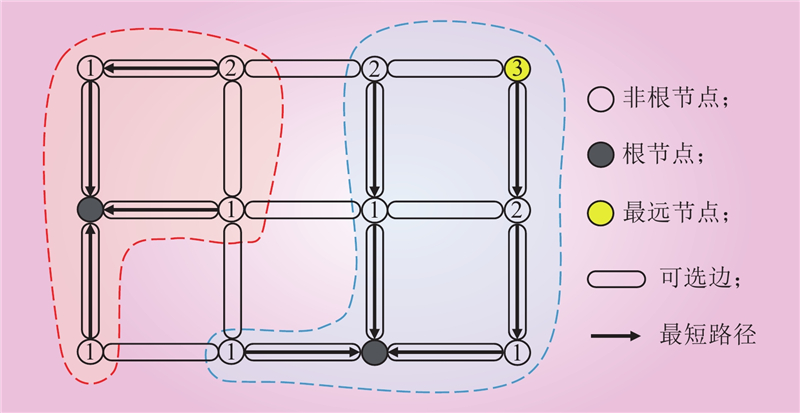
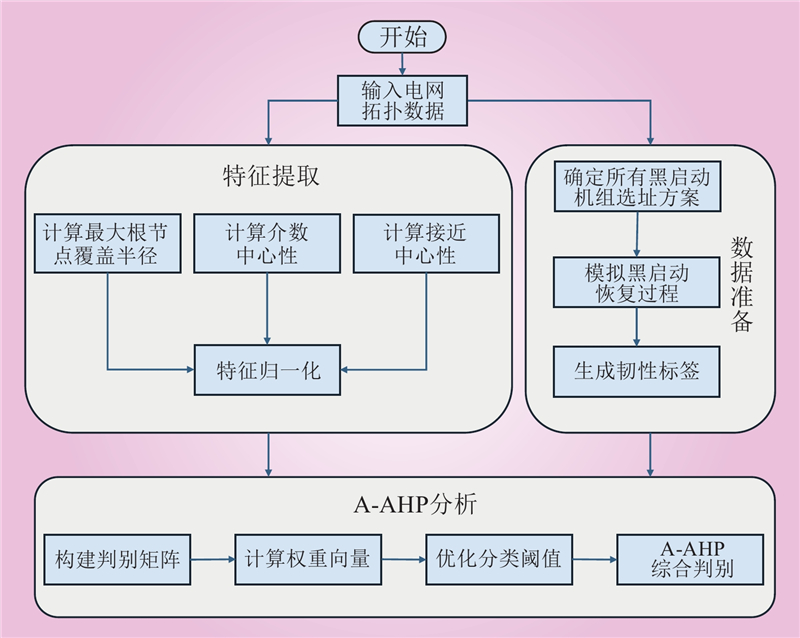
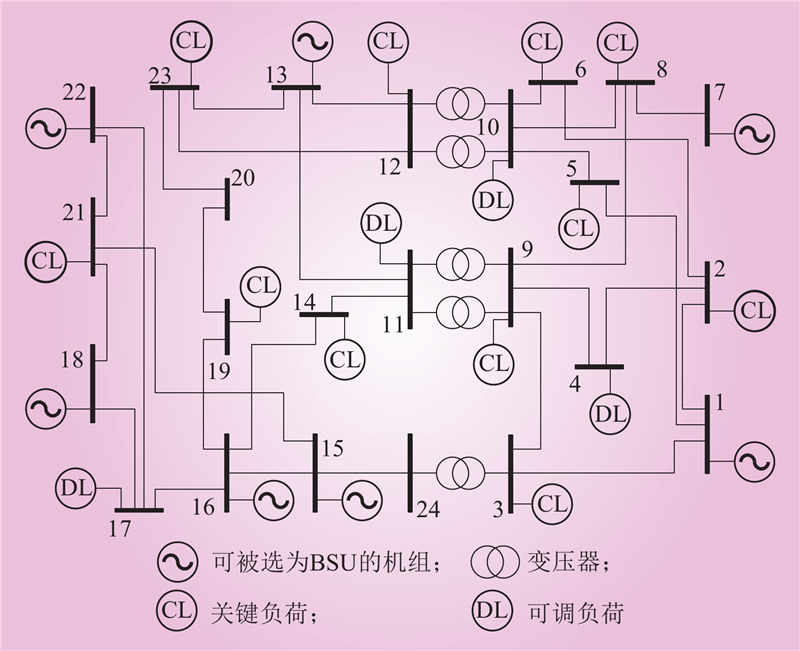
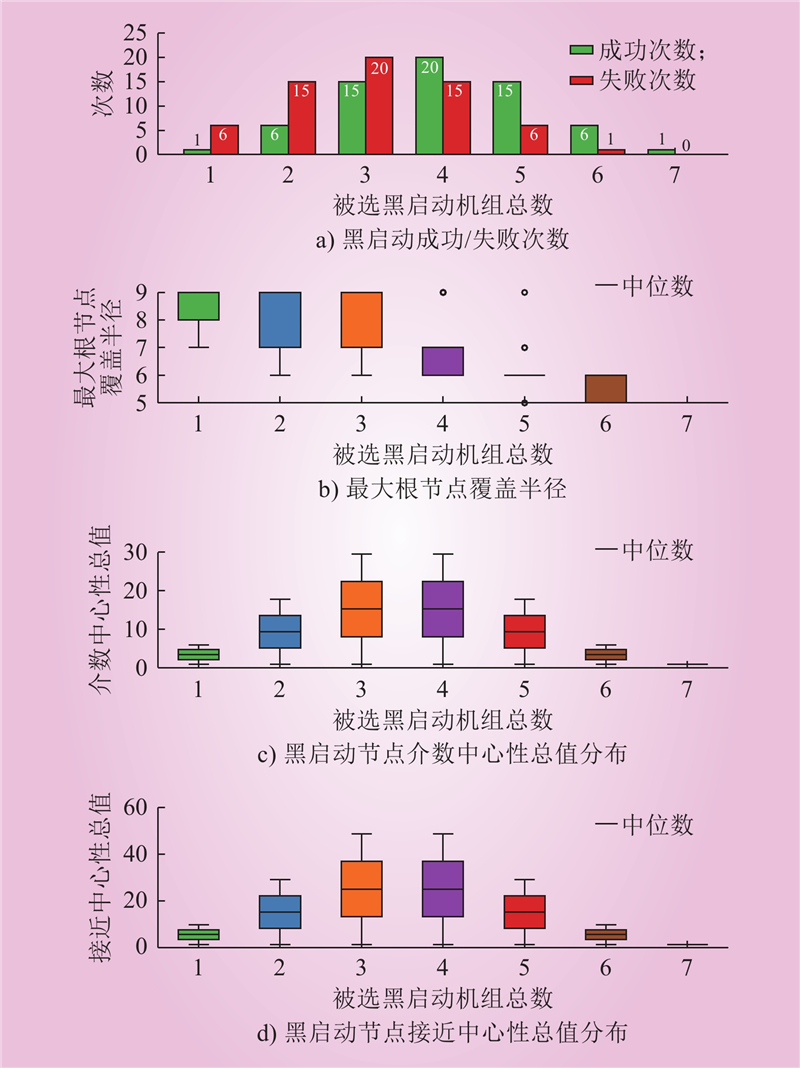
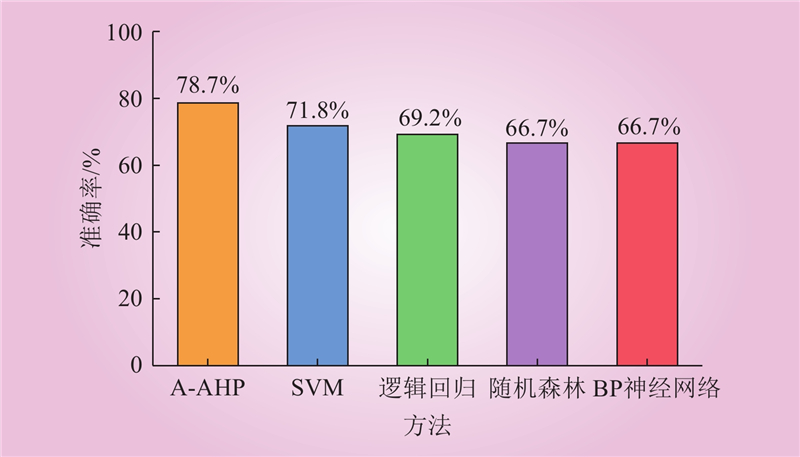
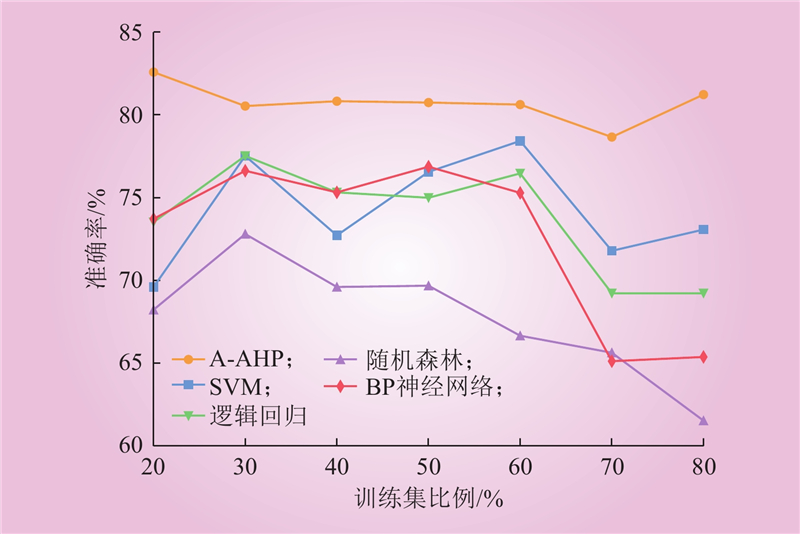
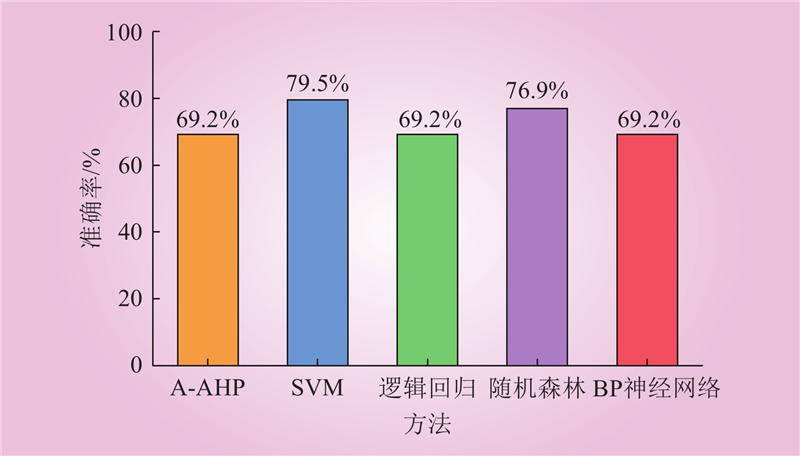
| 1 |
叶林, 李奕霖, 裴铭, 等. 寒潮天气小样本条件下的短期风电功率组合预测[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2023, 43 (2): 543- 555.
|
|
YE Lin, LI Yilin, PEI Ming, et al. Combined approach for short-term wind power forecasting under cold weather with small sample[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2023, 43 (2): 543- 555.
|
| 2 |
杨涛, 周洪, 魏凤, 等. 新型电力系统下的电网安全挑战与对策研究[J]. 电力信息与通信技术, 2024, 22 (8): 18- 26.
|
|
YANG Tao, ZHOU Hong, WEI Feng, et al. Challenges and countermeasures of grid security towards a new type of power system[J]. Electric Power Information and Communication Technology, 2024, 22 (8): 18- 26.
|
| 3 |
许守东, 王建, 李铭益, 等. 极端气象灾害下考虑MESS主动调控的配电网故障恢复策略[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2024, 52 (12): 45- 57.
|
|
XU Shoudong, WANG Jian, LI Mingyi, et al. Distribution network fault recovery strategy considering active control of an MESSin extreme weather[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2024, 52 (12): 45- 57.
|
| 4 |
侯祖锋, 王超, 徐春华, 等. 考虑负荷重要程度的配电网韧性提升策略及评估方法[J]. 电力科学与技术学报, 2024, 39 (3): 78- 85.
