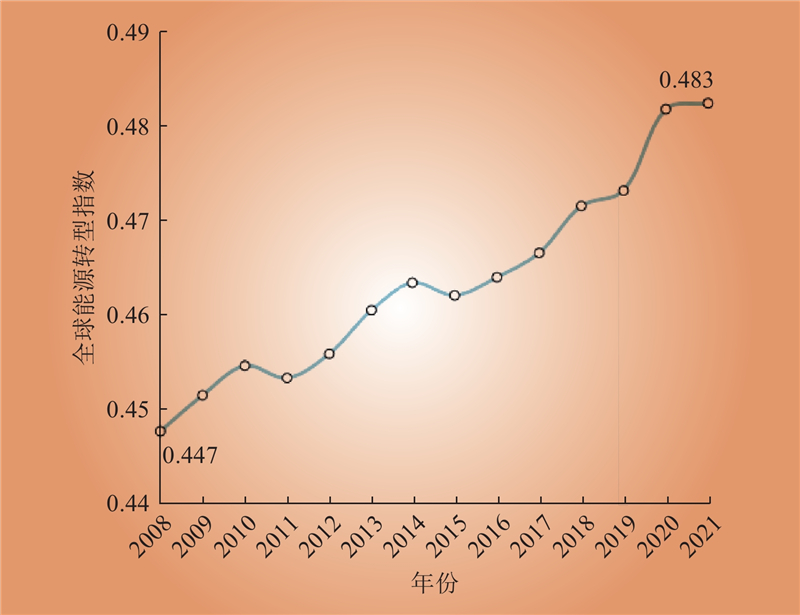
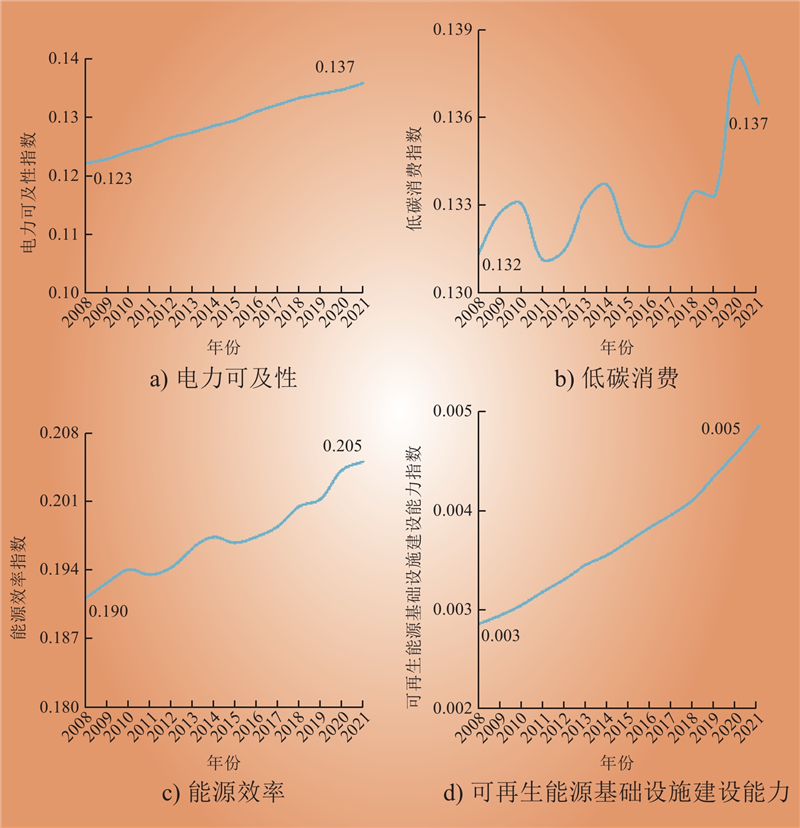
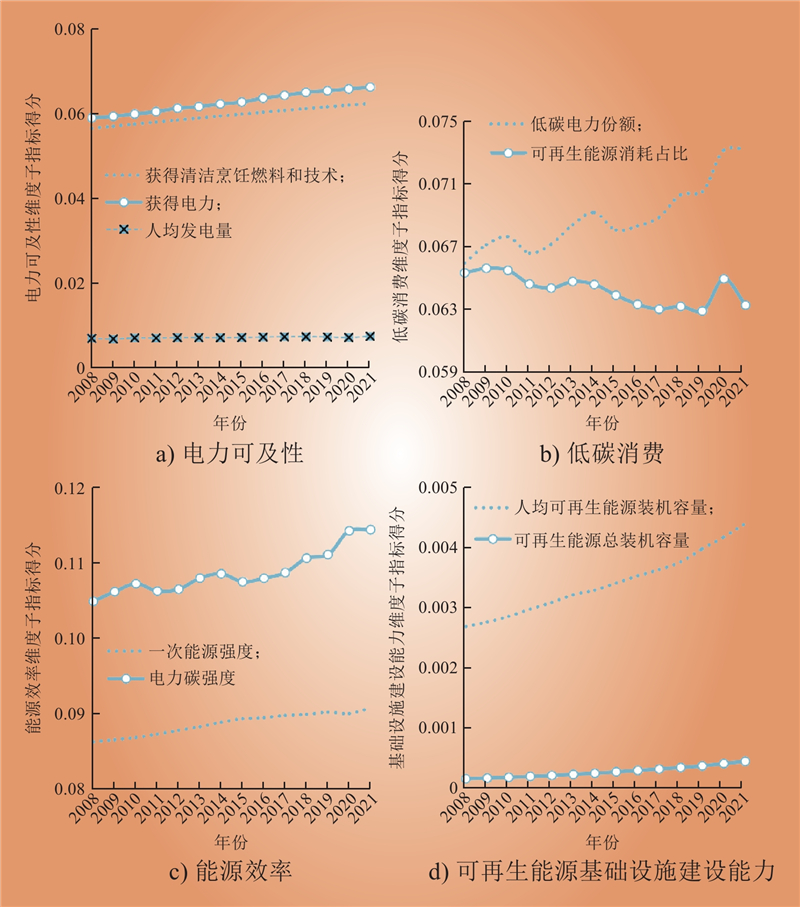
