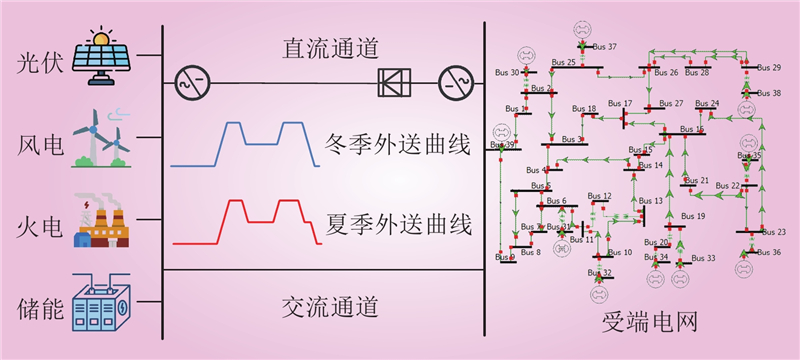
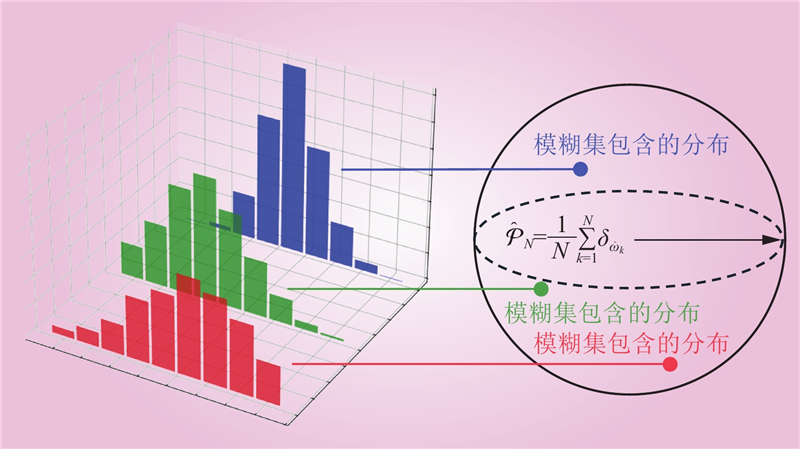
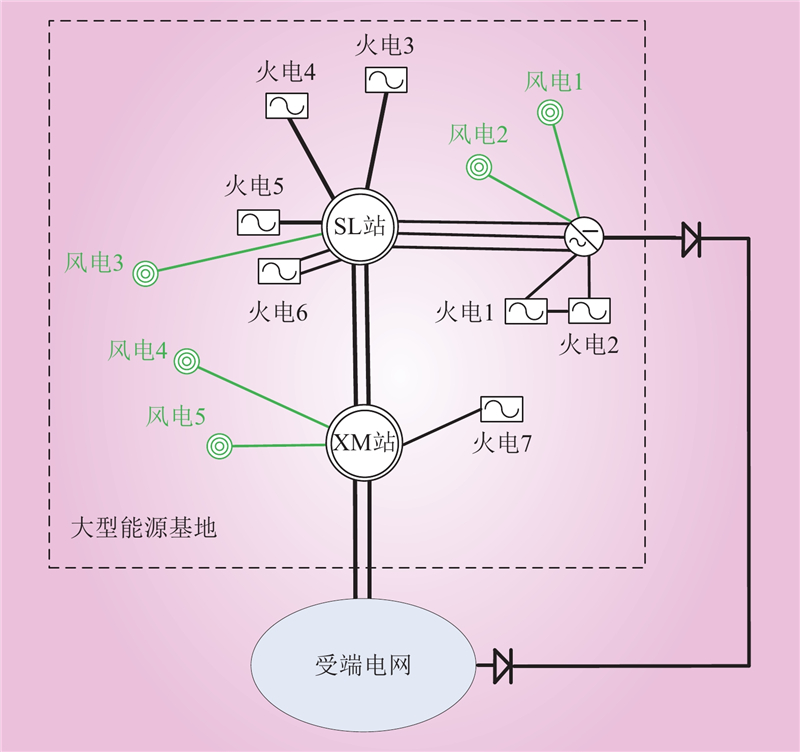
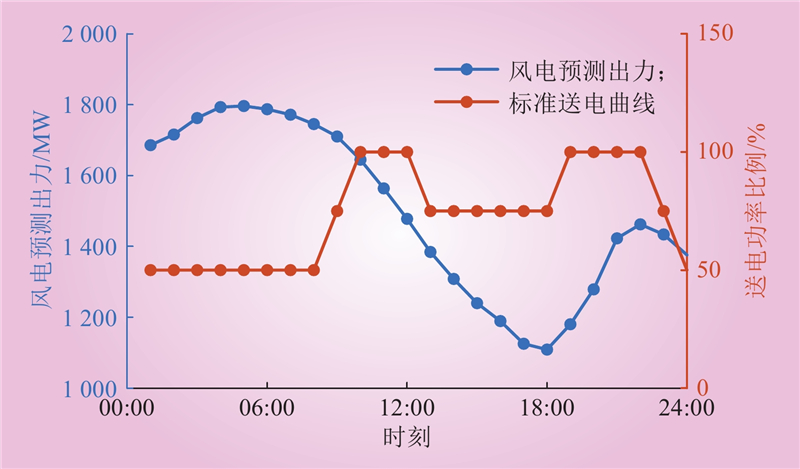
