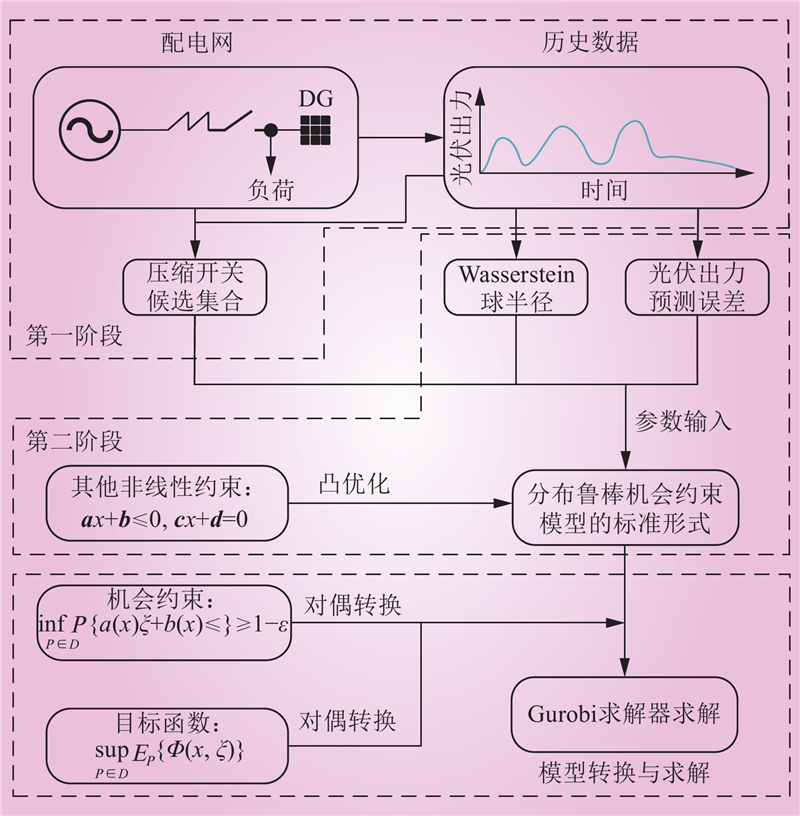
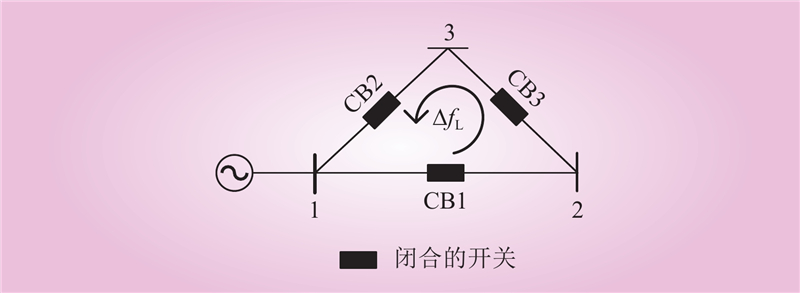
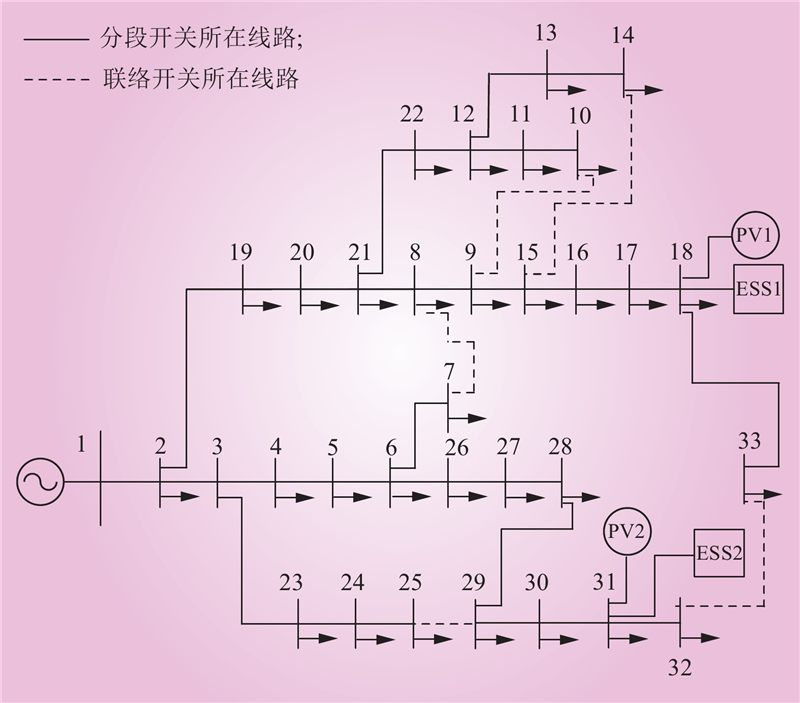
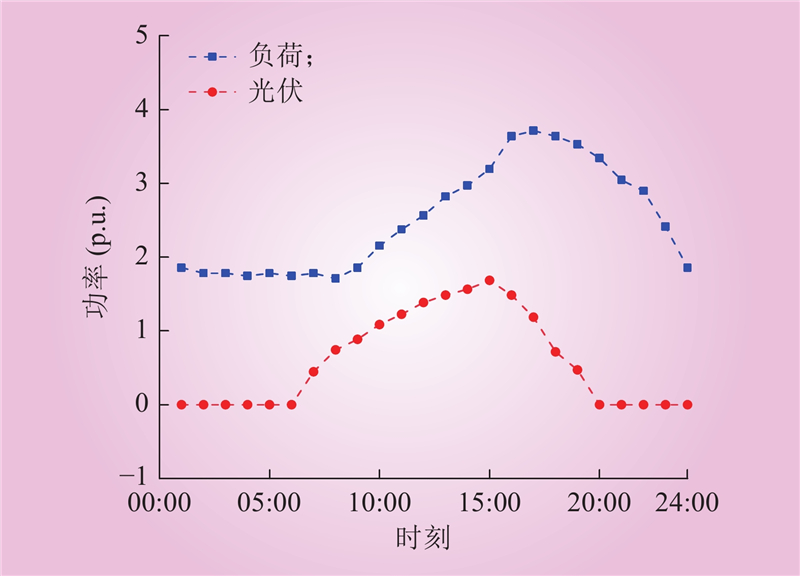
| 1 |
ZHAN J P, LIU W J, CHUNG C Y, et al. Switch opening and exchange method for stochastic distribution network reconfiguration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2020, 11 (4): 2995- 3007.
|
| 2 |
翟鹤峰, 杨明, 赵利刚, 等. 提升分布式电源接纳能力的配电网三相鲁棒动态重构[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2019, 43 (18): 35- 42.
|
|
ZHAI Hefeng, YANG Ming, ZHAO Ligang, et al. Three-phase robust dynamic reconfiguration of distribution network to improve acceptance ability of distributed generator[J]. Automation of Electric Systems, 2019, 43 (18): 35- 42.
|
| 3 |
ZHOU A P, ZHAI H F, YANG M, et al. Three-phase unbalanced distribution network dynamic reconfiguration: a distributionally robust approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2022, 13 (3): 2063- 2074.
|
| 4 |
LI Z C, JAZEBI S, DE LEÓN F. Determination of the optimal switching frequency for distribution system reconfiguration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery, 2017, 32 (4): 2060- 2069.
|
| 5 |
赵静翔, 牛焕娜, 王钰竹. 基于信息熵时段划分的主动配电网动态重构[J]. 电网技术, 2017, 41 (2): 402- 408.
|
|
ZHAO Jingxiang, NIU Huanna, WANG Yuzhu. Dynamic reconfiguration of active distribution network based on information entropy of time intervals[J]. Power System Technology, 2017, 41 (2): 402- 408.
|
| 6 |
WANG Q F, GUAN Y P, WANG J H. A chance-constrained two-stage stochastic program for unit commitment with uncertain wind power output[C]//2012 IEEE Power and Energy Society General Meeting. San Diego, CA, USA. IEEE, 2012: 1.
|
| 7 |