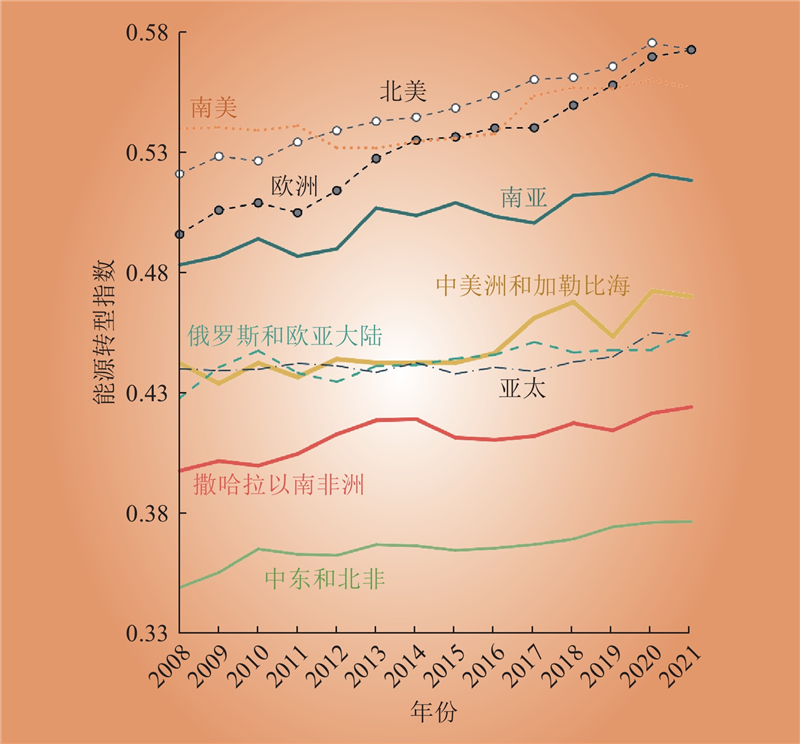
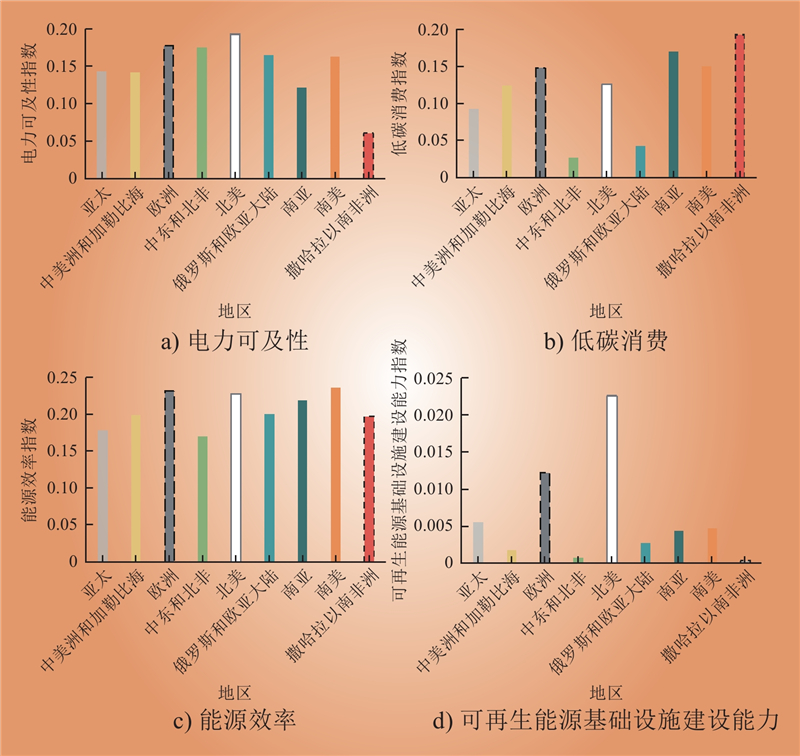
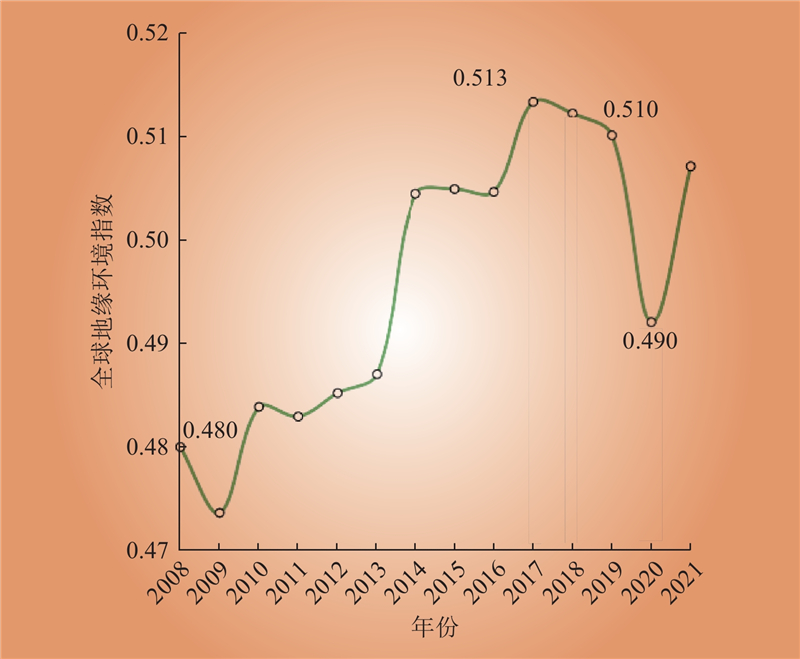
