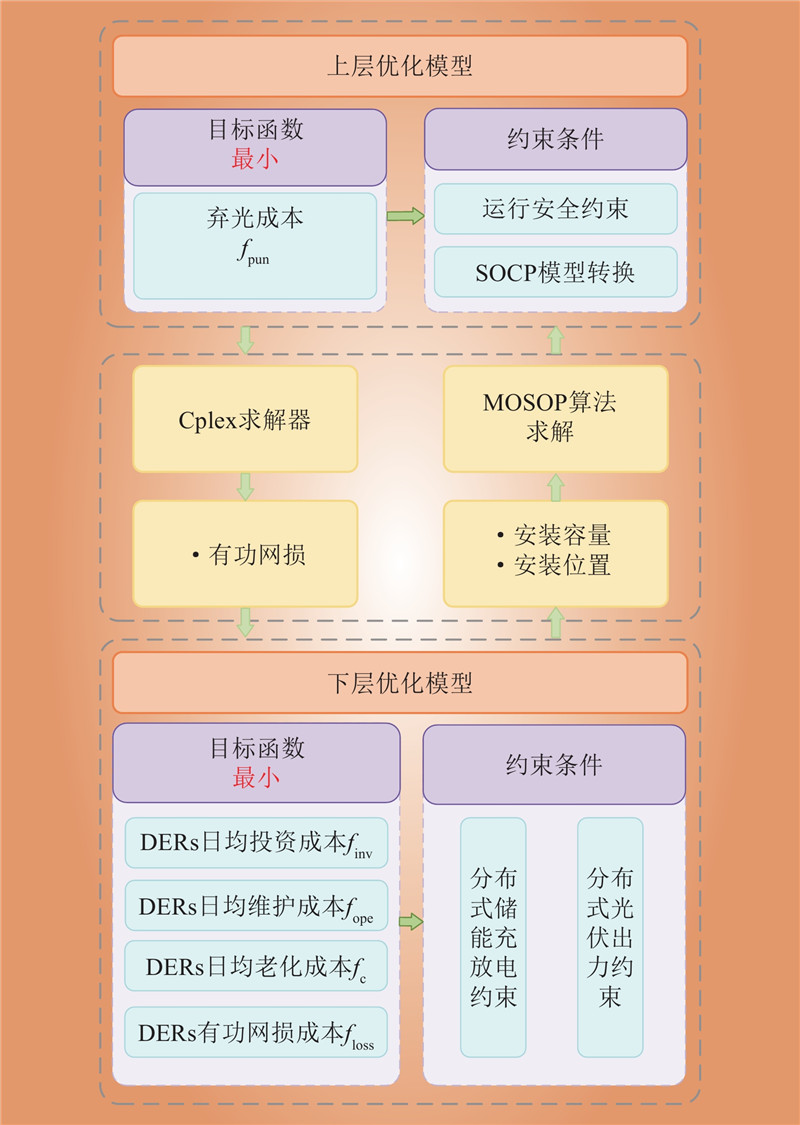
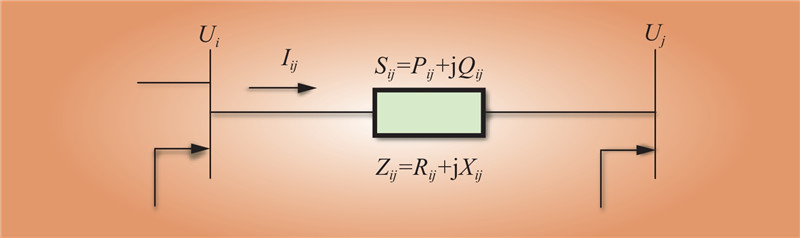
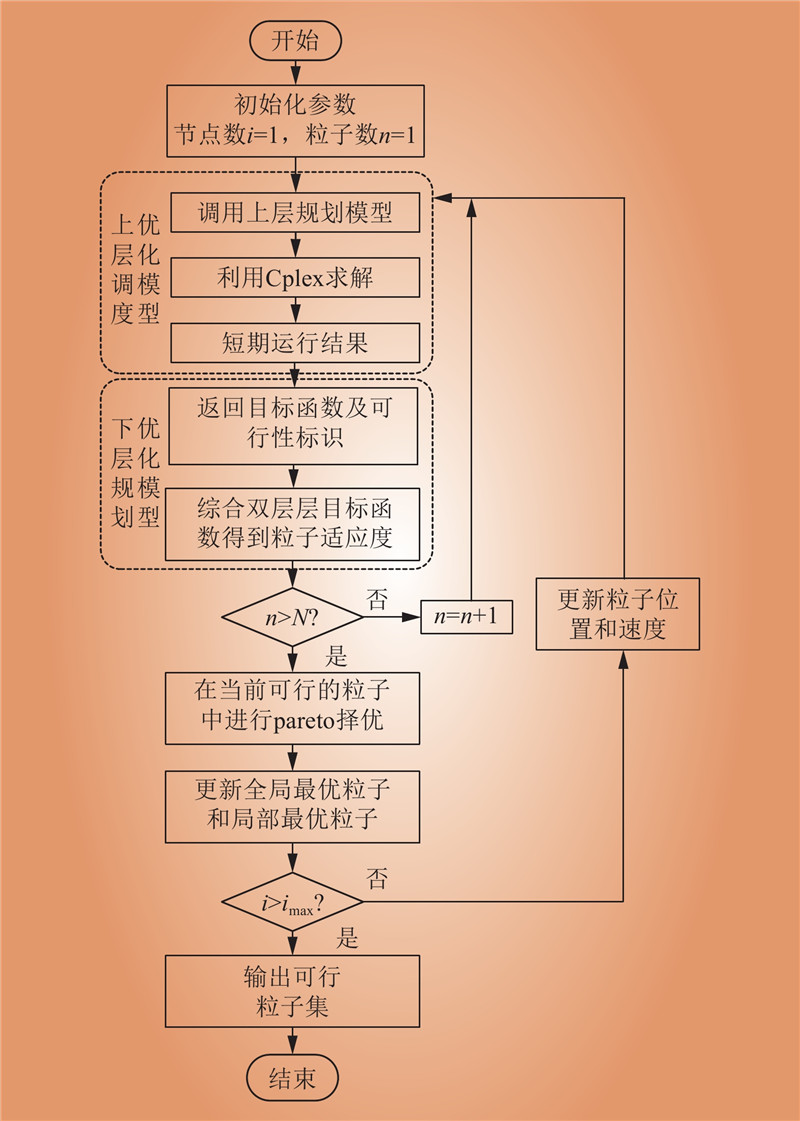
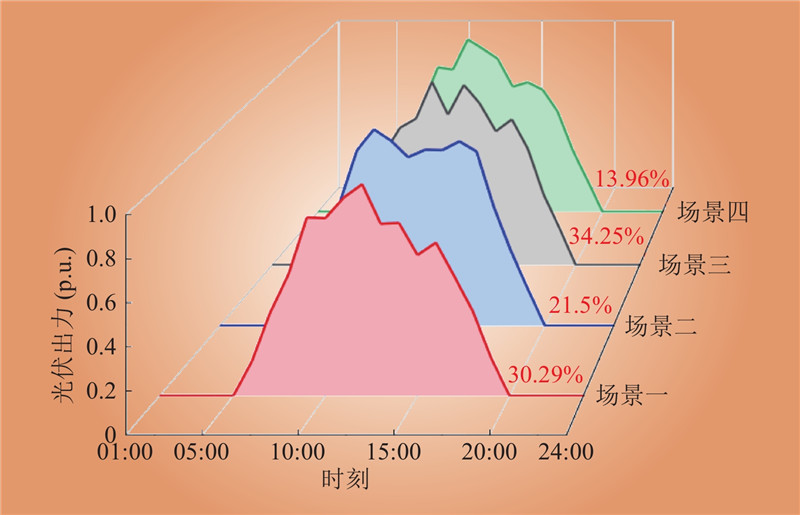
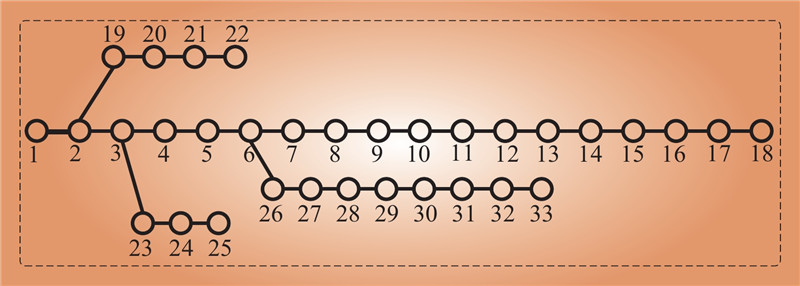
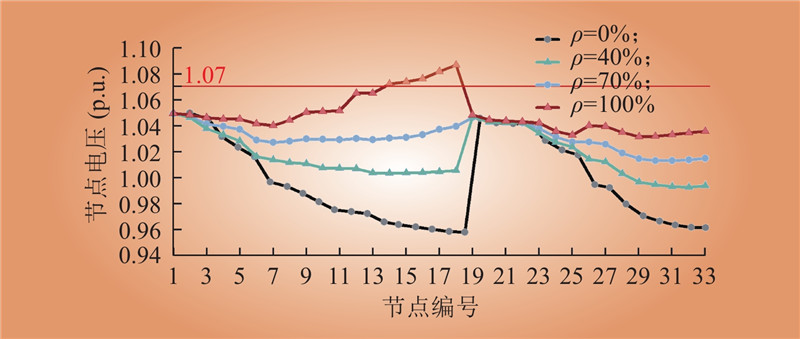
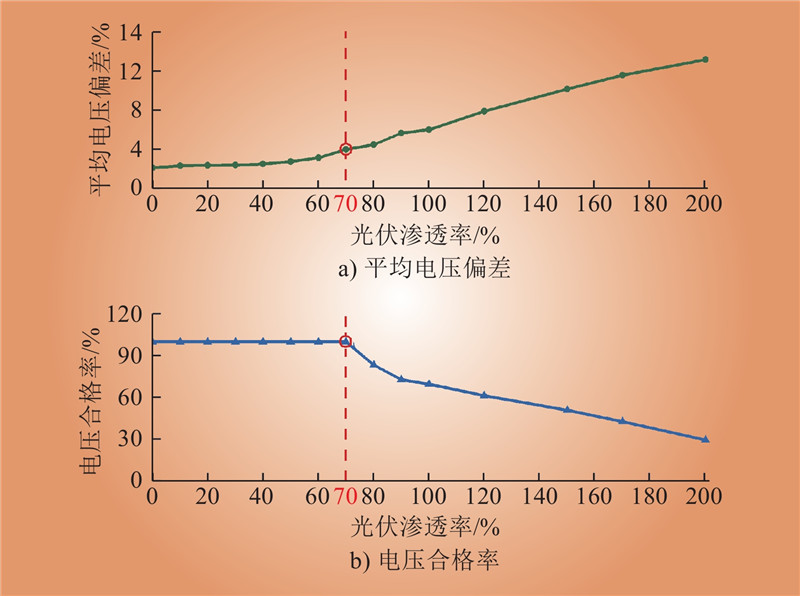
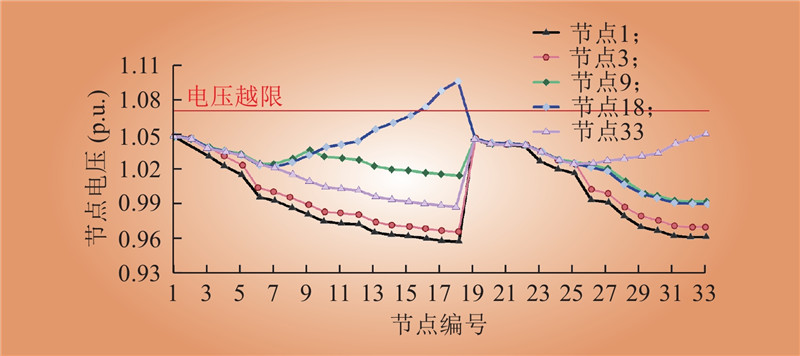
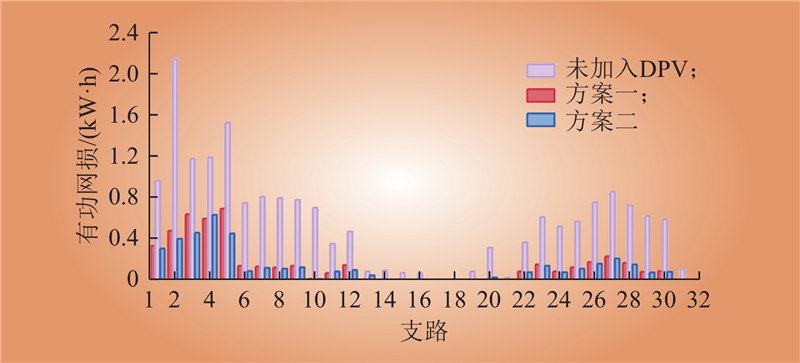
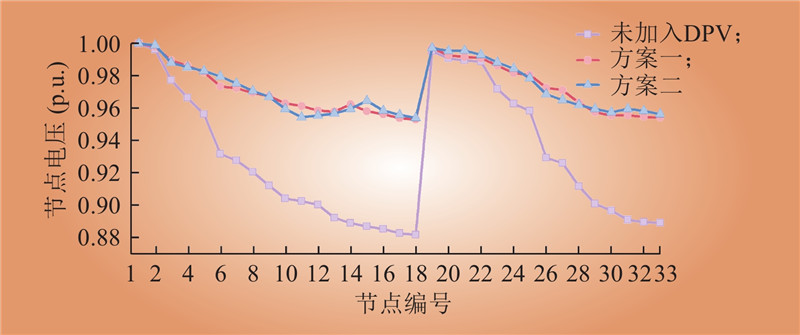
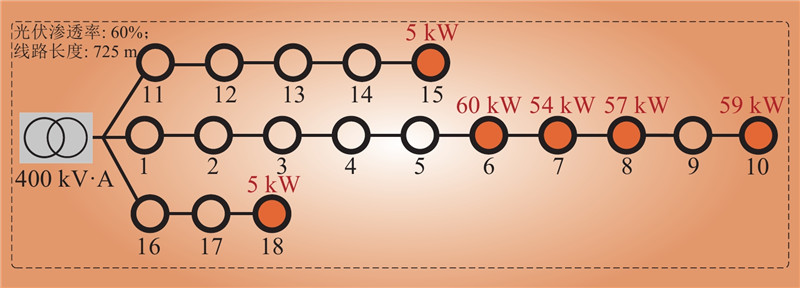
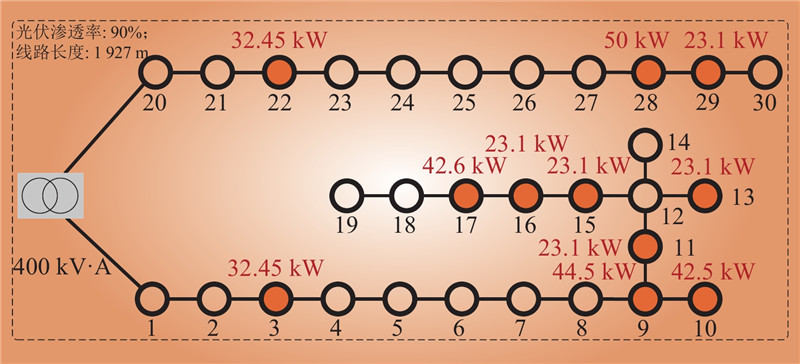
| 1 |