|
|
HOU Zufeng, WANG Chao, XU Chunhua, et al. Promotion strategy and evaluation method of distribution networkresilience considering load importance[J]. Journal of Electric Power Science and Technology, 2024, 39 (3): 78- 85.
|
| 5 |
郭明鑫, 李少岩, 顾雪平. 计及台风灾害全过程模拟的配电网差异化加固规划韧性提升方法[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2024, 52 (3): 62- 73.
|
|
GUO Mingxin, LI Shaoyan, GU Xueping. Differentiated reinforcement planning method for a distribution network consideringsimulation of the whole process of typhoon disasters[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2024, 52 (3): 62- 73.
|
| 6 |
王瑞欣, 孙吉广, 刘艳, 等. 计及新能源场站黑启动时空支撑能力的分区目标网架优化[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (10): 143- 149.
|
|
WANG Ruixin, SUN Jiguang, LIU Yan, et al. Optimization of power system black start partition target network taking into account the black start space-time support capability of new energy station[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (10): 143- 149.
|
| 7 |
龚逊东, 郭维嘉, 杨晨, 等. 基于动态孤岛的主动配电网多阶段故障恢复策略[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (1): 158- 166.
|
|
GONG Xundong, GUO Weijia, YANG Chen, et al. Multi-stage fault recovery strategy for active distribution networks based on dynamic islanding[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (1): 158- 166.
|
| 8 |
王涉, 梁双, 刘斯伟, 等. 西班牙4·28大停电事故分析及对中国电力发展的启示[J/OL]. 中国电力, 2025: 1–11. (2025-09-19). https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.3265.tm.20250918.1848.006.html.
|
|
WANG She, LIANG Shuang, LIU Siwei, et al. Analysis of 4·28 major power outages in Spain and Revelations on China's power development[J/OL]. Electric Power, 2025: 1–11. (2025-09-19). https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.3265.tm.20250918.1848.006.html.
|
| 9 |
黄玉雄, 李更丰, 张理寅, 等. 弹性配电系统动态负荷恢复的深度强化学习方法[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2022, 46 (8): 68- 78.
|
|
HUANG Yuxiong, LI Gengfeng, ZHANG Liyin, et al. Deep reinforcement learning method for dynamic load restoration of resilient distribution systems[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2022, 46 (8): 68- 78.
|
| 10 |
易俊, 卜广全, 郭强, 等. 巴西“3·21”大停电事故分析及对中国电网的启示[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2019, 43 (2): 1- 6.
|
|
YI Jun, BU Guangquan, GUO Qiang, et al. Analysis on blackout in Brazilian power grid on March 21, 2018 and its enlightenment to power grid in China[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2019, 43 (2): 1- 6.
|
| 11 |
张强, 赵晋泉, 戴则梅, 等. 基于目标级联分析的输配电网黑启动分布式协同优化方法[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2021, 45 (3): 111- 120.
|
|
ZHANG Qiang, ZHAO Jinquan, DAI Zemei, et al. Distributed coordinated optimization method for black-start of transmission and distribution networks based on analytical target cascading[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2021, 45 (3): 111- 120.
|
| 12 |
肖云鹏, 王锡凡, 王秀丽, 等. 面向高比例可再生能源的电力市场研究综述[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2018, 38 (3): 663- 674.
|
|
XIAO Yunpeng, WANG Xifan, WANG Xiuli, et al. Review on electricity market towards high proportion of renewable energy[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2018, 38 (3): 663- 674.
|
| 13 |
卢明, 郭志明, 孟高军, 等. 输电线路气象风险精细化建模及气象灾害的在线预警防御策略[J]. 电力科学与技术学报, 2024, 39 (1): 208- 217.
|
|
LU Ming, GUO Zhiming, MENG Gaojun, et al. Refined meteorological risk modeling of transmission lines and onlinewarning and defense strategies of meteorological disasters[J]. Journal of Electric Power Science and Technology, 2024, 39 (1): 208- 217.
|
| 14 |
叶学顺, 李昭, 刘科研, 等. 信息物理并发故障下的配电网供电恢复方法[J]. 电力信息与通信技术, 2024, 22 (9): 18- 25.
