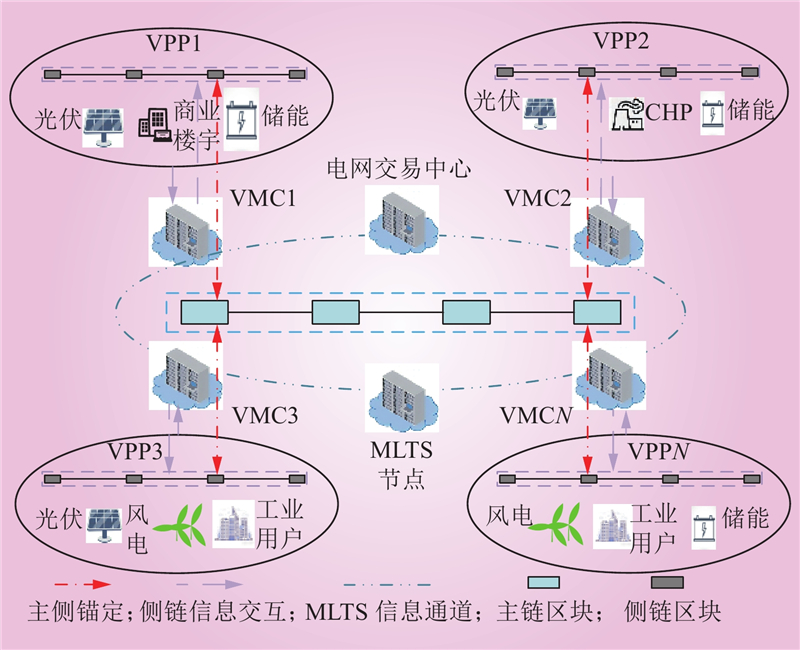
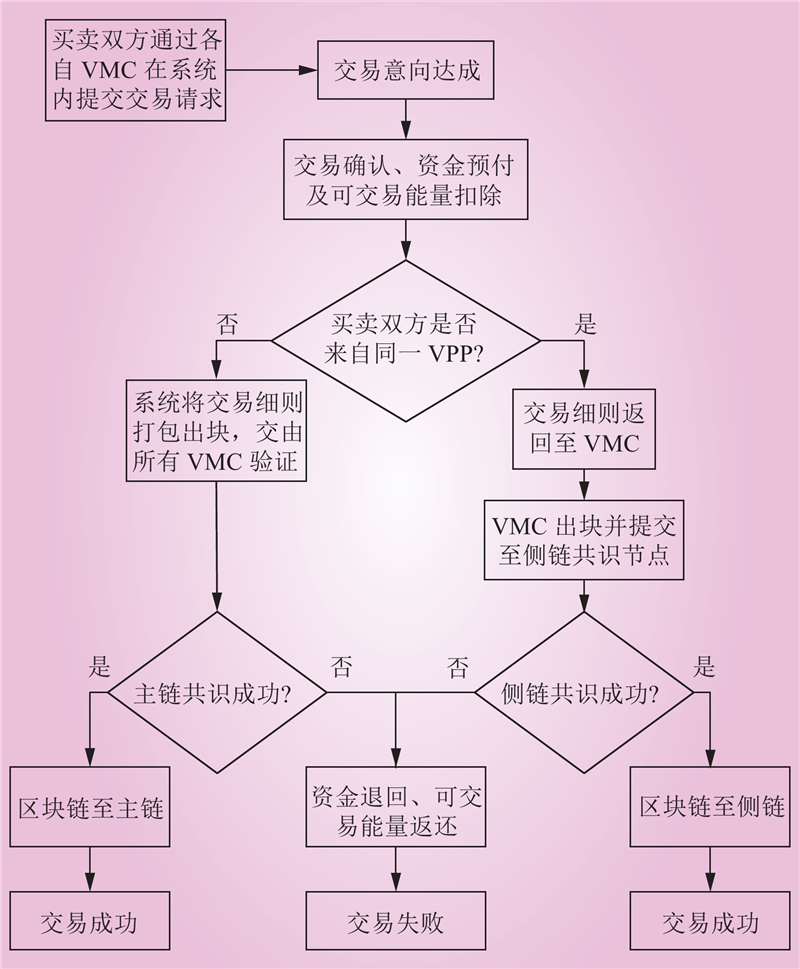
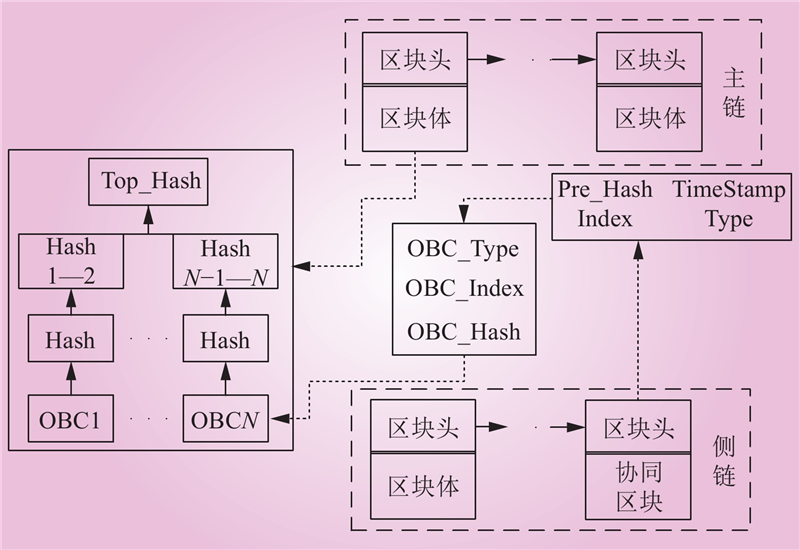
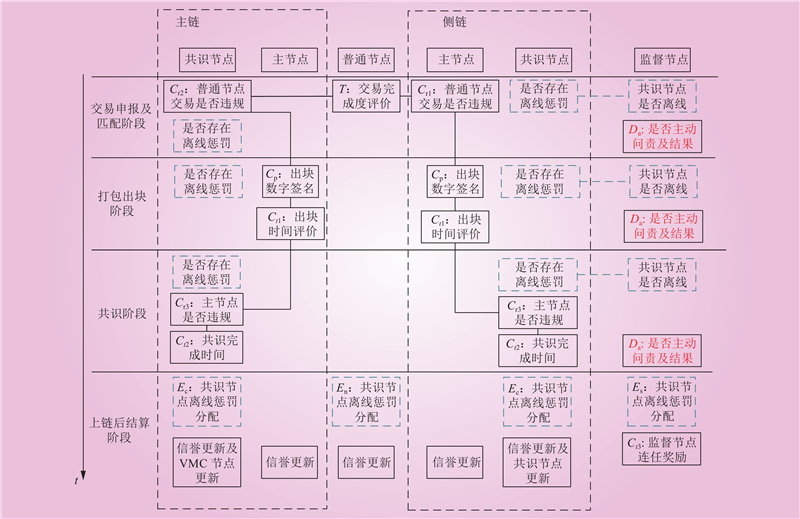
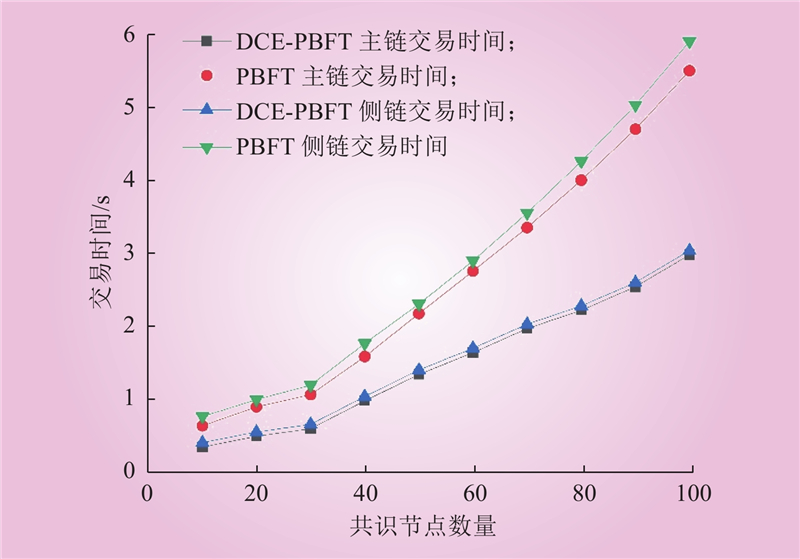
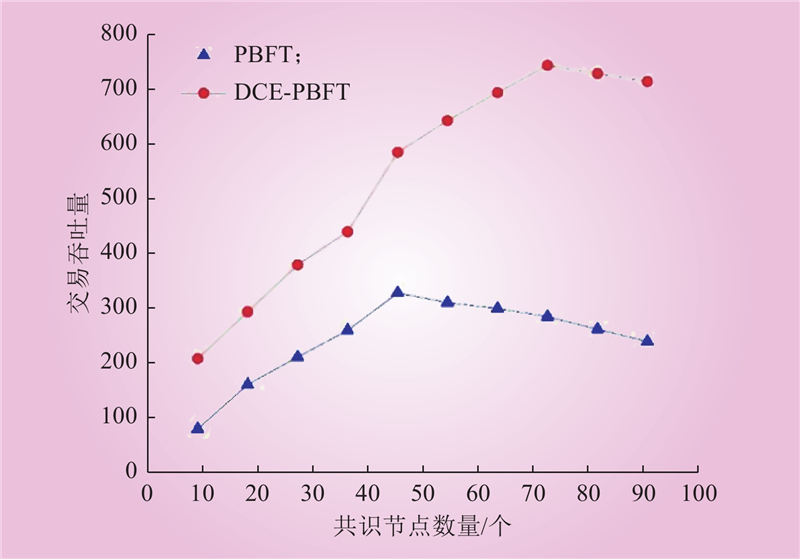
