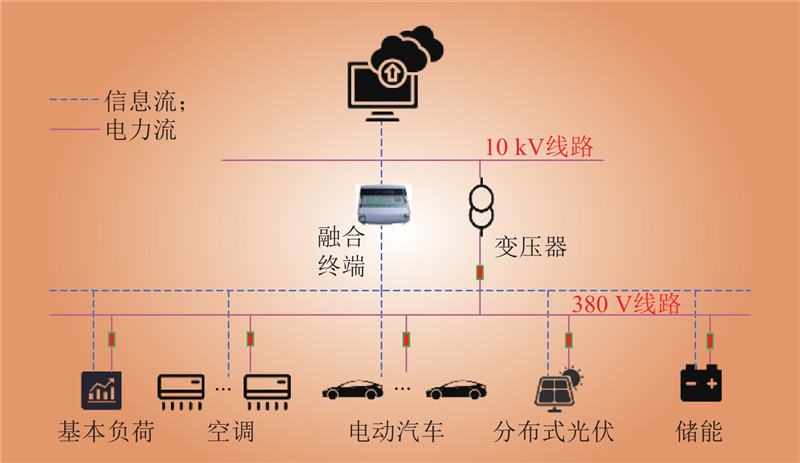
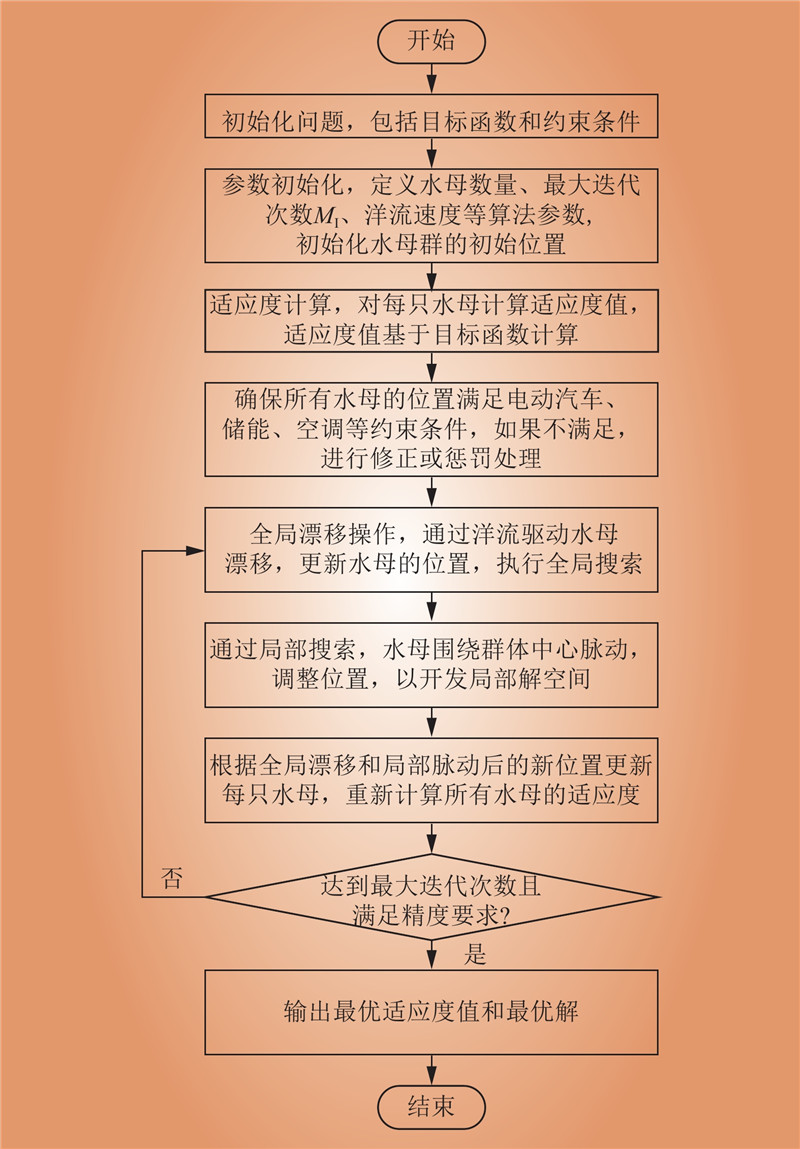
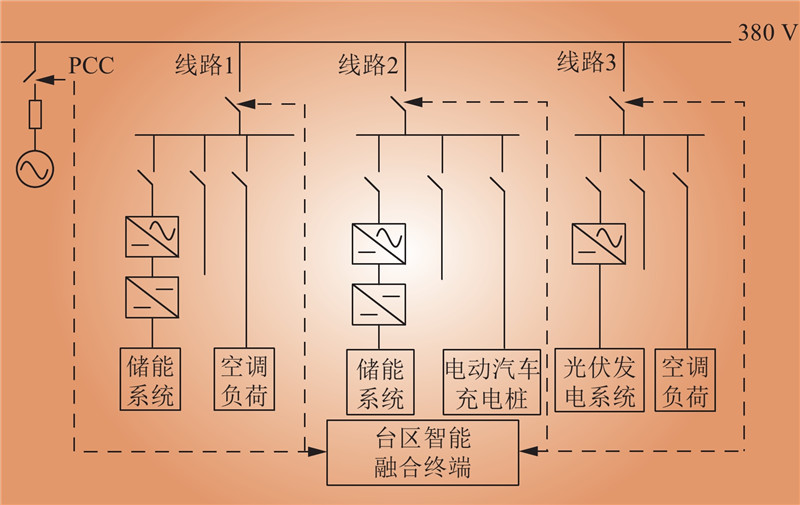
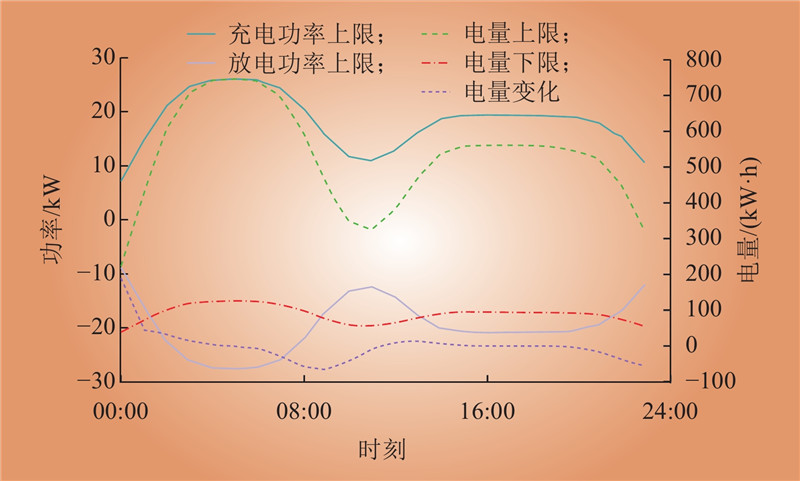
| 1 |
马钊, 张恒旭, 赵浩然, 等. 双碳目标下配用电系统的新使命和新挑战[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2022, 42 (19): 6931- 6945.
|
|
MA Zhao, ZHANG Hengxu, ZHAO Haoran, et al. New mission and challenge of power distribution and consumption system under dual-carbon target[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2022, 42 (19): 6931- 6945.
|
| 2 |
陈璨, 王晶, 于宗民, 等. 配电网自治单元规划研究综述与展望[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (12): 9- 19.
|
|
CHEN Can, WANG Jing, YU Zongmin, et al. Review and outlook of autonomous unit planning of distribution network[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (12): 9- 19.
|
| 3 |
李响, 张丹, 李秋燕, 等. 计及随机性的多分布式电源接入中压配电网承载能力评估[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2024, 52 (17): 150- 160.
|
|
LI Xiang, ZHANG Dan, LI Qiuyan, et al. Hosting capacity evaluation of distributed generators accessing a medium voltagedistribution network considering randomness[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2024, 52 (17): 150- 160.
|
| 4 |
