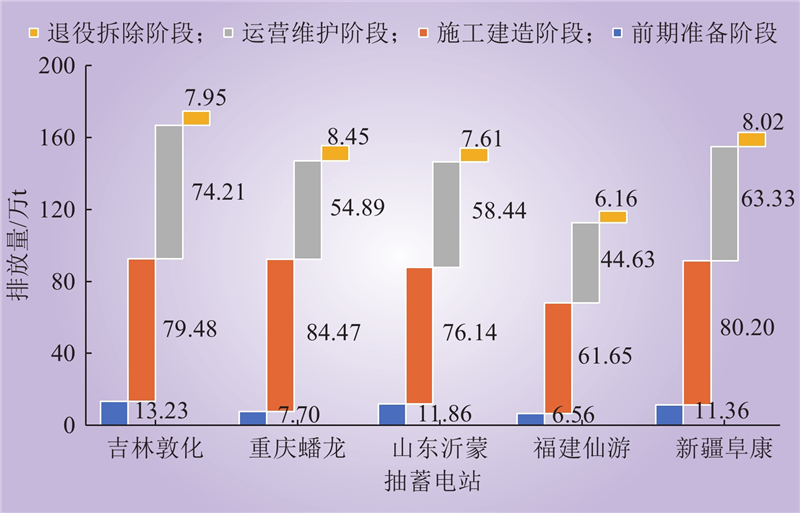
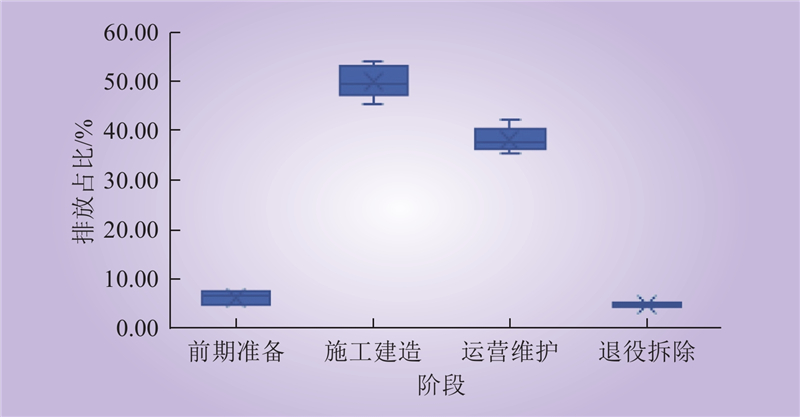
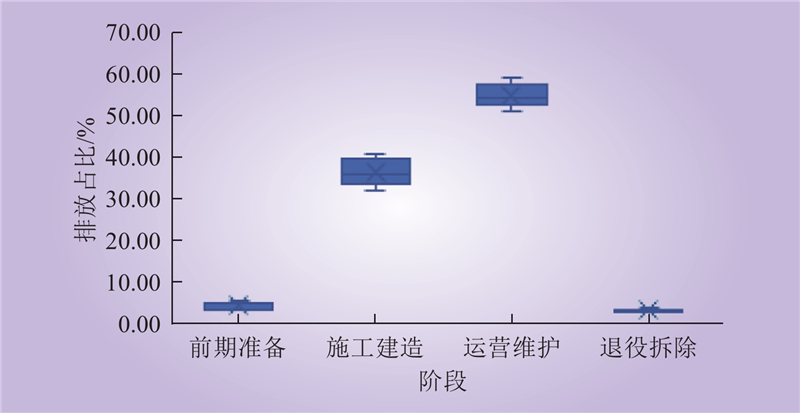
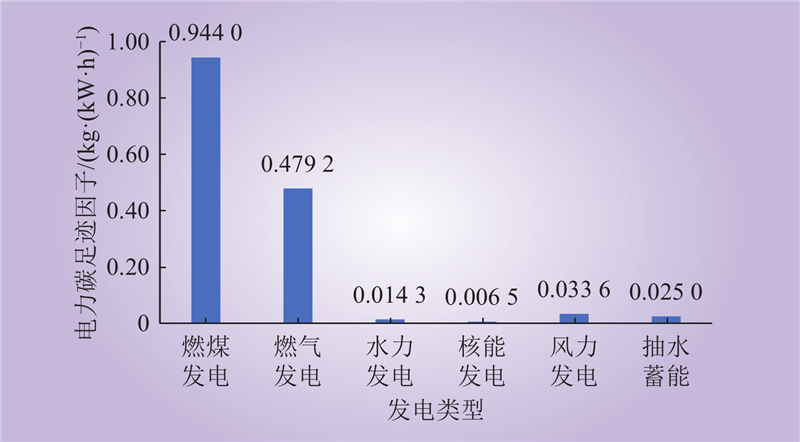
| 1 |
张智刚, 康重庆. 碳中和目标下构建新型电力系统的挑战与展望[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2022, 42 (8): 2806- 2819.