陈维江, 靳晓凌, 吴鸣, 等. 双碳目标下我国配电网形态快速演进的思考[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2024, 44 (17): 6811- 6818.
|
|
CHEN Weijiang, JIN Xiaoling, WU Ming, et al. Thinking on the rapid evolution of distribution network form under the carbon peaking and carbon neutrality goals[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2024, 44 (17): 6811- 6818.
|
| 2 |
王雯沁, 高红均, 王仁浚, 等. 考虑分布式电源支撑与农业设施协调的配电网分布鲁棒优化[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2023, 47 (21): 89- 98.
|
|
WANG Wenqin, GAO Hongjun, WANG Renjun, et al. Distributionally robust optimization of distribution network considering distributed generator support and agricultural facility coordination[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2023, 47 (21): 89- 98.
|
| 3 |
魏旭, 刘东, 高飞, 等. 双碳目标下考虑源网荷储协同优化运行的新型电力系统发电规划[J]. 电网技术, 2023, 47 (9): 3648- 3661.
|
|
WEI Xu, LIU Dong, GAO Fei, et al. Generation expansion planning of new power system considering collaborative optimal operation of source-grid-load-storage under carbon peaking and carbon neutrality[J]. Power System Technology, 2023, 47 (9): 3648- 3661.
|
| 4 |
郑亚先, 杨争林, 冯树海, 等. 碳达峰目标场景下全国统一电力市场关键问题分析[J]. 电网技术, 2022, 46 (1): 1- 20.
|
|
ZHENG Yaxian, YANG Zhenglin, FENG Shuhai, et al. Key issue analysis in national unified power market under target scenario of carbon emission peak[J]. Power System Technology, 2022, 46 (1): 1- 20.
|
| 5 |
张宇, 魏新迟, 冯凯辉, 等. 计及分布式光伏承载力的配电网侧独立储能充放电策略[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (4): 111- 117.
