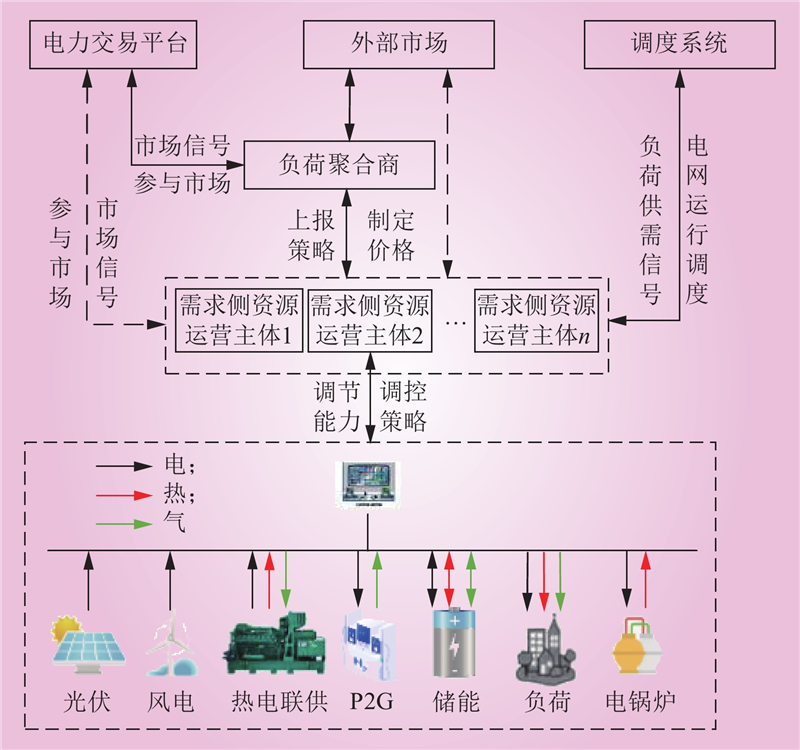
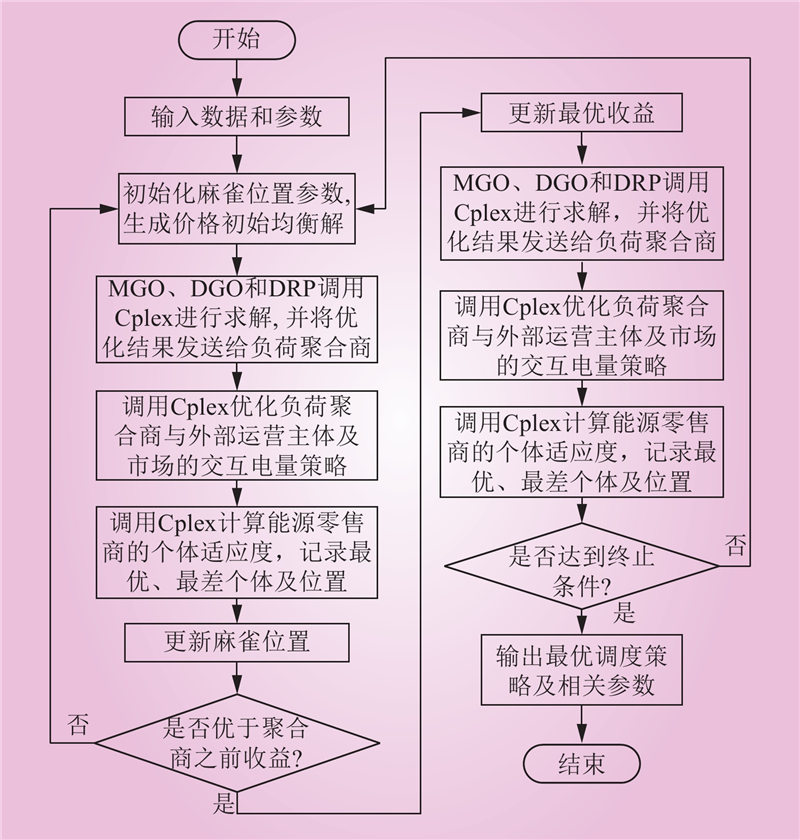
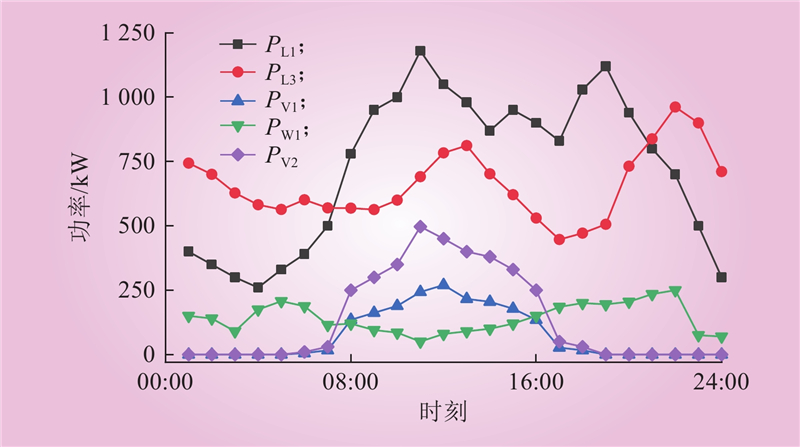
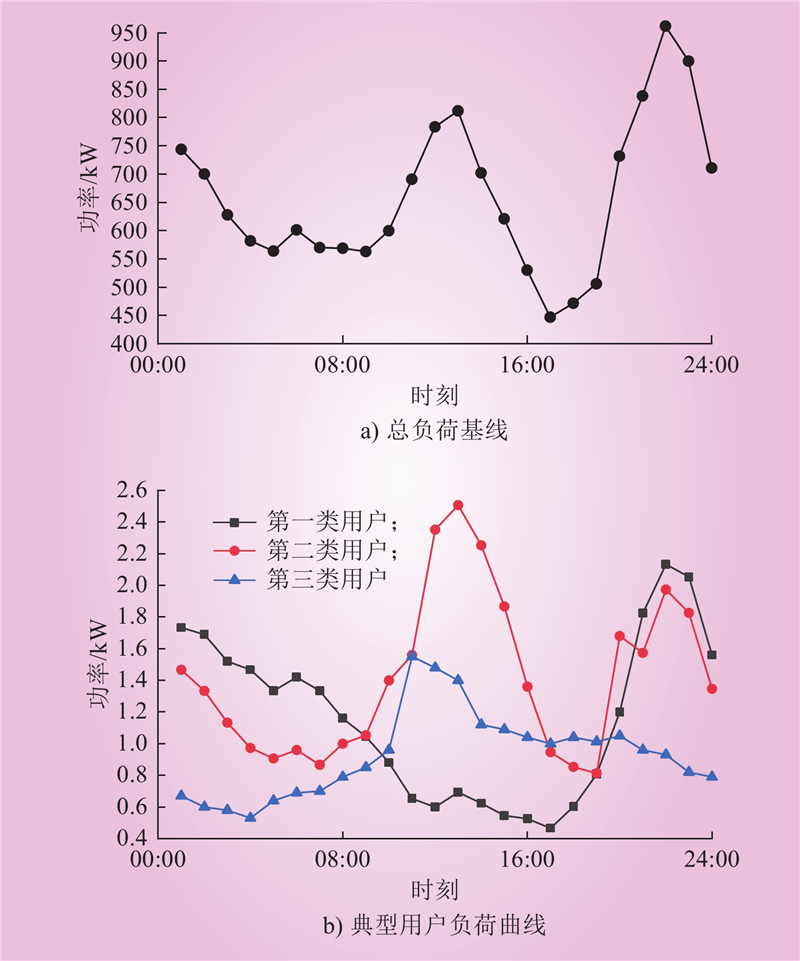
