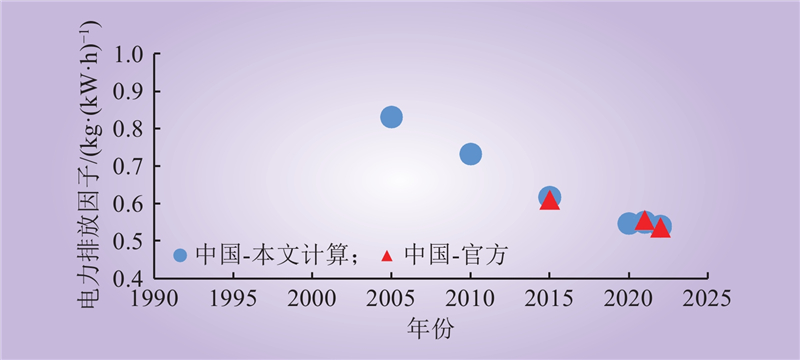
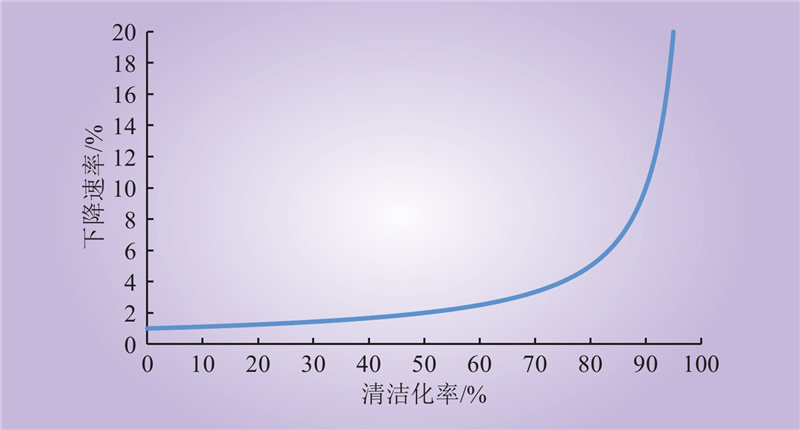
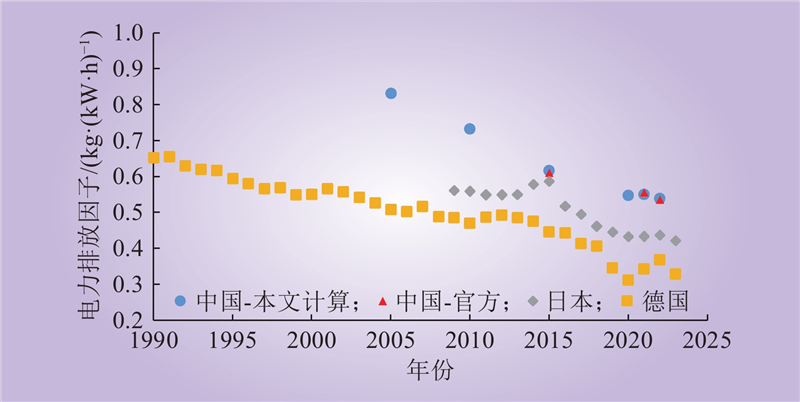
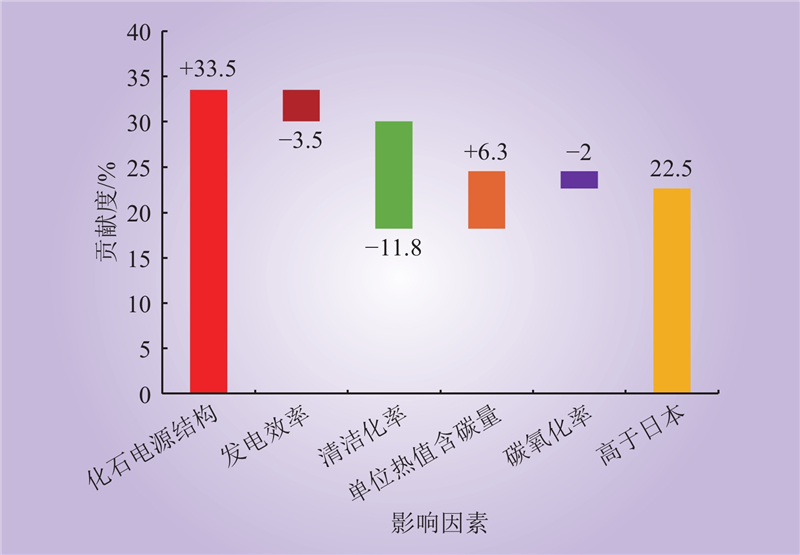
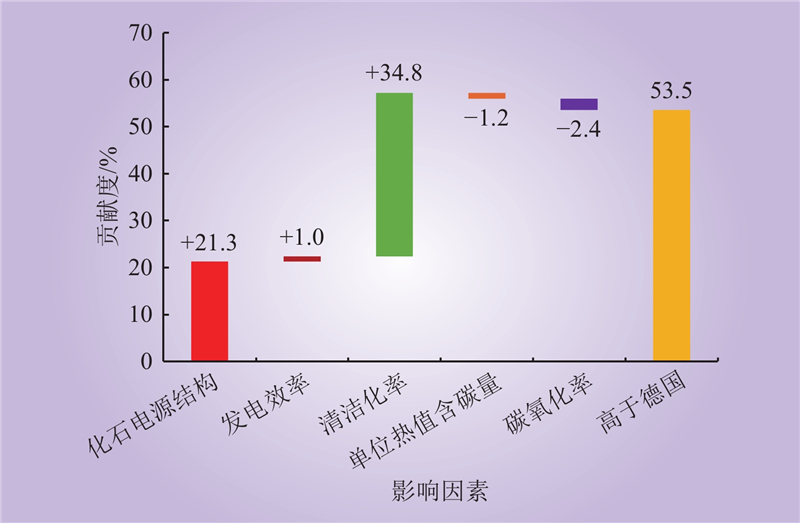
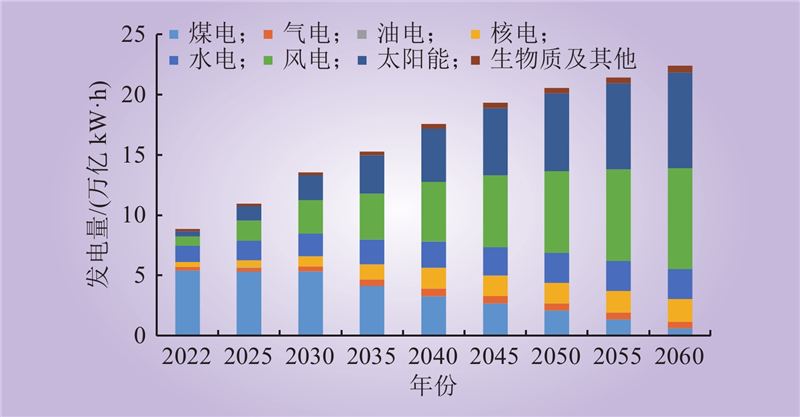
| 1 |
KAYA Y. Impact of carbon dioxide emission control on GNP growth: interpretation of proposed scenarios[R]. Paris: Response Strategies Working Group, 1990.
|
| 2 |
BOYD G, MCDONALD J F, ROSS M, et al. Separating the changing composition of U.S. manufacturing production from energy efficiency improvements: a divisia index approach[J]. The Energy Journal, 1987, 8 (2): 77- 96.
DOI
|
| 3 |
ANG W B, CHOI K H. Decomposition of aggregate energy and gas emission intensities for industry: a refined divisia index method[J]. The Energy Journal, 1997, 18 (3): 59- 73.