|
|
YE Xueshun, LI Zhao, LIU Keyan, et al. Distribution network power restoration under cyber-physical concurrent faults[J]. Electric Power Information and Communication Technology, 2024, 22 (9): 18- 25.
|
| 15 |
杨晓雨, 贾东梨, 刘科研, 等. 基于组合机器学习的配电网区域故障等级预测方法[J]. 电力信息与通信技术, 2024, 22 (11): 43- 51.
|
|
YANG Xiaoyu, JIA Dongli, LIU Keyan, et al. Regional Fault Level Prediction Method for Distribution Network Based onCombined Machine Learning[J]. Electric Power Information and Communication Technology, 2024, 22 (11): 43- 51.
|
| 16 |
PATSAKIS G, RAJAN D, ARAVENA I, et al. Optimal black start allocation for power system restoration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2018, 33 (6): 6766- 6776.
|
| 17 |
QIU F, WANG J H, CHEN C, et al. Optimal black start resource allocation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2016, 31 (3): 2493- 2494.
|
| 18 |
赵昱宣, 孙磊, 林振智, 等. 微网作为黑启动电源的电力系统网架重构优化策略[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2018, 42 (17): 9- 17, 147.
|
|
ZHAO Yuxuan, SUN Lei, LIN Zhenzhi, et al. Power network reconfiguration strategy with microgrids as black-start power sources[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2018, 42 (17): 9- 17, 147.
|
| 19 |
周宜昌, 刘艳, 顾雪平. 考虑多风电场黑启动价值的机组恢复顺序双层优化决策[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2020, 44 (16): 87- 97.
|
|
ZHOU Yichang, LIU Yan, GU Xueping. Bi-level optimization decision for unit recovery sequence considering black-start value of multiple wind farms[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2020, 44 (16): 87- 97.
|
| 20 |
LIAO S W, YAO W, HAN X N, et al. An improved two-stage optimization for network and load recovery during power system restoration[J]. Applied Energy, 2019, 249, 265- 275.
|
| 21 |
BHATT N, LIU S S, PODMORE R. System restoration tools: system restoration navigator integrated into EPRI operator training simulator (SRN/OTS)[J]. Journal of Power and Energy Engineering, 2015, 3 (4): 378- 383.
|
| 22 |
QIU F, LI P J. An integrated approach for power system restoration planning[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2017, 105 (7): 1234- 1252.
|
| 23 |
ISEMONGER A G. The viability of the competitive procurement of black start: lessons from the RTOs[J]. The Electricity Journal, 2007, 20 (8): 60- 67.
|
| 24 |
ALBERT R, ALBERT I, NAKARADO G L. Structural vulnerability of the North American power grid[J]. Physical Review E, 2004, 69 (2): 025103.
|
| 25 |
ROSATO V, BOLOGNA S, TIRITICCO F. Topological properties of high-voltage electrical transmission networks[J]. Electric Power Systems Research, 2007, 77 (2): 99- 105.
|
| 26 |
ROSAS-CASALS M, VALVERDE S, SOLÉ R V. Topological vulnerability of the European power grid under errors and attacks[J]. International Journal of Bifurcation and Chaos, 2007, 17 (7): 2465- 2475.
|
| 27 |
SOLÉ R V, ROSAS-CASALS M, COROMINAS-MURTRA B, et al. Robustness of the European power grids under intentional attack[J]. Physical Review E, 2008, 77 (2): 026102.
|
| 28 |
GANIN A A, MASSARO E, GUTFRAIND A, et al. Operational resilience: concepts, design and analysis[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6, 19540.
|
| 29 |
ALDERSON D L, BROWN G G, CARLYLE W M. Operational models of infrastructure resilience[J]. Risk Analysis, 2015, 35 (4): 562- 586.
|
| 30 |
ORDOUDIS C, PINSON P, MORALES J M, et al. An updated version of the IEEE RTS 24-bus system for electricity market and power system operation studies[J]. Technical University of Denmark, 2016, 13.
|
| 31 |
HOU Y H, LIU C C, SUN K, et al. Computation of milestones for decision support during system restoration[C]//IEEE Transactions on Power Systems. IEEE, 2010: 1399–1409.
|