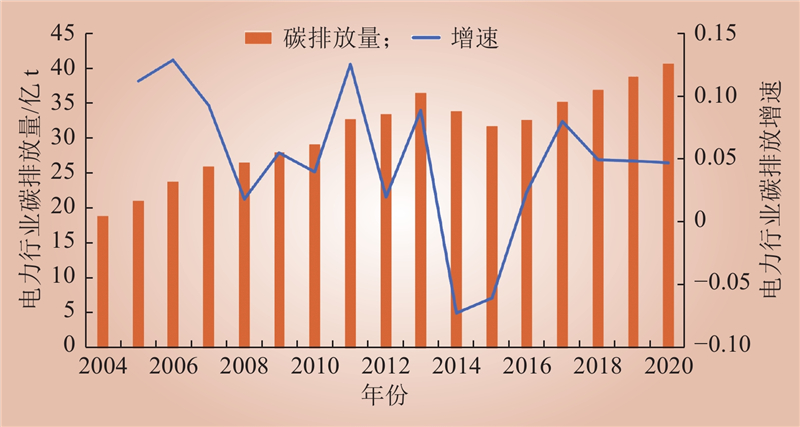
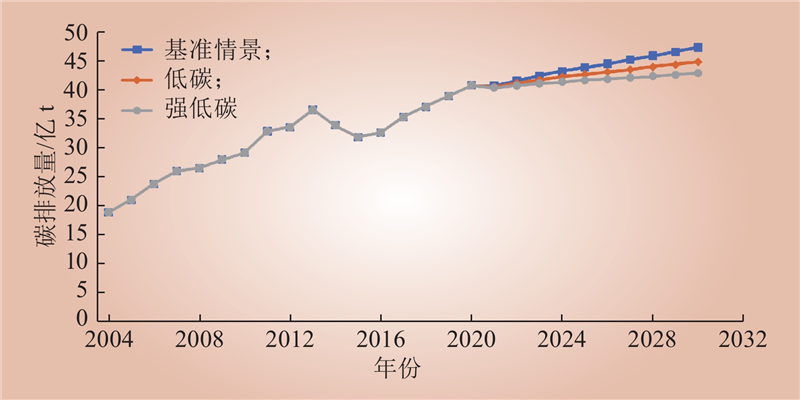
| 1 |
梁福生, 曹俐, 葛智越. 空间溢出视角下绿色信贷的碳排放效应研究: 基于财政分权的调节作用[J]. 调研世界, 2022, (10): 38- 48.
|
|
LIANG Fusheng, CAO Li, GE Zhiyue. Research on the carbon emission effect of green credit from the perspective of spatial spillover—moderating effect based on fiscal decentralization[J]. The World of Survey and Research, 2022, (10): 38- 48.
|
| 2 |
王成仁, 陈妍, 刘梦. 我国化石能源保供稳价形势研判及对策建议[J]. 价格理论与实践, 2023, (3): 31- 37, 64.
|
|
WANG Chengren, CHEN Yan, LIU Meng. Analysis and suggestions on the situation of ensuring supply and stabling price of fossil energy in China[J]. Price:Theory & Practice, 2023, (3): 31- 37, 64.
|
| 3 |
李海龙, 唐献凤. 区块链嵌入下电力企业新型碳绩效管理体系构建[J]. 财会月刊, 2023, 44 (7): 85- 92.
|
| 4 |
郭玲, 宁才晟, 王文烂. 中国林产品生产侧碳排放量的测度与效应分解: 基于多区域投入产出与结构分解分析模型[J]. 林业经济, 2022, 44 (5): 23- 40.
|
|
GUO Ling, NING Caisheng, WANG Wenlan. Measurement and effect decomposition of carbon emissions on the production side of forest products in China—based on the multi-regional input-output and structural decomposition analysis model[J]. Forestry Economics, 2022, 44 (5): 23- 40.
|
| 5 |
LIU B Q, SHI J X, WANG H, et al. Driving factors of carbon emissions in China: a joint decomposition approach based on meta-frontier[J]. Applied Energy, 2019, 256, 113986.
DOI
|
| 6 |
WANG Q W, CHIU Y H, CHIU C R. Driving factors behind carbon dioxide emissions in China: a modified production-theoretical decomposition analysis[J]. Energy Economics, 2015, 51, 252- 260.
