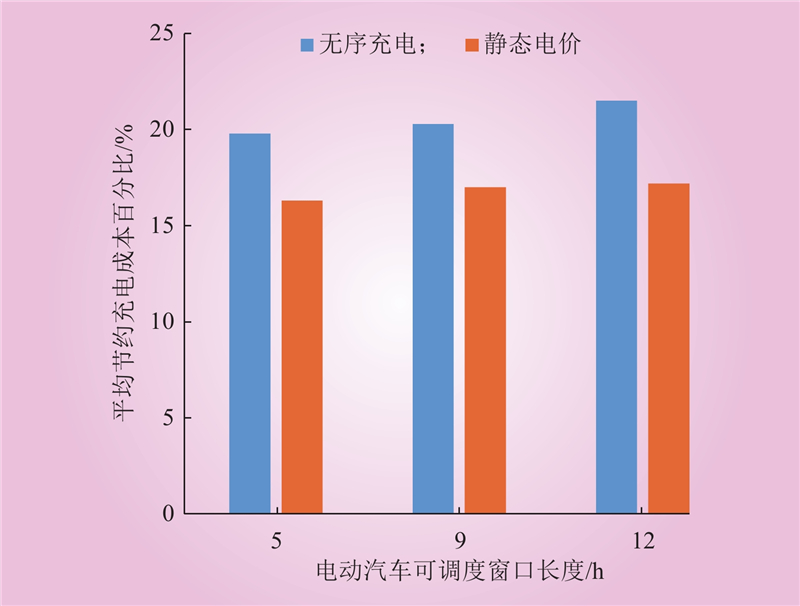
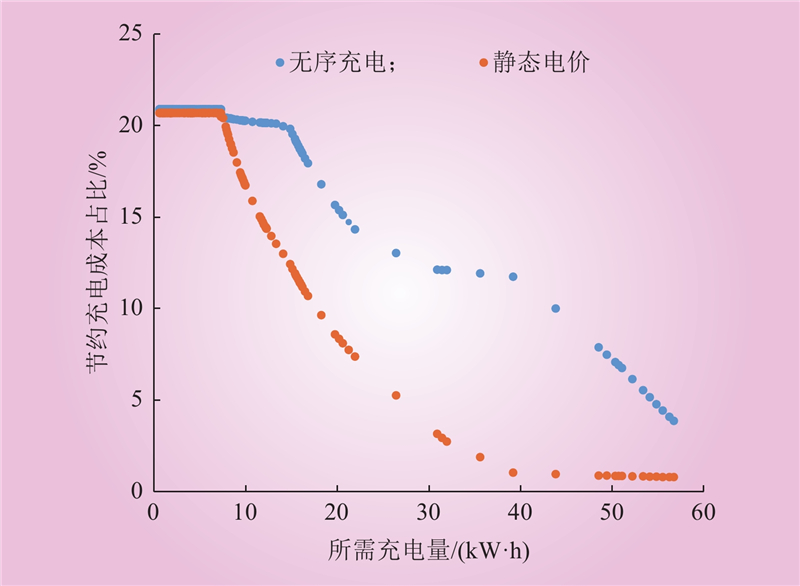
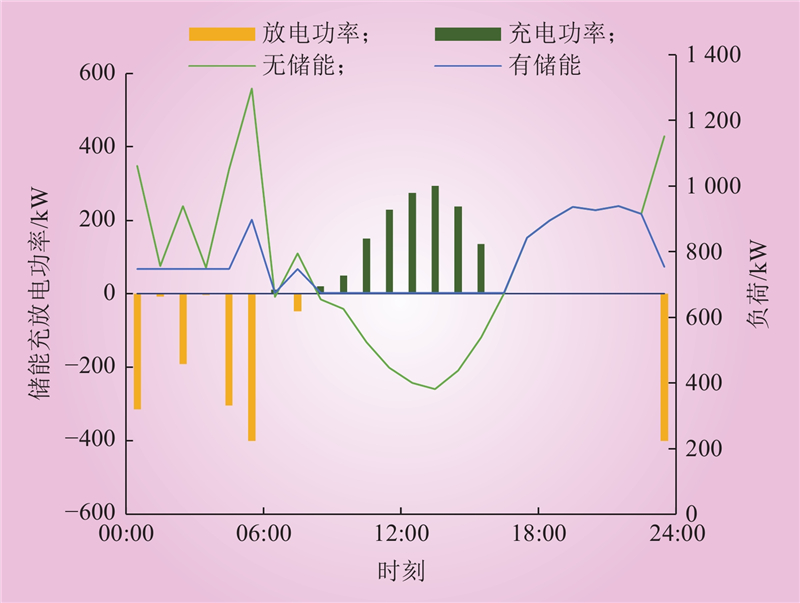
| 1 |
章建华, 林山青, 余兵, 等. 新型电力系统发展蓝皮书 [R]. 北京: 国家能源局, 2023.