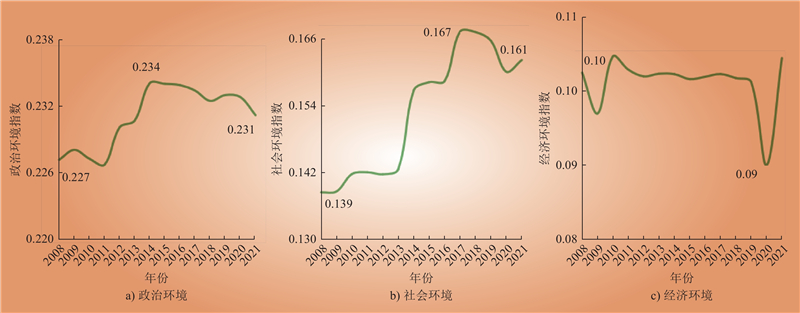
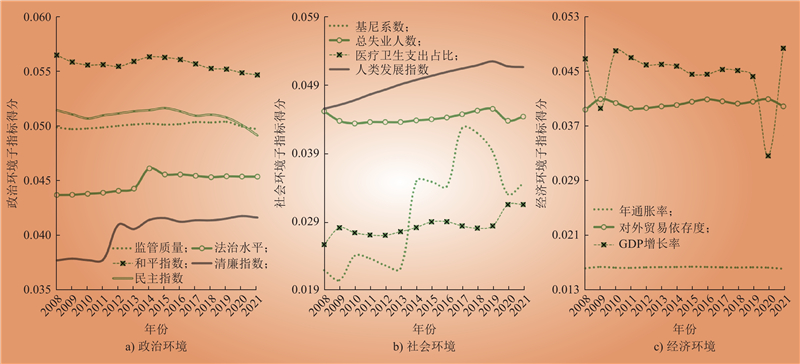