|
|
ZHANG Yu, WEI Xinchi, FENG Kaihui, et al. Charging and discharging strategies of independent energy storage for distribution grid side considering distributed PV carrying capacity[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (4): 111- 117.
|
| 6 |
MONTOYA O D, GRISALES-NOREÑA L F, GIL-GONZÁLEZ W. Simultaneous siting and sizing of PVs and D-STATCOMs in medium-voltage grids using the Cauchy-based distribution optimizer[J]. Results in Engineering, 2025, 25, 104407.
|
| 7 |
欧奕昊, 姜彤, 张一航, 等. 考虑变流器无功调节特性的含高比例分布式光伏配电网电压控制方法[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2024, 52 (20): 105- 118.
|
|
OU Yihao, JIANG Tong, ZHANG Yihang, et al. Voltage regulation method for a distribution network with high-penetration of distributed photovoltaic energy considering a converter's reactive power regulation characteristics[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2024, 52 (20): 105- 118.
|
| 8 |
张颖, 寇凌峰, 季宇, 等. 计及储能与分布式电源协同的配电网分层分区优化控制[J]. 中国电力, 2021, 54 (2): 104- 112.
|
|
ZHANG Ying, KOU Lingfeng, JI Yu, et al. Hierarchical and partitioned optimal control of distribution networks considering the coordination between energy storage and distributed generation systems[J]. Electric Power, 2021, 54 (2): 104- 112.
|
| 9 |
SUN W T, GE Y, LIU G J, et al. Siting and sizing method of GFM converters based on genetic algorithm[J]. Inventions, 2025, 10 (1): 13.
|
| 10 |
陈众, 徐翼, 吴辅朝, 等. 基于光伏消纳能力模拟评估的配电网最优消纳方案规划选择[J]. 电网技术, 2023, 47 (3): 1179- 1188.
|
|
CHEN Zhong, XU Yi, WU Fuchao, et al. Selection of optimal distribution planning based on simulation of photovoltaic absorption capacity[J]. Power System Technology, 2023, 47 (3): 1179- 1188.
|
| 11 |
尚博阳, 许寅, 王颖, 等. 参与辅助服务的用户侧储能优化配置及经济分析[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (2): 164- 170, 178.
|
|
SHANG Boyang, XU Yin, WANG Ying, et al. Optimal configuration and economic analysis of user-side energy storage participating in auxiliary services[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (2): 164- 170, 178.
|
| 12 |
唐雅洁, 李俊豪, 林达, 等. 考虑分布式光伏高效消纳与负荷损失最小的区域配电网应急资源协同配置策略[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2024, 44 (7): 78- 85.
|
|
TANG Yajie, LI Junhao, LIN Da, et al. Coordinated allocation strategy of emergency resource for regional distribution network considering distributed photovoltaic efficient absorption and minimum load loss[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2024, 44 (7): 78- 85.
|
| 13 |
陈韵含, 许寅, 王颖, 等. 考虑潜在恢复需求的城市配电网移动应急资源灾前布点[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2023, 47 (14): 105- 113.
|
|
CHEN Yunhan, XU Yin, WANG Ying, et al. Pre-disaster positioning of mobile emergency resources for urban distribution network considering potential restoration demand[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2023, 47 (14): 105- 113.
|
| 14 |
白望望, 杨德州, 李万伟, 等. 基于HC-MOPSO的储能电站两阶段选址定容方法[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (12): 148- 156.
|
|
BAI Wangwang, YANG Dezhou, LI Wanwei, et al. A two-stage site selection and capacity determination method for energy storage power stations based on HC-MOPSO[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (12): 148- 156.
|
| 15 |
王枭, 何怡刚, 马恒瑞, 等. 考虑规模化储能的配电网电压分布式控制[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2022, 42 (2): 25- 30, 55.
|
|
WANG Xiao, HE Yigang, MA Hengrui, et al. Distributed voltage control of distribution network considering large-scale energy storage[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2022, 42 (2): 25- 30, 55.
|
| 16 |
CHATZIGEORGIOU N G, THEOCHARIDES S, MAKRIDES G, et al. A review on battery energy storage systems: Applications, developments, and research trends of hybrid installations in the end-user sector[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2024, 86, 111192.
|
| 17 |
陈奇芳, 李若凡, 夏明超, 等. 计及多维性能评估的新型配电网光伏选址定容方法[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (10): 172- 178, 207.
|
|
CHEN Qifang, LI Ruofan, XIA Mingchao, et al. Photovoltaic site selection and capacity determination method for new distribution network considering multidimensional performance evaluation[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (10): 172- 178, 207.