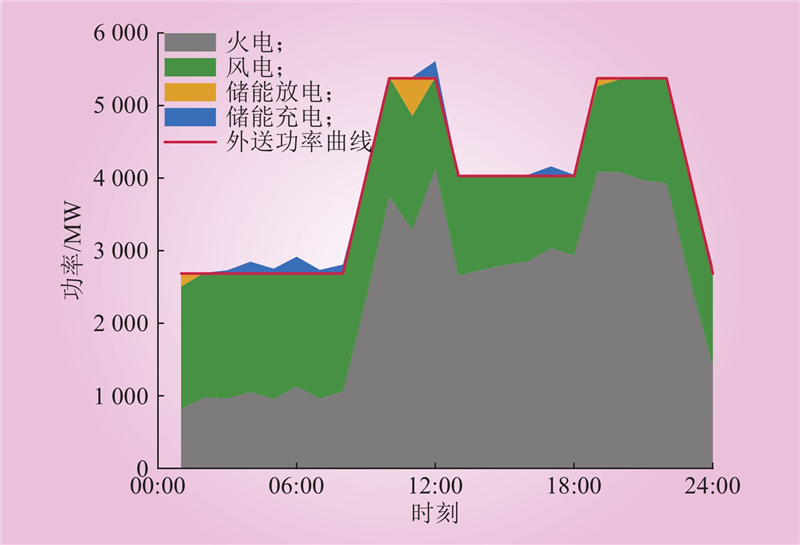
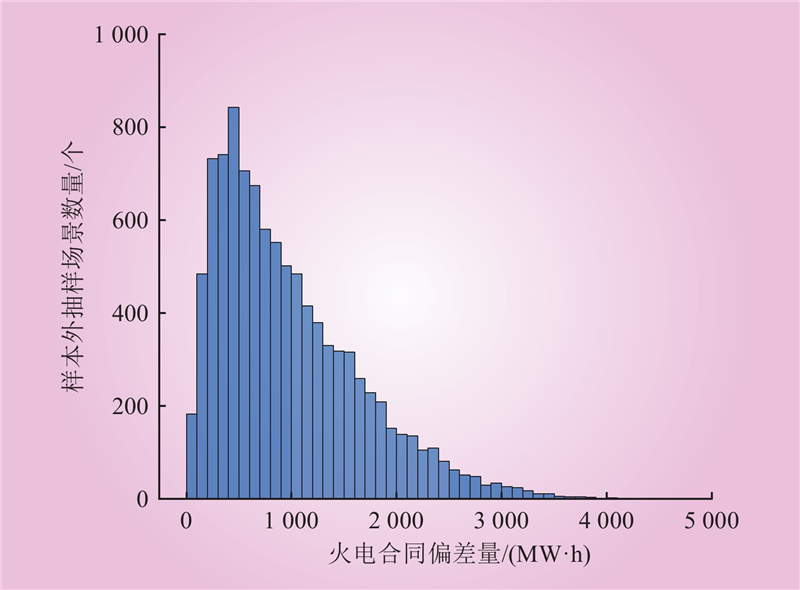
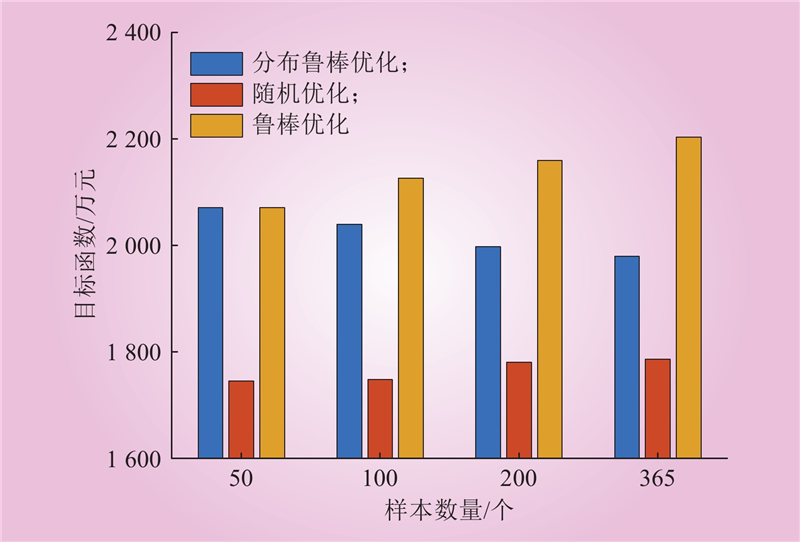
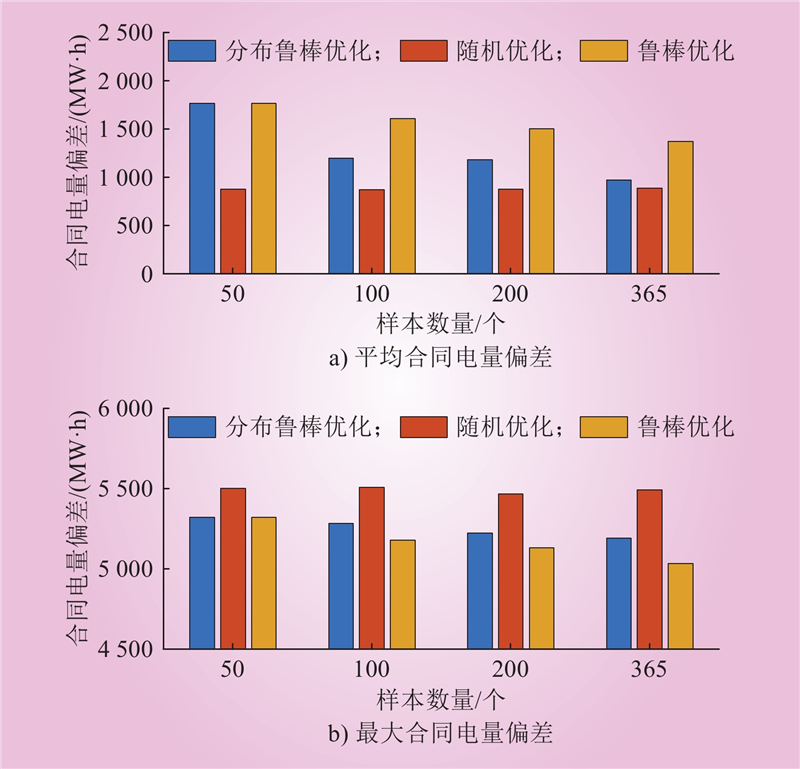
| 1 |
国家发展改革委, 国家能源局. 关于促进新时代新能源高质量发展的实施方案[EB/OL]. (2022-05-14)[2025-07-25]. https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2022-5/30/content_5693013.htm.