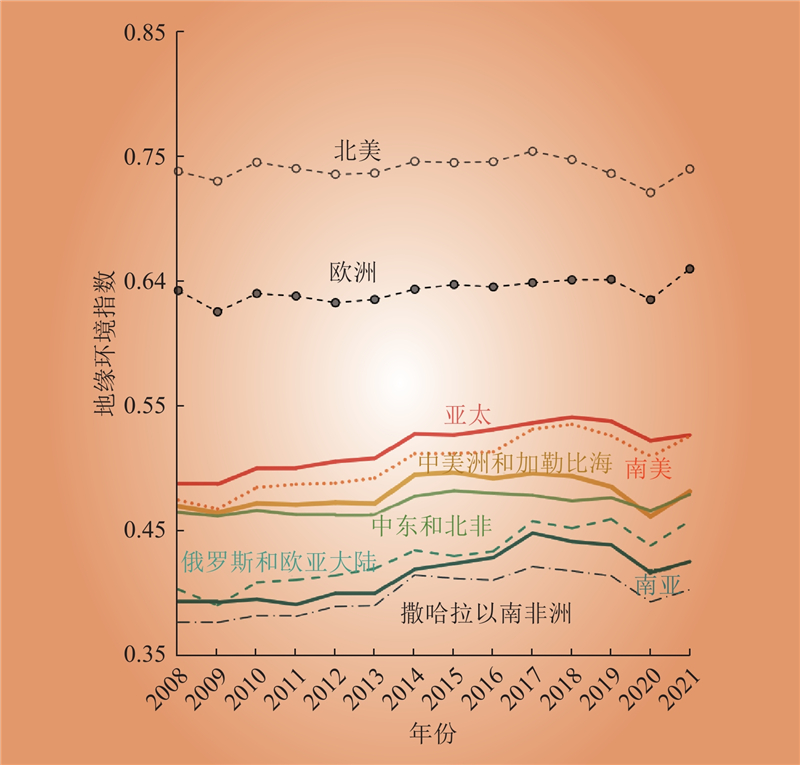
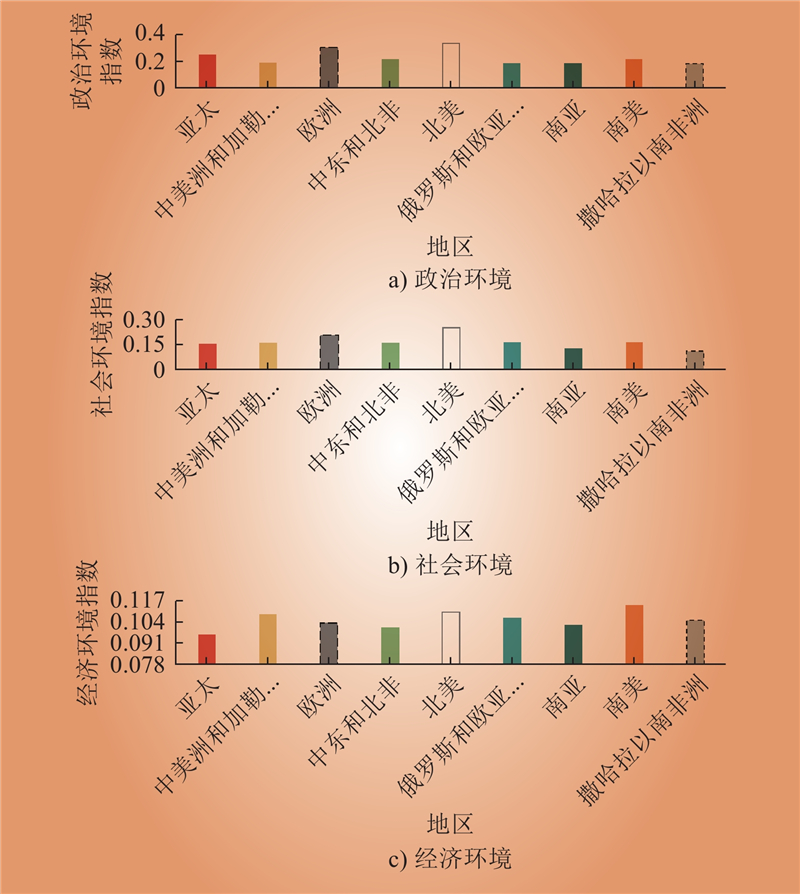
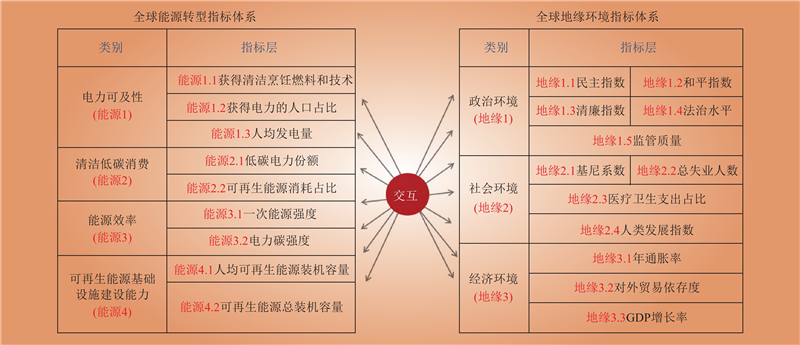