DOI
|
| 7 |
闫庆友, 王雅娴, 于振华, 等. 基于Shapley值的京津冀火电行业碳排放因素分解[J]. 生态经济, 2018, 34 (12): 29- 34.
|
|
YAN Qingyou, WANG Yaxian, YU Zhenhua, et al. Decomposition analysis of carbon dioxide emissions from thermal electricity generation in Beijing, Tianjin and Hebei: a study based on shapley value[J]. Ecological Economy, 2018, 34 (12): 29- 34.
|
| 8 |
OECD. Indicators to measure decoupling of environment pressure from economic growth[R]. Paris: OECD, 2002: 13-14.
|
| 9 |
向彩红, 覃秋蓓. 基于脱钩指数与LMDI的湖南省绿色低碳发展路径研究[J]. 环境科学导刊, 2022, 41 (3): 19- 26.
DOI
|
|
XIANG Caihong, QIN Qiubei. Study on green and low-carbon development path of Hunan province based on decoupling index and LMDI model[J]. Environmental Science Survey, 2022, 41 (3): 19- 26.
DOI
|
| 10 |
侯丽朋, 王琳, 钱瑶, 等. “双碳” 目标下闽三角碳排放脱钩状态及驱动机制分析[J]. 生态学报, 2022, 42 (23): 9663- 9676.
|
|
HOU Lipeng, WANG Lin, QIAN Yao, et al. Decoupling status and driving mechanisms of carbon emissions in the Golden Triangle of Southern Fujian under "carbon peaking and neutrality" goals[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2022, 42 (23): 9663- 9676.
|
| 11 |
杨英明, 孙健东. 世界主要国家能源消费碳排放脱钩及驱动因素研究[J]. 煤炭工程, 2019, 51 (7): 173- 177.
|
|
YANG Yingming, SUN Jiandong. Carbon emission decoupling and drivers of energy consumption in major countries[J]. Coal Engineering, 2019, 51 (7): 173- 177.
|
| 12 |
DONG J, LI C, WANG Q. Decomposition of carbon emission and its decoupling analysis and prediction with economic development: a case study of industrial sectors in Henan province[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021, 321, 129019.
DOI
|
| 13 |
曲健莹, 李科. 工业增长与二氧化碳排放“脱钩” 的测算与分析[J]. 西安交通大学学报(社会科学版), 2019, 39 (5): 92- 104.
|
|
QU Jianying, LI Ke. Measurement and analysis of "decoupling" between industrial growth and carbon dioxide emissions in China[J]. Journal of Xi'an Jiaotong University (Social Sciences), 2019, 39 (5): 92- 104.
|
| 14 |
李健, 王尧, 王颖. 天津市碳排放脱钩态势及碳减排潜力分析: 基于2007—2016年的面板数据[J]. 生态经济, 2019, 35 (4): 26- 32.
|
|
LI Jian, WANG Yao, WANG Ying. Tianjin carbon emissions decoupling analysis and carbon emission reduction potential: based on panel data from 2007 to 2016[J]. Ecological Economy, 2019, 35 (4): 26- 32.
|
| 15 |
陈赟, 沈浩, 王晓慧, 等. 基于Mann-Kendall趋势检验的城市能源碳达峰评估方法[J]. 上海交通大学学报, 2023, 57 (7): 928- 938.
|
|
CHEN Yun, SHEN Hao, WANG Xiaohui, et al. Assessment method for urban energy carbon emission peak based on Mann-Kendall trend test[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2023, 57 (7): 928- 938.
|
| 16 |
玉琦彤. 中国电力行业碳排放脱钩效应情景模拟[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2021, 44 (6): 194- 200.
|
|
YU Qitong. Scenario simulation of decoupling effect of carbon emission in China's power industry[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2021, 44 (6): 194- 200.
|
| 17 |
廖祖君, 张剑宇, 陈诗薇. 碳排放影响因素及达峰路径研究: 基于四川省的分析[J]. 软科学, 2023, 37 (9): 95- 101.
|
|
LIAO Zujun, ZHANG Jianyu, CHEN Shiwei. Factors influencing carbon emission and carbon peak reaching pathways: evidence from Sichuan province[J]. Soft Science, 2023, 37 (9): 95- 101.
|
| 18 |
马宇恒. 东北地区2030年碳排放达峰路径研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2018.
|
|
MA Yuheng. Study on the peak path of carbon emission in Northeast China in 2030[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2018.
|
| 19 |
马丁, 陈文颖. 中国2030年碳排放峰值水平及达峰路径研究[J]. 中国人口·资源与环境, 2016, 26 (增刊1): 1- 4.
|
| 20 |
ANG B W. Decomposition analysis for policymaking in energy: which is the preferred method?[J]. Energy policy, 2004, 32 (9): 1131- 1139.