郭雪丽, 胡志勇, 王爽, 等. 考虑大规模风光分层接入的配电网多层协调无功优化方法[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2024, 52 (12): 113- 122.
|
|
GUO Xueli, HU Zhiyong, WANG Shuang, et al. A multi-layer coordinated reactive power optimization method for a distribution networkconsidering large-scale distributed wind-photovoltaic hierarchical access[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2024, 52 (12): 113- 122.
|
| 5 |
CHANDAK S, ROUT P K. The implementation framework of a microgrid: a review[J]. International Journal of Energy Research, 2021, 45 (3): 3523- 3547.
|
| 6 |
梁思琪, 边晓燕, 刘天蔚, 等. 计及台区资源聚合功率的中低压配电系统低碳优化调度方法[J]. 电网技术, 2024, 48 (8): 3217- 3227.
|
|
LIANG Siqi, BIAN Xiaoyan, LIU Tianwei, et al. Low-carbon optimal dispatching method for the medium and low voltage distribution system considering the aggregated power of station resources[J]. Power System Technology, 2024, 48 (8): 3217- 3227.
|
| 7 |
周杨珺, 张斌, 黄伟翔, 等. 基于LSTM-BP组合模型的配电台区低电压预测[J]. 电力科学与技术学报, 2023, 38 (5): 177- 186.
|
|
ZHOU Yangjun, ZHANG Bin, HUANG Weixiang, et al. A low voltage prediction based on LSTM-BP combined model for distribution station area[J]. Journal of Electric Power Science and Technology, 2023, 38 (5): 177- 186.