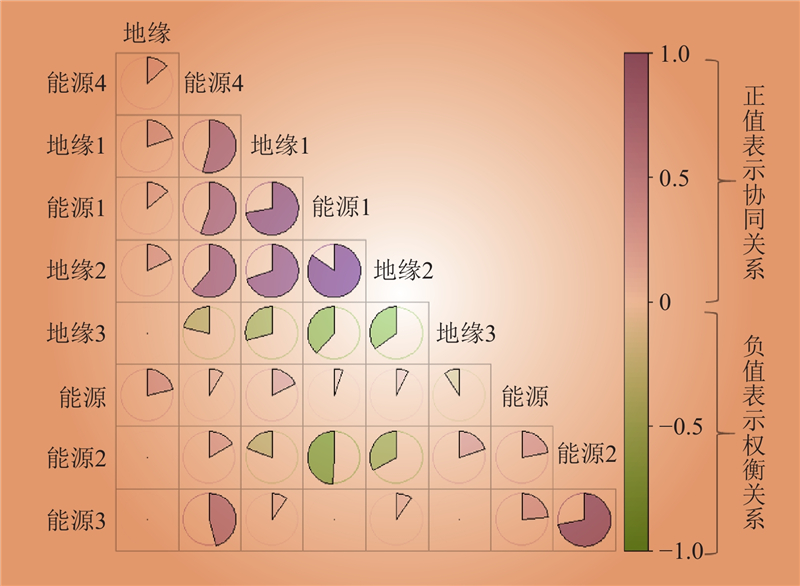
| 1 |
邹才能, 熊波, 李士祥, 等. 碳中和背景下世界能源转型与中国式现代化能源革命[J]. 石油科技论坛, 2024, 43 (1): 1- 17.