|
|
ZHANG Zhigang, KANG Chongqing. Challenges and prospects for constructing the new-type power system towards a carbon neutrality future[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2022, 42 (8): 2806- 2819.
|
| 2 |
但扬清, 王蕾, 郑伟民, 等. 高比例可再生能源接入背景下电网承载能力鲁棒提升策略[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (9): 104- 111.
|
|
DAN Yangqing, WANG Lei, ZHENG Weimin, et al. Robust improvement strategy for power grid hosting capacity with integration of high proportion of renewable energy[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (9): 104- 111.
|
| 3 |
国家发展改革委, 国家能源局. 关于加快推动新型储能发展的指导意见[J]. 电力设备管理, 2021 (7): 16- 17,40.
|
| 4 |
国家发展改革委. 关于进一步完善抽水蓄能价格形成机制的意见: 发改价格〔2021〕633号[A/OL]. (2021-4-30) [2025-5-30]. http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/2021-05/08/content_5605367.htm.
|
| 5 |
中国政府网. 《抽水蓄能中长期发展规划(2021—2035)》印发实施[A/OL]. (2021-09-09)[2025-04-10]. http://www.gov.cn/xinwen/202109/09/content_5636487.html.
|
| 6 |
北京市生态环境局, 北京市统计局. 关于公布纳入北京市碳排放权交易管理的2024年度碳排放单位名单的通知[A/OL]. (2024-08-06) [2025-05-30]. https://sthjj.beijing.gov.cn/bjhrb/index/xxgk69/zfxxgk43/fdzdgknr2/325924085/543475291/index.html.
|
| 7 |
GILES J. Methane quashes green credentials of hydropower[J]. Nature, 2006, 444 (7119): 524- 525.
|
| 8 |
QIU J. Chinese dam may be a methane menace[J]. Nature, 2009. DOI: 10.1038/news.2009.962.
|
| 9 |
中国环境报. 中国电力碳足迹因子客观反映了电力低碳转型成效| 系列解读一[R/OL]. https://chinapower.org.cn/index.php/detail/441205.html.
|
| 10 |
生态环境部, 国家统计局, 国家能源局. 关于发布2023年电力碳足迹因子数据的公告: 公告2025年第3号[A/OL]. (2025-01-21)[2025-08-06]. https://www.mee.gov.cn/xxgk2018/xxgk/xxgk01/202501/t20250123_1101226.html.
|
| 11 |
杜海龙, 李哲, 郭劲松. 基于ISO14067的长江上游某水电项目碳足迹分析[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2017, 26 (7): 1102- 1110.
|
|
DU Hailong, LI Zhe, GUO Jinsong. Carbon footprint of a large hydropower project in the upstream of the yangtze: following ISO14067[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 2017, 26 (7): 1102- 1110.
|
| 12 |
杜海龙. 金沙江大型水电站碳足迹的生命周期分析研究[D]. 重庆: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院重庆绿色智能技术研究院), 2017.
|
|
DU Hailong. Carbon footprint of typical hydro-projects in Jinsha River[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing Institute of Green and Intelligent Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2017.
|
| 13 |
宋国辉, 唐璐, 姜武, 等. 2×200 MW级某天然气热电联产项目的生命周期环境影响评价[J]. 中国电力, 2014, 47 (12): 149- 155.
|
|
SONG Guohui, TANG Lu, JIANG Wu, et al. Life-cycle environmental impact assessment of a typical 2×200 MW natural gas combined cycle-combined heat and power plant[J]. Electric Power, 2014, 47 (12): 149- 155.
|
| 14 |
刘含笑, 单思珂, 魏书洲, 等. 基于生命周期法的煤电碳足迹评估[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (7): 227- 237.