|
| 8 |
赖健, 许志浩, 康兵, 等. 基于ISSA-SVC的配电网高损台区窃电检测方法研究[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2024, 52 (12): 104- 112.
|
|
LAI Jian, XU Zhihao, KANG Bing, et al. A detection method for electricity theft in a high loss station area of a distributionnetwork based on ISSA-SVC[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2024, 52 (12): 104- 112.
|
| 9 |
杨宇, 文福拴, 周星龙, 等. 高光伏渗透率配电系统电压协同控制研究综述[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2023, 43 (10): 48- 58.
|
|
YANG Yu, WEN Fushuan, ZHOU Xinglong, et al. Research review of voltage cooperative control in distribution system with high photovoltaic penetration[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2023, 43 (10): 48- 58.
|
| 10 |
金国彬, 潘狄, 陈庆, 等. 考虑自适应实时调度的多电压等级直流配电网能量优化方法[J]. 电网技术, 2021, 45 (10): 3906- 3916.
|
|
JIN Guobin, PAN Di, CHEN Qing, et al. Energy optimization method of multi-voltage-level DC distribution network considering adaptive real-time scheduling[J]. Power System Technology, 2021, 45 (10): 3906- 3916.
|
| 11 |
蒋政, 罗威, 殷炜俊, 等. 面向台区通信网的边缘通算资源联合优化算法[J]. 电力信息与通信技术, 2024, 22 (4): 70- 76.
|
|
JIANG Zheng, LUO Wei, YIN Weijun, et al. A joint optimization algorithm of resource allocation for edge computing for communication networks in distribution transformer area[J]. Electric Power Information and Communication Technology, 2024, 22 (4): 70- 76.
|
| 12 |
肖茂然, 曾锃, 张震, 等. 计及源荷储的多台区负载均衡协同调控方法[J]. 电力信息与通信技术, 2024, 22 (9): 26- 32.
|
|
XIAO Maoran, ZENG Cheng, ZHANG Zhen, et al. Load balancing cooperative dispatching and control method considering source-load-storage in multiple transformer areas[J]. Electric Power Information and Communication Technology, 2024, 22 (9): 26- 32.
|
| 13 |
金旭, 张远实, 李明, 等. 考虑热舒适度的居民空调负荷调控潜力差异化评估[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2024, 48 (01): 50- 58.
|
|
JIN Xu, ZHANG Yuanshi, LI Ming, et al. Differentiation evaluation of regulation potential for residential air conditioning load considering thermal comfort[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2024, 48 (01): 50- 58.
|
| 14 |
朱旭, 孙元章, 杨博闻, 等. 考虑不确定性与非完全理性用能行为的电动汽车集群可调度潜力计算方法[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2022, 42 (10): 245- 254.
|
|
ZHU Xu, SUN Yuanzhang, YANG Bowen, et al. Calculation method of EV cluster's schedulable potential capacity considering uncertainties and bounded rational energy consumption behaviors[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2022, 42 (10): 245- 254.
|
| 15 |
吴界辰, 艾欣, 胡俊杰. 需求侧资源灵活性刻画及其在日前优化调度中的应用[J]. 电工技术学报, 2020, 35 (9): 1973- 1984.
|
|
WU Jiechen, AI Xin, HU Junjie. Methods for characterizing flexibilities from demand-side resources and their applications in the day-ahead optimal scheduling[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2020, 35 (9): 1973- 1984.
|
| 16 |
SABERI H, ZHANG C, DONG Z Y. Capacity of virtual energy storage system for frequency regulation services via a data-driven distributionally robust optimization method[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2023, 38 (3): 2134- 2147.
|
| 17 |
范宇辉, 姜婷玉, 黄奇峰, 等. 基于画像的工业园区需求响应潜力评估[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2024, 48 (1): 41- 49.
|
|
FAN Yuhui, JIANG Tingyu, HUANG Qifeng, et al. Portrait-based assessment on demand response potential of industrial parks[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2024, 48 (1): 41- 49.
|
| 18 |
WANG S Y, WU W C, CHEN Q Z, et al. Stochastic flexibility evaluation for virtual power plants by aggregating distributed energy resources[J]. CSEE Journal of Power and Energy Systems, 2024, 10 (3): 988- 999.
|
| 19 |
ZHOU M, WU Z Y, WANG J X, et al. Forming dispatchable region of electric vehicle aggregation in microgrid bidding[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2021, 17 (7): 4755- 4765.
|
| 20 |
ZHAO H T, WANG B, PAN Z G, et al. Aggregating additional flexibility from quick-start devices for multi-energy virtual power plants[J]. IEEE Transactions on Sustainable Energy, 2021, 12 (1): 646- 658.