DOI
|
|
ZOU Caineng, XIONG Bo, LI Shixiang, et al. World energy transformation and China's modern energy revolution under carbon neutrality background[J]. Petroleum Science and Technology Forum, 2024, 43 (1): 1- 17.
DOI
|
| 2 |
王轶楠, 卢静, 陈星彤, 等. 考虑多重因素叠加情景的能源清洁低碳转型风险评估[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (3): 183- 189.
DOI
|
|
WANG Yinan, LU Jing, CHEN Xingtong, et al. Risk assessment of clean and low-carbon energy transformation considering superimposed scenario of multiple factors[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (3): 183- 189.
DOI
|
| 3 |
周勤勇, 李根兆, 秦晓辉, 等. 能源革命下的电力系统范式转换分析[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (3): 1- 11.
DOI
|
|
ZHOU Qinyong, LI Genzhao, QIN Xiaohui, et al. Analysis of power system paradigm shift under energy revolution[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (3): 1- 11.
DOI
|
| 4 |
李昕蕾, 管玉瑶. 全球清洁能源转型中的能源国际正义及中国角色[J]. 东北亚论坛, 2024, 33 (6): 93- 109, 126.
DOI
|
|
LI Xinlei, GUAN Yuyao. International energy justice and China's role in the global clean energy transtion[J]. Northeast Asia Forum, 2024, 33 (6): 93- 109, 126.
DOI
|
| 5 |
杨富强, 陈怡心. “十四五”推动能源转型实现碳排放达峰[J]. 阅江学刊, 2021, 13 (4): 73- 85, 124.
DOI
|
|
YANG Fuqiang, CHEN Yixin. "The 14th Five-Year Plan" promotes energy transformation and achieves the peak of carbon emissions[J]. Yuejiang Academic Journal, 2021, 13 (4): 73- 85, 124.
DOI
|
| 6 |
赵宏图. 国际能源转型现状与前景[J]. 现代国际关系, 2009 (6): 35- 42.
|
|
ZHAO Hongtu. Current situation and prospects of international energy transition[J]. Contemporary International Relations, 2009 (6): 35- 42.
|
| 7 |
杨宇, 郭越, 樊杰, 等. 能源地理研究的发展与展望[J]. 地理学报, 2024, 79 (1): 147- 170.
DOI
|
|
YANG Yu, GUO Yue, FAN Jie, et al. The development and prospects of the study of energy geographies[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2024, 79 (1): 147- 170.
DOI
|
| 8 |
张所续. 浅析能源转型对地缘政治的影响[J]. 国土资源情报, 2019 (8): 26- 33.
DOI
|
|
ZHANG Suoxu. The impact of energy transition on geopolitics[J]. Land and Resources Information, 2019 (8): 26- 33.
DOI
|
| 9 |
杨宇, 于宏源, 鲁刚, 等. 世界能源百年变局与国家能源安全[J]. 自然资源学报, 2020, 35 (11): 2803- 2820.
DOI
|
|
YANG Yu, YU Hongyuan, LU Gang, et al. Interview on the unprecedented changes of energy geopolitics and national energy security[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2020, 35 (11): 2803- 2820.
DOI
|
| 10 |
杨宇, 郭越. 地理学视角下的能源-社会互动格局与逻辑: 《能源与社会: 思辨性透视》解读与评述[J]. 世界地理研究, 2024, 33 (8): 77- 86.
DOI
|
|
YANG Yu, GUO Yue. The landscape and logic of energy-society interactions from a geographical perspective: Interpretation and review of Energy and Society: a Critical Perspective[J]. World Regional Studies, 2024, 33 (8): 77- 86.
DOI
|
| 11 |
李岚春, 陈伟. 俄乌冲突背景下欧洲能源危机态势、应对及对中国的启示[J]. 全球科技经济瞭望, 2023, 38 (5): 56- 64.
DOI
|
|
LI Lanchun, CHEN Wei. Key points and response of the European energy crisis under the escalation of Russia-Ukraine conflict and its enlightenment to China[J]. Global Science, Technology and Economy Outlook, 2023, 38 (5): 56- 64.