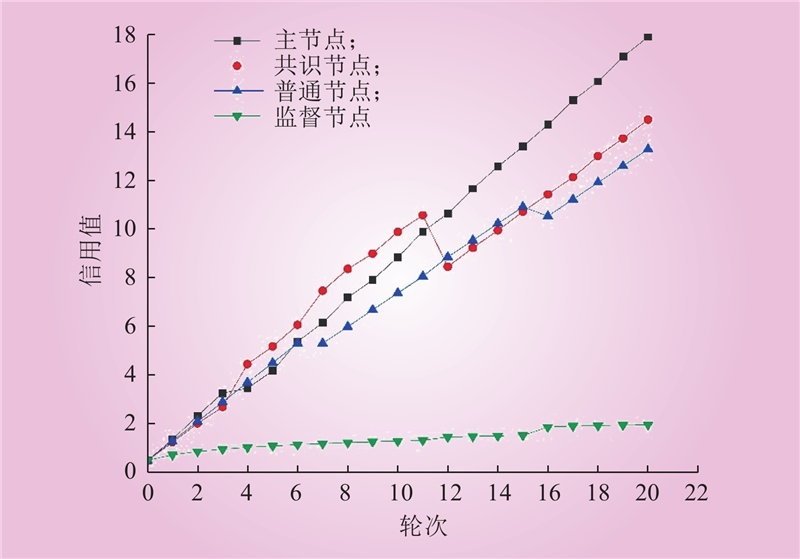
| 1 |
殷爽睿, 艾芊, 宋平, 等. 虚拟电厂分层互动模式与可信交易框架研究与展望[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2022, 46 (18): 118- 128.
|
|
YIN Shuangrui, AI Qian, SONG Ping, et al. Research and prospect of hierarchical interaction mode and trusted transaction framework for virtual power plant[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2022, 46 (18): 118- 128.
|
| 2 |
刘起兴, 胡亚平, 许丹莉, 等. 计及综合能源服务商调节域的综合需求响应市场机制[J]. 电网技术, 2021, 45 (5): 1932- 1943.