DOI
|
| 4 |
CHUNG H S, RHEE H C. A residual-free decomposition of the sources of carbon dioxide emissions: a case of the Korean industries[J]. Energy, 2001, 26 (1): 15- 30.
DOI
|
| 5 |
LEONTIEF W W, DANIEL F. Air pollution and the economic structure: empirical results of input-output comparisons[C]//Input-Output Techniques. Amsterdam: 1972: 9–23.
|
| 6 |
陈晓科, 周天睿, 李欣, 等. 电力系统的碳排放结构分解与低碳目标贡献分析[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2012, 36 (2): 18- 25.
|
|
CHEN Xiaoke, ZHOU Tianrui, LI Xin, et al. Structure identification of CO2 emission for power system and analysis of its low-carbon contribution[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2012, 36 (2): 18- 25.
|
| 7 |
王建军, 李莉. 基于随机性环境影响评估模型的电力消费和碳排放关系实证分析[J]. 电网技术, 2014, 38 (3): 628- 632.
|
|
WANG Jianjun, LI Li. Empirical analysis on relation between electricity consumption and carbon emission based on stochastic impacts by regression on population, affluence and technology model[J]. Power System Technology, 2014, 38 (3): 628- 632.
|
| 8 |
王常凯, 谢宏佐. 中国电力碳排放动态特征及影响因素研究[J]. 中国人口·资源与环境, 2015, 25 (4): 21- 27.
|
|
WANG Changkai, XIE Hongzuo. Analysis on dynamic characteristics and influencing factors of carbon emissions from electricity in China[J]. China Population, Resources and Environment, 2015, 25 (4): 21- 27.
|
| 9 |
刘婷, 白宏涛, 徐鹤. 中国典型区域含电力消费的碳排放驱动因素分解[J]. 环境污染与防治, 2017, 39 (11): 1278- 1283.
|
|
LIU Ting, BAI Hongtao, XU He. Studying on driving factors of carbon emission containing power consumption in typical provinces of China[J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2017, 39 (11): 1278- 1283.
|
| 10 |
刘敏. 电力行业碳排放因素分解及减排机制研究[D]. 大连: 大连海事大学, 2023.
|
|
LIU Min. Research on decomposition of carbon emission factors and emission reduction mechanismin electric power industry[D]. Dalian: Dalian Maritime University, 2023.
|
| 11 |
丁甜甜, 李玮. 经济增长与减排视角下电力行业碳峰值预测[J]. 科技管理研究, 2019, 39 (18): 246- 253.
|
|
DING Tiantian, LI Wei. Peak forecast of carbon emissions in the power industry from the perspective of economic growth and emission reduction[J]. Science and Technology Management Research, 2019, 39 (18): 246- 253.
|
| 12 |
徐国泉, 封士伟. 中国火电行业能源消费碳排放的时空演变特征[J]. 生态经济, 2024, 40 (2): 30- 38.
|
|
XU Guoquan, FENG Shiwei. Spatial-temporal evolution characteristics of carbon emissions from energy consumption in China's thermal power industry[J]. Ecological Economy, 2024, 40 (2): 30- 38.
|
| 13 |
宿雪莲. 中国八大区域电力部门碳排放2030年达峰的可行性评估: 因素分解、经济脱钩及预测分析[D]. 大连: 东北财经大学, 2020.
|
|
SU Xuelian. Feasibility of peaking carbon emissions of the power sector in China's eight regions by 2030: decomposition, decoupling, and prediction analysis[D]. Dalian: Dongbei University of Finance and Economics, 2020.
|
| 14 |
刘振笃. “一带一路” 背景下我国电力行业碳排放测度与影响因素分析: 基于LMDI分解方法和面板模型[D]. 兰州: 西北师范大学, 2024.