DOI
|
| 21 |
杨海柱, 田馥铭, 张鹏, 等. 基于CEEMD-FE和AOA-LSSVM的短期电力负荷预测[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2022, 50 (13): 126- 133.
|
|
YANG Haizhu, TIAN Fuming, ZHANG Peng, et al. Short-term load forecasting based on CEEMD-FE-AOA-LSSVM[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2022, 50 (13): 126- 133.
|
| 22 |
于霄宇, 纪正森, 嵇灵, 等. 双碳目标下我国电动汽车碳减排贡献潜力分析[J]. 智慧电力, 2024, 52 (2): 25- 31, 39.
|
|
YU Xiaoyu, JI Zhengsen, JI Ling, et al. Analysis on carbon emission reduction potential of electric vehicles in China under goal of carbon neutrality and carbon peaking[J]. Smart Power, 2024, 52 (2): 25- 31, 39.
|
| 23 |
张浩然, 汪晓东. 回归最小二乘支持向量机的增量和在线式学习算法[J]. 计算机学报, 2006, 29 (3): 400- 406.
DOI
|
|
ZHANG Haoran, WANG Xiaodong. Incremental and online learning algorithm for regression least squares support vector machine[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2006, 29 (3): 400- 406.
DOI
|
| 24 |
何忠华, 张涛, 胡娱欧, 等. 考虑大气污染防治措施影响的短期电力负荷预测模型研究[J]. 智慧电力, 2019, 47 (5): 1- 9.
DOI
|
|
HE Zhonghua, ZHANG Tao, HU Yuou, et al. Short-term electric load forecasting model considering the influence of air pollution prevention and control policy[J]. Smart Power, 2019, 47 (5): 1- 9.
DOI
|
| 25 |
王凤婷, 方恺, 于畅. 京津冀产业能源碳排放与经济增长脱钩弹性及驱动因素: 基于Tapio脱钩和LMDI模型的实证[J]. 工业技术经济, 2019, 38 (8): 32- 40.
|
|
WANG Fengting, FANG Kai, YU Chang. Decoupling between industrial energy-related carbon emissions and economic growth and its driving factors in Beijing, Tianjin and Hebei urban agglomeration—empirical study based on tapio decoupling and LMDI model[J]. Journal of Industrial Technological Economics, 2019, 38 (8): 32- 40.
|
| 26 |
The United Nations Economic and Social Affairs. World urbanization outlook report [EB/OL]. (2014-07-20)[2022-04-25].https://www.un.org/development/desa/zh/news/population/world-urbanization-prospects-2014.html.
|
| 27 |
廖华, 向福洲. 中国“十四五” 能源需求预测与展望[J]. 北京理工大学学报(社会科学版), 2021, 23 (2): 1- 8.
|
|
LIAO Hua, XIANG Fuzhou. Forecast and prospect of energy demand in china's "14th five-year" plan period[J]. Journal of Beijing Institute of Technology (Social Sciences Edition), 2021, 23 (2): 1- 8.
|
| 28 |
李平, 娄峰, 王宏伟. 2016—2035年中国经济总量及其结构分析预测[J]. 中国工程科学, 2017, 19 (1): 13- 20.
DOI
|
|
LI Ping, LOU Feng, WANG Hongwei. Analysis and forecast of China's total economy and its structure from 2016–2035[J]. Strategic Study of CAE, 2017, 19 (1): 13- 20.
DOI
|
| 29 |
国务院发展研究中心课题组. 认识人口基本演变规律 促进我国人口长期均衡发展[J]. 管理世界, 2022, 38 (1): 1- 19, 34, 20.
DOI
|
|
Group of the Development Research Center of the State Council. Understand the basic laws of population evolution and promote the long-term balanced development of China's population[J]. Journal of Management World, 2022, 38 (1): 1- 19, 34, 20.
DOI
|