DOI
|
| 12 |
杨宇, 夏四友, 钱肖颖. 能源转型的地缘政治研究[J]. 地理学报, 2022, 77 (8): 2050- 2066.
|
|
YANG Yu, XIA Siyou, QIAN Xiaoying. Geopolitics of the energy transition[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2022, 77 (8): 2050- 2066.
|
| 13 |
杨宇, 刘毅, 金凤君. 能源地缘政治视角下中国与中亚—俄罗斯国际能源合作模式[J]. 地理研究, 2015, 34 (2): 213- 224.
DOI
|
|
YANG Yu, LIU Yi, JIN Fengjun. Study on energy cooperation between China and the Central Asia and Russia under the view of energy geopolitics[J]. Geographical Research, 2015, 34 (2): 213- 224.
DOI
|
| 14 |
陈卫东. 能源转型与地缘政治互动[J]. 能源, 2014 (7): 54- 55.
|
|
CHEN Weidong. Interaction between energy transition and geopolitics[J]. Energy, 2014 (7): 54- 55.
|
| 15 |
ZHAO D, CAI J, SHEN L, et al. Delivery of energy sustainability: Applications of the "STAR" protocol to the Sustainable Development Goal 7 index and its interaction analysis[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2023, 389, 135884.
DOI
|
| 16 |
The World Bank. World Bank Open Data [DB/OL]. (2023-12-31)[2025-11-20]. https://data.worldbank.org/.
|
| 17 |
International Energy Agency. IEA Data and Statistics[DB/OL]. (2024-12-31)[2025-11-20]. https://www.iea.org/data-and-statistics.
|
| 18 |
Ember. Ember Data[DB/OL]. (2024-12-31)[2025-11-20]. https://ember-energy.org/data/.
|
| 19 |
International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA). IRENA Official Website[DB/OL]. (2024-12-31)[2025-11-20]. https://www.irena.org/.
|
| 20 |
KINSELLA D, RUSSETT B. Conflict emergence and escalation in interactive international dyads[J]. The Journal of Politics, 2002, 64 (4): 1045- 1068.
DOI
|
| 21 |
LIN Z, ALVAREZ-OTERO S, BEN BELGACEM S, et al. Role of sustainable finance, geopolitical risk and economic growth in renewable energy investment: Empirical evidence from China[J]. Geological Journal, 2023, 58 (9): 3339- 3347.
DOI
|
| 22 |
CALDARA D, IACOVIELLO M. Measuring geopolitical risk[J]. American Economic Review, 2022, 112 (4): 1194- 1225.
DOI
|
| 23 |
ALATAS S M. The South China Sea and energy security: Malaysia's reaction to emerging geopolitical reconfigurations[J]. African and Asian Studies, 2016, 15 (1): 33- 52.
DOI
|
| 24 |
ALI NASIR M, SPENCER D. War-associated geopolitical risks and uncertainty: Implications for real wages[J]. International Journal of Finance & Economics, 2025, 30 (1): 710- 728.
|
| 25 |
SHANG Y F, XIA Z W, XIAO Z Y, et al. An analysis of the time-lag effect of global geopolitical risk on business cycle based on visibility graph technique[J]. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 2024, 209, 123823.
DOI
|
| 26 |
FONTANA G, SAWYER M. The macroeconomics of near zero growth of GDP in a world of geopolitical risks and conflicts[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2024, 351, 119717.
DOI
|
| 27 |
Our World in Data. Democracy Index[DB/OL]. (2025-3-31)[2025-11-20]. https://ourworldindata.org/grapher/democracy-index-eiu.
|
| 28 |
Institute for Economics & Peace. Global Peace Index[EB/OL]. (2025-6-30)[2025-11-20]. https://www.economicsandpeace.org/global-peace-index/.
|
| 29 |
Transparency International. Corruption Perceptions Index[EB/OL]. (2025-2-28)[2025-11-20]. https://www.transparency.de/fileadmin/Redaktion/CPI2024_Report_EN.pdf.