AHMED H M A, ELTANTAWY A B, SALAMA M M A. A planning approach for the network configuration of AC-DC hybrid distribution systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2018, 9 (3): 2203- 2213.
|
| 8 |
LEE C, LIU C, MEHROTRA S, et al. Robust distribution network reconfiguration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2015, 6 (2): 836- 842.
|
| 9 |
HAGHIGHAT H, ZENG B. Distribution system reconfiguration under uncertain load and renewable generation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2016, 31 (4): 2666- 2675.
|
| 10 |
LEI S B, HOU Y H, QIU F, et al. Identification of critical switches for integrating renewable distributed generation by dynamic network reconfiguration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Sustainable Energy, 2018, 9 (1): 420- 432.
|
| 11 |
AKRAMI A, DOOSTIZADEH M, AMINIFAR F. Optimal reconfiguration of distribution network using μPMU measurements: a data-driven stochastic robust optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2020, 11 (1): 420- 428.
|
| 12 |
MAHDAVI M, ALHELOU H H, HESAMZADEH M R. An efficient stochastic reconfiguration model for distribution systems with uncertain loads[J]. IEEE Access, 2022, 10, 10640- 10652.
|
| 13 |
MAHDAVI M, ALHELOU H H, SIANO P, et al. Robust mixed-integer programing model for reconfiguration of distribution feeders under uncertain and variable loads considering capacitor banks, voltage regulators, and protective relays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2022, 18 (11): 7790- 7803.
|
| 14 |
HAJEBRAHIMI A, KAMWA I, ABDELAZIZ M M A, et al. Scenario-wise distributionally robust optimization for collaborative intermittent resources and electric vehicle aggregator bidding strategy[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2020, 35 (5): 3706- 3718.