|
| 2 |
徐文哲, 张哲任, 徐政. 适用于大规模纯新能源发电基地送出的混合式直流输电系统[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (4): 17- 27.
|
|
XU Wenzhe, ZHANG Zheren, XU Zheng. A hybrid HVDC topology suitable for large-scale pure clean energy power base transmission[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (4): 17- 27.
|
| 3 |
夏清, 陈启鑫, 谢开, 等. 中国特色、全国统一的电力市场关键问题研究(2): 我国跨区跨省电力交易市场的发展途径、交易品种与政策建议[J]. 电网技术, 2020, 44 (8): 2801- 2808.
|
|
XIA Qing, CHEN Qixin, XIE Kai, et al. Key issues of national unified electricity market with Chinese characteristics (2): development path, trading varieties and policy recommendations for inter-regional and inter-provincial electricity markets[J]. Power System Technology, 2020, 44 (8): 2801- 2808.
|
| 4 |
关立, 常江, 孙大雁, 等. 省间电力现货市场试运行分析及思考[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2024, 48 (11): 2- 10.
|
|
GUAN Li, CHANG Jiang, SUN Dayan, et al. Analysis and reflection on trial operation of inter-provincial electricity spot markets in China[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2024, 48 (11): 2- 10.
|
| 5 |
李明轩, 范越, 汪莹, 等. 新能源大基地风光储容量协调优化配置[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2024, 44 (3): 1- 8.
|
|
LI Mingxuan, FAN Yue, WANG Ying, et al. Coordinated optimal configuration of wind-photovoltaic-energy storage capacity for large-scale renewable energy bases[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2024, 44 (3): 1- 8.
|
| 6 |
李晖, 刘栋, 秦继朔, 等. 考虑风光出力不确定性的新能源基地直流外送随机规划方法研究[J]. 电网技术, 2024, 48 (7): 2795- 2803.
|
|
LI Hui, LIU Dong, QIN Jishuo, et al. Stochastic planning method for UHVDC transmission of renewable energy power base considering wind and photovoltaic output uncertainties[J]. Power System Technology, 2024, 48 (7): 2795- 2803.
|
| 7 |
崔杨, 李崇钢, 赵钰婷, 等. 考虑风-光-光热联合直流外送的源-网-荷多时段优化调度方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2022, 42 (2): 559- 573.
|
|
CUI Yang, LI Chonggang, ZHAO Yuting, et al. Source-grid-load multi-time interval optimization scheduling method considering wind-photovoltaic-photothermal combined DC transmission[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2022, 42 (2): 559- 573.
|
| 8 |
李湃, 王伟胜, 黄越辉, 等. 大规模新能源基地经特高压直流送出系统中长期运行方式优化方法[J]. 电网技术, 2023, 47 (1): 31- 44.
|
|
LI Pai, WANG Weisheng, HUANG Yuehui, et al. Method on optimization of medium and long term operation modes of large-scale renewable energy power base through UHVDC system[J]. Power System Technology, 2023, 47 (1): 31- 44.
|
| 9 |
杜刚, 赵冬梅, 刘鑫. 计及风电不确定性优化调度研究综述[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2023, 43 (7): 2608- 2627.
|
|
DU Gang, ZHAO Dongmei, LIU Xin. Research review on optimal scheduling considering wind power uncertainty[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2023, 43 (7): 2608- 2627.
|
| 10 |
贺帅佳, 阮贺彬, 高红均, 等. 分布鲁棒优化方法在电力系统中的理论分析与应用综述[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2020, 44 (14): 179- 191.
|
|
HE Shuaijia, RUAN Hebin, GAO Hongjun, et al. Overview on theory analysis and application of distributionally robust optimization[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2020, 44 (14): 179- 191.
|
| 11 |
OZTURK U A, MAZUMDAR M, NORMAN B A. A solution to the stochastic unit commitment problem using chance constrained programming[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2004, 19 (3): 1589- 1598.
|
| 12 |
彭院院, 周任军, 曾子琪, 等. 参与气电市场的虚拟电厂内部优化随机模型[J]. 中国电力, 2020, 53 (9): 181- 188.