|
|
LIU Zhendu. Measurement and influencing factors analysis of carbon emissions of the China's power industry in the context of the "the Belt and Road" initiative——based on the LMDI decomposition model and panel model[D]. Lanzhou: Northwest Normal University, 2024.
|
| 15 |
李泽艳. 内蒙古电力行业碳达峰情景分析研究[J]. 内蒙古科技与经济, 2023 (15): 3- 7.
|
|
LI Zeyan. Research on the scenario analysis of carbon peak in Inner Mongolia electric power industry[J]. Inner Mongolia Science Technology & Economy, 2023 (15): 3- 7.
|
| 16 |
曹俊文, 姜雯昱. 基于LMDI的电力行业碳排放影响因素分解研究[J]. 统计与决策, 2018, 34 (14): 128- 131.
|
| 17 |
汪颖翔, 黄河曲, 陈远, 等. 中国电力消费碳排放驱动因素分析: 基于LMDI分解方法[J]. 湖北经济学院学报(人文社会科学版), 2023, 20 (6): 38- 44.
|
| 18 |
余欣玥. 电力行业碳排放影响因素分解及多情景预测研究[D]. 北京: 华北电力大学, 2023.
|
|
YU Xinyue. Decomposition of influencing factors and multi-scenario prediction of carbon emission in power industry[D]. Beijing: North China Electric Power University, 2023.
|
| 19 |
彭皓月, 戴豪礽, 刘洪润. 电力碳排放特征及影响因素分析以重庆市为例[J]. 节能与环保, 2024 (1): 67- 75.
|
|
PENG Haoyue, DAI Haoreng, LIU Hongrun. Characteristics and driving factors of electric power carbon emission: a case study of Chongqing municipality[J]. Energy Conservation & Environmental Protection, 2024 (1): 67- 75.
|
| 20 |
王海静. 贵州省电力行业碳排放关键因素分解及达峰对策研究[D]. 贵阳: 贵州大学, 2021.
|
| 21 |
王天庆. 安徽省电力行业碳排放脱钩效应及影响因素研究[D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学, 2021.
|
|
WANG Tianqing. Research on decoupling effects and influencing factors of carbon emissions of Anhui power generation industry[D]. Hefei: Hefei University of Technology, 2021.
|
| 22 |
施应玲, 余欣玥. 基于LMDI和系统聚类的电力行业碳排放影响因素分析[J]. 生态经济, 2024, 40 (2): 22- 29.
|
|
SHI Yingling, YU Xinyue. An analysis of influencing factors of carbon emission in power industry based on LMDI and system clustering[J]. Ecological Economy, 2024, 40 (2): 22- 29.
|
| 23 |
张乘玮, 王健新, 李永峰. 基于LMDI分解方法的连云港市电力碳排放研究[J]. 能源与节能, 2022 (12): 76- 79, 112.
|
|
ZHANG Chengwei, WANG Jianxin, LI Yongfeng. Carbon emissions in electric power industry of Lianyungang City based on LMDI decomposition method[J]. Energy and Energy Conservation, 2022 (12): 76- 79, 112.
|
| 24 |
李旭东, 谭青博, 赵浩辰, 等. 碳达峰背景下中国电力行业碳排放因素和脱钩效应[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (5): 88- 98.
|
|
LI Xudong, TAN Qingbo, ZHAO Haochen, et al. Carbon emission factors and decoupling effects of China's power industry under the background of carbon peak[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (5): 88- 98.
|
| 25 |
玉琦彤. 中国电力行业碳排放脱钩效应情景模拟[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2021, 44 (6): 194- 200.
|
|
YU Qitong. Scenario simulation of decoupling effect of carbon emission in China’s power industry[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2021, 44 (6): 194- 200.
|
| 26 |
王海静, 王红蕾. 基于STIRPAT模型的贵州省电力行业碳峰值预测[J]. 生产力研究, 2021 (3): 108- 113.