|
|
ZHANG Jianhua, LIN Shanqing, YU Bing, et al. Blue book of new power system development[R]. Beijing: National Energy Administration, 2023.
|
| 2 |
国家发展和改革委员会, 国家能源局, 工业和信息化部, 等. 关于进一步提升电动汽车充电基础设施服务保障能力的实施意见: 发改能源规〔2022〕53号[A/OL]. (2022-01-10)[2025-02-20]. https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/2022-01/21/content_5669780.htm.
|
| 3 |
国家发展和改革委员会. 关于电动汽车用电价格政策有关问题的通知: 发改价格〔2014〕1668号[A/OL]. (2014-07-22)[2025-02-20]. https://zfxxgk.ndrc.gov.cn/web/iteminfo.jsp id=19564.
|
| 4 |
蔡湛, 李泽文, 邹睿奇, 等. 基于负荷转移的售电公司分时电价优化策略[J]. 南方电网技术, 2024, 18 (1): 77- 84.
|
|
CAI Zhan, LI Zewen, ZOU Ruiqi, et al. Optimization strategy of time-of-use electricity price for electricity selling companies based on load transfer[J]. Southern Power System Technology, 2024, 18 (1): 77- 84.
|
| 5 |
崔金栋, 罗文达, 周念成. 基于多视角的电动汽车有序充放电定价模型与策略研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2018, 38 (15): 4438- 4450, 4644.
|
|
CUI Jindong, LUO Wenda, ZHOU Niancheng. Research on pricing model and strategy of electric vehicle charging and discharging based on multi view[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2018, 38 (15): 4438- 4450, 4644.
|
| 6 |
朱永胜, 苗阳, 谢晓峰, 等. 新能源微电网多层级车网协同优化策略[J]. 智慧电力, 2023, 51 (2): 61- 68.
|
|
ZHU Yongsheng, MIAO Yang, XIE Xiaofeng, et al. Multi-level vehicle-grid collaborative optimization strategy for new energy microgrid[J]. Smart Power, 2023, 51 (2): 61- 68.
|
| 7 |
王世谦, 贾一博, 白宏坤, 等. 分时电价下电动汽车参与虚拟电厂的经济优化调度方法[J]. 电力需求侧管理, 2023, 25 (5): 19- 26.
|
|
WANG Shiqian, JIA Yibo, BAI Hongkun, et al. Economic optimization scheduling method of electric vehicle participating in virtual power plant under time-of-use price[J]. Power Demand Side Management, 2023, 25 (5): 19- 26.
|
| 8 |
康童, 朱吉然, 冯楚瑞, 等. 面向光储充一体化社区的有序充电策略研究[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2024, 52 (9): 132- 142.
|
|
KANG Tong, ZHU Jiran, FENG Churui, et al. An orderly charging strategy for a photovoltaic-storage-charging integrated community[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2024, 52 (9): 132- 142.
|
| 9 |
许博, 岳欣明, 关艳, 等. 针对用电负荷“峰谷倒挂”现象的混合型电力需求响应策略[J]. 系统工程理论与实践, 2022, 42 (8): 2129- 2138.
|
|
XU Bo, YUE Xinming, GUAN Yan, et al. A hybrid demand response strategy to solve the problem of "peak valley inversion" in power grid[J]. Systems Engineering-Theory & Practice, 2022, 42 (8): 2129- 2138.
|
| 10 |
李咸善, 周晓岚, 姚俊伟, 等. 考虑车主多模式需求响应模糊意愿的优化调度策略[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2023, 51 (2): 89- 101.
|
|
LI Xianshan, ZHOU Xiaolan, YAO Junwei, et al. Optimal dispatch strategy considering fuzzy intention of multi-mode demand response of vehicle owners[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2023, 51 (2): 89- 101.
|
| 11 |
MISHRA M K, PARIDA S K. A game theoretic horizon decomposition approach for real-time demand-side management[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2022, 13 (5): 3532- 3545.
|
| 12 |
MISHRA M K, PARIDA S K. A game theoretic approach for demand-side management using real-time variable peak pricing considering distributed energy resources[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2022, 16 (1): 144- 154.
|
| 13 |
王长春, 王果, 赵倩宇, 等. 考虑分时电价和充电利用率特征的大型电动汽车充电站负荷短期预测方法[J]. 南方电网技术, 2024, 18 (5): 75- 84.
|
|
WANG Changchun, WANG Guo, ZHAO Qianyu, et al. A short-term load forecasting method for large scale electric vehicle charging stations considering characteristics of charging utilization rate and time-of-use electricity price[J]. Southern Power System Technolog, 2024, 18 (5): 75- 84.
|
| 14 |
郭之栋, 胡存刚, 芮涛, 等. 基于动态电价机制的用户侧分布式储能电能交易策略[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (1): 28- 37.