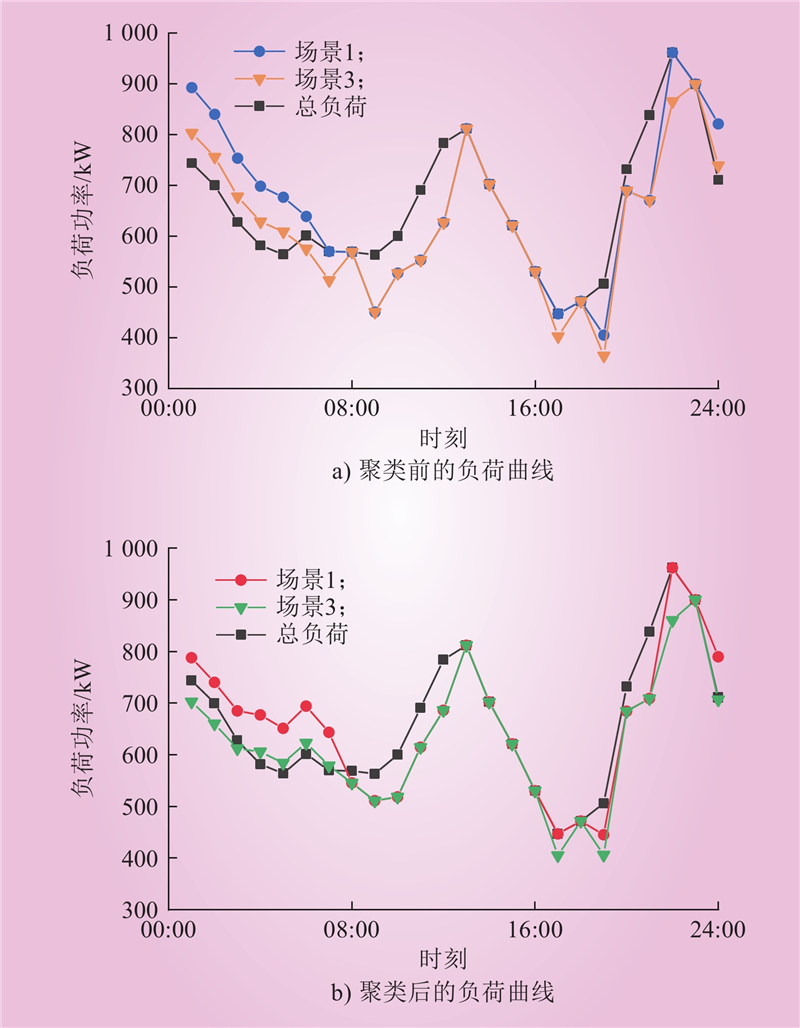
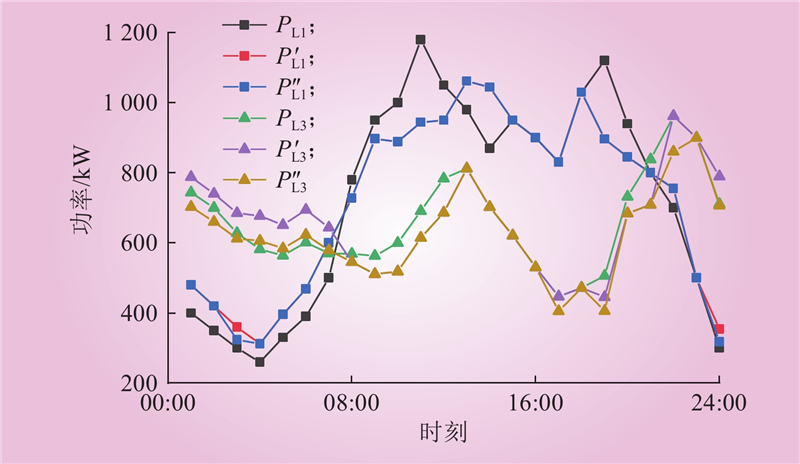
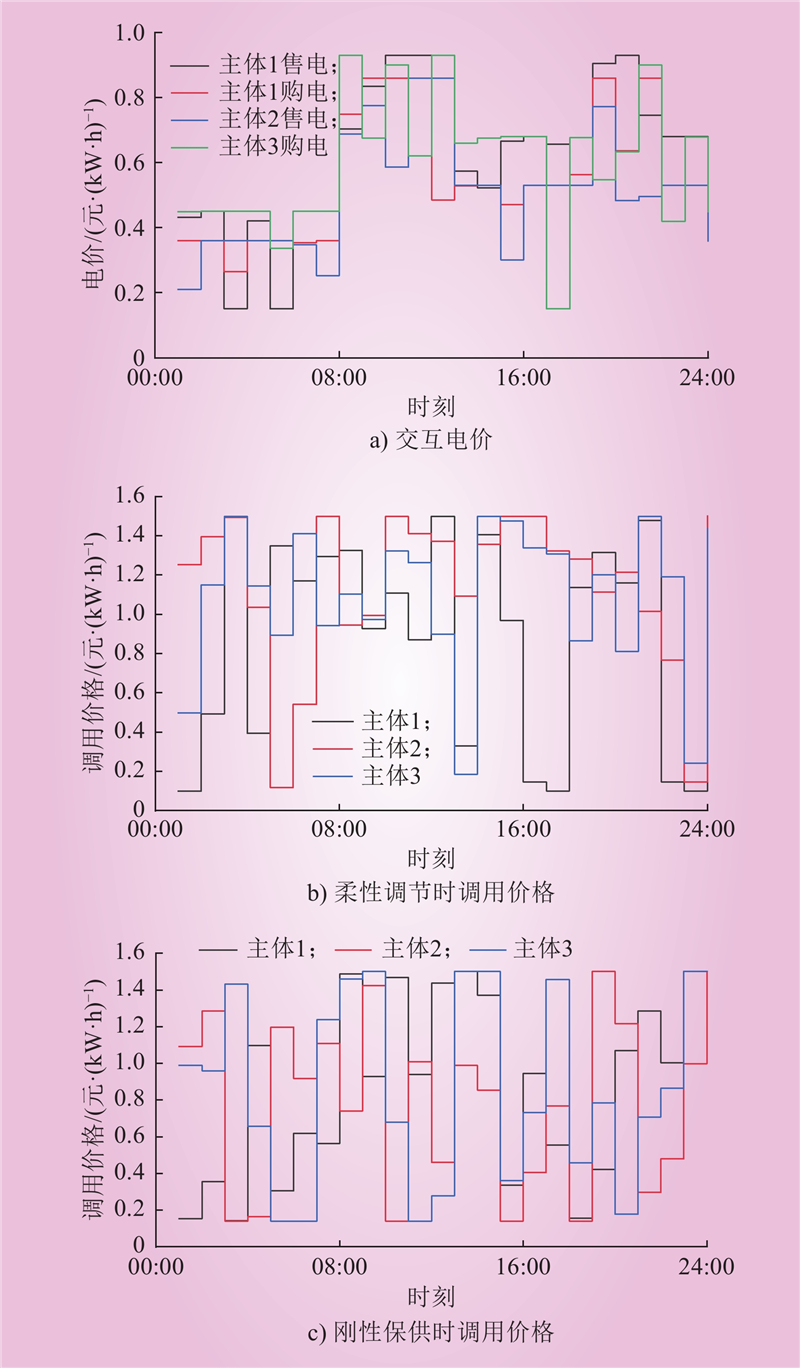
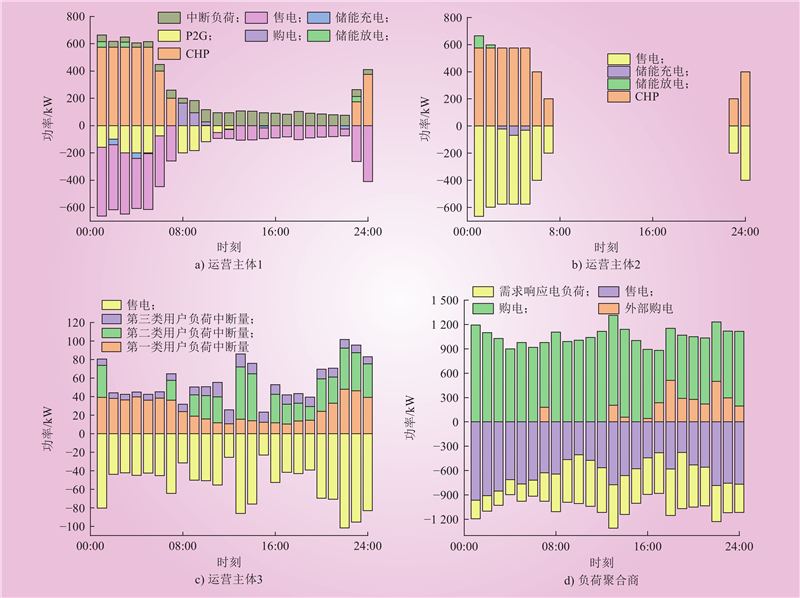
| 1 |
孙志媛, 彭博雅, 孙艳. 考虑多能互补的电力电量平衡优化调度策略[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (1): 115- 122.
|
|
SUN Zhiyuan, PENG Boya, SUN Yan. Optimal dispatch strategy of power and electricity balance based on multi-energy complementation[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (1): 115- 122.