|
|
LIU Qixing, HU Yaping, XU Danli, et al. Integrated demand response market mechanism considering adjustable region of integrated energy service providers[J]. Power System Technology, 2021, 45 (5): 1932- 1943.
|
| 3 |
郭威, 杨鹏, 张凯, 等. 基于区块链的微电网群电力交易方法[J]. 高电压技术, 2021, 47 (11): 3810- 3818.
|
|
GUO Wei, YANG Peng, ZHANG Kai, et al. Power transaction method of microgrid group based on blockchain[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2021, 47 (11): 3810- 3818.
|
| 4 |
佘维, 顾志豪, 杨晓宇, 等. 异构能源区块链的多能互补安全交易模型[J]. 电网技术, 2019, 43 (9): 3193- 3201.
|
|
SHE Wei, GU Zhihao, YANG Xiaoyu, et al. A model of multi-energy complementation and safety transaction on heterogeneous energy blockchain[J]. Power System Technology, 2019, 43 (9): 3193- 3201.
|
| 5 |
CUI S C, WANG Y W, XIAO J W, et al. A two-stage robust energy sharing management for prosumer microgrid[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2019, 15 (5): 2741- 2752.
|
| 6 |
YANG Q, WANG H, WANG T T, et al. Blockchain-based decentralized energy management platform for residential distributed energy resources in a virtual power plant[J]. Applied Energy, 2021, 294, 117026.
|
| 7 |
周洪益, 钱苇航, 柏晶晶, 等. 能源区块链的典型应用场景分析及项目实践[J]. 电力建设, 2020, 41 (2): 11- 20.
|
|
ZHOU Hongyi, QIAN Weihang, BAI Jingjing, et al. Typical application scenarios and project review of energy blockchain[J]. Electric Power Construction, 2020, 41 (2): 11- 20.
|
| 8 |
王蓓蓓, 李雅超, 赵盛楠, 等. 基于区块链的分布式能源交易关键技术[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2019, 43 (14): 53- 64.
|
|
WANG Beibei, LI Yachao, ZHAO Shengnan, et al. Key technologies on blockchain based distributed energy transaction[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2019, 43 (14): 53- 64.
|
| 9 |
刘威, 孙艺新, 陈睿欣, 等. 基于区块链的电力数据交易方案设计[J]. 中国电力, 2021, 54 (5): 17- 27.
|
|
LIU Wei, SUN Yixin, CHEN Ruixin, et al. Design of power data trading scheme based on blockchain[J]. Electric Power, 2021, 54 (5): 17- 27.
|
| 10 |
蔡金棋, 李淑贤, 樊冰, 等. 能源互联网中基于区块链的能源交易[J]. 电力建设, 2017, 38 (9): 24- 31.
|
|
CAI Jinqi, LI Shuxian, FAN Bing, et al. Blockchain based energy trading in energy Internet[J]. Electric Power Construction, 2017, 38 (9): 24- 31.
|
| 11 |
李彬, 曹望璋, 张洁, 等. 基于异构区块链的多能系统交易体系及关键技术[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2018, 42 (4): 183- 193.
|
|
LI Bin, CAO Wangzhang, ZHANG Jie, et al. Transaction system and key technologies of multi-energy system based on heterogeneous blockchain[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2018, 42 (4): 183- 193.
|
| 12 |
邵炜晖, 许维胜, 徐志宇, 等. 基于区块链的虚拟电厂模型研究[J]. 计算机科学, 2018, 45 (2): 25- 31.
|
|
SHAO Weihui, XU Weisheng, XU Zhiyu, et al. Study on virtual power plant model based on blockchain[J]. Computer Science, 2018, 45 (2): 25- 31.
|
| 13 |
邰雪, 孙宏斌, 郭庆来. 能源互联网中基于区块链的电力交易和阻塞管理方法[J]. 电网技术, 2016, 40 (12): 3630- 3638.
|
|
TAI Xue, SUN Hongbin, GUO Qinglai. Electricity transactions and congestion management based on blockchain in energy Internet[J]. Power System Technology, 2016, 40 (12): 3630- 3638.