|
|
PENG Yuanyuan, ZHOU Renjun, ZENG Ziqi, et al. Internal optimization stochastic model of virtual power plant participating in gas and electricity market[J]. Electric Power, 2020, 53 (9): 181- 188.
|
| 13 |
ZHAO C Y, WANG Q F, WANG J H, et al. Expected value and chance constrained stochastic unit commitment ensuring wind power utilization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2014, 29 (6): 2696- 2705.
|
| 14 |
WANG J, BOTTERUD A, BESSA R, et al. Wind power forecasting uncertainty and unit commitment[J]. Applied Energy, 2011, 88 (11): 4014- 4023.
|
| 15 |
WU L, SHAHIDEHPOUR M, LI T. Stochastic security-constrained unit commitment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2007, 22 (2): 800- 811.
|
| 16 |
KARAMI M, SHAYANFAR H A, AGHAEI J. Scenario-based security-constrained hydrothermal coordination with volatile wind power generation[J]. Renewable & Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2013, 28, 726- 737.
|
| 17 |
GORISSEN B L, YANIKOGLU I, DEN H. A practical guide to robust optimization[J]. Omega, 2015, 53, 124- 137.
|
| 18 |
汲国强, 吴文传, 张伯明. 考虑风电不确定性的机组检修鲁棒优化方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2015, 35 (12): 2919- 2926.
|
|
JI Guoqiang, WU Wenchuan, ZHANG Boming. Robust optimization method of generator maintenance schedule considering wind power integration[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2015, 35 (12): 2919- 2926.
|
| 19 |
杜浩程, 李世龙, 巨云涛, 等. 基于压缩开关候选集合的分布鲁棒配电网重构方法[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (10): 12- 24, 35.
|
|
DU Haocheng, LI Shilong, JU Yuntao, et al. Linear active disturbance rejection control parameter tuning method for energy storage converter with enhanced stability[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (10): 12- 24, 35.
|
| 20 |
WIESEMANN W, KUHN D, SIM M. Distributionally robust convex optimization[J]. Operations Research, 2014, 62 (6): 1358- 1376.
|
| 21 |
MOHAJERIN E P, KUHN D. Data-driven distributionally robust optimization using the Wasserstein metric: performance guarantees and tractable reformulations[J]. Mathematical Programming, 2018, 171 (1-2): 115- 166.
|
| 22 |
朱晓荣, 山雨琦. 考虑灵活性的储能容量多阶段分布鲁棒规划[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2023, 43 (6): 152- 159, 167.
|
|
ZHU Xiaorong, SHAN Yuqi. Multi-stage distributionally robust planning of energy storage capacity considering flexibility[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2023, 43 (6): 152- 159, 167.
|
| 23 |
ZHU R J, WEI H, BAI X Q. Wasserstein metric based distributionally robust approximate framework for unit commitment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2019, 34 (4): 2991- 3001.
|
| 24 |
DUAN C, FANG W L, JIANG L, et al. Distributionally robust chance-constrained approximate AC-OPF with Wasserstein metric[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2018, 33 (5): 4924- 4936.
|
| 25 |
WANG C, GAO R, QIU F, et al. Risk-based distributionally robust optimal power flow with dynamic line rating[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2018, 33 (6): 6074- 6086.
|
| 26 |
FOURNIER N, GUILLIN A. On the rate of convergence in Wasserstein distance of the empirical measure[J]. Probability Theory and Related Fields, 2015, 162, 707- 738.
|
| 27 |
ZHAO C Y, GUAN Y P. Data-driven risk-averse stochastic optimization with Wasserstein metric[J]. Operations Research Letters, 2018, 46 (2): 262- 267.
|
| 28 |
JABR R A. Adjustable robust OPF with renewable energy sources[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2013, 28 (4): 4742- 4751.
|
| 29 |
DUAN C, JIANG L, FANG W L. Data-driven affinely adjustable distributionally robust unit commitment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2018, 33 (2): 1385- 1398.
|
| 30 |
GAO R, KLEYWEGT A. Distributionally robust stochastic optimization with Wasserstein distance[J]. Mathematics of Operations Research, 2023, 48 (2): 603- 655.
|