|
| 2 |
李晓露, 徐婉云, 柳劲松, 等. 考虑时序相关性的需求侧资源可调节功率域聚合方法[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2024, 52 (15): 58- 68.
|
|
LI Xiaolu, XU Wanyun, LIU Jinsong, et al. Adjustable power domain aggregation method for demand-side resourcesconsidering temporal correlation[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2024, 52 (15): 58- 68.
|
| 3 |
孙玲玲, 高赐威, 谈健, 等. 负荷聚合技术及其应用[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2017, 41 (6): 159- 167.
|
|
SUN Lingling, GAO Ci Wei, TAN Jian, et al. Load polymerization technology and its application[J]. Power System Automation, 2017, 41 (6): 159- 167.
|
| 4 |
林卉, 周一辰, 李永刚, 等. 基于电动汽车两阶段充电站分配的聚合商定价方法[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2023, 51 (21): 44- 56.
|
|
LIN Hui, ZHOU Yichen, LI Yonggang, et al. Aggregator pricing methodology based on two-stage charging station allocation for electric vehicles[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2023, 51 (21): 44- 56.
|
| 5 |
刘东冉. 区域分布式能源系统参与电力交易辅助决策模型研究[D]. 北京: 华北电力大学, 2022.
|
|
LIU Dongran. Research on decision-making models for regional distributed energy resources SystemParticipating in energy trading[D]. Beijing: North China Electric Power University, 2022.
|
| 6 |
彭春华, 张金克, 陈露, 等. 计及差异化需求响应的微电网源荷储协调优化调度[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2020, 40 (3): 1- 7.
|
|
PENG Chunhua, ZHANG Jinke, CHEN Lu, et al. Source-load-storage coordinated optimal scheduling of microgrid considering differential demand response[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2020, 40 (3): 1- 7.
|
| 7 |
周孟然, 王旭, 邵帅, 等. 考虑需求响应和碳排放额度的微电网分层优化调度[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (10): 45- 53.
|
|
ZHOU Mengran, WANG Xu, SHAO Shuai, et al. Hierarchical optimal scheduling of microgrid considering demand response and carbon emission quota[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (10): 45- 53.
|
| 8 |
杨力俊, 潘伟, 田闻旭. 计及需求响应和风光不确定性的微电网多目标优化模型[J]. 电力需求侧管理, 2022, 24 (3): 1- 8.
|
|
YANG Lijun, PAN Wei, TIAN Wenxu. Multi-objective optimization model of microgrid considering demand response and uncertainty of wind power and photovoltaic[J]. Power Demand Side Management, 2022, 24 (3): 1- 8.
|
| 9 |
王鸣誉, 徐岩, 董浩然, 等. 计及需求响应的多微电网合作联盟调度优化[J]. 电测与仪表, 2024, 61 (11): 157- 164.
|
|
WANG Mingyu, XU Yan, DONG Haoran, et al. Scheduling optimization of multi-microgrid cooperative alliance considering demand response[J]. Electrical Measurement & Instrumentation, 2024, 61 (11): 157- 164.
|
| 10 |
陈昊宇, 黄顺杰, 樊志华, 等. 基于博弈的多微网需求响应[J]. 南方电网技术, 2017, 11 (2): 34- 40.
|
|
CHEN Haoyu, HUANG Shunjie, FAN Zhihua, et al. Demand response of multi-microgrid based on game theory[J]. Southern Power System Technology, 2017, 11 (2): 34- 40.
|
| 11 |
陈倩, 王维庆, 王海云. 计及需求响应和混合博弈含多微网主动配电网协调优化[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2023, 47 (9): 99- 109.
|
|
CHEN Qian, WANG Weiqing, WANG Haiyun. Coordinated optimization of active distribution network with multiple microgrids considering demand response and mixed game[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2023, 47 (9): 99- 109.
|
| 12 |
李鹏, 吴迪凡, 李雨薇, 等. 基于综合需求响应和主从博弈的多微网综合能源系统优化调度策略[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2021, 41 (4): 1307- 1321.
|
|
LI Peng, WU Difan, LI Yuwei, et al. Optimal Dispatch of Multi-microgrids Integrated Energy System Based on Integrated Demand Response and Stackelberg game[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2021, 41 (4): 1307- 1321.
|
| 13 |
龚诚嘉锐, 林顺富, 边晓燕, 等. 基于多主体主从博弈的负荷聚合商经济优化模型[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2022, 50 (2): 30- 40.