|
| 14 |
李飞, 徐弢, 林济铿, 等. 计及分布式电源出力和负荷不确定性的配电网孤岛划分[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2015, 39 (14): 105- 113, 132.
|
|
LI Fei, XU Tao, LIN Jikeng, et al. Island partition of distribution network considering uncertainty of distributed generators and loads[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2015, 39 (14): 105- 113, 132.
|
| 15 |
周洪益, 余爽, 柏晶晶, 等. 基于区块链技术的虚拟电厂交易管理模式研究[J]. 电力需求侧管理, 2021, 23 (1): 72- 76.
|
|
ZHOU Hongyi, YU Shuang, BAI Jingjing, et al. Research on trading pattern of virtual power plant based on blockchain technology[J]. Power Demand Side Management, 2021, 23 (1): 72- 76.
|
| 16 |
王栋, 李达, 冯景丽, 等. 考虑绿色属性的多微网间电能可信自治交易方法[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2022, 46 (23): 1- 10.
|
|
WANG Dong, LI Da, FENG Jingli, et al. Trustworthy and autonomous electricity trading method among multiple microgrids considering green property[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2022, 46 (23): 1- 10.
|
| 17 |
伊书鑫, 胡健, 路尧, 等. 电力现货市场中多虚拟电厂交易策略[J]. 控制工程, 2022, 29 (9): 1587- 1592.
|
|
YI Shuxin, HU Jian, LU Yao, et al. Trading strategy of multiple virtual power plants in the electricity spot market[J]. Control Engineering of China, 2022, 29 (9): 1587- 1592.
|
| 18 |
邱革非, 余欣蓉, 金乐婷, 等. 多虚拟电厂博弈的区域电网经济调度[J]. 电力系统及其自动化学报, 2021, 33 (6): 75- 83.
|
|
QIU Gefei, YU Xinrong, JIN Yueting, et al. Economic dispatching of regional power grid based on multi-virtual power plant game[J]. Proceedings of the CSU-EPSA, 2021, 33 (6): 75- 83.
|
| 19 |
宋嘉启, 杨永标, 徐青山, 等. 多虚拟电厂参与日前电力市场的鲁棒竞标博弈方法[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2023, 43 (5): 77- 85.
|
|
SONG Jiaqi, YANG Yongbiao, XU Qingshan, et al. Robust bidding game approach for multiple virtual power plants participating in day-ahead electricity market[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2023, 43 (5): 77- 85.
|
| 20 |
周步祥, 张越, 臧天磊, 等. 基于区块链的多虚拟电厂主从博弈优化运行[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2022, 46 (1): 155- 163.
|
|
ZHOU Buxiang, ZHANG Yue, ZANG Tianlei, et al. Blockchain-based stackelberg game optimal operation of multiple virtual power plants[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2022, 46 (1): 155- 163.
|
| 21 |
戴鹏. 基于实用拜占庭共识算法(PBFT)的区块链模型的评估与改进[D]. 北京: 北京邮电大学, 2019.
|
|
DAI Peng. Evalution and research of blockchain model based on practical byzantine consensus algorithm(PBFT)[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2019.
|
| 22 |
林洁瑜, 崔维平. 基于双链区块链的电力数据资产交易系统架构[J]. 中国电力, 2021, 54 (11): 164- 170, 180.
|
|
LIN Jieyu, CUI Weiping. Power-data-asset trading platform architecture based on double-chained blockchain[J]. Electric Power, 2021, 54 (11): 164- 170, 180.
|
| 23 |
李涛. 基于区块链的主从多链及其共识算法研究[D]. 成都: 电子科技大学, 2021.
|
|
LI Tao. Research on blockchain-based master-slave multichain and its consensus algorithm[D]. Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2021.
|
| 24 |
邹贤, 沈力, 张伟等. 基于信用评分的电力交易区块链改进RAFT共识机制[J]. 南方电网技术, 2022, 16 (6): 132- 139.
|
|
ZOU Xian, SHEN Li, ZHANG Wei, et al. Improved RAFT consensus mechanism for power transaction blockchain based on credit scoring[J]. Southern Power System Technology, 2022, 16 (6): 132- 139.
|