|
| 18 |
庞广明, 王鹏飞, 田超, 等. 基于ICOA算法的配电网分布式电源选址定容方法[J]. 太阳能学报, 2024, 45 (10): 211- 219.
|
|
PANG Guangming, WANG Pengfei, TIAN Chao, et al. Location and capacity determination method of distributed generation in distribution network based on icoa algorithm[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2024, 45 (10): 211- 219.
|
| 19 |
TIAN Z, LI X Y, NIU J D, et al. Enhancing operation flexibility of distributed energy systems: a flexible multi-objective optimization planning method considering long-term and temporary objectives[J]. Energy, 2024, 288, 129612.
|
| 20 |
张振芳, 撖奥洋, 刘同同, 等. 基于多策略改进SSA算法的分布式光伏选址定容规划[J]. 电气工程学报, 2024, 19 (4): 347- 356.
|
|
ZHANG Zhenfang, HAN Aoyang, LIU Tongtong, et al. Optimal sizing and siting of distributed PV based on multi-strategy improved SSA algorithm[J]. Journal of Electrical Engineering, 2024, 19 (4): 347- 356.
|
| 21 |
胡泽春, 蔡福霖, 冯建洲. 兼顾新能源消纳与频率电压支撑的电池储能系统优化规划[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2024, 44 (7): 3- 12.
|
|
HU Zechun, CAI Fulin, FENG Jianzhou. Optimal planning of battery energy storage system considering renewable energy consumption and frequency and voltage support[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2024, 44 (7): 3- 12.
|
| 22 |
安东, 杨德宇, 武文丽, 等. 基于改进多目标蜉蝣算法的配网电池储能系统最优选址定容[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2022, 50 (10): 31- 39.
|
|
AN Dong, YANG Deyu, WU Wenli, et al. Optimal location and sizing of battery energy storage systems in a distribution network based on a modified multi-objective mayfly algorithm[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2022, 50 (10): 31- 39.
|
| 23 |
TWAISAN K, BARıŞÇı N. Integrated distributed energy resources (DER) and microgrids: modeling and optimization of DERs[J]. Electronics, 2022, 11 (18): 2816.
|
| 24 |
杨博, 俞磊, 王俊婷, 等. 基于自适应蝠鲼觅食优化算法的分布式电源选址定容[J]. 上海交通大学学报, 2021, 55 (12): 1673- 1688.
|
|
YANG Bo, YU Lei, WANG Junting, et al. Optimal sizing and placement of distributed generation based on adaptive manta ray foraging optimization[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2021, 55 (12): 1673- 1688.
|
| 25 |
林国灏, 唐巍, 文钥棋. 基于多智能体的中低压交直流混合配电网优化调度[J]. 供用电, 2024, 41 (9): 2- 11.
|
|
LIN Guohao, TANG Wei, WEN Yueqi. Optimal scheduling method of medium and low voltage AC/DC hybrid distribution network based on multi-agent[J]. Distribution & Utilization, 2024, 41 (9): 2- 11.
|
| 26 |
吴璐阳, 辛洁晴, 王承民. 计入用户从众心理的分布式光伏装机容量预测[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2022, 46 (14): 83- 92.
|
|
WU Luyang, XIN Jieqing, WANG Chengmin. Installed capacity forecasting for distributed photovoltaic considering herd mentality of users[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2022, 46 (14): 83- 92.
|
| 27 |
GIANNELOS S, ZHANG T, PUDJIANTO D, et al. Investments in electricity distribution grids: strategic versus incremental planning[J]. Energies, 2024, 17 (11): 2724.
|
| 28 |
陈娟, 高江梅. 基于演化博弈的户用光伏整县开发协同机制及仿真[J]. 电网技术, 2023, 47 (2): 669- 684.
|
|
CHEN Juan, GAO Jiangmei. Coordination mechanism and simulation of household photovoltaic county development based on evolutionary game[J]. Power System Technology, 2023, 47 (2): 669- 684.
|
| 29 |
曹振其, 彭敏放, 沈美娥. 考虑源荷不确定性的分布式电源选址定容[J]. 电力系统及其自动化学报, 2021, 33 (2): 59- 65.
|
|
CAO Zhenqi, PENG Minfang, SHEN Meie. Siting and sizing of distributed generations considering uncertainties in source and load[J]. Proceedings of the CSU-EPSA, 2021, 33 (2): 59- 65.
|