|
|
LIU Hanxiao, SHAN Sike, WEI Shuzhou, et al. Life-cycle carbon footprint assessment of coal-fired power generation[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (7): 227- 237.
|
| 15 |
王怀斌. 光伏发电全生命周期碳足迹及减排潜力研究[J]. 中国能源, 2023, 45 (8): 34- 44.
|
|
WANG Huaibin. Life cycle carbon footprint and carbon emission reduction potential of photovoltaic power generation[J]. Energy of China, 2023, 45 (8): 34- 44.
|
| 16 |
李新航. 基于全生命周期的风电系统碳排放核算与分析[J]. 环境保护与循环经济, 2021, 41 (6): 5- 8, 45.
|
| 17 |
王兵, 姜鑫茹, 陆峰, 等. 全生命周期视角下煤基燃气发电碳足迹及成本评估[J/OL]. 煤炭学报, 1–17 [2025-05-26]. https://doi.org/10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2024.1592.
|
|
WANG Bing, JIANG Xinru, LU Feng, et al. Carbon footprint and cost assessment of coal-based gas power generation from the perspective of full life cycle[J/OL]. Journal of China Coal Society, 1–17 [2025-05-26]. https://doi.org/10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2024.1592.
|
| 18 |
侯公羽, 马骁赟, 杨振华, 等. 抽水蓄能电站全生命周期碳排放计算与分析[J]. 中国环境科学, 2023, 43 (S1): 326- 335.
|
|
HOU Gongyu, MA Xiaoyun, YANG Zhenhua, et al. Calculation and analysis of carbon emissions in the whole life cycle of pumped storage power stations[J]. China Environmental Science, 2023, 43 (S1): 326- 335.
|
| 19 |
PASCALE A, URMEE T, MOORE A. Life cycle assessment of a community hydroelectric power system in rural Thailand[J]. Renewable Energy, 2011, 36 (11): 2799- 2808.
|
| 20 |
RIBEIRO F D, DA SILVA G A. Life-cycle inventory for hydroelectric generation: a Brazilian case study[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2010, 18 (1): 44- 54.
|
| 21 |
SUWANIT W, GHEEWALA S H. Life cycle assessment of mini-hydropower plants in Thailand[J]. International Journal of Life Cycle Assessment, 2011, 16 (9): 849- 858.
|
| 22 |
李雨晨, 秦宇, 杨柳, 等. 长江上游大中型水库碳排放量估算与分析: 以IPCC国家温室气体清单指南为基础[J]. 湖泊科学, 2023, 35 (1): 131- 145.
|
|
LI Yuchen, QIN Yu, YANG Liu, et al. Estimation and analysis of carbon emissions from the large-and medium-sized reservoirs in the upper reaches of Changjiang River: on the basis of the IPCC national greenhouse gas inventory[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2023, 35 (1): 131- 145.
|
| 23 |
李哲, 王殿常. 从水库温室气体研究到水电碳足迹评价: 方法及进展[J]. 水利学报, 2022, 53 (02): 139- 153.
|
|
LI Zhe, WANG Dianchang. From reservoir greenhouse gas emissions to hydropower carbon footprint: methodology and advances[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2022, 53 (02): 139- 153.
|
| 24 |
WRI, WBCSD. GHG protocol: product life cycle accounting and reporting standard [S]. Washington: WRI, 2011.
|
| 25 |
张益兵, 朱朝勇, 武美辰, 等. 基于全生命周期评价的变压器碳足迹研究与分析[J]. 高压电器, 2024, 60 (11): 57- 67.
|
|
ZHANG Yibing, ZHU Chaoyong, WU Meichen, et al. Research and analysis of carbon footprint of transformer based on full life cycle assessment[J]. High Voltage Apparatus, 2024, 60 (11): 57- 67.
|
| 26 |
中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 建筑碳排放计算标准: GB/T 51366—2019[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2019.
|
| 27 |
张孝存. 建筑碳排放量化分析计算与低碳建筑结构评价方法研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2018.
|
|
ZHANG Xiaocun. Research on the quantitative analysis of building carbon emissions andassessment methods for low-carbon buildings and structures [D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2018.
|
| 28 |
申娟娟. 基于LCA的建筑碳足迹测算及减排对策研究[D]. 广州: 广东工业大学, 2019.