|
| 27 |
赵亚涛, 南新元, 王伟德. 基于LMDI-SD方法的火电行业碳排放峰值预测[J]. 计算机仿真, 2019, 36 (10): 116- 120, 428.
|
|
ZHAO Yatao, NAN Xinyuan, WANG Weide. Prediction of carbon emission peak in thermal power industry based on LMDI-SD method[J]. Computer Simulation, 2019, 36 (10): 116- 120, 428.
|
| 28 |
周原冰, 张士宁, 侯方心, 等. 电力行业碳达峰及促进全社会碳减排影响分析[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (9): 1- 9.
|
|
ZHOU Yuanbing, ZHANG Shining, HOU Fangxin, et al. Analysis of carbon peaking in power sector and its impact on promoting whole-society carbon emissions reduction[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (9): 1- 9.
|
| 29 |
张士宁, 马志远, 杨方, 等. 全球可再生能源发电减排技术及投资减排成效评估分析[J]. 全球能源互联网, 2020, 3 (4): 328- 338.
|
|
ZHANG Shining, MA Zhiyuan, YANG Fang, et al. Assessment of carbon emission reduction and costs of global renewable energy investment[J]. Journal of Global Energy Interconnection, 2020, 3 (4): 328- 338.
|
| 30 |
侯方心, 张士宁, 赵子健, 等. 实现《巴黎协定》目标下的全球能源互联网情景展望分析[J]. 全球能源互联网, 2020, 3 (1): 34- 43.
|
|
HOU Fangxin, ZHANG Shining, ZHAO Zijian, et al. Global energy interconnection scenario outlook and analysis in the context of achieving the Paris agreement goals[J]. Journal of Global Energy Interconnection, 2020, 3 (1): 34- 43.
|
| 31 |
李威武, 梁琛, 董晓阳, 等. 绿电绿证交易对电力碳排放因子影响分析[J]. 价值工程, 2023, 42 (32): 13- 15.
|
|
LI Weiwu, LIANG Chen, DONG Xiaoyang, et al. Analysis of the impact of green electricity and GEC trading on carbon emission factors of electricity[J]. Value Engineering, 2023, 42 (32): 13- 15.
|
| 32 |
林笃宇. 基于环境完整性考虑绿证应用的电网排放因子核算方法研究[J]. 能源与环境, 2024 (4): 154- 156.
|
| 33 |
陈政, 何耿生, 尚楠. 面向碳达峰碳中和的电网碳排放因子改进计算方法[J]. 南方电网技术, 2024, 18 (1): 153- 162.
|
|
CHEN Zheng, HE Gengsheng, SHANG Nan. Improved calculation method of power grid carbon emission factor for carbon peak and carbon neutrality goals[J]. Southern Power System Technology, 2024, 18 (1): 153- 162.
|
| 34 |
宋金伟, 杨维, 周春雷, 等. 跨电网的区域电力碳排放因子分布式计算方法[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2025, 49 (18): 25- 32.
|
|
SONG Jinwei, YANG Wei, ZHOU Chunlei, et al. Distributed calculation method for regional power carbon emission factors across power grids[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2025, 49 (18): 25- 32.
|
| 35 |
彭天海, 蔡萱, 瞿子涵, 等. 计及大规模电网分级分区解耦的区域电网供电碳排放因子计算模型研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2024, 44 (3): 894- 905.
|
|
PENG Tianhai, CAI Xuan, QU Zihan, et al. Research on calculation model of power supply carbon emission factor in regional power grid considering hierarchical and regional decoupling of large-scale power grid[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2024, 44 (3): 894- 905.
|
| 36 |
詹立琴, 汪磊磊. 建筑碳排放计算中电力碳排放因子的适宜性选择分析[J]. 绿色建筑, 2025, 17 (2): 135- 139, 163.
|
|
ZHAN Liqin, WANG Leilei. Analysis of the appropriateness of carbon emission factors for electricity in building carbon emission calculations[J]. Green Building, 2025, 17 (2): 135- 139, 163.
|
| 37 |
苏庆, 章若茵, 邱巨龙. 电力碳排放因子发展现状及本地化计算方法研究[J]. 能源研究与利用, 2024 (5): 20- 23.
|
| 38 |
贾敏, 张立, 张哲, 等. 动态省级电力CO2排放因子对区域碳达峰路径的影响[J]. 中国工程科学, 2024, 26 (4): 121- 133.