|
| 30 |
Quality of Government Institute. The Worldwide Governance Indicators (WGI) dataset[EB/OL]. (2024-11-10)[2025-11-20]. https://datafinder.qog.gu.se/dataset/wbgi.
|
| 31 |
United Nations Development Programme (UNDP). Human Development Index (HDI)[EB/OL]. (2025-10-10)[2025-11-20]. https://hdr.undp.org/data-center/human-development-index#/indicies/HDI.
|
| 32 |
DE WINTER J C F, GOSLING S D, POTTER J. Comparing the Pearson and Spearman correlation coefficients across distributions and sample sizes: a tutorial using simulations and empirical data[J]. Psychological Methods, 2016, 21 (3): 273- 290.
DOI
|
| 33 |
BÖLÜK G, KAPLAN R. Effectiveness of renewable energy incentives on sustainability: evidence from dynamic panel data analysis for the EU countries and Turkey[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2022, 29 (18): 26613- 26630.
DOI
|
| 34 |
王磊, 耿介坦, 尚舵, 等. 能源工业互联网发展研究[J]. 电力信息与通信技术, 2023, 21 (12): 27- 37.
|
|
WANG Lei, GENG Jietan, SHANG Duo, et al. Research on the development of energy industrial Internet[J]. Electric Power Information and Communication Technology, 2023, 21 (12): 27- 37.
|
| 35 |
CHOWDHURY A F M K, WESSEL J, WILD T, et al. Exploring sustainable electricity system development pathways in South America's MERCOSUR sub-region[J]. Energy Strategy Reviews, 2023, 49, 101150.
DOI
|
| 36 |
DAGHER L, FATTOUH B, JAMALI I. Oil price dynamics and energy transitions in the Middle East and North Africa: Economic implications and structural reforms[J]. Energy Policy, 2020, 139, 111329.
DOI
|
| 37 |
林利民. 新冠肺炎疫情与东亚地缘政治新变局[J]. 东亚评论, 2021 (2): 7- 19.
|
|
LIN Limin. COVID-19 pandemic and the new situation of geopolitics in East Asia[J]. East Asia Review, 2021 (2): 7- 19.
|
| 38 |
金瑞庭. 欧洲国家能源政策最新动向及对我国启示[J]. 中国经贸导刊, 2023 (11): 54- 55.
DOI
|
|
JIN Ruiting. The latest developments of European countries' energy policies and their implications for China[J]. China Economic & Trade Herald, 2023 (11): 54- 55.
DOI
|
| 39 |
叶列娜·捷列基娜, 徐向梅. 世界能源市场和俄罗斯的地缘政治利益[J]. 国际石油经济, 2004, 12 (4): 19- 22.
DOI
|
|
YELENA T, XU Xiangmei. World energy market and Russia's geopolitical interests[J]. International Petroleum Economics, 2004, 12 (4): 19- 22.
DOI
|
| 40 |
李昕蕾. 全球清洁能源治理的跨国主义范式: 多元网络化发展的特点、动因及挑战[J]. 国际观察, 2017 (6): 137- 154.
|
|
LI Xinlei. The transnational paradigm of global clean energy governance: characteristics, dynamics and challenges of pluralistic-networking development[J]. International Review, 2017 (6): 137- 154.
|
| 41 |
GOFORTH T, NOCK D, BROWN M, et al. Exploring equality and sustainability trade-offs of energy transition outcomes in the United States in 2050[J]. Applied Energy, 2024, 367, 123376.
DOI
|
| 42 |
SIKDAR A, BANI N Y B M, SALIMULLAH A H M, et al. Energy poverty and environmental quality nexus: empirical evidence from selected south Asian countries[J]. Ekonomikalia Journal of Economics, 2024, 2 (2): 119- 135.
DOI
|
| 43 |
傅质馨, 李紫嫣, 朱俊澎, 等. “双碳”目标下需求侧管理机制研究综述及展望[J]. 电力信息与通信技术, 2023, 21 (2): 1- 12.
|
|
FU Zhixin, LI Ziyan, ZHU Junpeng, et al. Overview and prospect of demand side management mechanism under "dual carbon" goal[J]. Electric Power Information and Communication Technology, 2023, 21 (2): 1- 12.
|