|
|
SHEN Juanjuan. Research on carbon footprint calculation and emission reduction measures of buildings basedon life-cycle assessment[D]. Guangzhou: Gangdong University of Technology, 2019.
|
| 29 |
生态环境部. 企业温室气体排放核算与报告指南 发电设施 [S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2022.
|
| 30 |
World Resources Institute, C40 Cities Climate Leadership Group, ICLEI-Local Governments for Sustainability. Global protocol for community-scale greenhouse gas emission inventories [S]. 2014.
|
| 31 |
Carbon footprint of products-requirements and guidelines for quantification and communication: ISO 14067—2013 [S].
|
| 32 |
国家市场监督管理总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 温室气体 产品碳足迹 量化要求和指南: GB/T 24067—2024[S].
|
| 33 |
黄阮明, 费斐, 李灏恩, 等. 基于全生命周期法的储能技术减排降碳效益评估[J]. 电力与能源, 2024, 45 (1): 71- 76.
|
|
HUANG Ruanming, FEI fei, LI Hao'en, et al. Evaluation of carbon reduction benefit of energy storage technology based on the whole life cycle method[J]. Power & Energy, 2024, 45 (1): 71- 76.
|
| 34 |
SIMON T R, INMAN D, HANES R, et al. Life cycle assessment of closed-loop pumped storage hydropower in the United States[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2023, 57 (33): 12251- 12258.
|
| 35 |
童荣鑫, 梁迅, 关庆锋, 等. 2000—2020年中国陆地土壤碳储量及土地管理碳汇核算[J]. 地理学报, 2023, 78 (9): 2209- 2222.
|
|
TONG Rongxin, LIANG Xun, GUAN Qingfeng, et al. Estimation of soil carbon storage change from land use and management at a high spatial resolution in China during 2000-2020[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2023, 78 (9): 2209- 2222.
|
| 36 |
李小军, 辛晓洲, 彭志晴. 2003—2012年中国地表太阳辐射时空变化及其影响因子[J]. 太阳能学报, 2017, 38 (11): 3057- 3066.
|
|
LI Xiaojun, XIN Xiaozhou, PENG Zhiqing. Change analysis of surface solar radiation in china from 2003 to 2012[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2017, 38 (11): 3057- 3066.
|
| 37 |
HERTWICH E G, GIBON T, BOUMAN E A, et al. Integrated life-cycle assessment of electricity-supply scenarios confirms global environmental benefit of low-carbon technologies[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2014, 112(20). DOI:10.1073/pnas.1312753111.
|
| 38 |
李朋, 白孝轩, 丁宁, 等. 水电碳足迹关键影响因素及区域化研究趋势[J]. 中国环境科学, 2025, 45 (4): 2251- 2263.
|
|
LI Peng, BAI Xiaoxuan, DING Ning, et al. Key factors influencing hydropower carbon footprint assessment and geo-regional research trends[J]. China Environmental Science, 2025, 45 (4): 2251- 2263.
|
| 39 |
IPCC. Climate change 2014: mitigation of climate change [R]. United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA: Cambridge University Press, 2014.
|
| 40 |
UBIERNA M, SANTOS C. D, MERCIER-BLAIS S. Water security and climate change: hydropower reservoir greenhouse gas emissions, in water security under climate change[R]. Singapore: Springer Singapore, 2022: 69–94.
|
| 41 |
张斌, 李哲, 李翀, 等. 水库温室气体净通量评估模型(G-res Tool)及在长江上游典型水库初步应用[J]. 湖泊科学, 2019, 31 (5): 1479- 1488.
|
|
ZHANG Bin, LI Zhe, LI Chong, et al. The net GHG flux assessment model of reservoir (G-res Tool) and its application in reservoirs in upper reaches of Yangtze River in China[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2019, 31 (5): 1479- 1488.
|
| 42 |
国家能源局. 2024年度中国电力市场发展报告[R/OL]. (2025-07-15)[2025-08-13]. https://www.nea.gov.cn/20250717/54ae0fdb11f04b39a5b670999c04ef81/c.html.
|
| 43 |
水电水利规划设计总院. 中国可再生能源发展报告: 2024年度[R/OL]. (2025-05-28) [2025-08-13]. http://www.creei.cn/web/content.html?id=7282.
|