|
| 15 |
马望, 高红均, 杨艳红, 等. 融入重构级别快速识别的配电网两阶段优化运行[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2022, 42 (14): 5154- 5168.
|
|
MA Wang, GAO Hongjun, YANG Yanhong, et al. Two-stage optimal operation for distribution network based on fast identification of reconfiguration level[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2022, 42 (14): 5154- 5168.
|
| 16 |
税月, 刘俊勇, 高红均, 等. 考虑风电不确定性的电气能源系统两阶段分布鲁棒协同调度[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2018, 42 (13): 43- 50, 75.
|
|
SHUI Yue, LIU Junyong, GAO Hongjun, et al. Two-stage distributed robust cooperative dispatch for integrated electricity and natural gas energy systems considering uncertainty of wind power[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2018, 42 (13): 43- 50, 75.
|
| 17 |
ZHENG W Y, HUANG W J, HILL D J, et al. An adaptive distributionally robust model for three-phase distribution network reconfiguration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2021, 12 (2): 1224- 1237.
|
| 18 |
CHEN Y W, GUO Q L, SUN H B, et al. A distributionally robust optimization model for unit commitment based on kullback–leibler divergence[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2018, 33 (5): 5147- 5160.
|
| 19 |
ZHOU A P, YANG M, WANG M Q, et al. A linear programming approximation of distributionally robust chance-constrained dispatch with Wasserstein distance[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2020, 35 (5): 3366- 3377.
|
| 20 |
竺如洁, 韦化, 白晓清. 多源动态最优潮流的分布鲁棒优化方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2020, 40 (11): 3489- 3497.
|
|
ZHU Rujie, WEI Hua, BAI Xiaoqing. Distributionally robust optimization of multi-energy dynamic optimal power flow[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2020, 40 (11): 3489- 3497.
|
| 21 |
曾捷, 童晓阳, 范嘉乐. 计及需求响应不确定性的电-气耦合配网系统动态分布鲁棒优化[J]. 电网技术, 2022, 46 (5): 1877- 1886.
|
|
ZENG Jie, TONG Xiaoyang, FAN Jiale. Dynamic distributionally robust optimization of integrated electric-gas distribution system considering demand response uncertainty[J]. Power System Technology, 2022, 46 (5): 1877- 1886.
|
| 22 |
CHEN Y, WEI W, LIU F, et al. Distributionally robust hydro-thermal-wind economic dispatch[J]. Applied Energy, 2016, 173, 511- 519.
|
| 23 |
WANG Z, BIAN Q Y, XIN H H, et al. A distributionally robust co-ordinated reserve scheduling model considering CVaR-based wind power reserve requirements[J]. IEEE Transactions on Sustainable Energy, 2016, 7 (2): 625- 636.
|
| 24 |
ZHOU Y Z, SHAHIDEHPOUR M, WEI Z N, et al. Distributionally robust co-optimization of energy and reserve for combined distribution networks of power and district heating[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2020, 35 (3): 2388- 2398.
|
| 25 |
WANG XIAOLU, YUEN-MAN PUN, ANTHONY MAN-CHO SO. Moment uncertainty[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2022, 70, 6216- 6231.
|
| 26 |
HAO B, CAI K Q, FANG Y P, et al. A moment-based distributionally robust optimization model for air traffic flow management[C]//2021 IEEE/AIAA 40th Digital Avionics Systems Conference (DASC). San Antonio, TX, USA. IEEE, 2021: 1-7.
|
| 27 |
ZHU R J, WEI H, BAI X Q. Wasserstein metric based distributionally robust approximate framework for unit commitment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2019, 34 (4): 2991- 3001.
|
| 28 |
ZHAO C Y, GUAN Y P. Data-driven risk-averse stochastic optimization with Wasserstein metric[J]. Operations Research Letters, 2018, 46 (2): 262- 267.
|
| 29 |
MOHAJERIN ESFAHANI P, KUHN D. Data-driven distributionally robust optimization using the Wasserstein metric: performance guarantees and tractable reformulations[J]. Mathematical Programming, 2018, 171 (1): 115- 166.
|
| 30 |
ZYMLER S, KUHN D, RUSTEM B. Distributionally robust joint chance constraints with second-order moment information[J]. Mathematical Programming, 2013, 137 (1): 167- 198.
|
| 31 |
SHI Z C, LIANG H, HUANG S J, et al. Distributionally robust chance-constrained energy management for islanded microgrids[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2019, 10 (2): 2234- 2244.
|
| 32 |
蔡智萍, 郭谋发, 魏正峰. 基于BP神经网络的低压配电网生命体触电识别方法研究[J]. 电网技术, 2022, 46 (4): 1614- 1623.
|
|
CAI Zhiping, GUO Moufa, WEI Zhengfeng. Research on recognition method of living body shock in low-voltage distribution network based on BP neural network[J]. Power System Technology, 2022, 46 (4): 1614- 1623.
|