|
|
GUO Zhidong , HU Cungang, RUI Tao, et al. User side distributed energy storage trading strategy based on dynamic electricity price mechanism[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (1): 28- 37.
|
| 15 |
邓衍辉, 李剑, 卢国强, 等. 考虑分区域动态电价机制引导的电动汽车充电优化策略[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2024, 52 (7): 33- 44.
|
|
DENG Yanhui, LI Jian, LU Guoqiang, et al. Charging optimization strategy of electric vehicles guided by the dynamic tariff mechanism of a subregion[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2024, 52 (7): 33- 44.
|
| 16 |
PACCAGNAN D, GENTILE B, PARISE F, et al. Nash and wardrop equilibria in aggregative games with coupling constraints[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2019, 64 (4): 1373- 1388.
|
| 17 |
JACQUOT P, WAN C. Nonatomic aggregative games with infinitely many types[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2022, 301 (3): 1149- 1165.
|
| 18 |
JACQUOT P, BEAUDE O, GAUBERT S, et al. Analysis and implementation of an hourly billing mechanism for demand response management[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2019, 10 (4): 4265- 4278.
|
| 19 |
BELGIOIOSO G, YI P, GRAMMATICO S, et al. Distributed generalized Nash equilibrium seeking: an operator-theoretic perspective[J]. IEEE Control Systems Magazine, 2022, 42 (4): 87- 102.
|
| 20 |
HUPEZ M, TOUBEAU J F, ATZENI I, et al. Pricing electricity in residential communities using game-theoretical billings[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2023, 14 (2): 1621- 1631.
|
| 21 |
BAHARLOUEI Z, NARIMANI H, HASHEMI M. On the convergence properties of autonomous demand side management algorithms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2018, 9 (6): 6713- 6720.
|
| 22 |
徐智威, 胡泽春, 宋永华, 等. 基于动态分时电价的电动汽车充电站有序充电策略[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2014, 34 (22): 3638- 3646.
|
|
XU Zhiwei, HU Zechun, SONG Yonghua, et al. Coordinated charging strategy for PEV charging stations based on dynamic time-of-use tariffs[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2014, 34 (22): 3638- 3646.
|
| 23 |
张良, 孙成龙, 蔡国伟, 等. 基于PSO算法的电动汽车有序充放电两阶段优化策略[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2022, 42 (5): 1837- 1852.
|
|
ZHANG Liang, SUN Chenglong, CAI Guowei, et al. Two-stage optimization strategy for coordinated charging and discharging of EVs based on PSO algorithm[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2022, 42 (5): 1837- 1852.
|
| 24 |
张西竹, 刘洵源, 杨文涛, 等. 动态分时电价机制下的电动汽车分层调度策略[J]. 电力建设, 2018, 39 (12): 73- 80.
|
|
ZHANG Xizhu, LIU Xunyuan, YANG Wentao, et al. A hierarchical scheduling strategy for electric vehicles under dynamic time-of-use tariff mechanism[J]. Electric Power Construction, 2018, 39 (12): 73- 80.
|
| 25 |
呙金瑞, 张智俊, 窦春霞. 基于信息间隙决策理论与动态分时电价的电动汽车接入虚拟电厂双层经济调度策略[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2022, 42 (10): 77- 85.
|
|
GUO Jinrui, ZHANG Zhijun, DOU Chunxia. Bi-level economic dispatch strategy for electric vehicles connecting to virtual power plant based on information gap decision theory and dynamic time-of-use price[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2022, 42 (10): 77- 85.
|
| 26 |
GLICKSBERG I L. A further generalization of the kakutani fixed point theorem, with application to Nash equilibrium points[J]. Proceedings of the American Mathematical Society, 1952, 3 (1): 170- 174.
|
| 27 |
邓盛盛, 陈皓勇, 肖东亮, 等. 考虑碳市场交易的寡头电力市场均衡分析[J]. 南方电网技术, 2024, 18 (1): 143- 152.
|
|
DENG Shengsheng, CHEN Haoyong, XIAO Dongliang, et al. Equilibrium analysis of oligopoly electricity market considering carbon market trading[J]. Southern Power System Technology, 2024, 18 (1): 143- 152.
|
| 28 |
FACCHINEI F, PANG J S. Finite-dimensional variational inequalities and complementarity problems[M]. New York: Springer, 2003.
|
| 29 |
杨健维, 黄宇, 王湘, 等. 基于动态概率潮流的住宅区电动汽车代理商定价策略[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2016, 36 (21): 5822- 5830, 6025.
|
|
YANG Jianwei, HUANG Yu, WANG Xiang, et al. A pricing strategy for electric vehicle aggregator in residential area based on dynamic probability power flow[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2016, 36 (21): 5822- 5830, 6025.
|