|
|
GONG Chengjiarui, LIN Shunfu, BIAN Xiaoyan, et al. Economic optimization model of a load aggregator based on the multi-agent Stackelberg game[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2022, 50 (2): 30- 40.
|
| 14 |
周鑫, 韩肖清, 李廷钧, 等. 计及需求响应和电能交互的多主体综合能源系统主从博弈优化调度策略[J]. 电网技术, 2022, 46 (9): 3333- 3346.
|
|
ZHOU Xin, HAN Xiaoqing, LI Tingjun, et al. Master-slave game optimal scheduling strategy for multi-agent integrated energy system based on demand response and power interaction[J]. Power System Technology, 2022, 46 (9): 3333- 3346.
|
| 15 |
齐彩娟, 陈宝生, 韦冬妮, 等. 考虑主从博弈定价模式的共享储能分布鲁棒优化配置方法研究[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (7): 40- 53.
|
|
QI Caijuan, CHE Bin, YANG Yan, et al. Master-slave game-based robust pricing method of shared energy storage considering renewable energy accommodation and energy storage participating in frequency modulation[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (7): 40- 53.
|
| 16 |
许小峰. 需求侧资源参与市场商业模式与投资决策[D]. 华北电力大学(北京), 2020.
|
|
XU Xiaofeng. Business Model and investment decision of demand-side resources in power markets[D]. Beijing: North China Electric Power University, 2020.
|
| 17 |
代心芸, 陈皓勇, 肖东亮, 等. 电力市场环境下工业需求响应技术的应用与研究综述[J]. 电网技术, 2022, 46 (11): 4169- 4186.
|
|
DAI Xinyun, CHEN Haoyong, XIAO Dongliang, et al. Review of applications and researches of industrial demand response technology under electricity market environment[J]. Power System Technology, 2022, 46 (11): 4169- 4186.
|
| 18 |
严兴煜, 高赐威, 陈涛, 等. 数字孪生虚拟电厂系统框架设计及其实践展望[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2023, 43 (2): 604- 619.
|
|
YAN Xingyu, GAO Ciwei, CHEN Tao, et al. Framework design and application prospect for digital twin virtual power plant system[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2023, 43 (2): 604- 619.
|
| 19 |
陈湘元,吴公平,龙卓,等.考虑源荷不确定性及用户侧需求响应的综合能源系统多时间尺度优化调度[J].电力科学与技术学报,2024,39(3):217-227.
|
|
CHEN Xiangyuan, WU Gongping, LONG Zhuo, et al.Multi-time scale optimal dispatch of integrated energy systems considering source-load uncertainty and user-side demand response[J].Journal of Electric Power Science and Technology,2024,39(3):217-227.
|
| 20 |
龚传正. 需求侧响应市场激励敏感度评估与成本收益研究[D]. 北京: 华北电力大学, 2022.
|
|
GONG Chuanzheng. Study on incentive sensitivity evaluation and cost-benefit of demand response market[D]. Beijing: North China Electric Power University, 2022.
|
| 21 |
王凌云, 安晓, 杨波, 等. 考虑负荷聚合商参与下的微网双层两阶段优化调度[J]. 三峡大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 43 (2): 86- 92.
|
|
WANG Lingyun, AN Xiao, YANG Bo, et al. Double level two-stage optimal scheduling of microgrid with the participation of load aggregator[J]. Journal of China Three Gorges University(Natural Sciences), 2021, 43 (2): 86- 92.
|
| 22 |
王树东, 杜巍, 林莉, 等. 基于合作博弈的需求侧响应下光储微电网优化配置[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2018, 46 (1): 129- 137.
|
|
WANG Shudong, DU Wei, LIN Li, et al. Optimal allocation of photovoltaic energy storage microgrid under the demand side response based on cooperative game[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2018, 46 (1): 129- 137.
|
| 23 |
崔杨, 曾鹏, 王铮, 等. 计及电价型需求侧响应含碳捕集设备的电–气–热综合能源系统低碳经济调度[J]. 电网技术, 2021, 45 (2): 447- 461.
|
|
CUI Yang, ZENG Peng, WANG Zheng, et al. Low-carbon economic dispatch of electricity-gas-heat integrated energy system with carbon capture equipment considering price-based demand response[J]. Power System Technology, 2021, 45 (2): 447- 461.
|