|
| 21 |
HOU Y X, ZHAO L, JIANG H W, et al. Two-layer control framework and aggregation response potential evaluation of air conditioning load considering multiple factors[J]. IEEE Access, 2024, 12, 34435- 34451.
|
| 22 |
詹祥澎, 杨军, 韩思宁, 等. 考虑电动汽车可调度潜力的充电站两阶段市场投标策略[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2021, 45 (10): 86- 96.
|
|
ZHAN Xiangpeng, YANG Jun, HAN Sining, et al. Two-stage market bidding strategy of charging station considering schedulable potential capacity of electric vehicle[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2021, 45 (10): 86- 96.
|
| 23 |
胡江溢, 郑涛, 金玉龙, 等. 计及用户决策不确定性与调频备用需求的空调负荷聚合策略[J]. 电网技术, 2022, 46 (9): 3534- 3542.
|
|
HU Jiangyi, ZHENG Tao, JIN Yulong, et al. An aggregation strategy of air conditioning loads considering uncertainty of customer behavior and frequency regulation demand[J]. Power System Technology, 2022, 46 (9): 3534- 3542.
|
| 24 |
惠红勋. 温控负荷参与电力系统动态响应的建模与控制方法研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2020.
|
|
HUI Hongxun. Modelling and control of thermostatically controlled loads for participating in dynamic response of power systems[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2020.
|
| 25 |
邵蓝锌, 万灿, 张晓波, 等. 考虑不确定性与交互功率的城市综合能源系统两阶段调度[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2023, 47 (9): 59- 69.
|
|
SHAO Lanxin, WAN Can, ZHANG Xiaobo, et al. Two-stage dispatching for urban integrated energy system considering uncertainty and interactive power[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2023, 47 (9): 59- 69.
|
| 26 |
张翔颖, 杨永标, 徐青山, 等. 基于多时段相似日理论的光伏功率组合预测方法[J]. 南方电网技术, 2023, 17 (2): 57- 65.
|
|
ZHANG Xiangying, YANG Yongbiao, XU Qingshan, et al. Photovoltaic power combination prediction method based on multi-temporal similarity day theory[J]. Southern Power System Technology, 2023, 17 (2): 57- 65.
|
| 27 |
李江南, 程韧俐, 周保荣, 等. 含碳捕集及电转氢设备的低碳园区综合能源系统随机优化调度[J]. 中国电力, 2024, 57 (5): 149- 156.
|
|
LI Jiangnan, CHENG Renli, ZHOU Baorong, et al. Stochastic optimal of integrated energy system in low-carbon parks considering carbon capture storage and power to hydrogen[J]. Electric Power, 2024, 57 (5): 149- 156.
|
| 28 |
SI F Y, WANG J K, HAN Y H, et al. Risk-averse multiobjective optimization for integrated electricity and heating system: an augment epsilon-constraint approach[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2022, 16 (4): 5142- 5153.
|
| 29 |
王海洋, 李珂, 张承慧, 等. 基于主从博弈的社区综合能源系统分布式协同优化运行策略[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2020, 40 (17): 5435- 5445.
|
|
WANG Haiyang, LI Ke, ZHANG Chenghui, et al. Distributed coordinative optimal operation of community integrated energy system based on Stackelberg game[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2020, 40 (17): 5435- 5445.
|
| 30 |
CHEN X, LI N. Leveraging two-stage adaptive robust optimization for power flexibility aggregation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2021, 12 (5): 3954- 3965.
|
| 31 |
CHOU J S, TRUONG D N. A novel metaheuristic optimizer inspired by behavior of jellyfish in ocean[J]. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2021, 389, 125535.
|
| 32 |
赵军, 张敏, 张世锋, 等. 计及碳交易和新能源不确定性的多微电网合作运行优化策略[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56 (5): 62- 71.
|
|
ZHAO Jun, ZHANG Min, ZHANG Shifeng, et al. Optimization strategy of multi-microgrid cooperative operation considering carbon trading and renewable energy uncertainties[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56 (5): 62- 71.
|
| 33 |
陈红湖. 考虑新能源出力不确定性的规模化变频空调集群优化调控[D]. 绵阳: 西南科技大学, 2023.
|
|
CHEN Honghu. Optimization and control of large-scale inverter airconditioning cluster considering the uncertainty of newenergy generation[D]. Mianyang: Southwest University of Science and Technology, 2023.
|
| 34 |
李嘉森, 王进, 杨蒙, 等. 基于随机优化的虚拟电厂热电联合经济优化调度[J]. 太阳能学报, 2023, 44 (9): 57- 65.
|
|
LI Jiasen, WANG Jin, YANG Meng, et al. Combined heat and power economic optimal dispatching in virtual power plant based on stochastic optimization[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2023, 44 (9): 57- 65.
|