DOI
|
|
JIA Min, ZHANG Li, ZHANG Zhe, et al. Impacts of dynamic province-level power-grid CO2 emission factor on regional carbon-peaking pathways[J]. Strategic Study of CAE, 2024, 26 (4): 121- 133.
DOI
|
| 39 |
江亿, 张吉, 张涛, 等. 电力动态碳排放责任因子[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2024, 44 (17): 7024- 7039.
|
|
JIANG Yi, ZHANG Ji, ZHANG Tao, et al. Dynamic carbon emission responsibility factor of electricity[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2024, 44 (17): 7024- 7039.
|
| 40 |
刘洋广. 基于动态碳排放因子的电力低碳优化调度策略[J]. 电器与能效管理技术, 2024 (12): 26- 32,68.
|
|
LIU Yangguang. Low carbon optimal dispatch strategy for electricity based on dynamic carbon emission factors[J]. Electrical & Energy Management Technology, 2024 (12): 26- 32,68.
|
| 41 |
李姚旺, 张宁, 杜尔顺, 等. 基于碳排放流的电力系统低碳需求响应机制研究及效益分析[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2022, 42 (8): 2830- 2842.
|
|
LI Yaowang, ZHANG Ning, DU Ershun, et al. Mechanism study and benefit analysis on power system low carbon demand response based on carbon emission flow[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2022, 42 (8): 2830- 2842.
|
| 42 |
崔杨, 邹新鹏, 赵钰婷, 等. 考虑动态电碳排放因子的新型电力系统电碳综合需求响应调度方法[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2024, 44 (10): 1- 7.
|
|
CUI Yang, ZOU Xinpeng, ZHAO Yuting, et al. Electricity-carbon integrated demand response scheduling method for new power system considering dynamic electricity-carbon emission factor[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2024, 44 (10): 1- 7.
|
| 43 |
生态环境部, 国家统计局. 2021年电力二氧化碳排放因子计算说明[S].
|
| 44 |
国家发展改革委办公厅. 关于做好2016、2017年度碳排放报告与核查及排放监测计划制定工作的通知: 发改办气候〔2017〕1989号[A/OL]. (2017-12-15)[2025-09-12]. https://www.ndrc.gov.cn/xxgk/zcfb/tz/201712/t20171215_962618_ext.html.
|
| 45 |
生态环境部, 国家统计局. 关于发布2021年电力二氧化碳排放因子的公告: 公告2024年第12号[A/OL].(2024-04-12)[2025-09-12]. https://wzq1.mee.gov.cn/xxgk2018/xxgk/xxgk01/202404/t20240412_1070565.html.
|
| 46 |
生态环境部, 国家统计局. 关于发布2022年电力二氧化碳排放因子的公告: 公告2024年第33号[A/OL](2024-12-26)[2025-09-12]. https://wzq1.mee.gov.cn/xxgk2018/xxgk/xxgk01/202412/t20241226_1099413.html.
|
| 47 |
国家统计局能源统计司. 中国能源统计年鉴2023[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2024.
|
| 48 |
中国电力企业联合会. 中国电力统计年鉴2023[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2023.
|
| 49 |
LADAGE S, BLUMENBERG M, FRANKE D, et al. On the climate benefit of a coal-to-gas shift in Germany's electric power sector[J]. Scientific Reports, 2021, 11, 11453.
DOI
|